Loading...
Searching...
No Matches
io/viewers/viewer3D-7-stdplane.cpp
This example shows the recognition of a simple standard digital plane with the COBA algorithm (class DGtal::COBAGenericStandardPlaneComputer). Green points belong to the naive plane. Grey points show farther points that also belong to the strip.
$ ./examples/io/viewers/viewer3D-7-stdplane
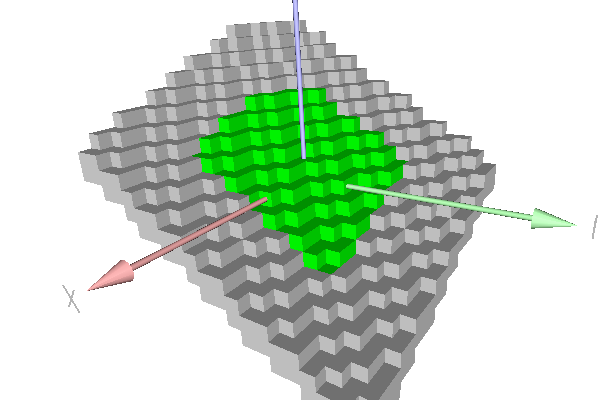
Piece of standard plane.
#include <cstdlib>
#include <iostream>
#include "DGtal/base/Common.h"
#include "DGtal/helpers/StdDefs.h"
#include "DGtal/io/viewers/PolyscopeViewer.h"
#include "DGtal/geometry/surfaces/COBAGenericStandardPlaneComputer.h"
using namespace std;
using namespace DGtal;
// Standard services - public :
/*
Displays in the \a viewer all the points in the \a domain that
satisfies the predicate \a pred.
*/
template <typename Viewer3D, typename Domain, typename Predicate>
void
displayPredicate( Viewer3D & viewer,
{
itB != itE; ++itB )
{
if ( pred( *itB ) )
viewer << *itB;
}
}
/*
Displays in the \a viewer all the points in the range [it,itE).
*/
template <typename Viewer3D, typename InputIterator>
void
displayRange( Viewer3D & viewer, InputIterator it, InputIterator itE )
{
for ( ; it != itE; ++it )
viewer << *it;
}
/*
Returns all the points in the \a domain that belongs to the standard
plane mu <= a*x+b*y+c*z < mu+|a|+|b|+|c|.
*/
template <typename Domain>
std::vector<typename Domain::Point> pointsInStandardPlane
typename Domain::Integer a,
typename Domain::Integer b,
typename Domain::Integer c,
typename Domain::Integer mu )
{
std::vector<Point> pts;
it != itE; ++it )
{
Point p = *it;
Integer r = a * p[ 0 ] + b * p[ 1 ] + c * p[ 2 ];
if ( ( mu <= r ) && ( r < mup ) )
pts.push_back( p );
}
return pts;
}
{
using namespace Z3i;
unsigned int nb = 0;
unsigned int nbok = 0;
unsigned int diameter = argc > 1 ? atoi( argv[ 1 ] ) : 10;
int a = argc > 2 ? atoi( argv[ 2 ] ) : 2;
int b = argc > 3 ? atoi( argv[ 3 ] ) : 3;
int c = argc > 4 ? atoi( argv[ 4 ] ) : 5;
int mu = argc > 5 ? atoi( argv[ 5 ] ) : 0;
<< mu << " <= " << a << " * x + "
<< b << " * y + " << c << " * z < "
Point( diameter, diameter, diameter ) );
typedef PlaneComputer::Primitive Primitive;
PlaneComputer plane;
plane.init( 2*diameter, 1, 1 );
std::vector<Point> recognized = pointsInStandardPlane( domain1,
a, b , c, mu );
++nb, nbok += plane.extend( recognized.begin(), recognized.end() ) ? 1 : 0;
<< ") All points are recognized." << std::endl;
<< std::endl;
Primitive strip = plane.primitive();
<< " axis=" << strip.mainAxis()
<< " axiswidth=" << strip.axisWidth()
<< " diag=" << strip.mainDiagonal()
<< " diagwidth=" << strip.diagonalWidth()
<< std::endl;
++nb, nbok += ( strip.diagonalWidth() < sqrt(3.0) ) ? 1 : 0;
<< ") Diagonal width < sqrt(3)." << std::endl;
PolyscopeViewer viewer;
Color red( 255, 0, 0 );
Color green( 0, 255, 0 );
Color grey( 200, 200, 200 );
Point( 2*diameter, 2*diameter, 2*diameter ) );
viewer << red;
for ( std::vector<Point>::const_iterator it = recognized.begin(),
itE = recognized.end(); it != itE; ++it )
if ( ! strip( *it ) ) viewer << *it;
viewer << green;
displayRange( viewer, plane.begin(), plane.end() );
viewer << grey;
displayPredicate( viewer, domain2, strip );
trace.info() << "- Points in green have been recognized as belonging to this standard plane." << std::endl;
trace.info() << "- Points in grey belongs also to the parallel strip of the recognized standard plane." << std::endl;
trace.info() << "- Points in red belongs to the parallel strip of the recognized standard plane but not to the input standard plane: NONE should be red." << std::endl;
viewer.show();
return 0;
}
// //
Aim: A class that recognizes pieces of digital planes of given axis width. When the diagonal width is...
Definition COBAGenericStandardPlaneComputer.h:129
void init(InternalInteger diameter, InternalInteger widthNumerator=NumberTraits< InternalInteger >::ONE, InternalInteger widthDenominator=NumberTraits< InternalInteger >::ONE)
Definition PolyscopeViewer.h:56
void beginBlock(const std::string &keyword="")
std::ostream & emphase()
std::ostream & info()
double endBlock()
Definition testClone2.cpp:346
MyDigitalSurface::ConstIterator ConstIterator
Definition greedy-plane-segmentation-ex2.cpp:90
DGtal is the top-level namespace which contains all DGtal functions and types.
Definition ClosedIntegerHalfPlane.h:49
Trace trace
STL namespace.
std::vector< typename Domain::Point > pointsInStandardPlane(const Domain &domain, typename Domain::Integer a, typename Domain::Integer b, typename Domain::Integer c, typename Domain::Integer mu)
Definition testChordGenericStandardPlaneComputer.cpp:60
void displayPredicate(Viewer3D &viewer, const Domain &domain, const Predicate &pred)
Definition viewer3D-7-planes.cpp:64