
Section 12 Sheep Diseases Overview
- Margaret Wilson
- Senior Research Officer, Central Veterinary Research Laboratory, DAFM, Backweston, Co. Kildare, Ireland
The Regional Veterinary Laboratories (RVLs) of the Department of Agriculture, Food and the Marine (DAFM) are engaged primarily in scanning (passive) surveillance by gathering data from post-mortem and clinical sample submissions. Analysis of this data provides an insight into trends of disease incidence and causes of mortality on Irish farms, thereby informing decision-making relevant to disease control at a national level. Tables and charts are generated with test results and post-mortem diagnoses from voluntary submissions of material (carcasses and clinical samples) to RVLs by farmers through their private veterinary practitioners (PVPs). Therefore, it should be noted that data reflects only those cases where the PVPs considered it appropriate to request a laboratory investigation and the herdowner was motivated to deliver the carcass to an RVL.
12.1 Diseases of Sheep
In 2018, approximately 1368 ovine carcases were submitted for post-mortem examination. This comprised 798 lambs (from birth to one year of age) and 570 adult sheep (over one year of age).
The range of diagnoses varies according to age of the animal. Thus results in this section are presented by age category. In order to facilitate presentation and comparison, conditions which affect given systems have been grouped together.
12.2 Lambs (birth to 12 months of age)
Conditions affecting the digestive system were the most frequent diagnosis in lambs, with approximately 21 per cent of all lamb submissions being categorised thus. Within this category, parasitic gastroenteritis accounted for 44 per cent of diagnoses and infectious enteritis accounting for 43 per cent. Strongyle spp. and Nematodirus spp. were the most common parasites detected. Within the infectious enteritis category, there were a great variety of agents identified with Coccidia spp. and Cryptosporidium spp. being most commonly detected. Other conditions affecting the digestive system included; watery mouth, rumenitis and colitis.
| Category | No. of Cases | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| GIT Infections | 170 | 21.3 |
| Systemic Infections | 97 | 12.2 |
| Respiratory Infections | 94 | 11.8 |
| Clostridial disease | 86 | 10.8 |
| Diagnosis not reached | 55 | 6.9 |
| Nutritional/metabolic conditions | 47 | 5.9 |
| GIT torsion/obstruction | 37 | 4.6 |
| Navel Ill/Joint Ill | 32 | 4.0 |
| CNS | 27 | 3.4 |
| Urinary Tract conditions | 18 | 2.3 |
| Liver disease | 17 | 2.1 |
| Perinatal Mortality | 16 | 2.0 |
| Cardiac/circulatory conditions | 15 | 1.9 |
| Hereditary and developmental abnormality | 13 | 1.6 |
| Integument/Musculoskeletal | 9 | 1.1 |
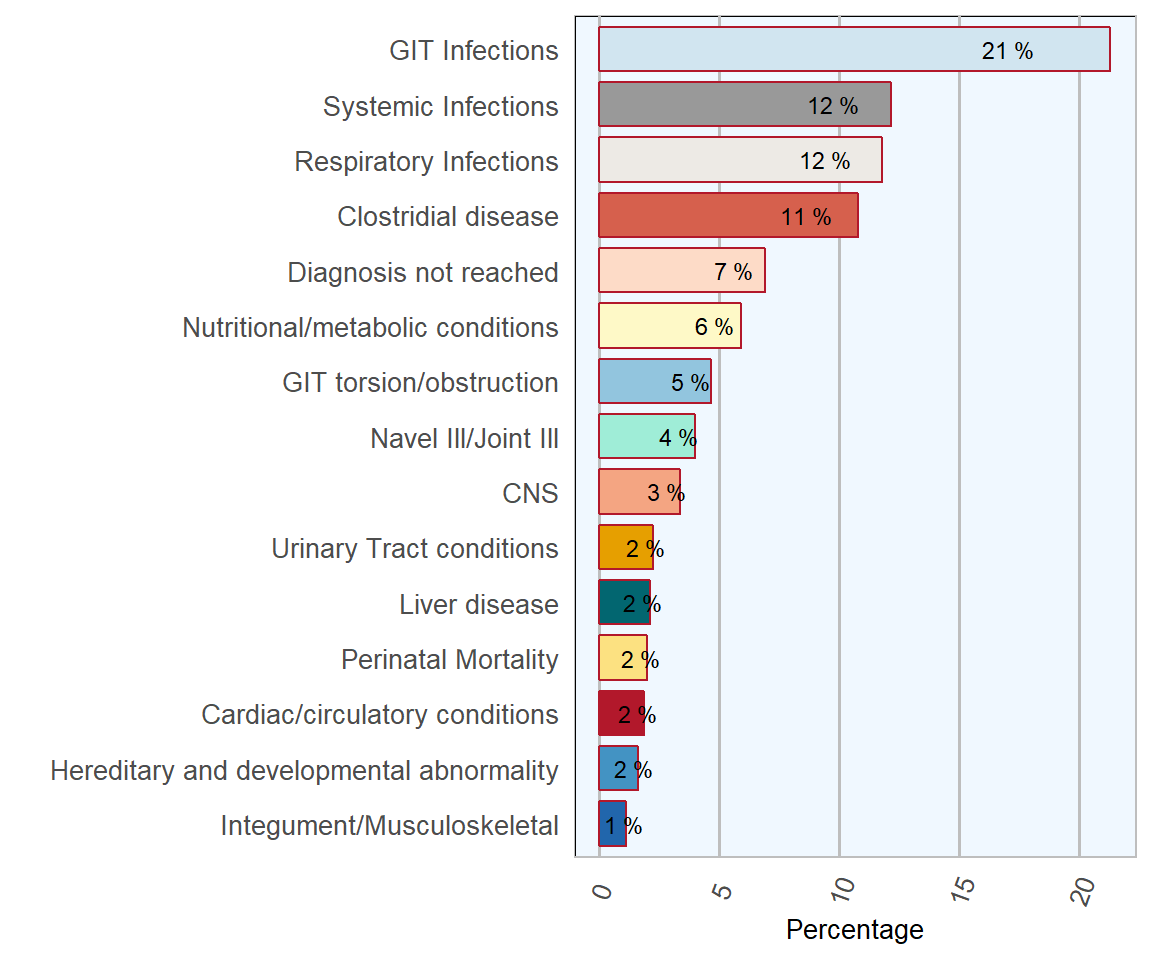
Figure 12.1: Conditions most frequently diagnosed on post-mortem examinations of lambs (from birth to one year of age) in 2018 (n= 798 ).
The next most frequently diagnosed conditions were systemic conditions, affecting approximately 12 per cent of cases and respiratory conditions affecting approximately 11.8 per cent of cases.
Within systemic conditions, bacteraemia/septicaemia, at 65 per cent, represents the largest diagnostic subcategory. Bacteraemia arises when bacterial infections succeed in overwhelming immune defences, is present in circulatory blood and can then result in embolic infection of multiple organs such as meninges, kidney,lung or liver. Septicaemia occurs where both pathogenic bacteria and their toxins are present in circulatory blood, toxins damage organs as they flow around the body resulting in toxaemia. Colloquially, this syndrome is known as blood poisoning and is characterised clinically by high temperature, shivering, weakness and inappetence. The most common agents identified in systemic infections were: E. coli, Bibersteinia trehalosi and Mannheimia haemolytica.
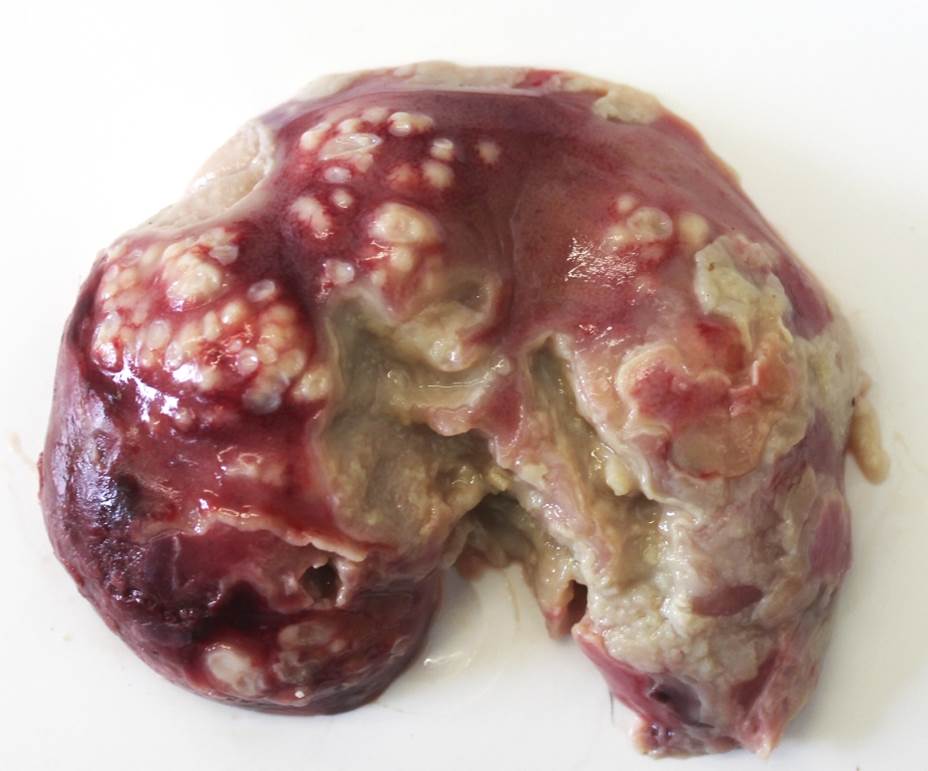
Figure 12.2: Lamb. White-spotted kidney: miliary 1–2 mm pus-filled white spots on renal cortical surface as a consequence of bacteraemia in a young lamb. Staphylococcus aureus isolated. Photo: Margaret Wilson.
Clostridial disease was diagnosed in one hundred and six cases. Eighty-six cases were in lambs, which are typically the most frequently affected age group. Pulpy kidney disease and enterotoxaemia were diagnosed most frequently. Both types of clostridial disease are associated with lamb stress and changes or increases of feed to lambs. Both result in rapid, often sudden, death and typically occur in well growing lambs. A breakdown of detected agents is presented in the Bovine and Ovine Clostridial Diseases section of this report.
Thirty-two cases of navel ill/joint ill were detected in lambs. Navel ill/joint ill is associated with poor umbilical hygiene, low colostrum intake and high environmental contamination in lambing area, allowing bacterial introduction via umbilical stump within the first few hours of life. Infections may remain localised and develop into an umbilical abscess, extend locally to cause peritonitis, ascend to infect the liver or become generalised involving joints and/or other organs.
12.3 Adult Sheep (over 12 months of age)
Liver disease was the most frequent diagnosis in adult sheep with 77 cases, of which 74 were liver fluke (Fasciola hepatica). Liver fluke remains a common and serious threat to sheep health and welfare.
| Category | No. of Cases | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| Liver disease | 77 | 13.5 |
| Respiratory Infections | 63 | 11.1 |
| Systemic Infections | 51 | 8.9 |
| Nutritional/metabolic conditions | 49 | 8.6 |
| Diagnosis not reached | 48 | 8.4 |
| CNS | 44 | 7.7 |
| GIT Infections | 40 | 7.0 |
| Reproductive Tract Conditions | 36 | 6.3 |
| Poisoning | 31 | 5.4 |
| GIT torsion/obstruction | 21 | 3.7 |
| Clostridial disease | 20 | 3.5 |
| Cardiac/circulatory conditions | 13 | 2.3 |
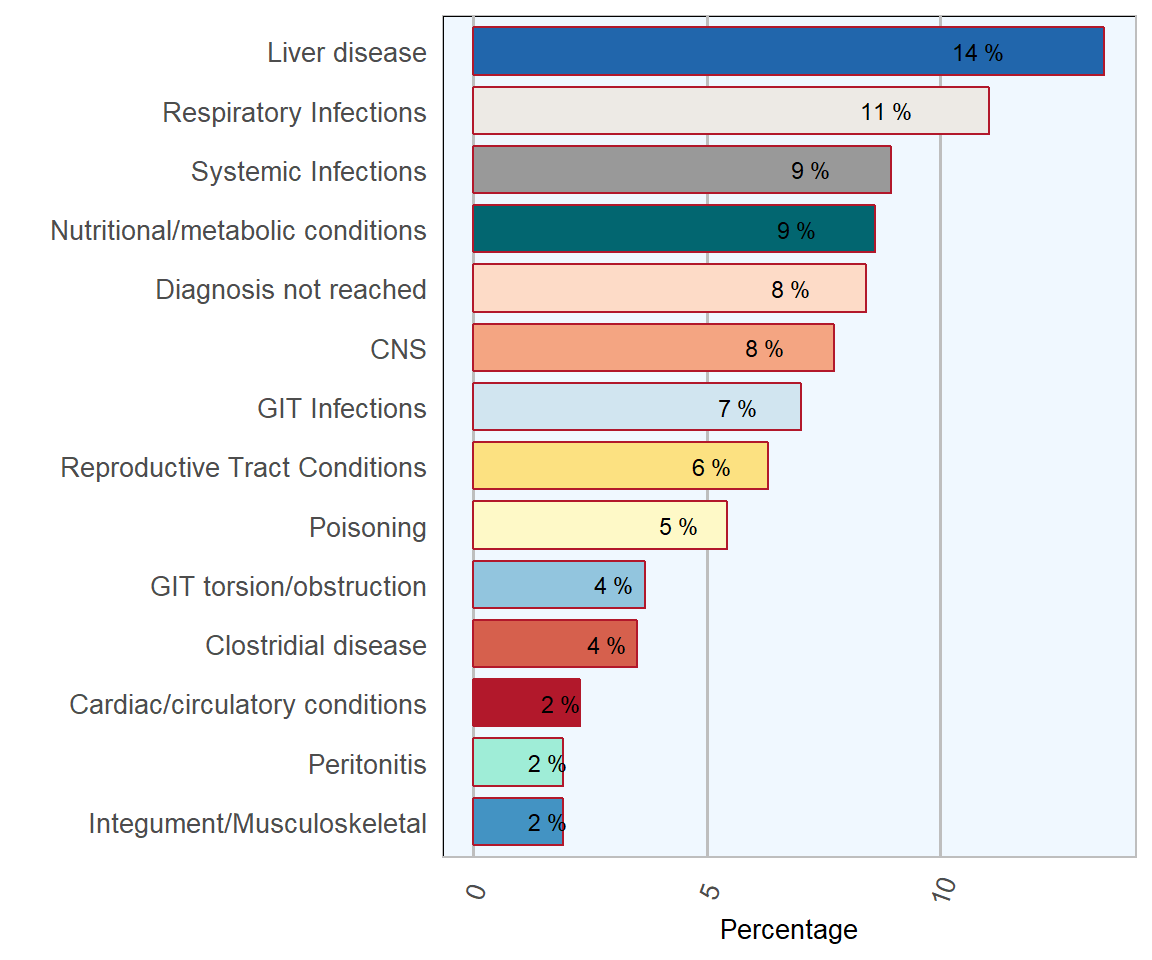
Figure 12.3: Conditions most frequently diagnosed (top 10 categories) on post-mortem examinations of adult sheep (over one year of age) in 2018 (n= 570 ).
The next most frequent diagnosis was respiratory infection, of which 63 cases, 65 percent, were pneumonia. The most commonly detected pneumonic agents were; Mannheimia haemolytica, Pasteurella multocida and Bibersteinia trehalosi.
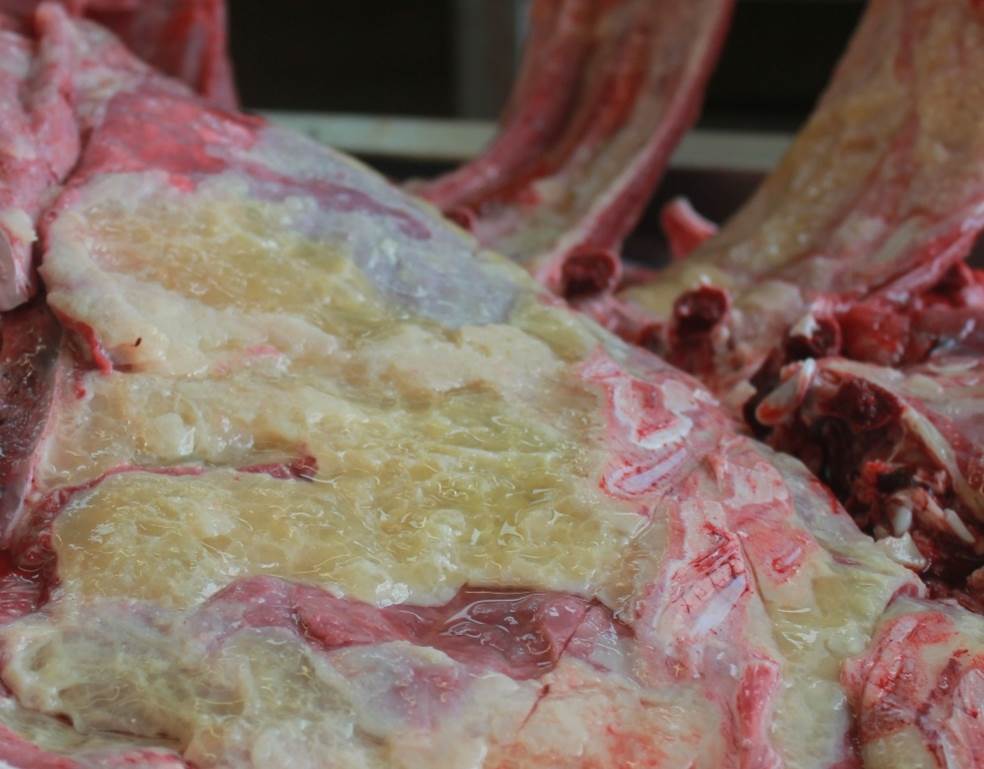
Figure 12.4: Sheep Lung: Severe diffuse fibrinosuppurative pleuropneumonia. Pasteurella multocida isolated. Photo: Margaret Wilson.
Six cases of Ovine Pulmonary Adenomatosis (OPA) were identified. OPA (Jaagsiekte) is a chronic incurable infectious lung tumor in sheep, caused by the Jaagsiekte sheep retrovirus. It has a long incubation period, therefore, it is most commonly detected in adult sheep. Clinical signs are of progressive respiratory illness and weight loss. Secondary bacterial pneumonia is common and often the ultimate cause of death. Post mortem examination of lungs remains the only means of accurately diagnosing Ovine Pulmonary Adenomatosis (Lee et al. 2017).
When it is necessary to carry out post mortem examinations in the field, it is essential that veterinary practitioners take the most appropriate samples for laboratory examination and also to preserve and package them properly. Pathologists at RVLs are available to give advice in this regard.
Central Nervous System diseases accounted for approximately 7.7 per cemt of adult sheep conditions diagnosed. Most commonly, CNS disease was attributed to Listeriosis (Listeria monocytogenes), based on bacterial isolation or presence of characteristic histological lesions in the brain.
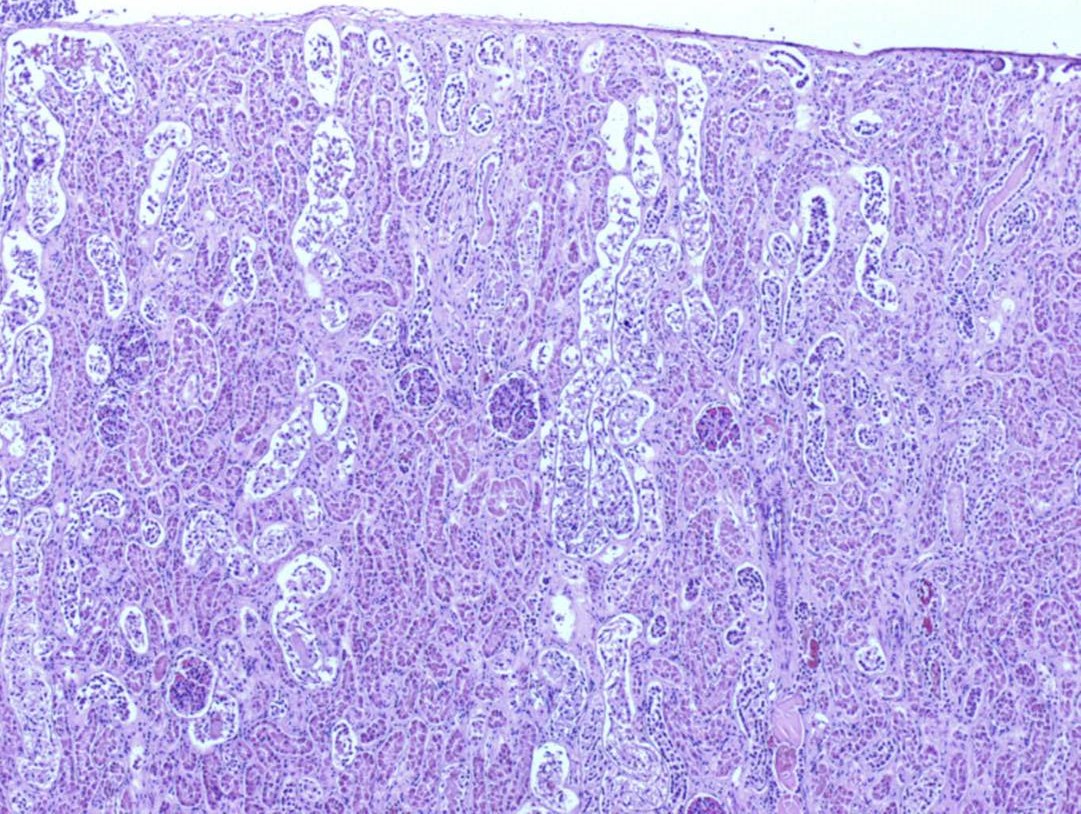
Figure 12.5: Lamb Kidney: Pulpy Kidney Disease: Severe acute proximal tubule necrosis and tubular protein casts. Clostrium perfringens epsilon toxin detected. H&E 10x magnification. Photo: Margaret Wilson.
Thirty-one cases of poisoning were diagnosed in sheep, with copper toxicosis being most frequent. Sheep are predisposed to copper toxicity as the species, relative to other ruminants, has reduced capacity for copper excretion in bile. As a result, excess copper intake in sheep can be fatal.
References
Lee, Alison Marie, Alan Wolfe, Joseph P. Cassidy, Locksley L. McV. Messam, John P. Moriarty, Ronan O’Neill, Claire Fahy, et al. 2017. “First Confirmation by Pcr of Jaagsiekte Sheep Retrovirus in Ireland and Prevalence of Ovine Pulmonary Adenocarcinoma in Adult Sheep at Slaughter.” Irish Veterinary Journal 70 (1): 33. doi:10.1186/s13620-017-0111-z.
A cooperative effort between the VLS and the SAT Section of the DAFM