5.2. Vapor compression machines¶
The major part of heat pumps and refrigerators are working using phase change. During the compression, the fluid is vapor so they are named Vapor compression machines.
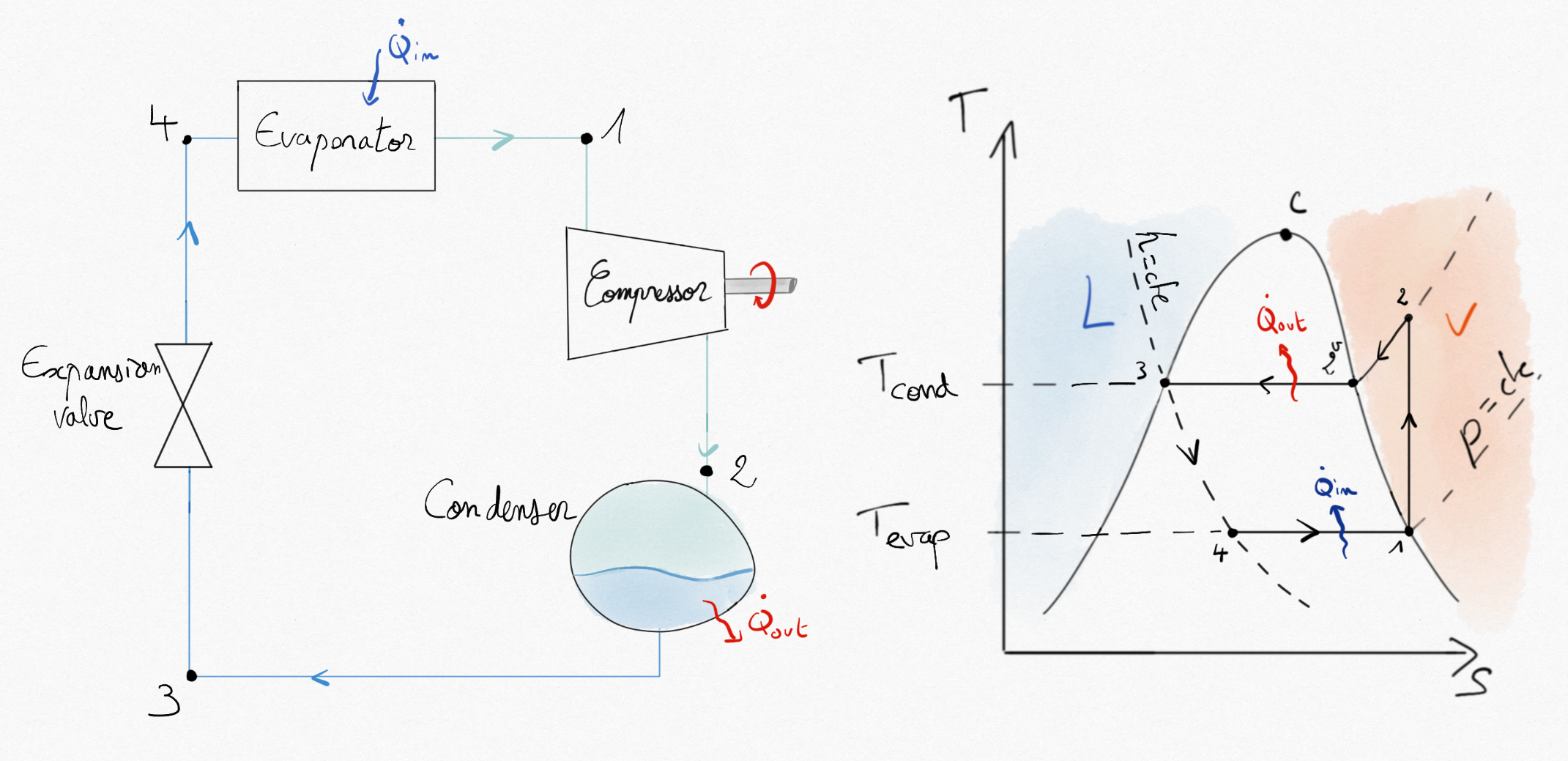
Figure 5.3: Vapor compression machine (Heat pump or Refrigerator) cycle.¶
Compared to the reverse Hirn cycle, the differences are:
In the compressor (generally a reciprocating compressor with piston), liquid may not be admitted. Point 1 shoul be at least saturated vapor.
The energy that can be obtained by using an expansion machine in transformation 3-4 is low compared to those necessary to compress vapor during transformation 1-2. Thus, it is replaced by a simple expansion valve (throttle valve) where the expansion becomes at constant enthalpy. This process is called laminating (Section 1.2.4: ).
As for any heat pump or refrigerator, (Eq.2.11, and Eq.2.10) the coefficients of performance of vapor compression machines are:
Because no machine is working in transformations 2-3 and 4-1, application of the balance energy equation reads:
such that the thermal efficiency of vapor compression machines becomes:
(5.2)¶
Caution
The fluid can not be considered as an ideal gas since a phase change occurs from liquid to vapor and reversely. In practice calculs are performed thanks to thermodynamics tables.