"""
Edited by: Yassin Riyazi
Main Author: Sajjad Shumaly
Date: 01-07-2025
Description: This module provides functions for edge extraction from images,
Changelog:
1. improve on the edge_extraction function, refer to the docstring for details.
"""
import os
import numpy as np
from collections import defaultdict
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def edge_extraction(gray, thr=40) -> tuple[np.ndarray, np.ndarray]:
assert isinstance(gray, np.ndarray), "\033[31m Input must be a NumPy array \033[0m"
assert gray.ndim == 2, "\033[31m Input must be a grayscale image (2D array) \033[0m"
assert gray[0,:].sum() < 5, "\033[31m Probably not bitWised \033[0m" # It acutuall save my time in 05-09-2025
"""
Extract edge pixels from an upscaled image using a threshold.
Caution:
Images are supposed to be bitwise_not

 This function detects the first pixel above the threshold from the left, right,
and top of the image to form a rough outline of detected objects. Duplicate points
are removed.
Parameters:
upscaled_image (np.ndarray): Input BGR image (as NumPy array or PIL Image).
thr (int): Threshold value for pixel intensity (0–255).
Returns:
Tuple[np.ndarray, np.ndarray]: Tuple of (i_list, j_list) representing the x and y
coordinates of edge points (with vertical flip on y).
Author:
- Yassin Riyazi (Using SIMD for speedup)
- Sajjad Shumaly
"""
height, width = gray.shape
# Mask where intensity is greater than threshold
mask = gray > thr
# Allocate edge pixel lists
i_list = []
j_list = []
# External left edge (first hit in each row from the left)
left_hits = np.argmax(mask, axis=1)
has_hit_left = mask[np.arange(height), left_hits]
rows_left = np.where(has_hit_left)[0]
i_list.extend(left_hits[rows_left])
j_list.extend(rows_left)
# External right edge (first hit in each row from the right)
right_hits = width - 1 - np.argmax(mask[:, ::-1], axis=1)
has_hit_right = mask[np.arange(height), right_hits]
rows_right = np.where(has_hit_right)[0]
i_list.extend(right_hits[rows_right])
j_list.extend(rows_right)
# External top edge (first hit in each column from the top)
top_hits = np.argmax(mask, axis=0)
has_hit_top = mask[top_hits, np.arange(width)]
cols_top = np.where(has_hit_top)[0]
i_list.extend(cols_top)
j_list.extend(top_hits[cols_top])
# Remove duplicates and flip y-coordinates
coords = set(zip(i_list, j_list))
if not coords:
return [], []
i_list, j_list = zip(*coords)
j_list = [height - 1 - j for j in j_list] # flip y-axis
return np.array(i_list), np.array(j_list)
def visualize_edge_extraction(i_list, j_list, simple=False,
upscaled_image=None,
):
if simple:
# Display the upscaled grayscale image with edges
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 8))
plt.imshow(upscaled_image, cmap='gray')
plt.scatter(i_list, j_list, c='red', s=1) # s is dot size
plt.title("Edge Points over Grayscale Image")
plt.axis('off')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
else:
# Threshold values to test
thresholds = [1, 10, 100]
for thr in thresholds:
# Run edge extraction
i_list, j_list = edge_extraction(upscaled_image, thr=thr)
# Create figure with 3 subplots
fig, axs = plt.subplots(1, 3, figsize=(18, 6))
# 1. Grayscale image
axs[0].imshow(upscaled_image, cmap='gray')
axs[0].set_title(f"Grayscale Image\nThreshold: {thr}")
axs[0].axis('off')
# 2. Edge-only image
edge_only = np.zeros_like(upscaled_image)
for i, j in zip(i_list, j_list):
if 0 <= j < edge_only.shape[0] and 0 <= i < edge_only.shape[1]:
edge_only[j, i] = 255
axs[1].imshow(edge_only, cmap='gray')
axs[1].set_title("Extracted Edges Only")
axs[1].axis('off')
# 3. Overlay
axs[2].imshow(upscaled_image, cmap='gray')
axs[2].scatter(i_list, j_list, c='red', s=2)
axs[2].set_title("Edges Overlaid")
axs[2].axis('off')
# Save and show
plt.tight_layout()
save_path = os.path.join(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__)),'doc',f"edge_extraction_thr_{thr}.png")
plt.savefig(save_path, dpi=300)
plt.show()
def DocMakerFor__visualize_edge_extraction():
import cv2
import sys
sys.path.append(os.path.abspath(os.path.join(os.path.dirname(__file__))))
from superResolution import initiation,upscale_image
model = initiation()
error_handling_kernel_size = (5,5)
kernel = np.ones(error_handling_kernel_size,np. uint8)
just_drop = cv2.imread("Projects/ContactAngle/frame_Extracted20250621_203528_DropNumber_01/000436.jpg")
just_drop = just_drop[:-15,:,:]
x1 = 15
upscaled_image = upscale_image(model, just_drop, kernel)
#keeping just external pixels as droplet curvature
i_list, j_list =edge_extraction( upscaled_image, thr=20)
visualize_edge_extraction(i_list, j_list,simple=False,upscaled_image=upscaled_image)
def advancing_pixel_selection(i_list, j_list, left_number_of_pixels=150):
"""
Selects pixels from the advancing (left) side of a droplet, with spatial filtering
and improved precision, ensuring even row distribution.
There is a logocal error in the code. Look at Projects/ContactAngle/CaMeasurer/advancing_pixel_selection_advacingPoints30.png
This function detects the first pixel above the threshold from the left, right,
and top of the image to form a rough outline of detected objects. Duplicate points
are removed.
Parameters:
upscaled_image (np.ndarray): Input BGR image (as NumPy array or PIL Image).
thr (int): Threshold value for pixel intensity (0–255).
Returns:
Tuple[np.ndarray, np.ndarray]: Tuple of (i_list, j_list) representing the x and y
coordinates of edge points (with vertical flip on y).
Author:
- Yassin Riyazi (Using SIMD for speedup)
- Sajjad Shumaly
"""
height, width = gray.shape
# Mask where intensity is greater than threshold
mask = gray > thr
# Allocate edge pixel lists
i_list = []
j_list = []
# External left edge (first hit in each row from the left)
left_hits = np.argmax(mask, axis=1)
has_hit_left = mask[np.arange(height), left_hits]
rows_left = np.where(has_hit_left)[0]
i_list.extend(left_hits[rows_left])
j_list.extend(rows_left)
# External right edge (first hit in each row from the right)
right_hits = width - 1 - np.argmax(mask[:, ::-1], axis=1)
has_hit_right = mask[np.arange(height), right_hits]
rows_right = np.where(has_hit_right)[0]
i_list.extend(right_hits[rows_right])
j_list.extend(rows_right)
# External top edge (first hit in each column from the top)
top_hits = np.argmax(mask, axis=0)
has_hit_top = mask[top_hits, np.arange(width)]
cols_top = np.where(has_hit_top)[0]
i_list.extend(cols_top)
j_list.extend(top_hits[cols_top])
# Remove duplicates and flip y-coordinates
coords = set(zip(i_list, j_list))
if not coords:
return [], []
i_list, j_list = zip(*coords)
j_list = [height - 1 - j for j in j_list] # flip y-axis
return np.array(i_list), np.array(j_list)
def visualize_edge_extraction(i_list, j_list, simple=False,
upscaled_image=None,
):
if simple:
# Display the upscaled grayscale image with edges
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 8))
plt.imshow(upscaled_image, cmap='gray')
plt.scatter(i_list, j_list, c='red', s=1) # s is dot size
plt.title("Edge Points over Grayscale Image")
plt.axis('off')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
else:
# Threshold values to test
thresholds = [1, 10, 100]
for thr in thresholds:
# Run edge extraction
i_list, j_list = edge_extraction(upscaled_image, thr=thr)
# Create figure with 3 subplots
fig, axs = plt.subplots(1, 3, figsize=(18, 6))
# 1. Grayscale image
axs[0].imshow(upscaled_image, cmap='gray')
axs[0].set_title(f"Grayscale Image\nThreshold: {thr}")
axs[0].axis('off')
# 2. Edge-only image
edge_only = np.zeros_like(upscaled_image)
for i, j in zip(i_list, j_list):
if 0 <= j < edge_only.shape[0] and 0 <= i < edge_only.shape[1]:
edge_only[j, i] = 255
axs[1].imshow(edge_only, cmap='gray')
axs[1].set_title("Extracted Edges Only")
axs[1].axis('off')
# 3. Overlay
axs[2].imshow(upscaled_image, cmap='gray')
axs[2].scatter(i_list, j_list, c='red', s=2)
axs[2].set_title("Edges Overlaid")
axs[2].axis('off')
# Save and show
plt.tight_layout()
save_path = os.path.join(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__)),'doc',f"edge_extraction_thr_{thr}.png")
plt.savefig(save_path, dpi=300)
plt.show()
def DocMakerFor__visualize_edge_extraction():
import cv2
import sys
sys.path.append(os.path.abspath(os.path.join(os.path.dirname(__file__))))
from superResolution import initiation,upscale_image
model = initiation()
error_handling_kernel_size = (5,5)
kernel = np.ones(error_handling_kernel_size,np. uint8)
just_drop = cv2.imread("Projects/ContactAngle/frame_Extracted20250621_203528_DropNumber_01/000436.jpg")
just_drop = just_drop[:-15,:,:]
x1 = 15
upscaled_image = upscale_image(model, just_drop, kernel)
#keeping just external pixels as droplet curvature
i_list, j_list =edge_extraction( upscaled_image, thr=20)
visualize_edge_extraction(i_list, j_list,simple=False,upscaled_image=upscaled_image)
def advancing_pixel_selection(i_list, j_list, left_number_of_pixels=150):
"""
Selects pixels from the advancing (left) side of a droplet, with spatial filtering
and improved precision, ensuring even row distribution.
There is a logocal error in the code. Look at Projects/ContactAngle/CaMeasurer/advancing_pixel_selection_advacingPoints30.png
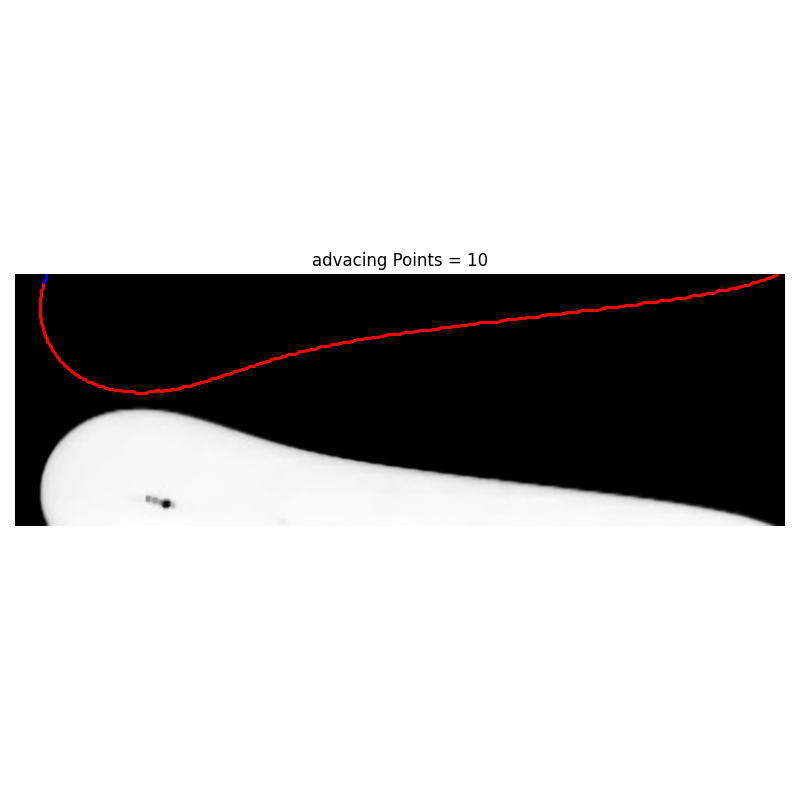
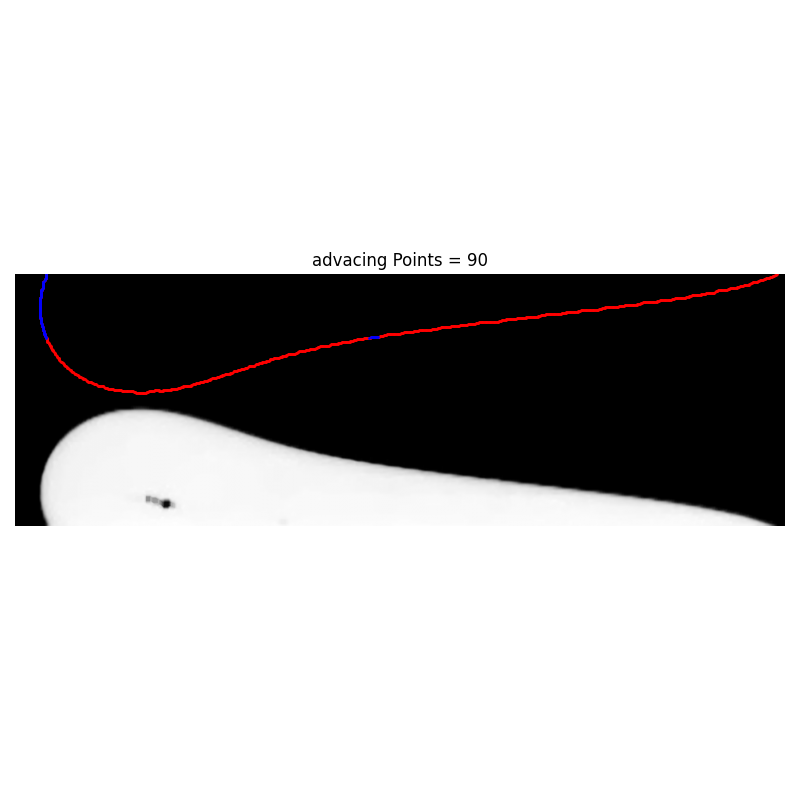


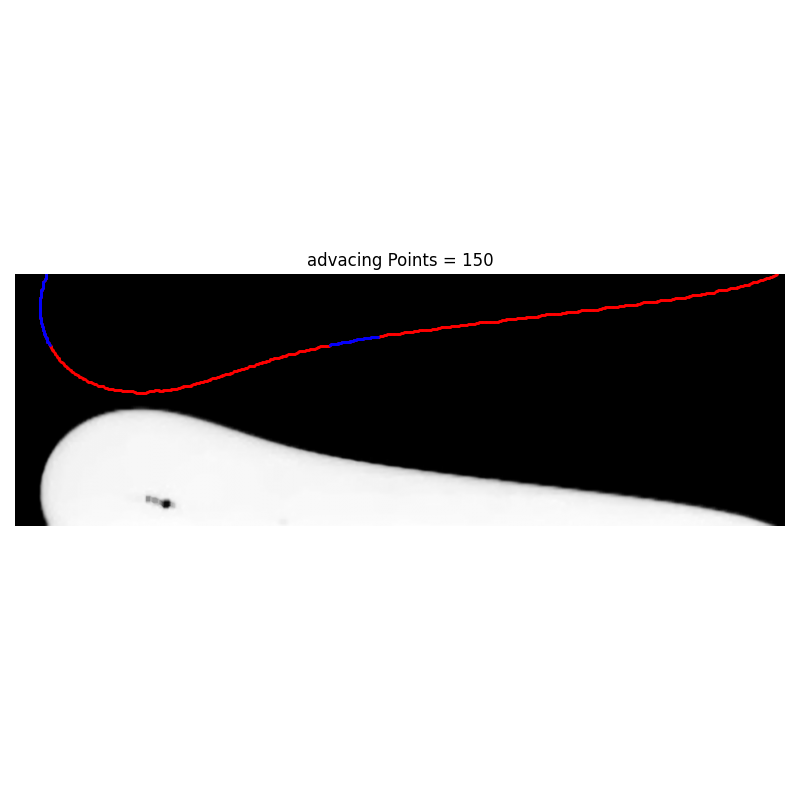 Args:
i_list (List[int]): x-coordinates (horizontal positions) of edge pixels.
j_list (List[int]): y-coordinates (vertical positions) of edge pixels.
left_number_of_pixels (int): Maximum number of pixels to return.
Returns:
Tuple[List[int], List[int]]: Selected advancing edge pixels (x, y).
Author:
- Sajjad Shumaly
"""
i_list = np.array(i_list)
j_list = np.array(j_list)
# Filter to left side of the droplet (left of center)
center_x = np.mean(i_list)
mask_left = (i_list < center_x)
# Filter out bottom rows (remove last 2 rows)
max_y = np.max(j_list)
mask_top = (j_list < max_y - 2)
# Combined mask for upper-left
mask = mask_left & mask_top
i_left = i_list[mask]
j_left = j_list[mask]
if len(i_left) == 0:
return [], []
# Group pixels by row (j) using a dictionary
row_dict = defaultdict(list)
for x, y in zip(i_left, j_left):
row_dict[y].append(x)
# Sort rows (top to bottom)
sorted_rows = sorted(row_dict.keys())
# Select pixels left-to-right per row until quota is filled
selected_i = []
selected_j = []
pixels_needed = left_number_of_pixels
for row in sorted_rows:
if pixels_needed <= 0:
break
x_coords = sorted(row_dict[row]) # left to right
n = min(len(x_coords), pixels_needed)
selected_i.extend(x_coords[:n])
selected_j.extend([row] * n)
pixels_needed -= n
return selected_i, selected_j
def Advancing_pixel_selection_Euclidean(i_list, j_list, left_number_of_pixels=150):
"""
Selects pixels from the advancing (left) side of a droplet, sorted by 2D Euclidean distance
from the leftmost point, returning specified number of pixels.
Args:
i_list (List[int]): x-coordinates (horizontal positions) of edge pixels.
j_list (List[int]): y-coordinates (vertical positions) of edge pixels.
left_number_of_pixels (int): Maximum number of pixels to return.
Returns:
Tuple[List[int], List[int]]: Selected advancing edge pixels (x, y).
Author:
- Sajjad Shumaly
"""
i_list = np.array(i_list)
j_list = np.array(j_list)
# Filter to left side of the droplet (left of center)
center_x = np.mean(i_list)
mask_left = (i_list < center_x)
# Filter out bottom rows (remove last 2 rows)
max_y = np.max(j_list)
mask_top = (j_list < max_y - 2)
# Combined mask for upper-left
mask = mask_left & mask_top
i_left = i_list[mask]
j_left = j_list[mask]
if len(i_left) == 0:
return [], []
# Group pixels by row (j) using a dictionary
row_dict = defaultdict(list)
for x, y in zip(i_left, j_left):
row_dict[y].append(x)
# Sort rows (top to bottom)
sorted_rows = sorted(row_dict.keys())
# Select pixels left-to-right per row until quota is filled
selected_i = []
selected_j = []
pixels_needed = left_number_of_pixels
for row in sorted_rows:
if pixels_needed <= 0:
break
x_coords = sorted(row_dict[row]) # left to right
n = min(len(x_coords), pixels_needed)
selected_i.extend(x_coords[:n])
selected_j.extend([row] * n)
pixels_needed -= n
return selected_i, selected_j
def Advancing_pixel_selection_Euclidean(i_list, j_list, left_number_of_pixels=150):
"""
Selects pixels from the advancing (left) side of a droplet, sorted by 2D Euclidean distance
from the leftmost point, returning specified number of pixels.
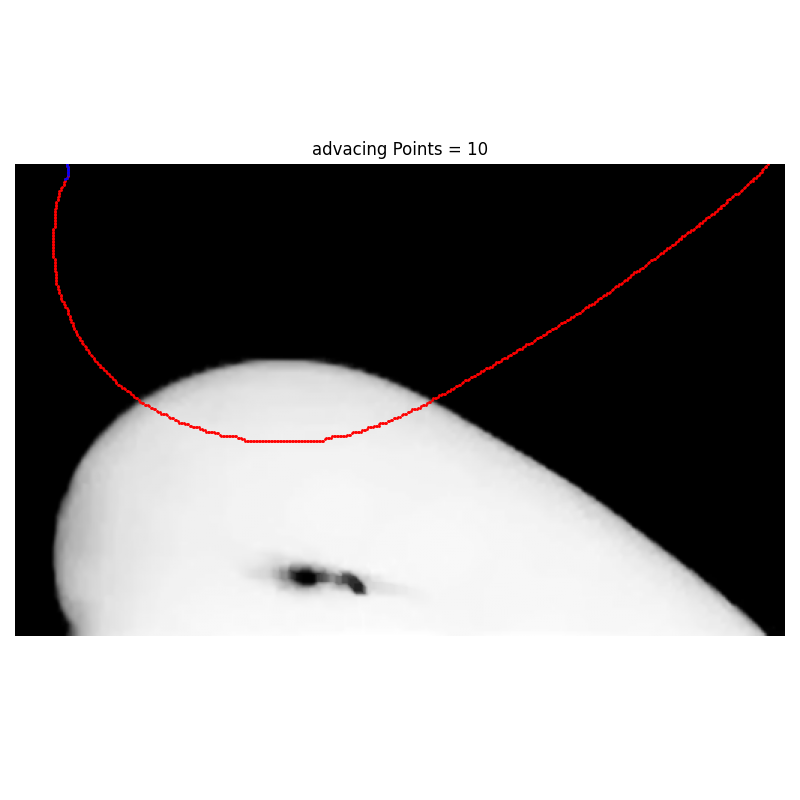
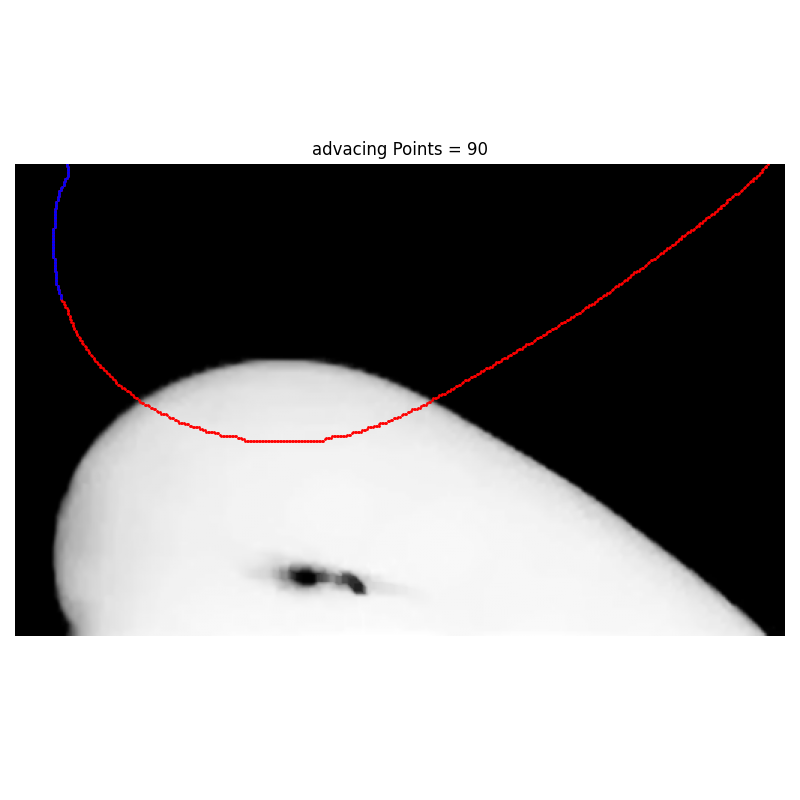
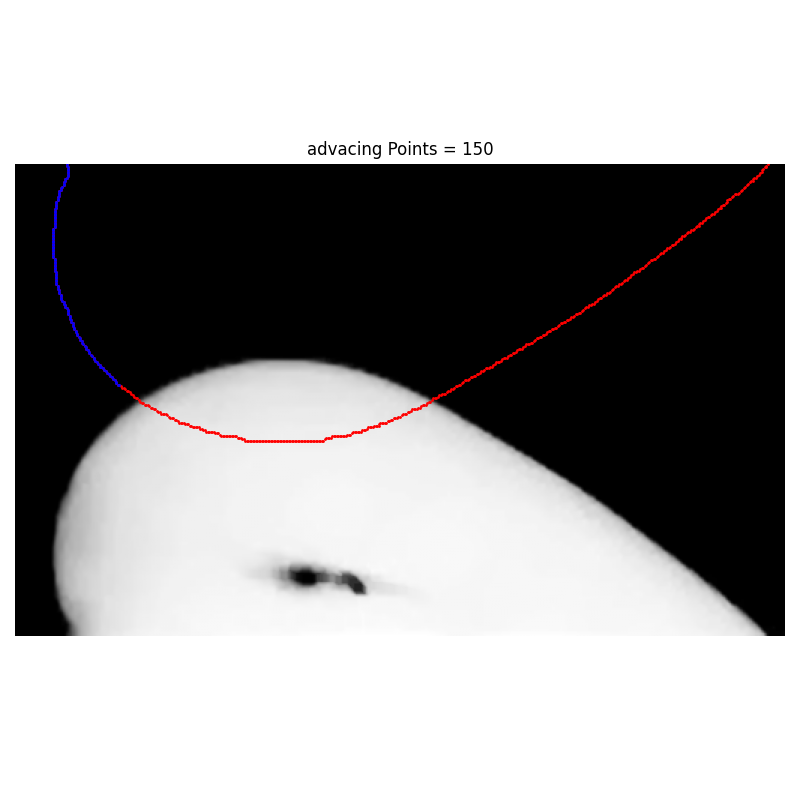

 Args:
i_list (List[int]): x-coordinates (horizontal positions) of edge pixels.
j_list (List[int]): y-coordinates (vertical positions) of edge pixels.
left_number_of_pixels (int): Number of pixels to return.
Returns:
Tuple[List[int], List[int]]: Selected advancing edge pixels (x, y).
Author:
- Yassin Riyazi (Norm2 based selection)
"""
# Convert to numpy arrays once
if isinstance(i_list, list):
i_array = np.array(i_list, dtype=np.float32)
j_array = np.array(j_list, dtype=np.float32)
if len(i_array) == 0:
return [], []
# Find origin (leftmost x-coordinate)
origin_x = np.min(i_array)
# Vectorized Euclidean distance calculation
distances = np.sqrt((i_array - origin_x)**2 + j_array**2)
# Get indices of sorted distances
sorted_indices = np.argsort(distances)[:left_number_of_pixels]
# Select pixels
selected_i = i_array[sorted_indices].tolist()
selected_j = j_array[sorted_indices].tolist()
return selected_i, selected_j
def Receding_pixel_selection_Euclidean(i_list, j_list, right_number_of_pixels=150):
"""
Selects pixels from the receding (right) side of a droplet, sorted by 2D Euclidean distance
from the leftmost point, returning specified number of pixels from both ends.
Args:
i_list (List[int]): x-coordinates (horizontal positions) of edge pixels.
j_list (List[int]): y-coordinates (vertical positions) of edge pixels.
left_number_of_pixels (int): Number of pixels to return.
Returns:
Tuple[List[int], List[int]]: Selected advancing edge pixels (x, y).
Author:
- Yassin Riyazi (Norm2 based selection)
"""
# Convert to numpy arrays once
if isinstance(i_list, list):
i_array = np.array(i_list, dtype=np.float32)
j_array = np.array(j_list, dtype=np.float32)
if len(i_array) == 0:
return [], []
# Find origin (leftmost x-coordinate)
origin_x = np.min(i_array)
# Vectorized Euclidean distance calculation
distances = np.sqrt((i_array - origin_x)**2 + j_array**2)
# Get indices of sorted distances
sorted_indices = np.argsort(distances)[:left_number_of_pixels]
# Select pixels
selected_i = i_array[sorted_indices].tolist()
selected_j = j_array[sorted_indices].tolist()
return selected_i, selected_j
def Receding_pixel_selection_Euclidean(i_list, j_list, right_number_of_pixels=150):
"""
Selects pixels from the receding (right) side of a droplet, sorted by 2D Euclidean distance
from the leftmost point, returning specified number of pixels from both ends.
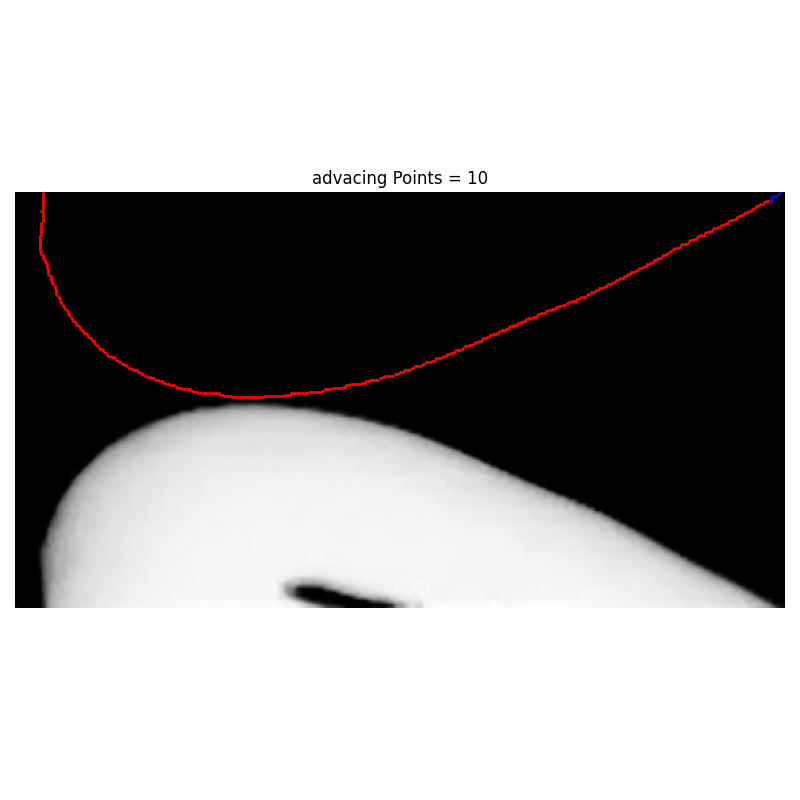

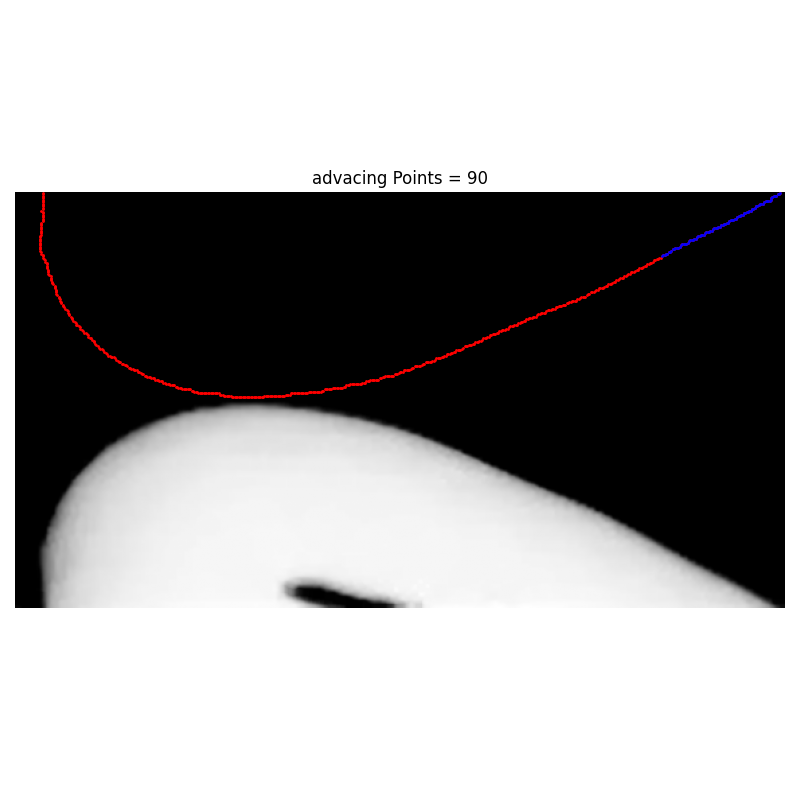
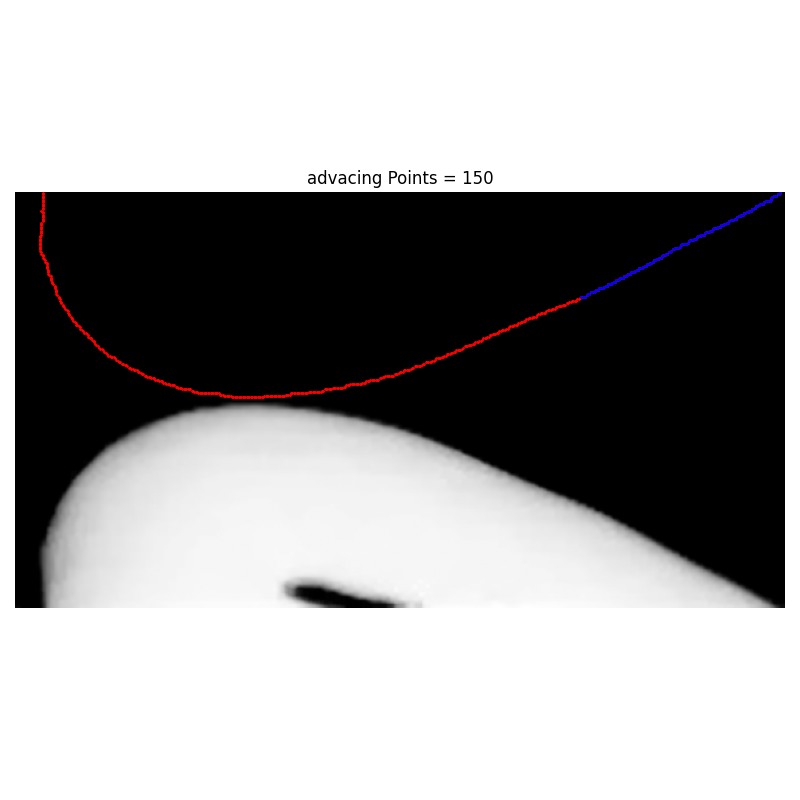 Args:
i_list (List[int]): x-coordinates (horizontal positions) of edge pixels.
j_list (List[int]): y-coordinates (vertical positions) of edge pixels.
left_number_of_pixels (int): Number of pixels to return from each end (total 2*left_number_of_pixels).
Returns:
Tuple[List[int], List[int]]: Selected receding edge pixels (x, y).
Author:
- Yassin Riyazi (Norm2 based selection)
"""
# Convert to numpy arrays once
i_array = np.array(i_list, dtype=np.float32)
j_array = np.array(j_list, dtype=np.float32)
if len(i_array) == 0:
return [], []
# Find origin (leftmost x-coordinate)
origin_x = np.max(i_array)
# Vectorized Euclidean distance calculation
distances = np.sqrt((i_array - origin_x)**2 + j_array**2)
# Get indices of sorted distances
sorted_indices = np.argsort(distances)[:right_number_of_pixels]
# Select pixels
selected_i = i_array[sorted_indices].tolist()
selected_j = j_array[sorted_indices].tolist()
return selected_i, selected_j
def DocMakerFor__pixel_selection_Euclidean(fFuncname = Receding_pixel_selection_Euclidean):
import cv2
import sys
sys.path.append(os.path.abspath(os.path.join(os.path.dirname(__file__))))
from superResolution import initiation,upscale_image
model = initiation()
error_handling_kernel_size = (5,5)
kernel = np.ones(error_handling_kernel_size,np. uint8)
just_drop = cv2.imread("Projects/ContactAngle/frame_Extracted20250714_024547_DropNumber_01/000014.jpg")
just_drop = just_drop[:-15,:,:]
x1 = 15
upscaled_image = upscale_image(model, just_drop, kernel)
#keeping just external pixels as droplet curvature
i_list, j_list = edge_extraction( upscaled_image, thr=20)
#extracting the desired number of pixels as input of the polynomial fitting
cm_on_pixel_ratio = 0.0039062
num_px_ratio = (0.0039062)/cm_on_pixel_ratio
left_number_of_pixels = int(120*num_px_ratio)
right_number_of_pixels = int(120*num_px_ratio)
for left_number_of_pixels in [10,30,60,90,120,150,200]:
i_left, j_left = fFuncname(i_list,j_list, left_number_of_pixels)
# Display the upscaled grayscale image with edges
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 8))
plt.imshow(upscaled_image, cmap='gray')
plt.scatter(i_list, j_list, c='red', s=1) # s is dot size
plt.scatter(i_left, j_left, c='blue', s=1) # s is dot size
plt.title(f"advacing Points = {left_number_of_pixels}")
plt.axis('off')
plt.tight_layout()
save_path = os.path.join(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__)),'doc',f"{fFuncname.__name__}_advacingPoints{left_number_of_pixels}.png")
plt.savefig(save_path,)
# plt.show()
if __name__ == "__main__":
# DocMakerFor__visualize_edge_extraction()
DocMakerFor__pixel_selection_Euclidean()
# import sys
# import os
# # Add the absolute path to the ./src folder
# sys.path.append(os.path.abspath(os.path.join(os.path.dirname(__file__), '..' )))
Args:
i_list (List[int]): x-coordinates (horizontal positions) of edge pixels.
j_list (List[int]): y-coordinates (vertical positions) of edge pixels.
left_number_of_pixels (int): Number of pixels to return from each end (total 2*left_number_of_pixels).
Returns:
Tuple[List[int], List[int]]: Selected receding edge pixels (x, y).
Author:
- Yassin Riyazi (Norm2 based selection)
"""
# Convert to numpy arrays once
i_array = np.array(i_list, dtype=np.float32)
j_array = np.array(j_list, dtype=np.float32)
if len(i_array) == 0:
return [], []
# Find origin (leftmost x-coordinate)
origin_x = np.max(i_array)
# Vectorized Euclidean distance calculation
distances = np.sqrt((i_array - origin_x)**2 + j_array**2)
# Get indices of sorted distances
sorted_indices = np.argsort(distances)[:right_number_of_pixels]
# Select pixels
selected_i = i_array[sorted_indices].tolist()
selected_j = j_array[sorted_indices].tolist()
return selected_i, selected_j
def DocMakerFor__pixel_selection_Euclidean(fFuncname = Receding_pixel_selection_Euclidean):
import cv2
import sys
sys.path.append(os.path.abspath(os.path.join(os.path.dirname(__file__))))
from superResolution import initiation,upscale_image
model = initiation()
error_handling_kernel_size = (5,5)
kernel = np.ones(error_handling_kernel_size,np. uint8)
just_drop = cv2.imread("Projects/ContactAngle/frame_Extracted20250714_024547_DropNumber_01/000014.jpg")
just_drop = just_drop[:-15,:,:]
x1 = 15
upscaled_image = upscale_image(model, just_drop, kernel)
#keeping just external pixels as droplet curvature
i_list, j_list = edge_extraction( upscaled_image, thr=20)
#extracting the desired number of pixels as input of the polynomial fitting
cm_on_pixel_ratio = 0.0039062
num_px_ratio = (0.0039062)/cm_on_pixel_ratio
left_number_of_pixels = int(120*num_px_ratio)
right_number_of_pixels = int(120*num_px_ratio)
for left_number_of_pixels in [10,30,60,90,120,150,200]:
i_left, j_left = fFuncname(i_list,j_list, left_number_of_pixels)
# Display the upscaled grayscale image with edges
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 8))
plt.imshow(upscaled_image, cmap='gray')
plt.scatter(i_list, j_list, c='red', s=1) # s is dot size
plt.scatter(i_left, j_left, c='blue', s=1) # s is dot size
plt.title(f"advacing Points = {left_number_of_pixels}")
plt.axis('off')
plt.tight_layout()
save_path = os.path.join(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__)),'doc',f"{fFuncname.__name__}_advacingPoints{left_number_of_pixels}.png")
plt.savefig(save_path,)
# plt.show()
if __name__ == "__main__":
# DocMakerFor__visualize_edge_extraction()
DocMakerFor__pixel_selection_Euclidean()
# import sys
# import os
# # Add the absolute path to the ./src folder
# sys.path.append(os.path.abspath(os.path.join(os.path.dirname(__file__), '..' )))
 This function detects the first pixel above the threshold from the left, right,
and top of the image to form a rough outline of detected objects. Duplicate points
are removed.
Parameters:
upscaled_image (np.ndarray): Input BGR image (as NumPy array or PIL Image).
thr (int): Threshold value for pixel intensity (0–255).
Returns:
Tuple[np.ndarray, np.ndarray]: Tuple of (i_list, j_list) representing the x and y
coordinates of edge points (with vertical flip on y).
Author:
- Yassin Riyazi (Using SIMD for speedup)
- Sajjad Shumaly
"""
height, width = gray.shape
# Mask where intensity is greater than threshold
mask = gray > thr
# Allocate edge pixel lists
i_list = []
j_list = []
# External left edge (first hit in each row from the left)
left_hits = np.argmax(mask, axis=1)
has_hit_left = mask[np.arange(height), left_hits]
rows_left = np.where(has_hit_left)[0]
i_list.extend(left_hits[rows_left])
j_list.extend(rows_left)
# External right edge (first hit in each row from the right)
right_hits = width - 1 - np.argmax(mask[:, ::-1], axis=1)
has_hit_right = mask[np.arange(height), right_hits]
rows_right = np.where(has_hit_right)[0]
i_list.extend(right_hits[rows_right])
j_list.extend(rows_right)
# External top edge (first hit in each column from the top)
top_hits = np.argmax(mask, axis=0)
has_hit_top = mask[top_hits, np.arange(width)]
cols_top = np.where(has_hit_top)[0]
i_list.extend(cols_top)
j_list.extend(top_hits[cols_top])
# Remove duplicates and flip y-coordinates
coords = set(zip(i_list, j_list))
if not coords:
return [], []
i_list, j_list = zip(*coords)
j_list = [height - 1 - j for j in j_list] # flip y-axis
return np.array(i_list), np.array(j_list)
def visualize_edge_extraction(i_list, j_list, simple=False,
upscaled_image=None,
):
if simple:
# Display the upscaled grayscale image with edges
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 8))
plt.imshow(upscaled_image, cmap='gray')
plt.scatter(i_list, j_list, c='red', s=1) # s is dot size
plt.title("Edge Points over Grayscale Image")
plt.axis('off')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
else:
# Threshold values to test
thresholds = [1, 10, 100]
for thr in thresholds:
# Run edge extraction
i_list, j_list = edge_extraction(upscaled_image, thr=thr)
# Create figure with 3 subplots
fig, axs = plt.subplots(1, 3, figsize=(18, 6))
# 1. Grayscale image
axs[0].imshow(upscaled_image, cmap='gray')
axs[0].set_title(f"Grayscale Image\nThreshold: {thr}")
axs[0].axis('off')
# 2. Edge-only image
edge_only = np.zeros_like(upscaled_image)
for i, j in zip(i_list, j_list):
if 0 <= j < edge_only.shape[0] and 0 <= i < edge_only.shape[1]:
edge_only[j, i] = 255
axs[1].imshow(edge_only, cmap='gray')
axs[1].set_title("Extracted Edges Only")
axs[1].axis('off')
# 3. Overlay
axs[2].imshow(upscaled_image, cmap='gray')
axs[2].scatter(i_list, j_list, c='red', s=2)
axs[2].set_title("Edges Overlaid")
axs[2].axis('off')
# Save and show
plt.tight_layout()
save_path = os.path.join(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__)),'doc',f"edge_extraction_thr_{thr}.png")
plt.savefig(save_path, dpi=300)
plt.show()
def DocMakerFor__visualize_edge_extraction():
import cv2
import sys
sys.path.append(os.path.abspath(os.path.join(os.path.dirname(__file__))))
from superResolution import initiation,upscale_image
model = initiation()
error_handling_kernel_size = (5,5)
kernel = np.ones(error_handling_kernel_size,np. uint8)
just_drop = cv2.imread("Projects/ContactAngle/frame_Extracted20250621_203528_DropNumber_01/000436.jpg")
just_drop = just_drop[:-15,:,:]
x1 = 15
upscaled_image = upscale_image(model, just_drop, kernel)
#keeping just external pixels as droplet curvature
i_list, j_list =edge_extraction( upscaled_image, thr=20)
visualize_edge_extraction(i_list, j_list,simple=False,upscaled_image=upscaled_image)
def advancing_pixel_selection(i_list, j_list, left_number_of_pixels=150):
"""
Selects pixels from the advancing (left) side of a droplet, with spatial filtering
and improved precision, ensuring even row distribution.
There is a logocal error in the code. Look at Projects/ContactAngle/CaMeasurer/advancing_pixel_selection_advacingPoints30.png
This function detects the first pixel above the threshold from the left, right,
and top of the image to form a rough outline of detected objects. Duplicate points
are removed.
Parameters:
upscaled_image (np.ndarray): Input BGR image (as NumPy array or PIL Image).
thr (int): Threshold value for pixel intensity (0–255).
Returns:
Tuple[np.ndarray, np.ndarray]: Tuple of (i_list, j_list) representing the x and y
coordinates of edge points (with vertical flip on y).
Author:
- Yassin Riyazi (Using SIMD for speedup)
- Sajjad Shumaly
"""
height, width = gray.shape
# Mask where intensity is greater than threshold
mask = gray > thr
# Allocate edge pixel lists
i_list = []
j_list = []
# External left edge (first hit in each row from the left)
left_hits = np.argmax(mask, axis=1)
has_hit_left = mask[np.arange(height), left_hits]
rows_left = np.where(has_hit_left)[0]
i_list.extend(left_hits[rows_left])
j_list.extend(rows_left)
# External right edge (first hit in each row from the right)
right_hits = width - 1 - np.argmax(mask[:, ::-1], axis=1)
has_hit_right = mask[np.arange(height), right_hits]
rows_right = np.where(has_hit_right)[0]
i_list.extend(right_hits[rows_right])
j_list.extend(rows_right)
# External top edge (first hit in each column from the top)
top_hits = np.argmax(mask, axis=0)
has_hit_top = mask[top_hits, np.arange(width)]
cols_top = np.where(has_hit_top)[0]
i_list.extend(cols_top)
j_list.extend(top_hits[cols_top])
# Remove duplicates and flip y-coordinates
coords = set(zip(i_list, j_list))
if not coords:
return [], []
i_list, j_list = zip(*coords)
j_list = [height - 1 - j for j in j_list] # flip y-axis
return np.array(i_list), np.array(j_list)
def visualize_edge_extraction(i_list, j_list, simple=False,
upscaled_image=None,
):
if simple:
# Display the upscaled grayscale image with edges
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 8))
plt.imshow(upscaled_image, cmap='gray')
plt.scatter(i_list, j_list, c='red', s=1) # s is dot size
plt.title("Edge Points over Grayscale Image")
plt.axis('off')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
else:
# Threshold values to test
thresholds = [1, 10, 100]
for thr in thresholds:
# Run edge extraction
i_list, j_list = edge_extraction(upscaled_image, thr=thr)
# Create figure with 3 subplots
fig, axs = plt.subplots(1, 3, figsize=(18, 6))
# 1. Grayscale image
axs[0].imshow(upscaled_image, cmap='gray')
axs[0].set_title(f"Grayscale Image\nThreshold: {thr}")
axs[0].axis('off')
# 2. Edge-only image
edge_only = np.zeros_like(upscaled_image)
for i, j in zip(i_list, j_list):
if 0 <= j < edge_only.shape[0] and 0 <= i < edge_only.shape[1]:
edge_only[j, i] = 255
axs[1].imshow(edge_only, cmap='gray')
axs[1].set_title("Extracted Edges Only")
axs[1].axis('off')
# 3. Overlay
axs[2].imshow(upscaled_image, cmap='gray')
axs[2].scatter(i_list, j_list, c='red', s=2)
axs[2].set_title("Edges Overlaid")
axs[2].axis('off')
# Save and show
plt.tight_layout()
save_path = os.path.join(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__)),'doc',f"edge_extraction_thr_{thr}.png")
plt.savefig(save_path, dpi=300)
plt.show()
def DocMakerFor__visualize_edge_extraction():
import cv2
import sys
sys.path.append(os.path.abspath(os.path.join(os.path.dirname(__file__))))
from superResolution import initiation,upscale_image
model = initiation()
error_handling_kernel_size = (5,5)
kernel = np.ones(error_handling_kernel_size,np. uint8)
just_drop = cv2.imread("Projects/ContactAngle/frame_Extracted20250621_203528_DropNumber_01/000436.jpg")
just_drop = just_drop[:-15,:,:]
x1 = 15
upscaled_image = upscale_image(model, just_drop, kernel)
#keeping just external pixels as droplet curvature
i_list, j_list =edge_extraction( upscaled_image, thr=20)
visualize_edge_extraction(i_list, j_list,simple=False,upscaled_image=upscaled_image)
def advancing_pixel_selection(i_list, j_list, left_number_of_pixels=150):
"""
Selects pixels from the advancing (left) side of a droplet, with spatial filtering
and improved precision, ensuring even row distribution.
There is a logocal error in the code. Look at Projects/ContactAngle/CaMeasurer/advancing_pixel_selection_advacingPoints30.png