Linear Search
A simple approach is to do a linear search, i.e
- Start from the leftmost element of arr[] and one by one compare x with each element of arr[]
- If x matches with an element, return the index.
- If x doesn’t match with any of elements, return -1.
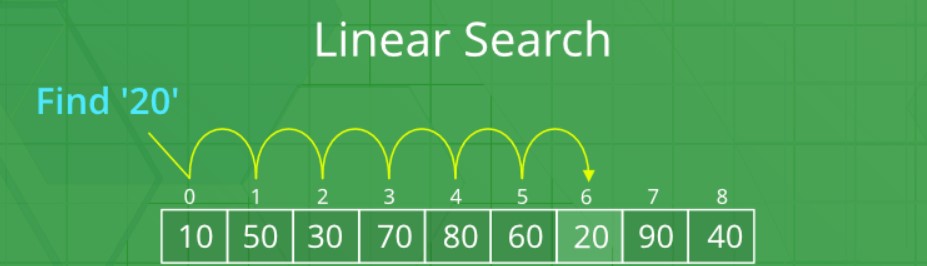
Example
/* C++ code to linearly search x in arr[]. If x
is present then return its location, otherwise
return -1 */
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int search(int arr[], int n, int x)
{
int i;
for(i = 0; i < n; i++)
if(arr[i] == x)
return i;
return -1;
}
int main(void)
{
int arr[] = { 2, 3, 4, 10, 40 };
int x = 10;
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
// Function call
int result = search(arr, n, x);
(result == -1)
? cout << "Element is not present in array"
: cout << "Element is present at index " << result;
return 0;
}
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int search(int arr[], int n, int x)
{
int i;
for(i = 0; i < n; i++)
if(arr[i] == x)
return i;
return -1;
}
int main(void)
{
int arr[] = { 2, 3, 4, 10, 40 };
int x = 10;
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
// Function call
int result = search(arr, n, x);
(result == -1)
? cout << "Element is not present in array"
: cout << "Element is present at index " << result;
return 0;
}
Output
Element is present at index 3
The time complexity of the above algorithm is O(n).
Linear search is rarely used practically because other search algorithms such as the binary search
algorithm and hash tables allow significantly faster-searching comparison to Linear search.