NAM 2019 pMuTT Workshop¶
Instructions and materials for the "Theory, Applications, and Tools for Kinetic Modeling" workshop can be found on our documentation page.
Table of Contents¶
| 1. Virtual Kinetic Laboratory Ecosystem
| 2. Useful Links
| 3. Constants
|-- 3.1. Access common constants in appropriate units
|-- 3.2. Convert between units
|-- 3.3. Convert between equivalent quantities
| 4. Exercise 1
| 5. Creating statistical mechanical objects using StatMech
|-- 5.1. Supported StatMech models
|--|-- 5.1.1 Translations
|--|-- 5.1.2. Vibrations
|--|-- 5.1.3. Rotations
|--|-- 5.1.4. Electronic
|--|-- 5.1.5. Miscellaneous
|-- 5.2. Initializing StatMech modes individually
|-- 5.3. Initializing StatMech modes using presets
| 6. Plot Thermodynamic Quantities
| 7. Exercise 2
| 8. Creating empirical objects
|-- 8.1. Inputting a NASA polynomial directly
|-- 8.2. Fitting an empirical object to a StatMech object
| 9. Input/Output
|-- 9.1. Input via Excel
|-- 9.2. Output via Thermdat
| 10. Reactions
| 11. Exercise 3
| 12. Solutions
|-- 12.1. Solution 1
|-- 12.2. Solution 2
|-- 12.3. Solution 3
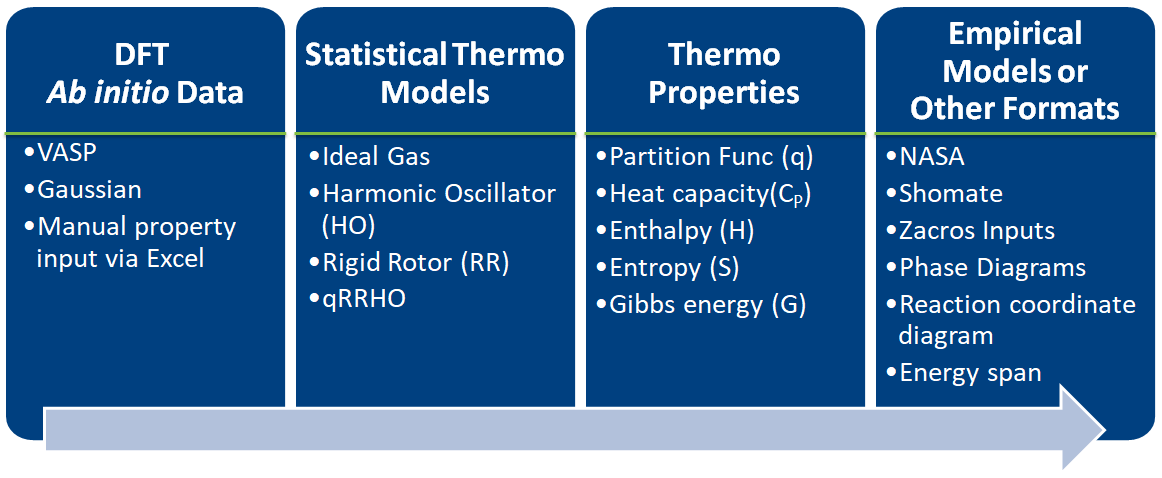
1. Virtual Kinetic Laboratory Ecosystem¶

- Estimates thermochemical and kinetic parameters using statistical mechanics, transition state theory
- Writes input files for kinetic models and eases thermodynamic analysis
- Implemented in Python
- Easy to learn
- Heavily used in scientific community
- Object-oriented approach is a natural analogy to chemical phenomenon
- Library approach allows users to define the starting point and end point
2. Useful Links¶
- Documentation: find the most updated documentation
- Issues: report bugs, request features, receive help
- Examples: see examples
3. Constants¶
The constants module has a wide variety of functions for constants and unit conversion.
3.1. Access common constants in appropriate units¶
Below, we access Planck's constant in J s.
from pmutt import constants as c
h1 = c.h('eV s', bar=True)
print('h = {} eV s'.format(h1))
3.2. Convert between units¶
Below, we convert 12 atm of pressure to psi.
from pmutt import constants as c
P_atm = 12. # atm
P_psi = c.convert_unit(num=P_atm, initial='atm', final='psi')
print('{} atm = {} psi'.format(P_atm, P_psi))
3.3. Convert between equivalent quantities¶
Below, we convert 1000 wavenumbers (cm-1) to frequency.
from pmutt import constants as c
wave_num = 1000. # cm-1
freq = c.wavenumber_to_freq(wave_num) # Hz
print('{} cm-1 = {} Hz'.format(wave_num, freq))
4. Exercise 1¶
Using pmutt.constants, calculate the dimensionless enthalpy (H/RT) using the following information:
- H = 0.5 eV
- T = 77 F
# Fill in your answer for Exercise 1 here
5. Creating statistical mechanical objects using StatMech¶
Molecules show translational, vibrational, rotational, electronic, and nuclear modes.
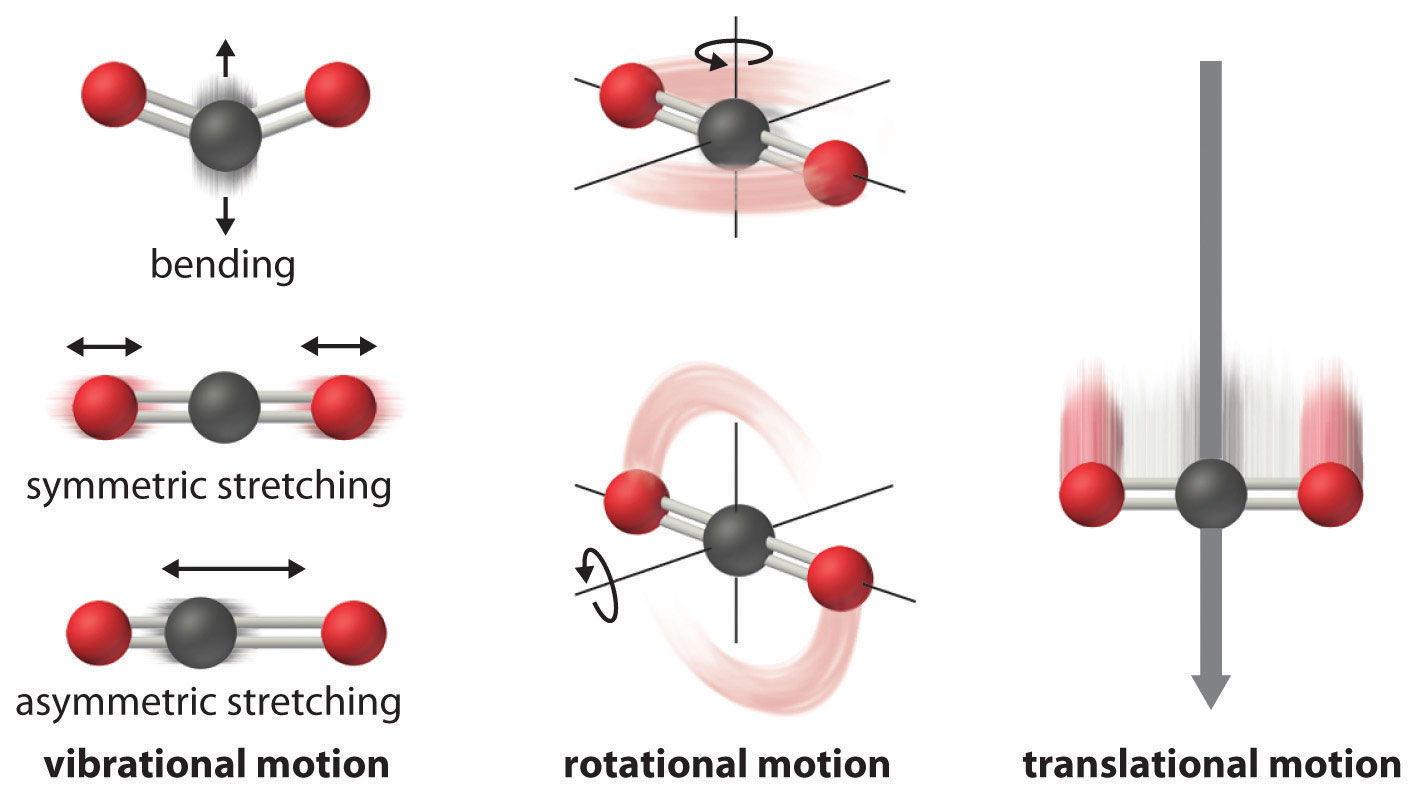
5.1. Supported StatMech modes¶
The StatMech object allows us to specify translational, vibrational, rotational, electronic and nuclear modes independently, which gives flexibility in what behavior you would like. Below are the available modes.
5.1.2. Vibrations¶
HarmonicVib- Harmonic vibrationsQRRHOVib- Quasi rigid rotor harmonic oscillator. Low frequency modes are treated as rigid rotations.EinsteinVib- Each atom in the crystal vibrates as independent 3D harmonic oscillatorsDebyeVib- Improves uponEinsteinVibby considering simultaneous vibrations. Improves accuracy at lower temperatures.
5.1.3. Rotations¶
RigidRotor- Molecule can be rotated with no change in bond properties
5.1.4. Electronic¶
GroundStateElec- Electronic ground state of the systemLSR- Linear Scaling Relationship to estimate binding energies using reference adsorbate
5.1.5. Miscellaneous¶
EmptyMode- Default mode if not specified. Does not contribute to any propertiesConstantMode- Specify arbitrary values to thermodynamic quantities
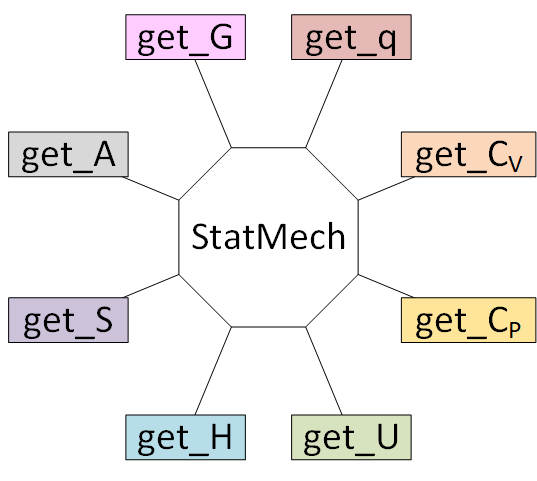
Using a StatMech mode gives you access to all the common thermodynamic properties.
For this example, we will use a hydrogen molecule as an ideal gas:
- translations with no interaction between molecules
- harmonic vibrations
- rigid rotor rotations
- ground state electronic structure
- no contribution from nuclear modes.
5.2. Initializing StatMech modes individually¶
from ase.build import molecule
from pmutt.statmech import StatMech, trans, vib, rot, elec
H2_atoms = molecule('H2')
'''Translational'''
H2_trans = trans.FreeTrans(n_degrees=3, atoms=H2_atoms)
'''Vibrational'''
H2_vib = vib.HarmonicVib(vib_wavenumbers=[4342.]) # vib_wavenumbers in cm-1
'''Rotational'''
H2_rot = rot.RigidRotor(symmetrynumber=2, atoms=H2_atoms)
'''Electronic'''
H2_elec = elec.GroundStateElec(potentialenergy=-6.77,spin=0) # potentialenergy in eV
'''StatMech Initialization'''
H2_statmech = StatMech(name='H2',
trans_model=H2_trans,
vib_model=H2_vib,
rot_model=H2_rot,
elec_model=H2_elec)
'''Calculate thermodynamic properties'''
H_statmech = H2_statmech.get_H(T=298., units='kJ/mol')
S_statmech = H2_statmech.get_S(T=298., units='J/mol/K')
print('H_H2(T=298 K) = {:.1f} kJ/mol'.format(H_statmech))
print('S_H2(T=298 K) = {:.2f} J/mol/K'.format(S_statmech))
5.3. Initializing StatMech modes using presets¶
Commonly used models can be accessed via presets. The currently supported models are:
idealgas- Ideal gasesharmonic- Typical for surface specieselectronic- Only has electronic modesplaceholder- No contribution to any propertyconstant- Use arbitrary constants to thermodynamic properties
from ase.build import molecule
from pmutt.statmech import StatMech, presets
H2_statmech = StatMech(atoms=molecule('H2'),
vib_wavenumbers=[4342.], # cm-1
symmetrynumber=2,
potentialenergy=-6.77, # eV
spin=0.,
**presets['idealgas'])
'''Calculate thermodynamic properties'''
H_statmech = H2_statmech.get_H(T=298., units='kJ/mol')
S_statmech = H2_statmech.get_S(T=298., units='J/mol/K')
print('H_H2(T=298 K) = {:.1f} kJ/mol'.format(H_statmech))
print('S_H2(T=298 K) = {:.2f} J/mol/K'.format(S_statmech))
6. Plot Thermodynamic Quantities¶
Use pmutt.plot_1D and pmutt.plot_2D to plot any function with respect to 1 or 2 variables.
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from pmutt import plot_1D, plot_2D
T = np.linspace(300., 500.)
f1, ax1 = plot_1D(H2_statmech,
x_name='T', x_values=T,
methods=('get_H', 'get_S', 'get_G'),
get_H_kwargs={'units': 'kcal/mol'},
get_S_kwargs={'units': 'cal/mol/K'},
get_G_kwargs={'units': 'kcal/mol'})
f1.set_size_inches(6, 6)
f1.set_dpi(200)
plt.show()
7. Exercise 2¶
- Create a
StatMechobject for ideal gas-phase H2O. The necessary inputs are given below.
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| atoms | molecule('H2O') |
| Potential Energy (eV) | -6.7598 |
| Symmetry number | 2 |
| Spin | 0 |
| Vibrational Wavenumbers (cm-1) | 3825.434, 3710.264, 1582.432 |
Calculate the Gibbs energy in eV for H2O at T = 500 K and P = 2 bar.
Create a
StatMechobject for a Cu crystal using theDebyeVibmodel for the vibration mode andGroundStateElecmodel for electronic mode. The necessary inputs are given below.
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Debye Temperature (K) | 310 |
| Interaction energy (eV) | 0 |
| Potential energy (eV) | -14.922356 |
- Plot the H (in eV) and S (in eV/K) for Cu between T = 300 - 700 K.
# Fill in your answer for Exercise 2 here
# 1.
# 2.
# 3.
# 4.
8. Creating empirical objects¶
Currently, pMuTT supports NASA polynomials and Shomate polynomials. They can be initialized in three ways:
- passing in the polynomials directly
- from a model (e.g.
StatMech,Shomate) (from_model) - from heat capacity, enthalpy and entropy data (
from_data)
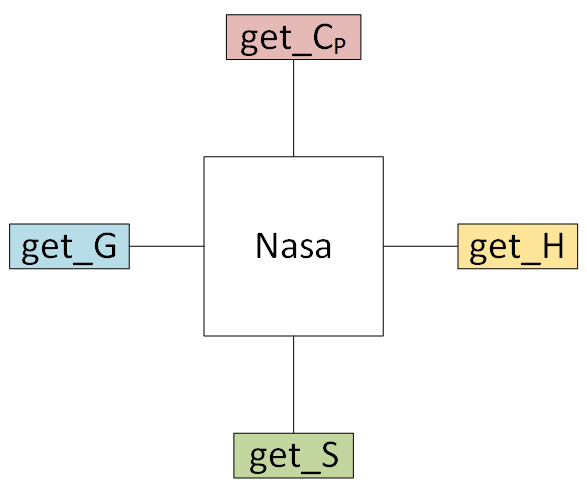
8.1. Inputting a NASA polynomial directly¶
The H2 NASA polynomial from the Burcat database is represented as:
H2 TPIS78H 2 G 200.000 3500.000 1000.000 1
3.33727920E+00-4.94024731E-05 4.99456778E-07-1.79566394E-10 2.00255376E-14 2
-9.50158922E+02-3.20502331E+00 2.34433112E+00 7.98052075E-03-1.94781510E-05 3
2.01572094E-08-7.37611761E-12-9.17935173E+02 6.83010238E-01 4This can be translated to pMuTT syntax using:
from pmutt.empirical.nasa import Nasa
# Initialize NASA polynomial
H2_nasa = Nasa(name='H2',
elements={'H': 2},
phase='G',
T_low=200., T_mid=1000., T_high=3500.,
a_low=[2.34433112E+00, 7.98052075E-03, -1.94781510E-05,
2.01572094E-08, -7.37611761E-12, -9.17935173E+02,
6.83010238E-01],
a_high=[3.33727920E+00, -4.94024731E-05, 4.99456778E-07,
-1.79566394E-10, 2.00255376E-14, -9.50158922E+02,
-3.20502331E+00])
# Calculate thermodynamic quantities using the same syntax as StatMech
H_H2 = H2_nasa.get_H(units='kcal/mol', T=298.)
print('H_H2(T=298 K) = {} kcal/mol'.format(H_H2))
# Show thermodynamic quantities vs. T
T = np.linspace(200., 3500.)
f2, ax2 = plot_1D(H2_nasa,
x_name='T', x_values=T,
methods=('get_H', 'get_S', 'get_G'),
get_H_kwargs={'units': 'kcal/mol'},
get_S_kwargs={'units': 'cal/mol/K'},
get_G_kwargs={'units': 'kcal/mol'})
f2.set_size_inches(6, 6)
f2.set_dpi(200)
plt.show()
8.2. Fitting an empirical object to a StatMech object¶
Empirical objects can be made directly using StatMech objects and the from_model method.
H2_nasa = Nasa.from_model(name='H2',
T_low=200.,
T_high=3500.,
model=H2_statmech)
# Compare the statistical mechanical model to the empirical model
f3, ax3 = H2_nasa.plot_statmech_and_empirical(Cp_units='J/mol/K',
H_units='kJ/mol',
S_units='J/mol/K',
G_units='kJ/mol')
f3.set_size_inches(6, 8)
f3.set_dpi(200)
plt.show()
9. Input/Output¶
pMuTT has more IO functionality than below. See this page for supported IO functions.
9.1. Input via Excel¶
Encoding each object in Python can be tedious. You can read several species from Excel spreadsheets using pmutt.io.excel.read_excel. Note that this function returns a list of dictionaries. This output allows you to initialize whichever object you want using kwargs syntax. There are also special rules that depend on the header name.
Below, we show an example importing species data from a spreadsheet and creating a series of NASA polynomials.
import os
from pprint import pprint
from pathlib import Path
from pmutt.io.excel import read_excel
from pmutt.empirical.nasa import Nasa
# Find the location of Jupyter notebook
# Note that normally Python scripts have a __file__ variable but Jupyter notebook doesn't.
# Using pathlib can overcome this limiation
try:
notebook_folder = os.path.dirname(__file__)
except NameError:
notebook_folder = Path().resolve()
os.chdir(notebook_folder)
# Read the data from Excel
ab_initio_data = read_excel(io='./input/NH3_Input_Data.xlsx', sheet_name='species')
pprint(ab_initio_data)
# Create NASA polynomials using **kwargs syntax
nasa_species = []
for species_data in ab_initio_data:
single_nasa_species = Nasa.from_model(T_low=100.,
T_high=1500.,
**species_data)
nasa_species.append(single_nasa_species)
# Print out a table using enthalpy, entropy, Gibbs energy at 298 K for each species
print('Name Enthalpy (kcal/mol) Entropy (cal/mol/K) Gibbs energy (kcal/mol)')
print('--------------------------------------------------------------------------------')
for single_nasa_species in nasa_species:
name = single_nasa_species.name
H = single_nasa_species.get_H(units='kcal/mol', T=298.)
S = single_nasa_species.get_S(units='cal/mol/K', T=298.)
G = single_nasa_species.get_G(units='kcal/mol', T=298.)
print('{:12} {:10.1f} {:15.1f} {:15.1f}'.format(name, H, S, G))
9.2. Output via Thermdat¶
The thermdat format uses NASA polynomials to represent several species. It has a very particular format so doing it manually is error-prone. You can write a list of Nasa objects to thermdat format using pmutt.io.thermdat.write_thermdat.
Below, we write a thermdat file using the species imported from the spreadsheet.
from pmutt.io.thermdat import write_thermdat
write_thermdat(filename='./output/thermdat', nasa_species=nasa_species)
Similarly, a list of Nasa objects can be read from a thermdat using pmutt.io.thermdat.read_thermdat.
from pmutt.io.thermdat import read_thermdat
nasa_species = read_thermdat('./output/thermdat')
10. Reactions¶
Reaction objects can be created by putting together Nasa, Shomate and StatMech objects.
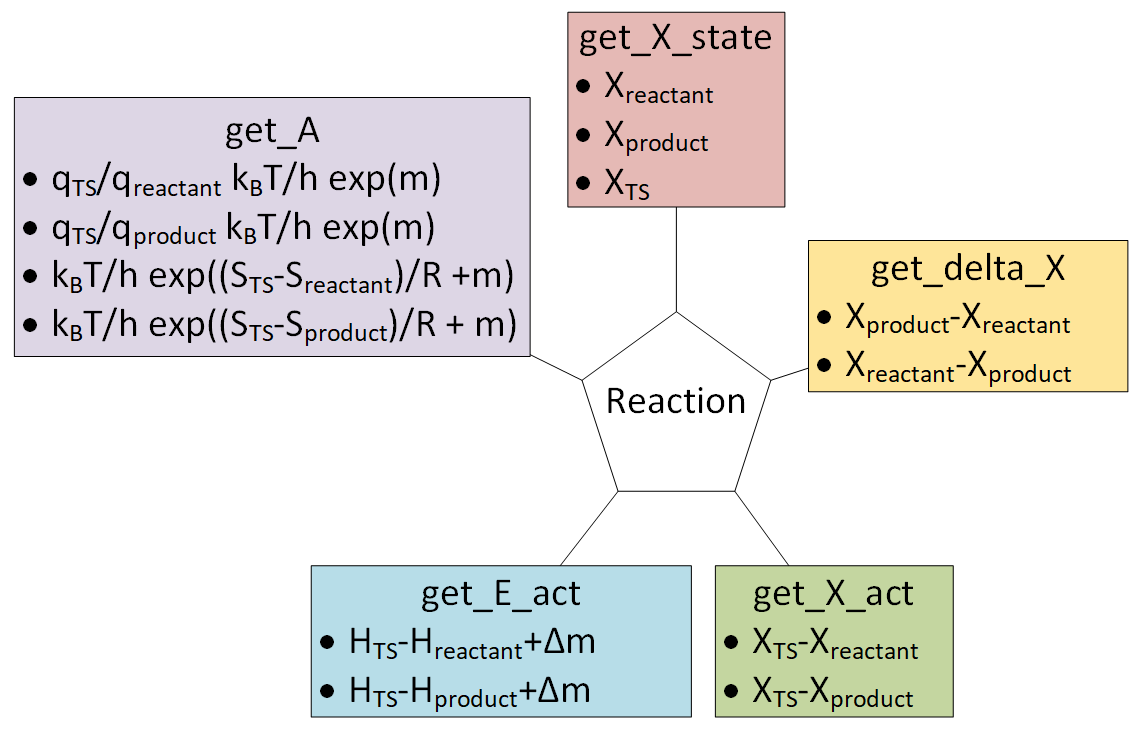
The from_string method is the easiest way to create a Reaction object. It requires the relevant species to be in a dictionary and a string to describe the reaction.
We will demonstrate its use for the formation of NH3.
from pmutt.empirical.nasa import Nasa
from pmutt.empirical.shomate import Shomate
from pmutt.reaction import Reaction
# Create species. Note that you can mix different types of species
species = {
'H2': StatMech(name='H2', atoms=molecule('H2'),
vib_wavenumbers=[4342.], # cm-1
symmetrynumber=2,
potentialenergy=-6.77, # eV
spin=0.,
**presets['idealgas']),
'N2': Nasa(name='N2', T_low=300., T_mid=643., T_high=1000.,
a_low=[3.3956319945669633, 0.001115707689025668,
-4.301993779374381e-06, 6.8071424019295535e-09,
-3.2903312791047058e-12, -191001.55648623788,
3.556111439828502],
a_high=[4.050329990684662, -0.0029677854067980108,
5.323485005316287e-06, -3.3518122405333548e-09,
7.58446718337381e-13, -191086.2004520406,
0.6858235504924011]),
'NH3': Shomate(name='NH3', T_low=300., T_high=1000.,
a=[18.792357134351683, 44.82725349479501,
-10.05898449447048, 0.3711633831565547,
0.2969942466370908, -1791.225746924463,
203.9035662274934, 1784.714638346206]),
}
# Define the formation of water reaction
rxn = Reaction.from_string('1.5H2 + 0.5N2 = NH3', species)
# Calculate forward change in enthalpy
H_rxn_fwd = rxn.get_delta_H(units='kcal/mol', T=300.)
print('Delta H_fwd(T = 300 K) = {:.1f} kcal/mol'.format(H_rxn_fwd))
# Calculate reverse change in enthalpy
H_rxn_rev = rxn.get_delta_H(units='kcal/mol', T=300., rev=True)
print('Delta H_rev(T = 300 K) = {:.1f} kcal/mol'.format(H_rxn_rev))
# Calculate enthalpy of reactants
H_react = rxn.get_H_state(units='kcal/mol', T=300., state='reactants')
print('H_reactants(T = 300 K) = {:.1f} kcal/mol'.format(H_react))
11. Exercise 3¶
Use
pmutt.io.thermdat.read_thermdatto read the thermdat from './output/thermdat'.Convert the list of
Nasato a dictionary ofNasausingpmutt.pmutt_list_to_dict. The syntax to use the function is shown below.
from pmutt import pmutt_list_to_dict
species_dict = pmutt_list_to_dict(species_list)Create a
Reactionfrom the string:NH3(S) + RU(S) = TS1_NH3(S) = NH2(S) + H(S)and the dictionary from step 2.Calculate the forward reaction enthalpy in kcal/mol at 298 K using
Reaction.get_delta_H.Calculate the forward activation energy in kcal/mol at 298 K using
Reaction.get_E_act.
# Fill in your answer for Exercise 3
# 1.
# 2.
# 3.
# 4.
# 5.
12. Solutions¶
12.1. Solution to Exercise 1¶
from pmutt import constants as c
# Define information given
H = 0.5 # eV
T = 77 # F
# Calculate H/RT
HoRT = H/c.R('eV/K')/c.convert_unit(77, initial='F', final='K')
print('H/RT = {}'.format(HoRT))
12.2. Solution to Exercise 2¶
from ase.build import molecule
from pmutt import plot_1D
from pmutt.statmech import StatMech, presets
from pmutt.statmech.vib import DebyeVib
from pmutt.statmech.elec import GroundStateElec
# 1. Create H2O molecule
H2O_statmech = StatMech(atoms=molecule('H2O'),
potentialenergy=-6.7598,
symmetrynumber=2,
spin=0,
vib_wavenumbers=[3825.434, 3710.264, 1582.432],
**presets['idealgas'])
# 2. Calculate Gibbs energy of H2O at T = 500 K and P = 2 bar
T = 500. # K
P = 2. # bar
G_H2O = H2O_statmech.get_G(units='eV', T=T, P=P)
print('G_H2O(T = 500 K, P = 2 bar) = {} eV'.format(G_H2O))
# 3. Create Cu crystal
Cu_vib = DebyeVib(debye_temperature=310., interaction_energy=0.)
Cu_elec = GroundStateElec(potentialenergy=-14.922356)
Cu_statmech = StatMech(vib_model=Cu_vib, elec_model=Cu_elec)
# 4. Plot the 1D profile for H and S between 300 K and 700 K
T = np.linspace(300., 700.) # K
f2, ax2 = plot_1D(Cu_statmech,
x_name='T', x_values=T,
methods=('get_H', 'get_S'),
get_H_kwargs={'units': 'eV'},
get_S_kwargs={'units': 'eV/K'})
f2.set_size_inches(6, 6)
f2.set_dpi(200)
plt.show()
12.3. Solution to Exercise 3¶
from pmutt.io.thermdat import read_thermdat
from pmutt import pmutt_list_to_dict
from pmutt.reaction import Reaction
# 1. Read the thermdat file
species_list = read_thermdat('./output/thermdat')
# 2. Convert the list of Nasa to a dictionary of Nasa
species_dict = pmutt_list_to_dict(species_list)
# 3. Create a Reaction from the specified string
rxn = Reaction.from_string('NH3(S) + RU(S) = TS1_NH3(S) = NH2(S) + H(S)', species_dict)
# 4. Calculate the reaction enthalpy
H_rxn = rxn.get_delta_H(units='kcal/mol', T=298.)
print('H_rxn = {:.1f} kcal/mol'.format(H_rxn))
# 5. Calculate the forward activation energy
Ea = rxn.get_E_act(units='kcal/mol', T=298.)
print('Ea_fwd = {:.1f} kcal/mol'.format(Ea))