
Section 1 Diseases of Cattle Overview
- Jim O’Donovan,
- Research Officer, Cork Regional Veterinary Laboratory, Model Fam Road, Bishoptown, Cork, Ireland
The Regional Veterinary Laboratories (RVLs) of the Department of Agriculture, Food and the Marine (DAFM) are engaged primarily in scanning (passive) surveillance by gathering data from post-mortem and clinical sample submissions. Analysis of this data provides an insight into trends of disease incidence and causes of mortality on Irish farms, thereby informing decision-making relevant to disease control at a national level. Tables and charts are generated with test results and post-mortem diagnoses from voluntary submissions of material (carcasses and clinical samples) to RVLs by farmers through their private veterinary practitioners (PVPs). Therefore, it should be noted that data reflects only those cases where PVPs considered it appropriate to request laboratory investigation and the herdowner was motivated to deliver the carcass to an RVL.
This section presents the most commonly diagnosed causes of death in cattle presented for post-mortem examination at RVLs.
The range of diagnoses of animals submitted for post-mortem examination varies according to age of the animal, thus the results in this section are presented by age category. In order to facilitate presentation and comparison, conditions which affect given systems have been grouped together.
During 2018, 2902 cattle carcasses were submitted for examination. Geographical distribution of herds submitting bovine cases, colour coded by RVL where the carcases were examined, is illustrated in Figure 1.1.
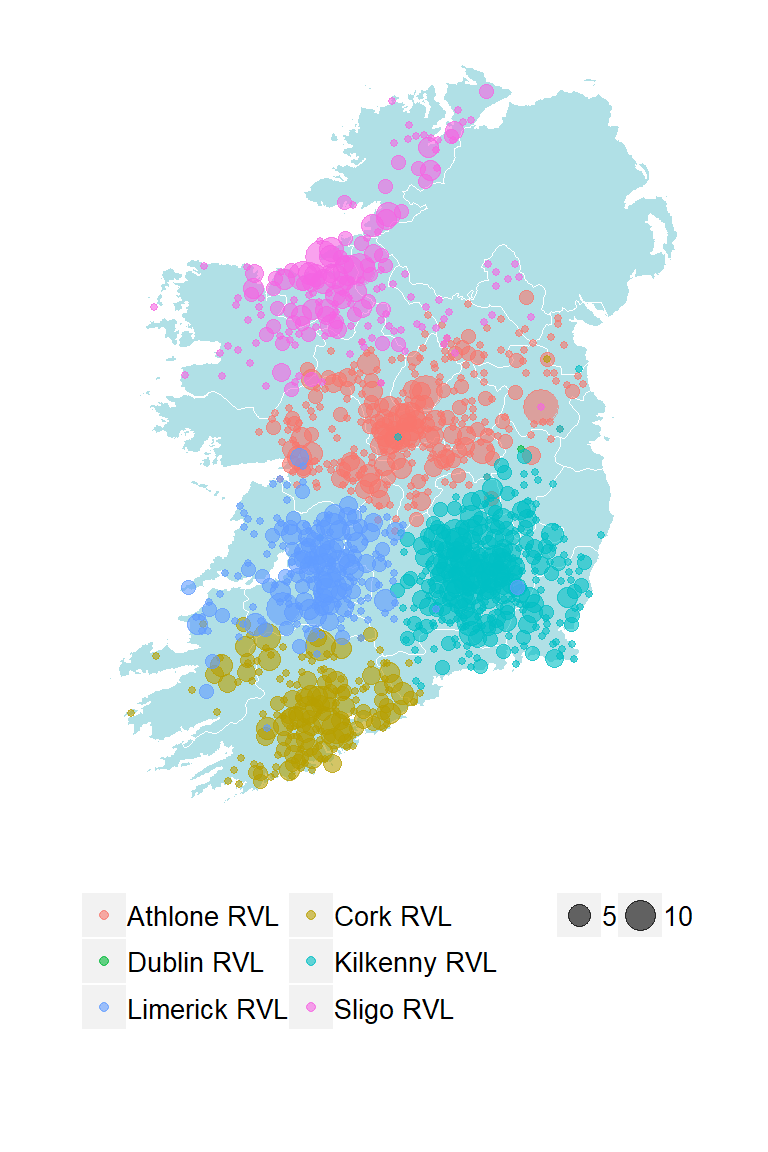
Figure 1.1: Distribution of bovine carcasses. Bovine carcasses (excluding foetuses), aggregated and mapped at their DED (District Electoral Division) and colour-coded by the Regional Veterinary Laboratory of submission (n= 2902 )
1.1 Neonatal Calves (birth to one month of age)
The trend of gastrointestinal infections being the most frequently diagnosed cause of death in neonatal calves continued in 2018 (Table 1.1 & Figure @ref(fig:neonetalfig}). The deaths of almost thirty per cent of calves in this age group were attributed to gastrointestinal infections. Not surprisingly, a number of these cases had hypogammaglobulinaemia recorded as well, indicating failure of passive transfer of humoral immunity from dam to calf.
Systemic infections (sepsis) continued as the second most frequently diagnosed cause of death in DAFM laboratories. In the last three years, systemic infections reached a peak of 24 per cent of deaths in 2016 (DAFM 2016), but in 2018 the percentage of neonatal calves with systemic infections fell to 17.8 per cent.
| Category | No. of Cases | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| GIT Infections | 253 | 29.9 |
| Systemic Infections | 150 | 17.8 |
| Respiratory Infections | 97 | 11.5 |
| Navel Ill/Joint Ill | 65 | 7.7 |
| Nutritional/metabolic conditions | 53 | 6.3 |
| Hereditary and developmental abnormality | 50 | 5.9 |
| GIT torsion/obstruction | 35 | 4.1 |
| GIT ulcer/perforation/foreign body | 25 | 3.0 |
| Diagnosis not reached | 24 | 2.8 |
| Peritonitis | 18 | 2.1 |
| Integument/Musculoskeletal | 13 | 1.5 |
| Unclassified | 11 | 1.3 |
| Cardiac/circulatory conditions | 9 | 1.1 |
| Fractures/Calving injuries | 8 | 1.0 |
| Liver disease | 5 | 0.6 |
| Urinary Tract conditions | 5 | 0.6 |
| Bovine Neonatal Pancytopaenia | 4 | 0.5 |
| CNS | 4 | 0.5 |
| Trauma | 4 | 0.5 |
| Abscessation | 3 | 0.4 |
| BVD/Mucosal disease | 3 | 0.4 |
| Poisoning | 2 | 0.2 |
| Reproductive Tract Conditions | 2 | 0.2 |
| Clostridial disease | 1 | 0.1 |
| Tick Borne Fever | 1 | 0.1 |
Navel ill/ joint ill has stayed at a level consistent with previous years at 7.7 per cent. Escherichia coli and Trueperella pyogenes were the infectious agents most frequently isolated. Similarly, the rate of peritonitis cases has stayed at 2.1 per cent, with Trueperella pyogenes and Escherichia coli commonly isolated from such cases.
Respiratory infections are normally responsible for about one in ten deaths in neonatal calves, and at 11.5 per cent, 2018 was a typical year.
Nutritional and metabolic conditions equate to 6.3 per cent of diagnoses in neonatal calves. This category includes failure of passive transfer of humoral immunity (hypogammaglobulinaemia) and ruminal milk drinking.
Hereditary and developmental abnormalities were recorded in DAFM laboratories in almost 6 per cent of carcasses submitted. Common diagnoses in this category include intestinal atresia and cardiac defects. Cardiac abnormalities most commonly noted were ventricular and atrial septum defects and persistent patent foramen ovale (Figure 1.3).
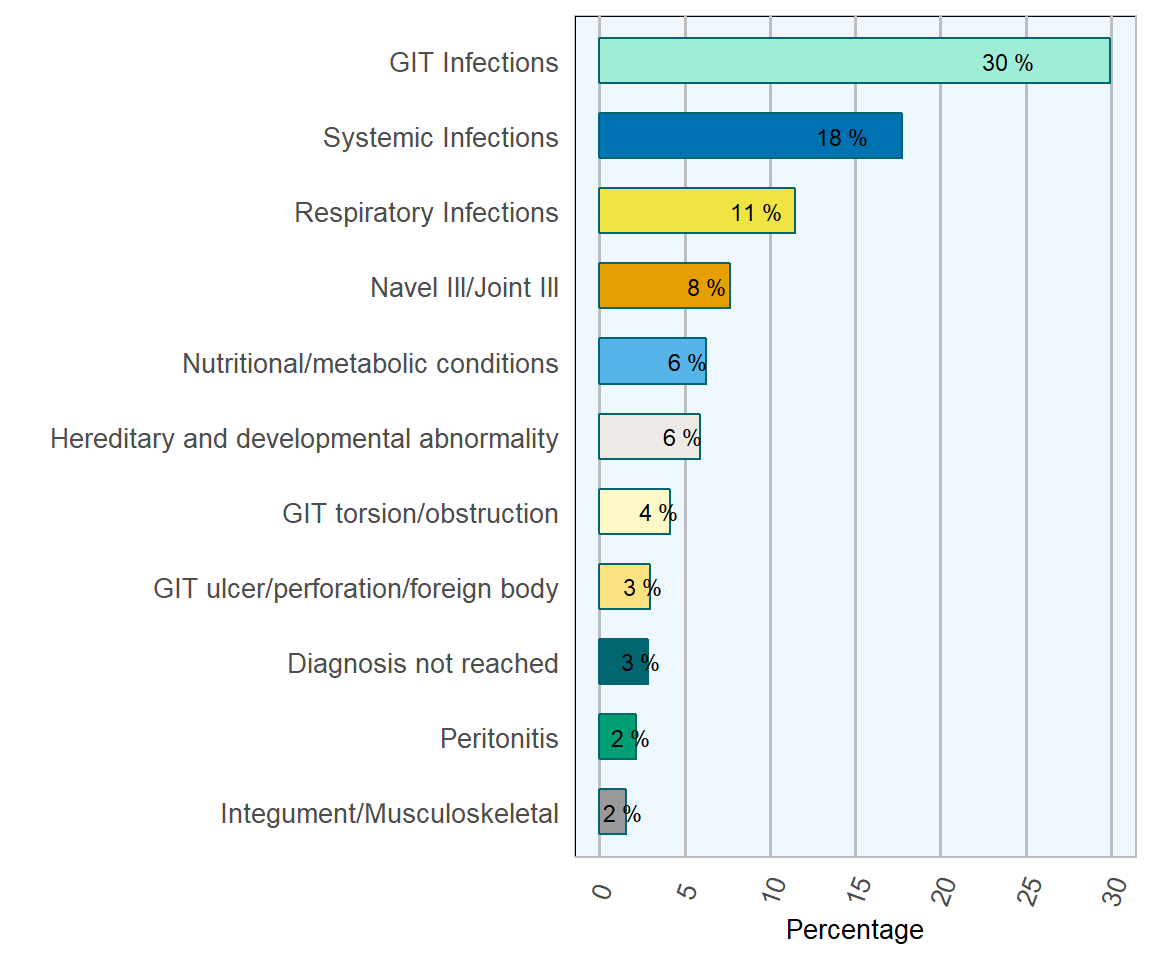
Figure 1.2: Diagnoses of neonatal calves. Conditions most frequently diagnosed on post-mortem examinations of bovine neonatal calves in 2018 (n= 845 ).
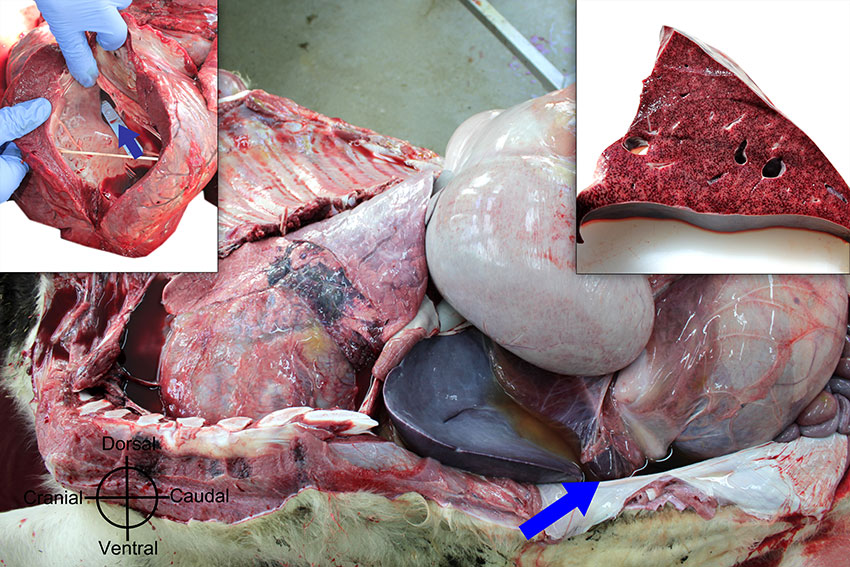
Figure 1.3: Septal defect. Enlarged liver, ascites (arrow) and pulmonary oedema observed in chronic passive congestion as result of a congenital ventricular septal defect (arrow in left inset). Right inset: Accentuated hepatic lobular pattern (nutmeg liver) due to chronic passive congestion. Photo: Cosme Sánchez-Miguel.
1.2 Calves (one to five months of age)
Respiratory infections are by far the biggest cause of mortality among 1–5 month old calves in Ireland (Table 1.2 & Figure 1.4). They accounted for 34.3 per cent of deaths in this age group. Examination of data for the last few years shows that respiratory infections are responsible for an increasing percentage of deaths in this age category, though this has leveled off recently. The percentage of respiratory infections in this age category has risen by approximately 8 per cent since 2014. A breakdown of detected agents in these cases is presented in the Bovine Respiratory Disease section of this report.
| Category | No. of Cases | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| Respiratory Infections | 235 | 34.3 |
| GIT Infections | 91 | 13.3 |
| GIT torsion/obstruction | 56 | 8.2 |
| Systemic Infections | 52 | 7.6 |
| GIT ulcer/perforation/foreign body | 42 | 6.1 |
| Nutritional/metabolic conditions | 33 | 4.8 |
| Diagnosis not reached | 30 | 4.4 |
| Clostridial disease | 22 | 3.2 |
| CNS | 20 | 2.9 |
| Poisoning | 14 | 2.0 |
| Navel Ill/Joint Ill | 13 | 1.9 |
| Peritonitis | 13 | 1.9 |
| Cardiac/circulatory conditions | 12 | 1.8 |
| Urinary Tract conditions | 12 | 1.8 |
| Hereditary and developmental abnormality | 9 | 1.3 |
| Tuberculosis | 8 | 1.2 |
| Integument/Musculoskeletal | 7 | 1.0 |
Gastro-intestinal tract (GIT) infections (13.3 per cent) and systemic infections (7.6 per cent) remain similar to the trend of previous years as the second and third most frequently diagnosed conditions accounting for one in five of diagnosed causes of death. Common bacterial agents implicated include Salmonella enterica Dublin and Escherichia coli. Coccidia (Eimeria spp.) are the most frequently detected GIT pathogens in this age group.
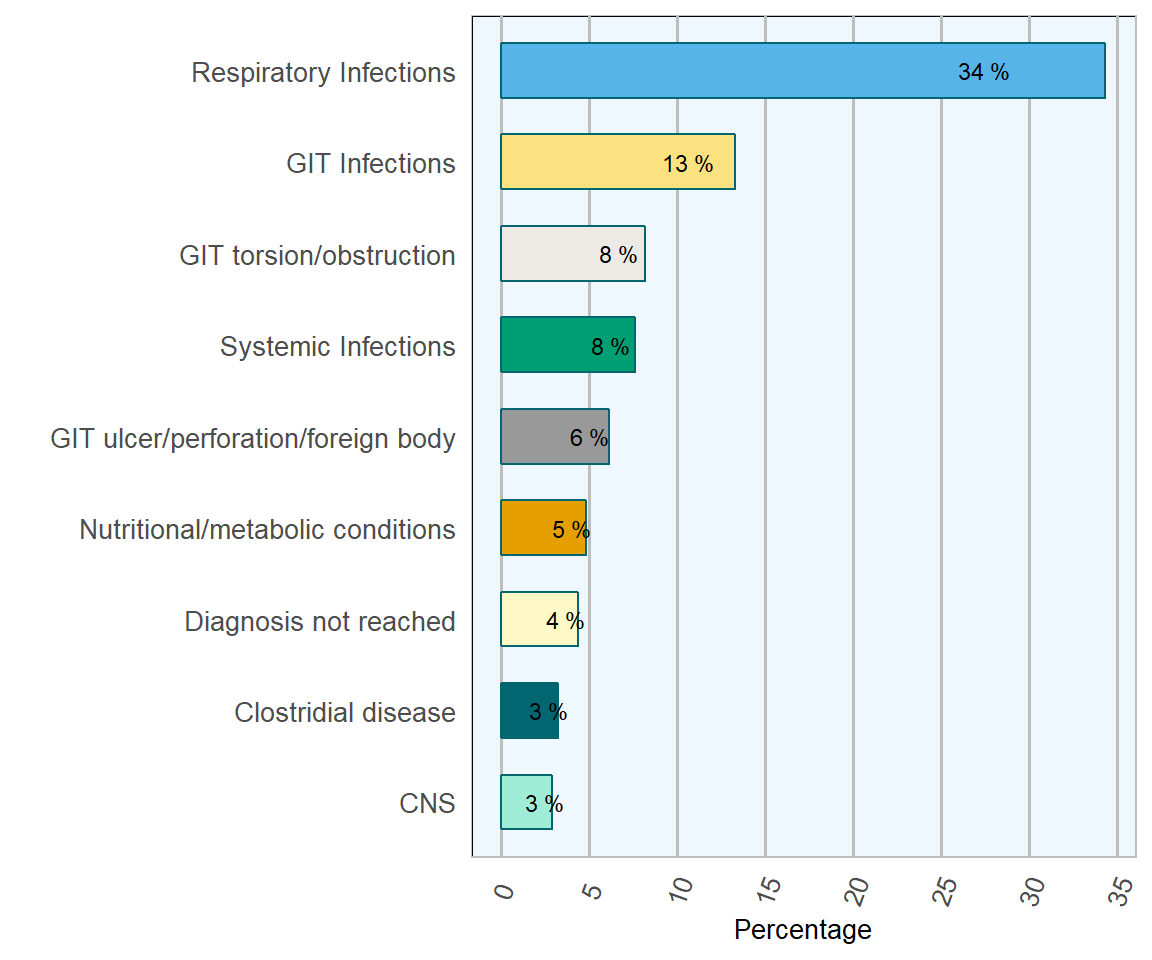
Figure 1.4: Diagnoses of calves. Conditions most frequently diagnosed on post-mortem examinations of calves (1–5 months old) in 2018 (n= 669 )
Navel ill/ joint ill, consequences of navel infections at birth, were diagnosed in 1.9 per cent of calves in this age group presented to DAFM laboratories. Diagnosis of peritonitis in this age category has remained at a consistent level, between 1 and 3 per cent, from 2014 to 2018.
GIT ulcers and perforations continued to be a frequent diagnosis in 2018 accounting for 8.2 per cent of diagnoses. Perforating abomasal ulcers, leading to leakage of stomach contents and peritonitis, accounted for the majority of these cases (Figure 1.5).
GIT torsion/obstruction was recorded in 8.2 per cent of calves. Torsions of intestines, full mesentery, abomasum, omasum and reticulum were recorded. There was no fluctuation in their occurrence from previous years. Nutritional and metabolic conditions were diagnosed in 4.8 per cent of calves. The leading diagnoses in this category were ruminal acidosis and malnutrition.
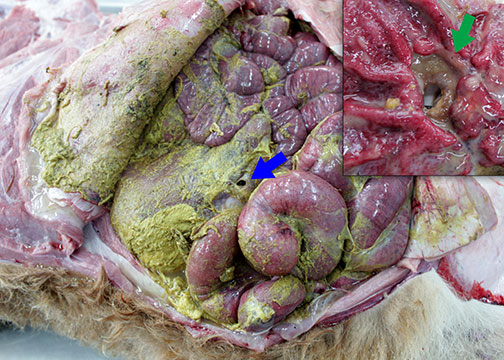
Figure 1.5: Fibrinous peritonitis. Peritonitis resulting from a perforating abomasal ulcer (inset). Photo: Cosme Sánchez-Miguel.
1.3 Weanlings (six months to one year of age)
As in previous years, respiratory infections were the most commonly diagnosed cause of mortality (32.3 per cent) in this age group (Table 1.3 & Figure 1.7.
GIT infections were identified as the second most common cause of death in six to 12 month-old weanlings in Ireland at 21.6 per cent.
Clostridial diseases were the third biggest grouping of cause of mortality in this age group (8.7 per cent).
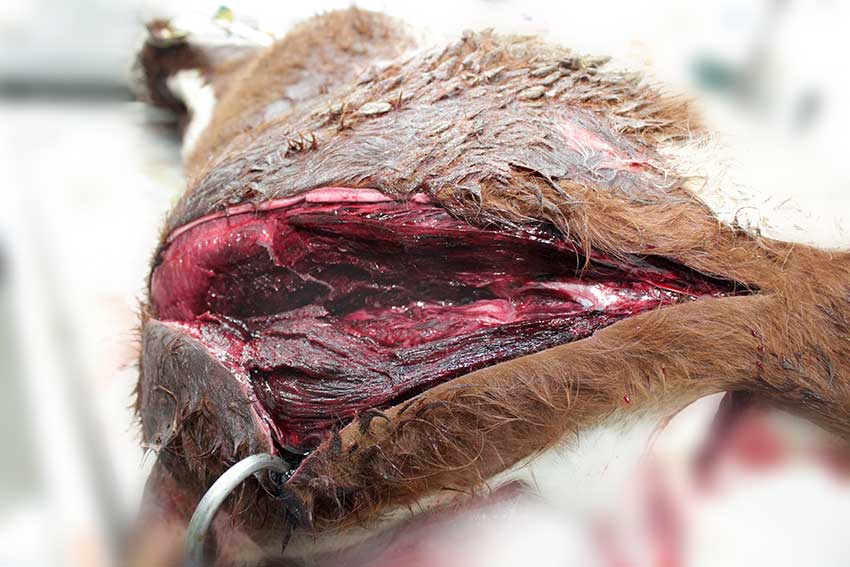
Figure 1.6: Clostridial myositis (blackleg). Muscular necrosis and oedema in the gluteus muscle of a weanling. Photo: Cosme Sánchez-Miguel.
Diseases of the central nervous system (CNS) were diagnosed in 2.1 per cent of carcases in Ireland in 2018. Diseases in this category include cerebro-cortical necrosis, encephalopathies, encephalitis/meningitis and thrombotic meningo-encephalitis.
| Category | No. of Cases | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| Respiratory Infections | 138 | 32.3 |
| GIT Infections | 92 | 21.6 |
| Clostridial disease | 37 | 8.7 |
| Diagnosis not reached | 37 | 8.7 |
| Systemic Infections | 22 | 5.2 |
| Poisoning | 14 | 3.3 |
| Cardiac/circulatory conditions | 11 | 2.6 |
| Nutritional/metabolic conditions | 11 | 2.6 |
| Integument/Musculoskeletal | 10 | 2.3 |
| CNS | 9 | 2.1 |
| Tuberculosis | 9 | 2.1 |
| GIT torsion/obstruction | 6 | 1.4 |
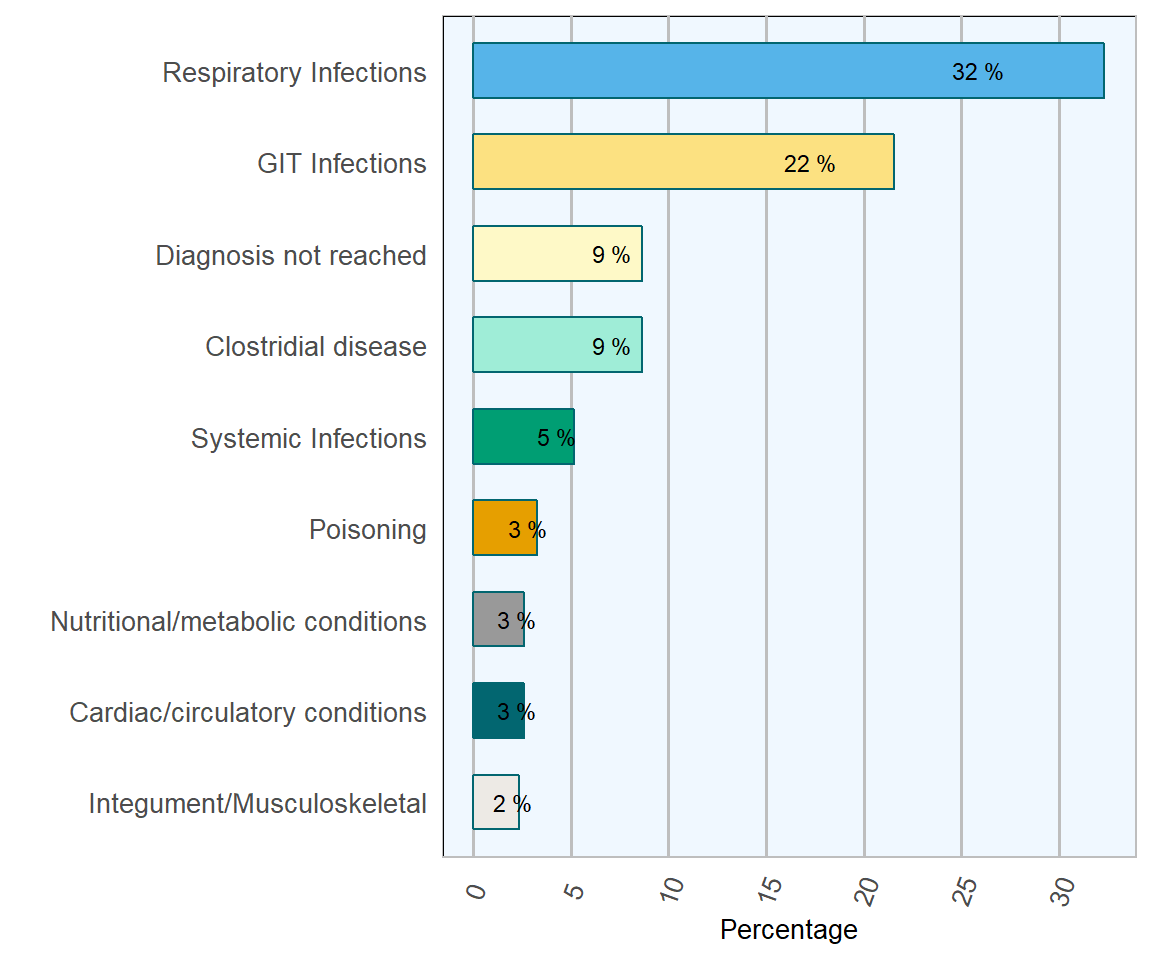
Figure 1.7: Diagnoses in weanlings. Conditions most frequently diagnosed on post-mortem examinations of weanlings (6–12 months old) in 2018 (n= 396 )
| Category | No. of Cases | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| Respiratory Infections | 85 | 15.7 |
| Diagnosis not reached | 83 | 15.3 |
| Cardiac/circulatory conditions | 47 | 8.7 |
| GIT Infections | 32 | 5.9 |
| Nutritional/metabolic conditions | 32 | 5.9 |
| Clostridial disease | 29 | 5.3 |
| Peritonitis | 28 | 5.2 |
| Poisoning | 26 | 4.8 |
| CNS | 22 | 4.0 |
| GIT ulcer/perforation/foreign body | 22 | 4.0 |
| Systemic Infections | 22 | 4.0 |
| Urinary Tract conditions | 13 | 2.4 |
| Integument/Musculoskeletal | 12 | 2.2 |
| Reproductive Tract Conditions | 11 | 2.0 |
| Liver disease | 10 | 1.8 |
| Babesiosis | 9 | 1.7 |
| GIT torsion/obstruction | 9 | 1.7 |
| Tumour | 8 | 1.5 |
| Unclassified | 8 | 1.5 |
| Abscessation | 7 | 1.3 |
| Johne’s Disease | 6 | 1.1 |
| Tuberculosis | 6 | 1.1 |
1.4 Adult Cattle (over 12 months of age)
Similar to previous years, respiratory diseases accounted for 15.7 per cent of adult deaths, (Table 1.4 & Figure 1.8). This incidence has remained roughly static in Ireland since 2014.
Cardiac/circulatory system conditions were the second biggest diagnosis in adult cattle in Ireland, occurring in 8.7 per cent of cases. Endocarditis, pericarditis, caudal vena cava thrombosis, haemorrhage and haemolysis were common diagnoses in this category. T. pyogenes was regularly isolated from cases of endocarditis, pericarditis and caudal vena cava thrombosis.
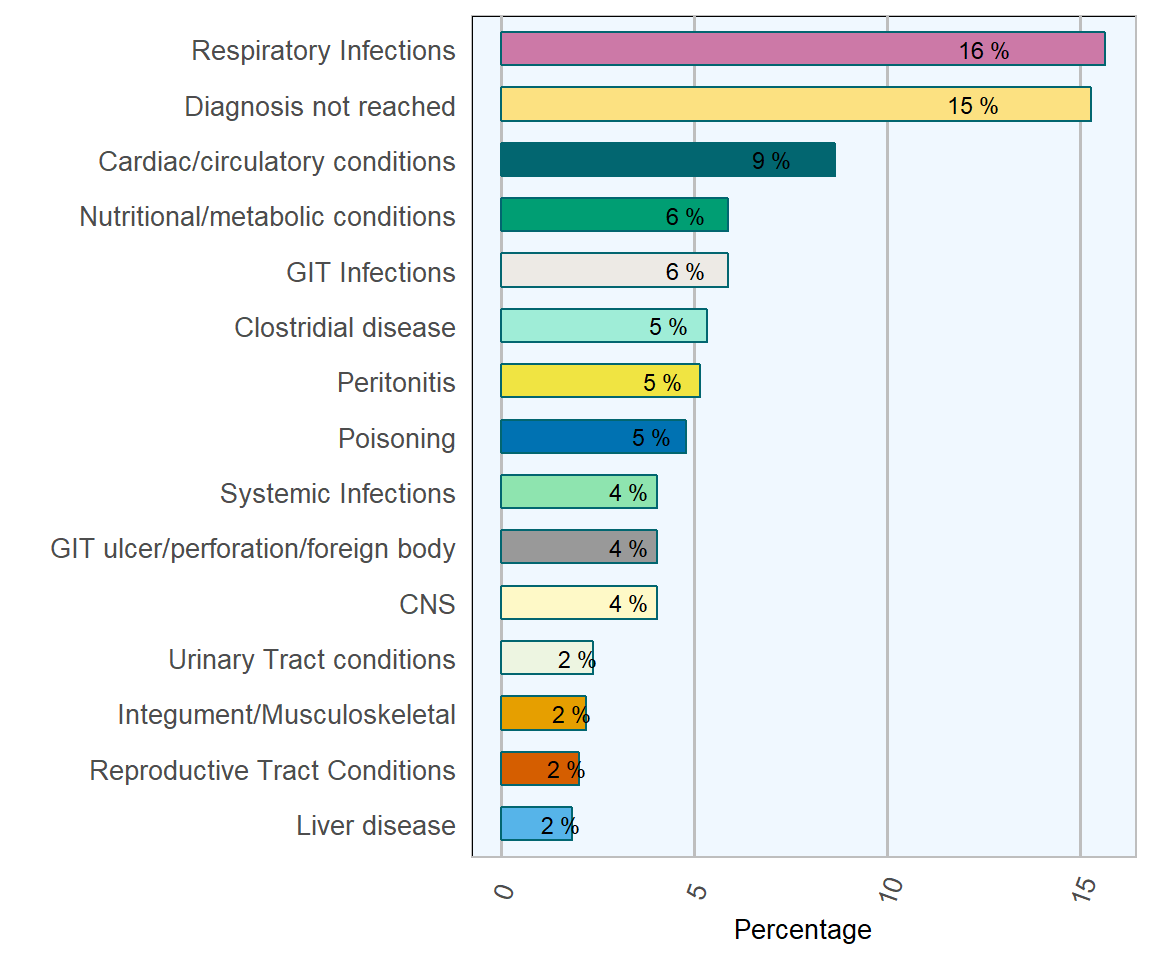
Figure 1.8: Diagnoses of adult cattle. Conditions most frequently diagnosed on post-mortem examinations of adult cattle (over 12 months old) in 2018 (n= 527 )
Clostridial disease only accounted for 5.3 per cent of adult cattle deaths diagnosed and included cases of blackleg (Figure 1.6), malignant oedema, botulism and tetanus. Cases of GIT ulceration/perforation and foreign body accounted for 4.3 per cent of deaths, a slight decrease on rates in previous years. Hardware disease or traumatic reticuloperitionitis account for a significant proportion of these cases every year. Peritonitis diagnoses equated to 5.2 per cent in Ireland, in keeping with the trend of previous years.
References
DAFM. 2016. “All-Island Animal Disease Surveillance Report.” Dept. of Agriculture, Food; the Marine. https://www.agriculture.gov.ie/media/migration/animalhealthwelfare/labservice/rvlreports/AIDSRReport016230118.pdf.
A cooperative effort between the VLS and the SAT Section of the DAFM