Megatron-LM and Megatron Core
=============================
GPU-optimized library for training transformer models at scale
[](https://docs.nvidia.com/Megatron-Core/developer-guide/latest/index.html)
[](./CHANGELOG.md)
[](./LICENSE)
## About
This repository contains two components: **Megatron-LM** and **Megatron Core**.
**Megatron-LM** is a reference example that includes Megatron Core plus pre-configured training scripts. Best for research teams, learning distributed training, and quick experimentation.
**Megatron Core** is a composable library with GPU-optimized building blocks for custom training frameworks. It provides transformer building blocks, advanced parallelism strategies (TP, PP, DP, EP, CP), mixed precision support (FP16, BF16, FP8, FP4), and model architectures. Best for framework developers and ML engineers building custom training pipelines.
**[Megatron Bridge](https://github.com/NVIDIA-NeMo/Megatron-Bridge)** provides bidirectional Hugging Face ↔ Megatron checkpoint conversion with production-ready recipes.
## Quick Start
Install Megatron Core with pip:
1. Install Megatron Core with required dependencies:
```bash
pip install --no-build-isolation megatron-core[mlm,dev]
```
2. Clone repository for examples:
```bash
git clone https://github.com/NVIDIA/Megatron-LM.git
cd Megatron-LM
pip install --no-build-isolation .[mlm,dev]
```
# Latest News
- **[2026/01]** **[Dynamic Context Parallelism](https://developer.nvidia.com/blog/speeding-up-variable-length-training-with-dynamic-context-parallelism-and-nvidia-megatron-core/)** - Up to 1.48x speedup for variable-length sequence training with adaptive CP sizing.
- **[2025/12]** **Megatron Core development has moved to GitHub!** All development and CI now happens in the open. We welcome community contributions.
- **[2025/10]** **[Megatron Dev Branch](https://github.com/NVIDIA/Megatron-LM/tree/dev)** - early access branch with experimental features.
- **[2025/10]** **[Megatron Bridge](https://github.com/NVIDIA-NeMo/Megatron-Bridge)** - Bidirectional converter for interoperability between Hugging Face and Megatron checkpoints, featuring production-ready recipes for popular models.
- **[2025/08]** **[MoE Q3-Q4 2025 Roadmap](https://github.com/NVIDIA/Megatron-LM/issues/1729)** - Comprehensive roadmap for MoE features including DeepSeek-V3, Qwen3, advanced parallelism strategies, FP8 optimizations, and Blackwell performance enhancements.
- **[2025/08]** **[GPT-OSS Model](https://github.com/NVIDIA/Megatron-LM/issues/1739)** - Advanced features including YaRN RoPE scaling, attention sinks, and custom activation functions are being integrated into Megatron Core.
- **[2025/06]** **[Megatron MoE Model Zoo](https://github.com/yanring/Megatron-MoE-ModelZoo)** - Best practices and optimized configurations for training DeepSeek-V3, Mixtral, and Qwen3 MoE models with performance benchmarking and checkpoint conversion tools.
- **[2025/05]** Megatron Core v0.11.0 brings new capabilities for multi-data center LLM training ([blog](https://developer.nvidia.com/blog/turbocharge-llm-training-across-long-haul-data-center-networks-with-nvidia-nemo-framework/)).
Previous News
- **[2024/07]** Megatron Core v0.7 improves scalability and training resiliency and adds support for multimodal training ([blog](https://developer.nvidia.com/blog/train-generative-ai-models-more-efficiently-with-new-nvidia-Megatron-Core-functionalities/)).
- **[2024/06]** Megatron Core added supports for Mamba-based models. Check out our paper [An Empirical Study of Mamba-based Language Models](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2406.07887) and [code example](https://github.com/NVIDIA/Megatron-LM/tree/ssm/examples/mamba).
- **[2024/01 Announcement]** NVIDIA has released the core capabilities in **Megatron-LM** into [**Megatron Core**](https://github.com/NVIDIA/Megatron-LM/tree/main/megatron/core) in this repository. Megatron Core expands upon Megatron-LM's GPU-optimized techniques with more cutting-edge innovations on system-level optimizations, featuring composable and modular APIs.
# Project Structure
```
Megatron-LM/
├── megatron/
│ ├── core/ # Megatron Core (kernels, parallelism, building blocks)
│ │ ├── models/ # Transformer models
│ │ ├── transformer/ # Transformer building blocks
│ │ ├── tensor_parallel/ # Tensor parallelism
│ │ ├── pipeline_parallel/ # Pipeline parallelism
│ │ ├── distributed/ # Distributed training (FSDP, DDP)
│ │ ├── optimizer/ # Optimizers
│ │ ├── datasets/ # Dataset loaders
│ │ ├── inference/ # Inference engines and server
│ │ └── export/ # Model export (e.g. TensorRT-LLM)
│ ├── training/ # Training scripts
│ ├── legacy/ # Legacy components
│ ├── post_training/ # Post-training (quantization, distillation, pruning, etc.)
│ └── rl/ # Reinforcement learning (RLHF, etc.)
├── examples/ # Ready-to-use training examples
├── tools/ # Utility tools
├── tests/ # Comprehensive test suite
└── docs/ # Documentation
```
# Performance Benchmarking
For our latest performance benchmarking results, please refer to [NVIDIA Megatron Bridge Performance Summary](https://docs.nvidia.com/nemo/megatron-bridge/latest/performance-summary.html).
Our codebase efficiently trains models from 2B to 462B parameters across thousands of GPUs, achieving up to **47% Model FLOP Utilization (MFU)** on H100 clusters.
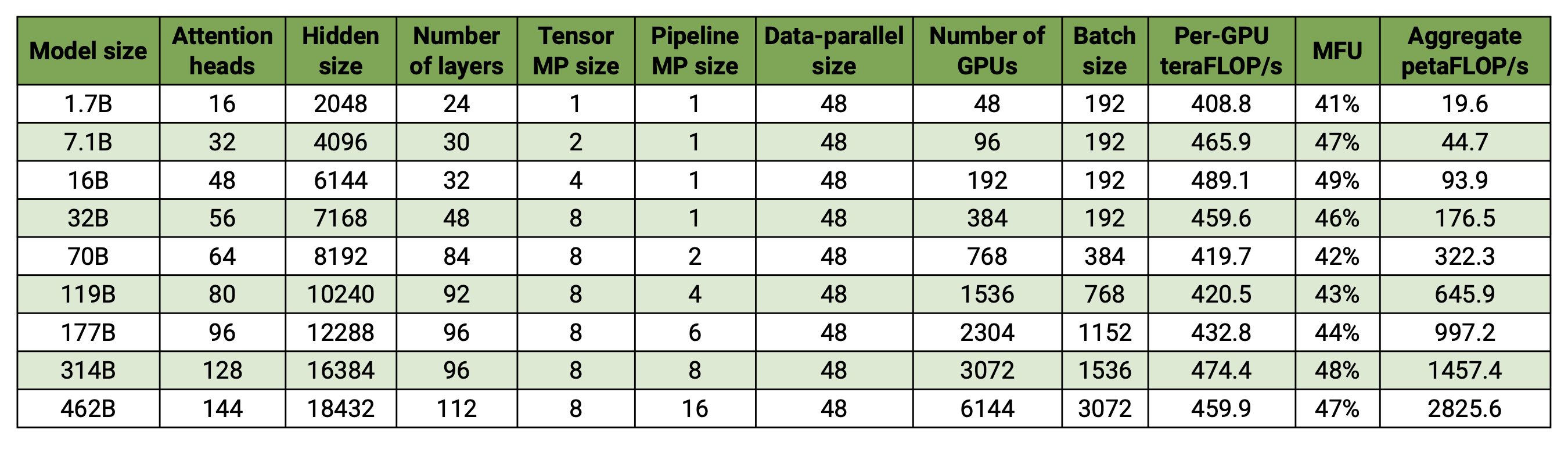
**Benchmark Configuration:**
- **Vocabulary size**: 131,072 tokens
- **Sequence length**: 4096 tokens
- **Model scaling**: Varied hidden size, attention heads, and layers to achieve target parameter counts
- **Communication optimizations**: Fine-grained overlapping with DP (`--overlap-grad-reduce`, `--overlap-param-gather`), TP (`--tp-comm-overlap`), and PP (enabled by default)
**Key Results:**
- **6144 H100 GPUs**: Successfully benchmarked 462B parameter model training
- **Superlinear scaling**: MFU increases from 41% to 47-48% with model size
- **End-to-end measurement**: Throughputs include all operations (data loading, optimizer steps, communication, logging)
- **Production ready**: Full training pipeline with checkpointing and fault tolerance
- *Note: Performance results measured without training to convergence*
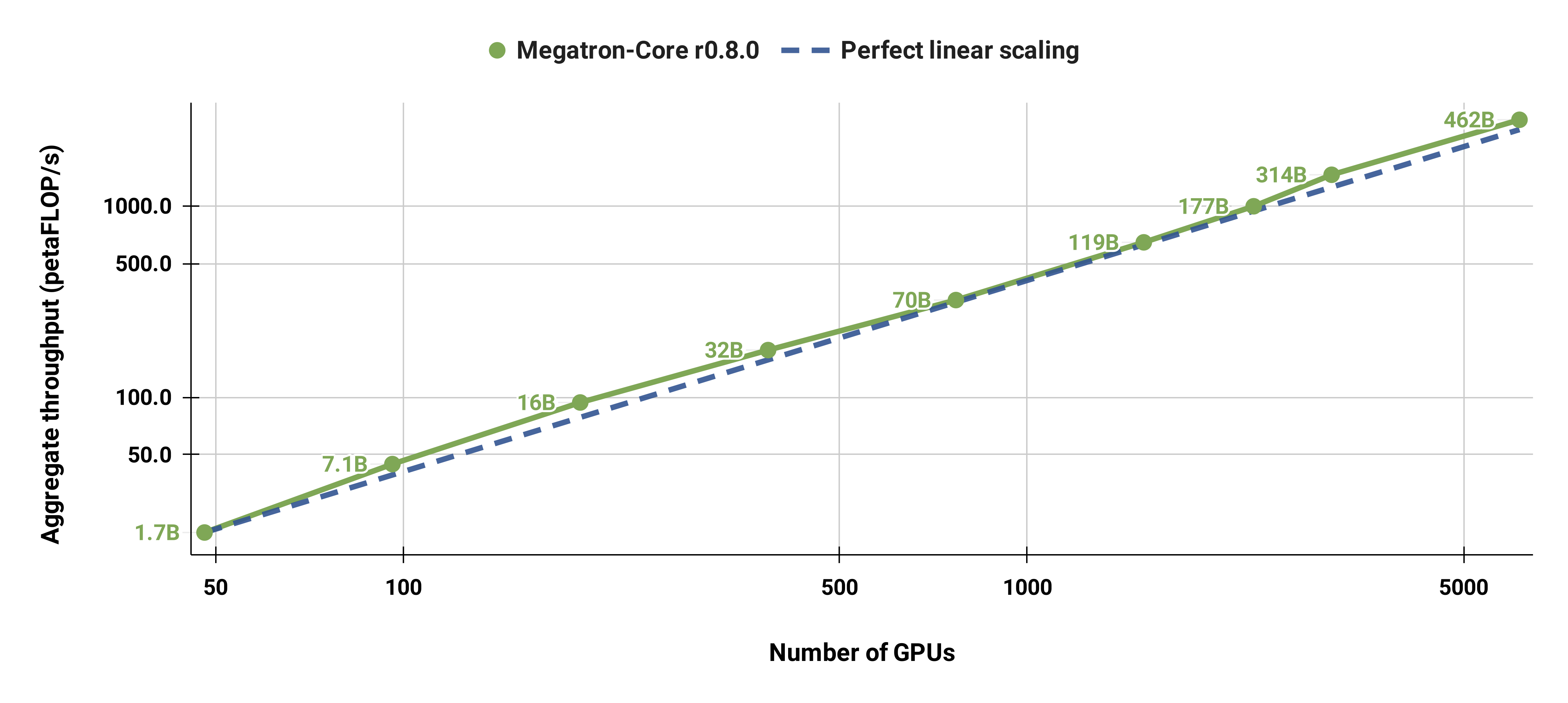
## Weak Scaling Results
Our weak scaled results show superlinear scaling (MFU increases from 41% for the smallest model considered to 47-48% for the largest models); this is because larger GEMMs have higher arithmetic intensity and are consequently more efficient to execute.
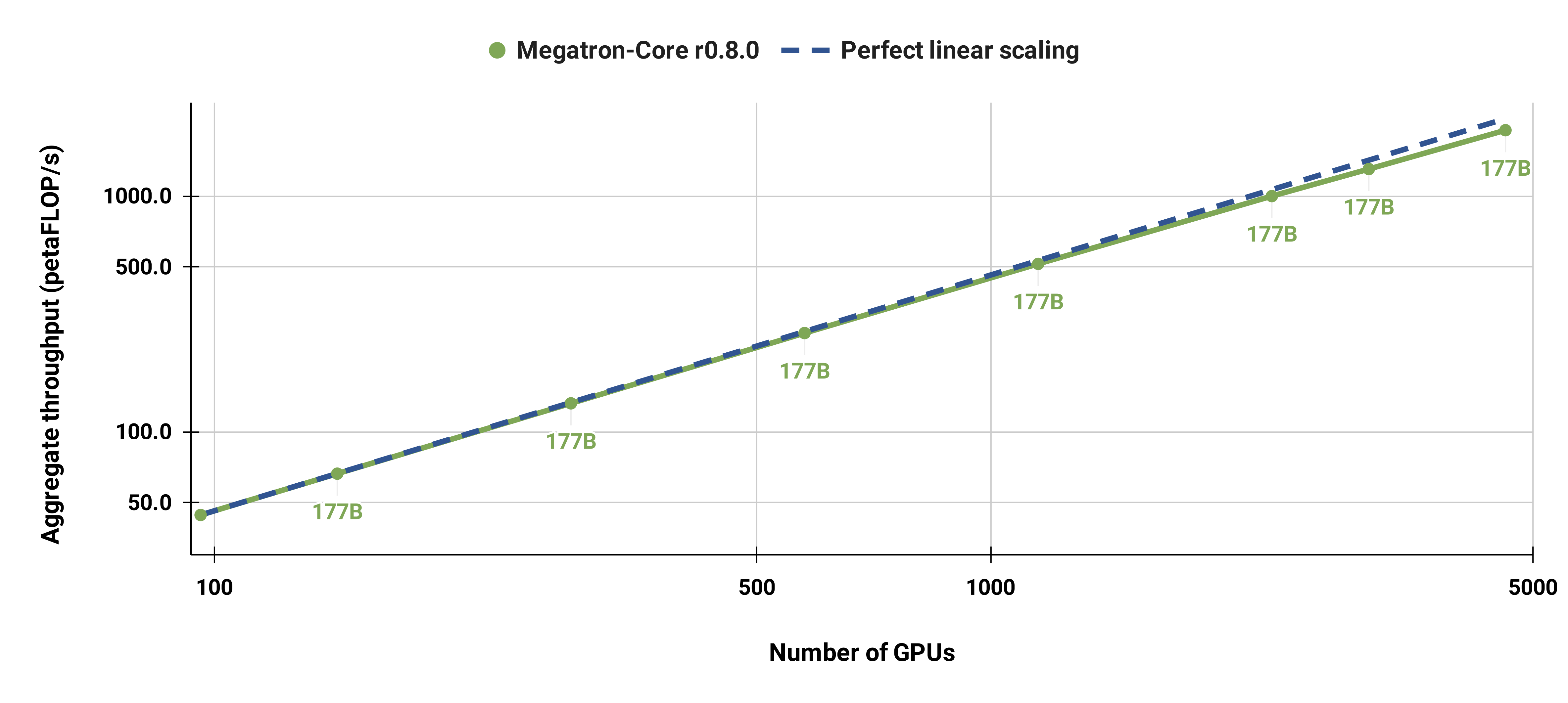
## Strong Scaling Results
We also strong scaled the standard GPT-3 model (our version has slightly more than 175 billion parameters due to larger vocabulary size) from 96 H100 GPUs to 4608 GPUs, using the same batch size of 1152 sequences throughout. Communication becomes more exposed at larger scale, leading to a reduction in MFU from 47% to 42%.
# Roadmaps
- **[MoE Roadmap](https://github.com/NVIDIA/Megatron-LM/issues/1729)** - DeepSeek-V3, Qwen3, advanced parallelism, FP8 optimizations, and Blackwell enhancements
# Resources
## Getting Help
- 📖 **[Documentation](https://docs.nvidia.com/Megatron-Core/)** - Official documentation
- 🐛 **[Issues](https://github.com/NVIDIA/Megatron-LM/issues)** - Bug reports and feature requests
## Contributing
We ❤️ contributions! Ways to contribute:
- 🐛 **Report bugs** - Help us improve reliability
- 💡 **Suggest features** - Shape the future of Megatron Core
- 📝 **Improve docs** - Make Megatron Core more accessible
- 🔧 **Submit PRs** - Contribute code improvements
**→ [Contributing Guide](./CONTRIBUTING.md)**
## Citation
If you use Megatron in your research or project, we appreciate that you use the following citations:
```bibtex
@article{megatron-lm,
title={Megatron-LM: Training Multi-Billion Parameter Language Models Using Model Parallelism},
author={Shoeybi, Mohammad and Patwary, Mostofa and Puri, Raul and LeGresley, Patrick and Casper, Jared and Catanzaro, Bryan},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:1909.08053},
year={2019}
}
```