# Introduction to Prompt Learning
## Background
Prompt-learning has been a widely-used paradigm in the field of Natural Language Processing (NLP), especially when data is limited. It follows the idea of pretraining-finetuning paradigm, where pre-trained language models (PLMs) will be adapted to various downstream tasks. Instead of adding task-specific objectives in finetuning, prompt-learning converts each original task to a specific prompting function. This process is named prompt engineering.
## Prompt Engineering
Their are two main approaches in prompt engineering: cloze prompts and prefix prompts. Cloze prompts are more suitable in downstream tasks using masked LMs, while prefix prompts are generally used in text generation tasks.
### Cloze Prompts
Generally, the input texts and labels can be obtained from the task dataset. These data will be rearranged into a cloze-style phrase, which includes two steps:
1. Applying a template which consists of an input slot, an answer slot, and self-defined natural language texts
2. Applying a verbalizer that maps the original labels to answers for the answer slot.
As shown in the following example, the dataset contains two input texts: premise and hypothesis. The label indicates the relationship between premise and hypothesis, and there are three possible text strings for label: entailment, contradiction and neutral.
We can design a meaningful cloze template as below
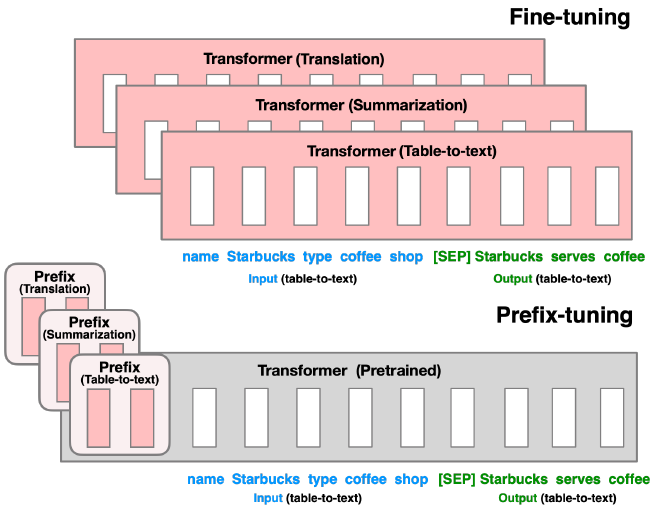
### Prefix Prompts
Instead of designing a prompt in real natural language, prefix prompts directly modifies the embedding space. It inserts a sequence of task-specific vectors and freezes the LM parameters. An advantage of prefix prompts is that embeddings of templates are no longer limited by parameters in pre-trained LMs.
Here is an example that compares prefix tuning and fine-tuning in the embedding space of transformers,the grey parts of the transformer are frozen during prefix tuning:
## Reference
Liu, P. (2021, July 28). Pre-train, Prompt, and Predict: A Systematic Survey of Prompting. . . arXiv.Org. https://arxiv.org/abs/2107.13586
Ding, N. (2021, November 3). OpenPrompt: An Open-source Framework for Prompt-learning. arXiv.Org. https://arxiv.org/abs/2111.01998
Schick, T. (2020, January 21). Exploiting Cloze Questions for Few Shot Text Classification and. . . arXiv.Org. https://arxiv.org/abs/2001.07676
Li, X. L. (2021, January 1). Prefix-Tuning: Optimizing Continuous Prompts for Generation. arXiv.Org. https://arxiv.org/abs/2101.00190