"""
Author: Yassin Riyazi
Date: 01-07-2025
Description: This script detects drops in images by analyzing pixel intensity changes.
Caution:
Code will fail if there are more than one drop in the image.
Images should have exactly 5 rows of black pixels at the bottom of the image.
It works with tilted setup drop images, on other drop shape it is untested.
It intended for leveled images, and not tested on normal images.
If a smudge hit a drop, result are untested.
To make code versatile, normalize based on the number of height pixels with maximum brightness./ otherwise overflow may occur.
I failed, I don't know how does it generate 130000 from summing pixels.
And it is really costly to cast float to int.
Add timing decorator:
- Test general time
[detection] Ran 10000 times
[detection] Avg execution time: 0.000407 seconds
[detection] Avg peak memory usage: 158.18 KiB
- Optimize image resizing and processing time.
- Check effect of transposing on performance.
[detection] Ran 10000 times
[detection] Avg execution time: 0.000407 seconds
[detection] Avg peak memory usage: 158.18 KiB
With if with Transpose:
[detection] Ran 10000 times
[detection] Avg execution time: 0.000477 seconds
[detection] Avg peak memory usage: 158.18 KiB
with if without Transpose:
[detection] Ran 10000 times
[detection] Avg execution time: 0.000475 seconds
[detection] Avg peak memory usage: 158.18 KiB
!!! If is more damaging than transpose, because it is not optimized for numpy arrays.
!!! And probably inside numpy transpose happens for calculating the sum.
Code execution is 480 microseconds.
TODO:
- [05-09-2025] Type hinting for numpy arrays.
Learned:
Loading a function from a submodule in the same directory is tricky.
def __init__(self,) -> None:
try:
from .DropCoordinateSystem import EdgePointSorter
except:
from DropCoordinateSystem import EdgePointSorter
self.EdgePointSorter = EdgePointSorter
self.rows: Dict[str, npt.NDArray[np.float64]] = {}
"""
import os
import pickle
from time import time
import cv2
import glob
import subprocess
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from numpy import typing as npt
from typing import Dict, List, Tuple, Type, Union
def walk_forward(array: npt.NDArray[np.float64],
steep: float = 0.0025) -> int:
"""
Walk forward from the start index until we find a value greater than 0.
Steep: a parameter that defines the steepness of the slope to detect the drop.
args:
array (np.ndarray): The array to walk through.
steep (float): The steepness of the slope to detect the drop.
returns:
int: The index where the drop is detected.
"""
for i in range(10, len(array)-10, 1):
if np.abs(array[i] - array[i-1])> steep:
return i - 1
raise ValueError("No drop detected in the image. Please check the image or parameters.")
return None
def backward(array: npt.NDArray[np.float64],
steep: float = 0.0025) -> int:
"""
Walk forward from the start index until we find a value greater than 0.
Steep: a parameter that defines the steepness of the slope to detect the drop.
args:
array (np.ndarray): The array to walk through.
steep (float): The steepness of the slope to detect the drop.
returns:
int: The index where the drop is detected.
if want to include wider drops with low slope decrease the sensitivity of the slope.
For example, if you want to detect drops with low surface tension, surfactant, slope should be less than 0.0025
"""
for i in range(len(array)-10, 10, -1):
if np.abs(array[i] - array[i-1])> steep:
return i
raise ValueError("No drop detected in the image. Please check the image or parameters.")
return None
kernel = cv2.getStructuringElement(cv2.MORPH_ELLIPSE, (13, 13))
def detect_drop(image:cv2.Mat,
dims:tuple[int, int],
show:bool = False,
scaleDownFactor_x:int = 5,
scaleDownFactory:int = 2)-> npt.NDArray[np.float64]:
"""
Trying to detect images with less than 2ms delay.
[V] 0. Convert image to grayscale,
[V] 1. Resizing image,
[V] 2. Applying gaussian blur (morphologyEx worked better than Gaussian blur),
[-] 3. Transposing image (Optimization purposes) [Didn't improve any thing and because of if damaged was more than benefits],
[V] 4. Summation over rows
[-] 5. Normalize images based on height and maximum brightness,
[V] 6. Finding beginning of the drop and ending of the drop,
and finally drawing a rectangle around the drop.
args:
image (cv2.Mat): Input image to detect drops.
dims (tuple[int, int]): Dimensions of the input image.
show (bool): Whether to show the processed image and plot the sum of rows.
scaleDownFactor_x (int): Factor to scale down the width of the image.
scaleDownFactory (int): Factor to scale down the height of the image.
returns:
np.ndarray: Sum of rows of the processed image.
Caution:
Code will fail if there are more than one drop in the image.
Images should have exactly 5 rows of black pixels at the bottom of the image.
It works with tilted setup drop images, on other drop shape it is untested
TODO:
Going to test with C.
"""
resized_image = image
if len(resized_image.shape) == 3: # Check if the image is colored
# Convert the image to grayscale if it is colored
resized_image = cv2.cvtColor(resized_image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# Resize the image to a smaller size for faster processing
resized_image = cv2.resize(resized_image, (dims[1]//scaleDownFactor_x, dims[0]//scaleDownFactory))
## Close operation fills small dark holes # Kernel size depends on spot size
resized_image = cv2.morphologyEx(resized_image, cv2.MORPH_CLOSE, kernel)
"""
Opening is just another name of erosion followed by dilation.
It is useful in removing noise, as we explained above. Here we use the function,
https://docs.opencv.org/4.x/d9/d61/tutorial_py_morphological_ops.html
"""
vv = resized_image.sum(axis=0)
# vv = vv/(dims[0]-15)/scaleDownFactory # Normalize the sum of rows
vv = vv/vv.mean() # Normalize the sum of rows to have a mean of 1
if show:
print("Sum of rows:", vv.shape, "image shape", resized_image.shape)
resized_image = cv2.flip(resized_image, 1) # not neccessary
print("Sum of rows:", vv.shape)
ax = plt.figure().add_subplot(111)
ax.imshow(resized_image[:,::-1],alpha=0.5, cmap='gray')
# flipping the image to match the original orientation
_temp = vv*-255
_temp = _temp - _temp.min() # Normalize the sum of rows to have a minimum of 0
ax.plot(_temp)
ax.set_title("Sum of Rows")
ax.set_xlabel("Column Index")
ax.set_ylabel("Sum Value")
plt.show()
return vv
def detection(image:cv2.Mat,
scaleDownFactor:int) -> tuple[int, int]:
"""
Detects the drop in the image by analyzing pixel intensity changes.
For testing purposes, it returns the indices of the beginning and end of the drop.
Args:
image (cv2.Mat): Input image to detect drops.
scaleDownFactor (int): Factor to scale down the image for processing.
Returns:
tuple[int, int]: Indices of the beginning and end of the drop in the image.
"""
vv = detect_drop(image,image.shape, show=False, scaleDownFactor_x=scaleDownFactor)
endpoint = walk_forward(vv)
beginning = backward(vv)
return beginning, endpoint
def detect_dropV2(image:cv2.Mat,dims:tuple[int, int],show: bool = False,scaleDownFactor_x:int = 5, scaleDownFactory:int =2
)-> tuple[npt.NDArray[np.float64], npt.NDArray[np.float64]]:
"""
Same as V1 but added a version some that has seen the morphologyEx version image.
Because if you have small drops in the end side of slide, which is highly probable it confuses the slope and the length of drop will be around 1000 pixels which is cause failure in 4S-SROF and other algorithms.
args:
image (cv2.Mat): Input image to detect drops.
dims (tuple[int, int]): Dimensions of the input image.
show (bool): Whether to show the processed image and plot the sum of rows.
scaleDownFactor_x (int): Factor to scale down the width of the image.
scaleDownFactory (int): Factor to scale down the height of the image.
returns:
np.ndarray: Sum of rows of the processed image.
np.ndarray: Sum of rows of the morphologyEx processed image.
"""
resized_image = image
# resized_image = cv2.cvtColor(resized_image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# Resize the image to a smaller size for faster processing
resized_image = cv2.resize(resized_image, (dims[1]//scaleDownFactor_x, dims[0]//scaleDownFactory))
vv = resized_image.sum(axis=0)
# vv = vv/(dims[0]-15)/scaleDownFactory # Normalize the sum of rows
vv = vv/vv.mean() # Normalize the sum of rows to have a mean of 1
resized_image = cv2.morphologyEx(resized_image, cv2.MORPH_CLOSE, kernel)
## Close operation fills small dark holes # Kernel size depends on spot size
vv_mor = resized_image.sum(axis=0)
vv_mor = vv_mor/vv_mor.mean() # Normalize the sum of rows to have a mean of 1
if show:
print("Sum of rows:", vv.shape, "image shape", resized_image.shape)
resized_image = cv2.flip(resized_image, 1) # not necessary
print("Sum of rows:", vv.shape)
cv2.imshow("Resized Image", resized_image)
plt.plot(vv)
plt.title("Sum of Rows")
plt.xlabel("Column Index")
plt.ylabel("Sum Value")
plt.show()
return vv, vv_mor
def detectionV2(image:cv2.Mat,
scaleDownFactor:int,
drop_width:int = 300) -> tuple[int, int]:
"""
Detects the drop in the image by analyzing pixel intensity changes.
For testing purposes, it returns the indices of the beginning and end of the drop.
Args:
image (cv2.Mat): Input image to detect drops.
scaleDownFactor (int): Factor to scale down the image for processing.
Returns:
tuple[int, int]: Indices of the beginning and end of the drop in the image.
"""
assert image is not None, "Input image is None"
assert isinstance(image, np.ndarray), "Input image is not a valid numpy array"
assert len(image.shape) == 2, "Input image should be a grayscale image"
vv, vv_mor = detect_dropV2(image,image.shape, show=False, scaleDownFactor_x=scaleDownFactor)
endpoint = walk_forward(vv_mor)
beginning = backward(vv)
endpoint = int(endpoint * scaleDownFactor)
beginning = int(beginning * scaleDownFactor)
if (beginning - endpoint > drop_width):
print(image)
endpoint = walk_forward(vv_mor, steep=0.005)
endpoint = int(endpoint * scaleDownFactor)
# beginning = backward(vv)
# beginning = int(beginning * scaleDownFactor_x)
return beginning, endpoint
def extendLength(array: npt.NDArray[np.float64],
new_length: int) -> npt.NDArray[np.float64]:
"""
Extend the length of the array to a new length by repeating the entire array.
Args:
array (np.ndarray): The input array to extend.
new_length (int): The desired new length of the array.
Returns:
np.ndarray: The extended array with the new length.
"""
# Example array
x = len(array)
# Repeat each element
repeats = new_length // x # Number of times to repeat each element (3)
extended_arr = np.repeat(array, repeats)[:new_length]
return extended_arr
def draw_bounds(image:cv2.Mat,
start:int, end:int,
scaleDownFactor:int, thickness:int=2,
Array:npt.NDArray[np.float64] | None = None) -> None:
"""
Draw a rectangle on the image from start to end.
For testing purposes, it draws a rectangle on the image to visualize the detected drop.
Args:
image (cv2.Mat): Input image to draw the rectangle on.
start (int): Starting index of the rectangle.
end (int): Ending index of the rectangle.
scaleDownFactor (int): Factor to scale down the image.
thickness (int): Thickness of the rectangle border.
Returns:
None: Displays the image with the rectangle drawn.
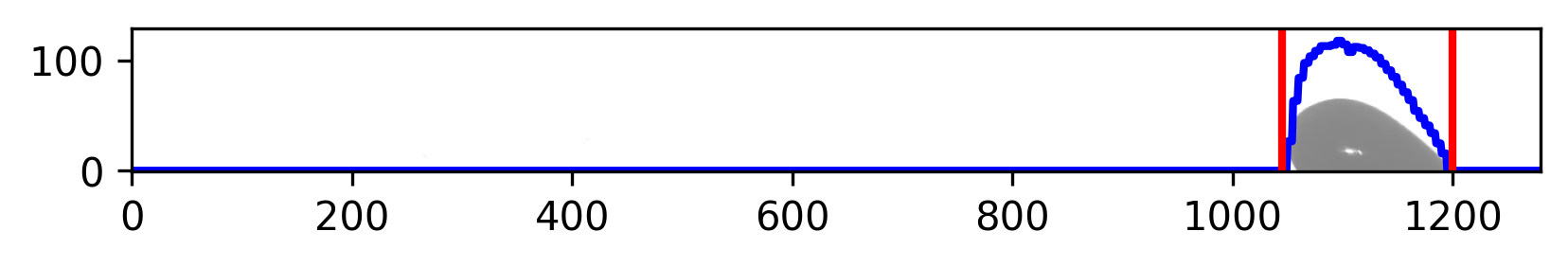 os.path.relpath(os.path.join(os.path.dirname(__file__), 'doc',f"{__name__}.png"),'Main')
"""
ax = plt.figure().add_subplot(111)
plt.imshow(image[::-1, :], alpha=0.5, cmap='gray')
if Array is not None:
_temp = Array*-255
_temp = _temp - _temp.min() # Normalize the sum of rows to have a minimum of 0
_temp = extendLength(_temp, image.shape[1])
ax.plot(_temp, color='blue', linewidth=thickness)
ax.axis('on') # or 'off' to hide axis
ax.axvline(x=start*scaleDownFactor, color='red', linewidth=thickness)
ax.axvline(x=end*scaleDownFactor, color='red', linewidth=thickness)
ax.invert_yaxis() # Invert y-axis to match the image orientation
plt.savefig(os.path.join(os.path.dirname(__file__), 'doc',f"{draw_bounds.__name__}_{time()}.png"), dpi=300, bbox_inches='tight')
plt.show()
def crop_and_save_image(image: npt.NDArray[np.float64],
output_path: str,
x1: int, x2: int,
tolerance: int = 3) -> None:
"""
Crops a region from the input image and saves it to the output path.
Args:
input_path (str): Path to the input image.
output_path (str): Path to save the cropped image.
x1 (int): Top-left x-coordinate.
x2 (int): Bottom-right x-coordinate.
Raises:
ValueError: If the crop coordinates are invalid or image cannot be loaded.
Example:
crop_and_save_image("input.jpg", "output.jpg", 10, 20, 100, 200)
"""
if x1 >= x2:
raise ValueError("Invalid crop coordinates: x1 >= x2 or y1 >= y2")
cropped = image[:, x1-tolerance:x2+tolerance]
cropped = cv2.bitwise_not(cropped)
cv2.imwrite(output_path, cropped)
class Detect_Template():
def __init__(self,) -> None:
raise NotImplementedError("This is a template class. Please implement the __init__ method.")
def forward(self,
image: str,
_image: npt.NDArray[np.float64],
SaveAddress: str,
endpoint: int,
beginning: int,
drop_width: int = 300,
tolerance_width: float = 1.13,
) -> None:
raise NotImplementedError("This is a template class. Please implement the forward method.")
def Finish(self, SaveAddressCSV: str) -> None:
raise NotImplementedError("This is a template class. Please implement the Finish method.")
def CleanUp(self, addresses: list[str]) -> None:
# Clean up folders on failure
for address in addresses:
if os.path.exists(address):
subprocess.run(["rm", "-rf", address])
class DetectCropSave(Detect_Template):
def __init__(self,) -> None:
self.rows: list[Dict[str, Union[str, int]]] = []
def forward(self,
image: str,
_image: npt.NDArray[np.float64],
SaveAddress: str,
endpoint: int,
beginning: int,
drop_width: int = 300,
tolerance_width: float = 1.13,
) -> None:
img_name = os.path.basename(image)
save_path = os.path.join(SaveAddress, img_name)
crop_and_save_image(_image, save_path, endpoint, beginning, tolerance=int((tolerance_width-1) * drop_width/2))
self.rows.append({'image': img_name, 'endpoint': endpoint, 'beginning': beginning})
def Finish(self, SaveAddressCSV: str) -> None:
# Save results as a single CSV file
csv_path = os.path.join(SaveAddressCSV, 'detections.csv')
df = pd.DataFrame(self.rows)
df.to_csv(csv_path, index=False)
class DetectEdgeSave(Detect_Template):
def __init__(self,) -> None:
try:
from .DropCoordinateSystem import EdgePointSorter
except:
from DropCoordinateSystem import EdgePointSorter
self.EdgePointSorter = EdgePointSorter
self.rows: Dict[str, npt.NDArray[np.float64]] = {}
def forward(self,
image: str,
_image: npt.NDArray[np.float64],
SaveAddress: str,
endpoint: int,
beginning: int,
drop_width: int = 300,
tolerance_width: float = 1.13,
) -> None:
x2, x1 = beginning, endpoint
X = self.EdgePointSorter(_image[:-1,x1:x2])
X[:, 0], X[:, 1] = X[:, 0]+x1, X[:, 1]+1
self.rows[image] = X
def Finish(self, SaveAddressCSV: str) -> None:
with open(os.path.join(SaveAddressCSV, 'detections.pkl'), 'wb') as f:
pickle.dump(self.rows, f)
def Main(experiment: str,
SaveAddress: str,
SaveAddressCSV: str,
extension: str = '.png',
scaleDownFactor_x: int = 5,
drop_width: int = 300,
tolerance_width: float = 1.13,
_morphologyEx: bool = False,
Detect: Type[Detect_Template] = DetectCropSave) -> None:
"""
Crops all images for a single experiment folder and saves crop info to CSV.
Caution:
Adaptive approach to detect drops in images.
In this function width of the detected drop should be around 300 pixels or 115% of the image width. other wise the steep value will be adjusted to 0.005 from 0.0025. Some time a small drop in the end of slide can be sitting and that is enough to cause problems in the detection. We end up with a really wide image.
args:
experiment (str): Path to the experiment folder containing images.
SaveAddress (str): Optional path to save cropped images.
SaveAddressCSV (str): Optional path to save CSV file with crop info.
extension (str): File extension of images to process (default: '.png').
scaleDownFactor_x (int): Factor to scale down the images for processing.
drop_width (int): Initial width of the drop to be detected. According to my experiment it is usually 150 in beginning and goes up to 450 for drops with surfactant.
tolerance_width (float): Tolerance width for drop detection (default: 1.13).
_morphologyEx (bool): Whether to apply morphologyEx operation on the image (default: False).
raises:
ValueError: If no images are found in the experiment folder.
ValueError: If the crop coordinates are invalid.
Example:
>>> Main("path/to/experiment", "path/to/save/cropped_images", "path/to/save/csv", extension='.png', scaleDownFactor_x=5, drop_width=300, tolerance_width=1.13)
returns:
None
"""
images = sorted(glob.glob(os.path.join(experiment, '*' + extension)))
if not images:
return
if not os.path.isdir(SaveAddress):
os.makedirs(SaveAddress, exist_ok=True)
if not os.path.isdir(SaveAddressCSV):
os.makedirs(SaveAddressCSV, exist_ok=True)
Detector = Detect()
try:
for image in images:
frame = cv2.imread(image)
_image = frame.copy()
if len(frame.shape) == 3:
frame = cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
if _morphologyEx:
frame = cv2.morphologyEx(frame, cv2.MORPH_CLOSE, kernel)
beginning, endpoint = detectionV2(image = frame,
scaleDownFactor = scaleDownFactor_x,
drop_width = drop_width)
drop_width = int (tolerance_width * (beginning - endpoint))
Detector.forward(image,
frame,
SaveAddress,
endpoint,
beginning,
tolerance_width)
Detector.Finish(SaveAddressCSV)
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error processing {experiment}: {e}")
Detector.CleanUp([SaveAddress, SaveAddressCSV])
def perfMeasure()-> None:
"""
Measure the performance of the drop detection algorithm.
This function is a placeholder for performance measurement logic.
args:
None: No arguments are required.
returns:
None: This function does not return any value.
os.path.relpath(os.path.join(os.path.dirname(__file__), 'doc',f"{__name__}.png"),'Main')
"""
ax = plt.figure().add_subplot(111)
plt.imshow(image[::-1, :], alpha=0.5, cmap='gray')
if Array is not None:
_temp = Array*-255
_temp = _temp - _temp.min() # Normalize the sum of rows to have a minimum of 0
_temp = extendLength(_temp, image.shape[1])
ax.plot(_temp, color='blue', linewidth=thickness)
ax.axis('on') # or 'off' to hide axis
ax.axvline(x=start*scaleDownFactor, color='red', linewidth=thickness)
ax.axvline(x=end*scaleDownFactor, color='red', linewidth=thickness)
ax.invert_yaxis() # Invert y-axis to match the image orientation
plt.savefig(os.path.join(os.path.dirname(__file__), 'doc',f"{draw_bounds.__name__}_{time()}.png"), dpi=300, bbox_inches='tight')
plt.show()
def crop_and_save_image(image: npt.NDArray[np.float64],
output_path: str,
x1: int, x2: int,
tolerance: int = 3) -> None:
"""
Crops a region from the input image and saves it to the output path.
Args:
input_path (str): Path to the input image.
output_path (str): Path to save the cropped image.
x1 (int): Top-left x-coordinate.
x2 (int): Bottom-right x-coordinate.
Raises:
ValueError: If the crop coordinates are invalid or image cannot be loaded.
Example:
crop_and_save_image("input.jpg", "output.jpg", 10, 20, 100, 200)
"""
if x1 >= x2:
raise ValueError("Invalid crop coordinates: x1 >= x2 or y1 >= y2")
cropped = image[:, x1-tolerance:x2+tolerance]
cropped = cv2.bitwise_not(cropped)
cv2.imwrite(output_path, cropped)
class Detect_Template():
def __init__(self,) -> None:
raise NotImplementedError("This is a template class. Please implement the __init__ method.")
def forward(self,
image: str,
_image: npt.NDArray[np.float64],
SaveAddress: str,
endpoint: int,
beginning: int,
drop_width: int = 300,
tolerance_width: float = 1.13,
) -> None:
raise NotImplementedError("This is a template class. Please implement the forward method.")
def Finish(self, SaveAddressCSV: str) -> None:
raise NotImplementedError("This is a template class. Please implement the Finish method.")
def CleanUp(self, addresses: list[str]) -> None:
# Clean up folders on failure
for address in addresses:
if os.path.exists(address):
subprocess.run(["rm", "-rf", address])
class DetectCropSave(Detect_Template):
def __init__(self,) -> None:
self.rows: list[Dict[str, Union[str, int]]] = []
def forward(self,
image: str,
_image: npt.NDArray[np.float64],
SaveAddress: str,
endpoint: int,
beginning: int,
drop_width: int = 300,
tolerance_width: float = 1.13,
) -> None:
img_name = os.path.basename(image)
save_path = os.path.join(SaveAddress, img_name)
crop_and_save_image(_image, save_path, endpoint, beginning, tolerance=int((tolerance_width-1) * drop_width/2))
self.rows.append({'image': img_name, 'endpoint': endpoint, 'beginning': beginning})
def Finish(self, SaveAddressCSV: str) -> None:
# Save results as a single CSV file
csv_path = os.path.join(SaveAddressCSV, 'detections.csv')
df = pd.DataFrame(self.rows)
df.to_csv(csv_path, index=False)
class DetectEdgeSave(Detect_Template):
def __init__(self,) -> None:
try:
from .DropCoordinateSystem import EdgePointSorter
except:
from DropCoordinateSystem import EdgePointSorter
self.EdgePointSorter = EdgePointSorter
self.rows: Dict[str, npt.NDArray[np.float64]] = {}
def forward(self,
image: str,
_image: npt.NDArray[np.float64],
SaveAddress: str,
endpoint: int,
beginning: int,
drop_width: int = 300,
tolerance_width: float = 1.13,
) -> None:
x2, x1 = beginning, endpoint
X = self.EdgePointSorter(_image[:-1,x1:x2])
X[:, 0], X[:, 1] = X[:, 0]+x1, X[:, 1]+1
self.rows[image] = X
def Finish(self, SaveAddressCSV: str) -> None:
with open(os.path.join(SaveAddressCSV, 'detections.pkl'), 'wb') as f:
pickle.dump(self.rows, f)
def Main(experiment: str,
SaveAddress: str,
SaveAddressCSV: str,
extension: str = '.png',
scaleDownFactor_x: int = 5,
drop_width: int = 300,
tolerance_width: float = 1.13,
_morphologyEx: bool = False,
Detect: Type[Detect_Template] = DetectCropSave) -> None:
"""
Crops all images for a single experiment folder and saves crop info to CSV.
Caution:
Adaptive approach to detect drops in images.
In this function width of the detected drop should be around 300 pixels or 115% of the image width. other wise the steep value will be adjusted to 0.005 from 0.0025. Some time a small drop in the end of slide can be sitting and that is enough to cause problems in the detection. We end up with a really wide image.
args:
experiment (str): Path to the experiment folder containing images.
SaveAddress (str): Optional path to save cropped images.
SaveAddressCSV (str): Optional path to save CSV file with crop info.
extension (str): File extension of images to process (default: '.png').
scaleDownFactor_x (int): Factor to scale down the images for processing.
drop_width (int): Initial width of the drop to be detected. According to my experiment it is usually 150 in beginning and goes up to 450 for drops with surfactant.
tolerance_width (float): Tolerance width for drop detection (default: 1.13).
_morphologyEx (bool): Whether to apply morphologyEx operation on the image (default: False).
raises:
ValueError: If no images are found in the experiment folder.
ValueError: If the crop coordinates are invalid.
Example:
>>> Main("path/to/experiment", "path/to/save/cropped_images", "path/to/save/csv", extension='.png', scaleDownFactor_x=5, drop_width=300, tolerance_width=1.13)
returns:
None
"""
images = sorted(glob.glob(os.path.join(experiment, '*' + extension)))
if not images:
return
if not os.path.isdir(SaveAddress):
os.makedirs(SaveAddress, exist_ok=True)
if not os.path.isdir(SaveAddressCSV):
os.makedirs(SaveAddressCSV, exist_ok=True)
Detector = Detect()
try:
for image in images:
frame = cv2.imread(image)
_image = frame.copy()
if len(frame.shape) == 3:
frame = cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
if _morphologyEx:
frame = cv2.morphologyEx(frame, cv2.MORPH_CLOSE, kernel)
beginning, endpoint = detectionV2(image = frame,
scaleDownFactor = scaleDownFactor_x,
drop_width = drop_width)
drop_width = int (tolerance_width * (beginning - endpoint))
Detector.forward(image,
frame,
SaveAddress,
endpoint,
beginning,
tolerance_width)
Detector.Finish(SaveAddressCSV)
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error processing {experiment}: {e}")
Detector.CleanUp([SaveAddress, SaveAddressCSV])
def perfMeasure()-> None:
"""
Measure the performance of the drop detection algorithm.
This function is a placeholder for performance measurement logic.
args:
None: No arguments are required.
returns:
None: This function does not return any value.
 [detection_perf] Ran 1000 times
[detection_perf] Avg execution time: 0.000442 seconds
[detection_perf] Avg peak memory usage: 158.03 KiB
"""
import sys
import os
# Add the absolute path to the ./src folder
sys.path.append(os.path.abspath(os.path.join(os.path.dirname(__file__), '../../', 'Utils/Performance')))
# Now you can import normally
from Performance_mesurements import average_performance,measure_performance # type: ignore
@average_performance(runs=1_000)
def detection_perf(image: cv2.Mat|npt.NDArray[np.float64],scaleDownFactor: int):
vv = detect_drop(image,image.shape, show=False, scaleDownFactor_x=scaleDownFactor)
endpoint = walk_forward(vv)
beginning = backward(vv)
return beginning, endpoint
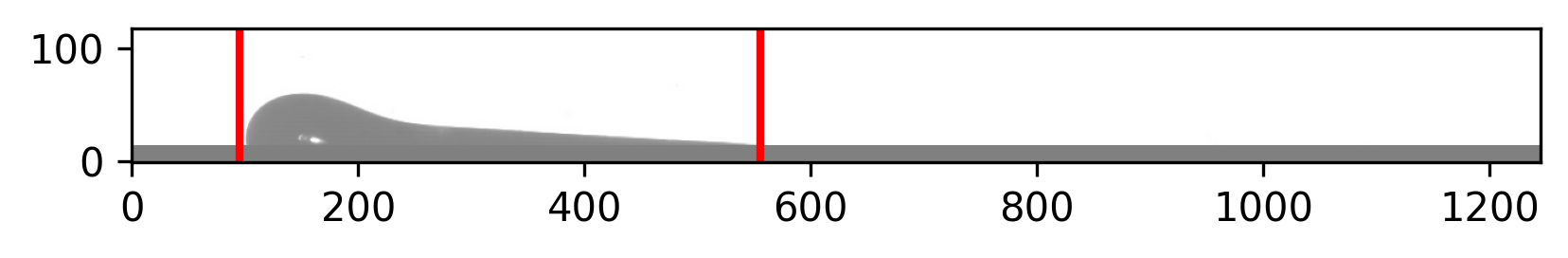
scaleDownFactor = 5
image_path = "src/PyThon/ContactAngle/DropDetection/doc/Long Drop.jpg"
image = cv2.imread(image_path)
beginning, endpoint = detection_perf(image, scaleDownFactor)
draw_bounds(image, beginning, endpoint,scaleDownFactor)
if __name__ == "__main__":
#%% Performance Measurement
# # Load the image
# scaleDownFactor = 5
# image_path = "src/PyThon/ContactAngle/DropDetection/doc/frame_002150.png"
# image = cv2.imread(image_path)
# # beginning, endpoint = detection_perf(image, scaleDownFactor)
# beginning, endpoint = detect_drop(image, image.shape, show=True, scaleDownFactor_x=scaleDownFactor)
# draw_bounds(image, beginning, endpoint, scaleDownFactor)
# perfMeasure()
#%% Running Main function for a single experiment/
# For the PINN drop coordinate system detection.
Main(experiment = '/media/d2u25/Dont/frames_Process_30/280/S3-SDS10_D/T110_06_0.005882541474',
SaveAddress = '/media/d2u25/Dont/frames_Process_30_PINN/280/S3-SDS10_D/T110_06_0.005882541474',
SaveAddressCSV = '/media/d2u25/Dont/frames_Process_30_PINN/280/S3-SDS10_D/T110_06_0.005882541474',
extension = '.png',
Detect = DetectEdgeSave)
[detection_perf] Ran 1000 times
[detection_perf] Avg execution time: 0.000442 seconds
[detection_perf] Avg peak memory usage: 158.03 KiB
"""
import sys
import os
# Add the absolute path to the ./src folder
sys.path.append(os.path.abspath(os.path.join(os.path.dirname(__file__), '../../', 'Utils/Performance')))
# Now you can import normally
from Performance_mesurements import average_performance,measure_performance # type: ignore
@average_performance(runs=1_000)
def detection_perf(image: cv2.Mat|npt.NDArray[np.float64],scaleDownFactor: int):
vv = detect_drop(image,image.shape, show=False, scaleDownFactor_x=scaleDownFactor)
endpoint = walk_forward(vv)
beginning = backward(vv)
return beginning, endpoint
scaleDownFactor = 5
image_path = "src/PyThon/ContactAngle/DropDetection/doc/Long Drop.jpg"
image = cv2.imread(image_path)
beginning, endpoint = detection_perf(image, scaleDownFactor)
draw_bounds(image, beginning, endpoint,scaleDownFactor)
if __name__ == "__main__":
#%% Performance Measurement
# # Load the image
# scaleDownFactor = 5
# image_path = "src/PyThon/ContactAngle/DropDetection/doc/frame_002150.png"
# image = cv2.imread(image_path)
# # beginning, endpoint = detection_perf(image, scaleDownFactor)
# beginning, endpoint = detect_drop(image, image.shape, show=True, scaleDownFactor_x=scaleDownFactor)
# draw_bounds(image, beginning, endpoint, scaleDownFactor)
# perfMeasure()
#%% Running Main function for a single experiment/
# For the PINN drop coordinate system detection.
Main(experiment = '/media/d2u25/Dont/frames_Process_30/280/S3-SDS10_D/T110_06_0.005882541474',
SaveAddress = '/media/d2u25/Dont/frames_Process_30_PINN/280/S3-SDS10_D/T110_06_0.005882541474',
SaveAddressCSV = '/media/d2u25/Dont/frames_Process_30_PINN/280/S3-SDS10_D/T110_06_0.005882541474',
extension = '.png',
Detect = DetectEdgeSave) os.path.relpath(os.path.join(os.path.dirname(__file__), 'doc',f"{__name__}.png"),'Main')
"""
ax = plt.figure().add_subplot(111)
plt.imshow(image[::-1, :], alpha=0.5, cmap='gray')
if Array is not None:
_temp = Array*-255
_temp = _temp - _temp.min() # Normalize the sum of rows to have a minimum of 0
_temp = extendLength(_temp, image.shape[1])
ax.plot(_temp, color='blue', linewidth=thickness)
ax.axis('on') # or 'off' to hide axis
ax.axvline(x=start*scaleDownFactor, color='red', linewidth=thickness)
ax.axvline(x=end*scaleDownFactor, color='red', linewidth=thickness)
ax.invert_yaxis() # Invert y-axis to match the image orientation
plt.savefig(os.path.join(os.path.dirname(__file__), 'doc',f"{draw_bounds.__name__}_{time()}.png"), dpi=300, bbox_inches='tight')
plt.show()
def crop_and_save_image(image: npt.NDArray[np.float64],
output_path: str,
x1: int, x2: int,
tolerance: int = 3) -> None:
"""
Crops a region from the input image and saves it to the output path.
Args:
input_path (str): Path to the input image.
output_path (str): Path to save the cropped image.
x1 (int): Top-left x-coordinate.
x2 (int): Bottom-right x-coordinate.
Raises:
ValueError: If the crop coordinates are invalid or image cannot be loaded.
Example:
crop_and_save_image("input.jpg", "output.jpg", 10, 20, 100, 200)
"""
if x1 >= x2:
raise ValueError("Invalid crop coordinates: x1 >= x2 or y1 >= y2")
cropped = image[:, x1-tolerance:x2+tolerance]
cropped = cv2.bitwise_not(cropped)
cv2.imwrite(output_path, cropped)
class Detect_Template():
def __init__(self,) -> None:
raise NotImplementedError("This is a template class. Please implement the __init__ method.")
def forward(self,
image: str,
_image: npt.NDArray[np.float64],
SaveAddress: str,
endpoint: int,
beginning: int,
drop_width: int = 300,
tolerance_width: float = 1.13,
) -> None:
raise NotImplementedError("This is a template class. Please implement the forward method.")
def Finish(self, SaveAddressCSV: str) -> None:
raise NotImplementedError("This is a template class. Please implement the Finish method.")
def CleanUp(self, addresses: list[str]) -> None:
# Clean up folders on failure
for address in addresses:
if os.path.exists(address):
subprocess.run(["rm", "-rf", address])
class DetectCropSave(Detect_Template):
def __init__(self,) -> None:
self.rows: list[Dict[str, Union[str, int]]] = []
def forward(self,
image: str,
_image: npt.NDArray[np.float64],
SaveAddress: str,
endpoint: int,
beginning: int,
drop_width: int = 300,
tolerance_width: float = 1.13,
) -> None:
img_name = os.path.basename(image)
save_path = os.path.join(SaveAddress, img_name)
crop_and_save_image(_image, save_path, endpoint, beginning, tolerance=int((tolerance_width-1) * drop_width/2))
self.rows.append({'image': img_name, 'endpoint': endpoint, 'beginning': beginning})
def Finish(self, SaveAddressCSV: str) -> None:
# Save results as a single CSV file
csv_path = os.path.join(SaveAddressCSV, 'detections.csv')
df = pd.DataFrame(self.rows)
df.to_csv(csv_path, index=False)
class DetectEdgeSave(Detect_Template):
def __init__(self,) -> None:
try:
from .DropCoordinateSystem import EdgePointSorter
except:
from DropCoordinateSystem import EdgePointSorter
self.EdgePointSorter = EdgePointSorter
self.rows: Dict[str, npt.NDArray[np.float64]] = {}
def forward(self,
image: str,
_image: npt.NDArray[np.float64],
SaveAddress: str,
endpoint: int,
beginning: int,
drop_width: int = 300,
tolerance_width: float = 1.13,
) -> None:
x2, x1 = beginning, endpoint
X = self.EdgePointSorter(_image[:-1,x1:x2])
X[:, 0], X[:, 1] = X[:, 0]+x1, X[:, 1]+1
self.rows[image] = X
def Finish(self, SaveAddressCSV: str) -> None:
with open(os.path.join(SaveAddressCSV, 'detections.pkl'), 'wb') as f:
pickle.dump(self.rows, f)
def Main(experiment: str,
SaveAddress: str,
SaveAddressCSV: str,
extension: str = '.png',
scaleDownFactor_x: int = 5,
drop_width: int = 300,
tolerance_width: float = 1.13,
_morphologyEx: bool = False,
Detect: Type[Detect_Template] = DetectCropSave) -> None:
"""
Crops all images for a single experiment folder and saves crop info to CSV.
Caution:
Adaptive approach to detect drops in images.
In this function width of the detected drop should be around 300 pixels or 115% of the image width. other wise the steep value will be adjusted to 0.005 from 0.0025. Some time a small drop in the end of slide can be sitting and that is enough to cause problems in the detection. We end up with a really wide image.
args:
experiment (str): Path to the experiment folder containing images.
SaveAddress (str): Optional path to save cropped images.
SaveAddressCSV (str): Optional path to save CSV file with crop info.
extension (str): File extension of images to process (default: '.png').
scaleDownFactor_x (int): Factor to scale down the images for processing.
drop_width (int): Initial width of the drop to be detected. According to my experiment it is usually 150 in beginning and goes up to 450 for drops with surfactant.
tolerance_width (float): Tolerance width for drop detection (default: 1.13).
_morphologyEx (bool): Whether to apply morphologyEx operation on the image (default: False).
raises:
ValueError: If no images are found in the experiment folder.
ValueError: If the crop coordinates are invalid.
Example:
>>> Main("path/to/experiment", "path/to/save/cropped_images", "path/to/save/csv", extension='.png', scaleDownFactor_x=5, drop_width=300, tolerance_width=1.13)
returns:
None
"""
images = sorted(glob.glob(os.path.join(experiment, '*' + extension)))
if not images:
return
if not os.path.isdir(SaveAddress):
os.makedirs(SaveAddress, exist_ok=True)
if not os.path.isdir(SaveAddressCSV):
os.makedirs(SaveAddressCSV, exist_ok=True)
Detector = Detect()
try:
for image in images:
frame = cv2.imread(image)
_image = frame.copy()
if len(frame.shape) == 3:
frame = cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
if _morphologyEx:
frame = cv2.morphologyEx(frame, cv2.MORPH_CLOSE, kernel)
beginning, endpoint = detectionV2(image = frame,
scaleDownFactor = scaleDownFactor_x,
drop_width = drop_width)
drop_width = int (tolerance_width * (beginning - endpoint))
Detector.forward(image,
frame,
SaveAddress,
endpoint,
beginning,
tolerance_width)
Detector.Finish(SaveAddressCSV)
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error processing {experiment}: {e}")
Detector.CleanUp([SaveAddress, SaveAddressCSV])
def perfMeasure()-> None:
"""
Measure the performance of the drop detection algorithm.
This function is a placeholder for performance measurement logic.
args:
None: No arguments are required.
returns:
None: This function does not return any value.
os.path.relpath(os.path.join(os.path.dirname(__file__), 'doc',f"{__name__}.png"),'Main')
"""
ax = plt.figure().add_subplot(111)
plt.imshow(image[::-1, :], alpha=0.5, cmap='gray')
if Array is not None:
_temp = Array*-255
_temp = _temp - _temp.min() # Normalize the sum of rows to have a minimum of 0
_temp = extendLength(_temp, image.shape[1])
ax.plot(_temp, color='blue', linewidth=thickness)
ax.axis('on') # or 'off' to hide axis
ax.axvline(x=start*scaleDownFactor, color='red', linewidth=thickness)
ax.axvline(x=end*scaleDownFactor, color='red', linewidth=thickness)
ax.invert_yaxis() # Invert y-axis to match the image orientation
plt.savefig(os.path.join(os.path.dirname(__file__), 'doc',f"{draw_bounds.__name__}_{time()}.png"), dpi=300, bbox_inches='tight')
plt.show()
def crop_and_save_image(image: npt.NDArray[np.float64],
output_path: str,
x1: int, x2: int,
tolerance: int = 3) -> None:
"""
Crops a region from the input image and saves it to the output path.
Args:
input_path (str): Path to the input image.
output_path (str): Path to save the cropped image.
x1 (int): Top-left x-coordinate.
x2 (int): Bottom-right x-coordinate.
Raises:
ValueError: If the crop coordinates are invalid or image cannot be loaded.
Example:
crop_and_save_image("input.jpg", "output.jpg", 10, 20, 100, 200)
"""
if x1 >= x2:
raise ValueError("Invalid crop coordinates: x1 >= x2 or y1 >= y2")
cropped = image[:, x1-tolerance:x2+tolerance]
cropped = cv2.bitwise_not(cropped)
cv2.imwrite(output_path, cropped)
class Detect_Template():
def __init__(self,) -> None:
raise NotImplementedError("This is a template class. Please implement the __init__ method.")
def forward(self,
image: str,
_image: npt.NDArray[np.float64],
SaveAddress: str,
endpoint: int,
beginning: int,
drop_width: int = 300,
tolerance_width: float = 1.13,
) -> None:
raise NotImplementedError("This is a template class. Please implement the forward method.")
def Finish(self, SaveAddressCSV: str) -> None:
raise NotImplementedError("This is a template class. Please implement the Finish method.")
def CleanUp(self, addresses: list[str]) -> None:
# Clean up folders on failure
for address in addresses:
if os.path.exists(address):
subprocess.run(["rm", "-rf", address])
class DetectCropSave(Detect_Template):
def __init__(self,) -> None:
self.rows: list[Dict[str, Union[str, int]]] = []
def forward(self,
image: str,
_image: npt.NDArray[np.float64],
SaveAddress: str,
endpoint: int,
beginning: int,
drop_width: int = 300,
tolerance_width: float = 1.13,
) -> None:
img_name = os.path.basename(image)
save_path = os.path.join(SaveAddress, img_name)
crop_and_save_image(_image, save_path, endpoint, beginning, tolerance=int((tolerance_width-1) * drop_width/2))
self.rows.append({'image': img_name, 'endpoint': endpoint, 'beginning': beginning})
def Finish(self, SaveAddressCSV: str) -> None:
# Save results as a single CSV file
csv_path = os.path.join(SaveAddressCSV, 'detections.csv')
df = pd.DataFrame(self.rows)
df.to_csv(csv_path, index=False)
class DetectEdgeSave(Detect_Template):
def __init__(self,) -> None:
try:
from .DropCoordinateSystem import EdgePointSorter
except:
from DropCoordinateSystem import EdgePointSorter
self.EdgePointSorter = EdgePointSorter
self.rows: Dict[str, npt.NDArray[np.float64]] = {}
def forward(self,
image: str,
_image: npt.NDArray[np.float64],
SaveAddress: str,
endpoint: int,
beginning: int,
drop_width: int = 300,
tolerance_width: float = 1.13,
) -> None:
x2, x1 = beginning, endpoint
X = self.EdgePointSorter(_image[:-1,x1:x2])
X[:, 0], X[:, 1] = X[:, 0]+x1, X[:, 1]+1
self.rows[image] = X
def Finish(self, SaveAddressCSV: str) -> None:
with open(os.path.join(SaveAddressCSV, 'detections.pkl'), 'wb') as f:
pickle.dump(self.rows, f)
def Main(experiment: str,
SaveAddress: str,
SaveAddressCSV: str,
extension: str = '.png',
scaleDownFactor_x: int = 5,
drop_width: int = 300,
tolerance_width: float = 1.13,
_morphologyEx: bool = False,
Detect: Type[Detect_Template] = DetectCropSave) -> None:
"""
Crops all images for a single experiment folder and saves crop info to CSV.
Caution:
Adaptive approach to detect drops in images.
In this function width of the detected drop should be around 300 pixels or 115% of the image width. other wise the steep value will be adjusted to 0.005 from 0.0025. Some time a small drop in the end of slide can be sitting and that is enough to cause problems in the detection. We end up with a really wide image.
args:
experiment (str): Path to the experiment folder containing images.
SaveAddress (str): Optional path to save cropped images.
SaveAddressCSV (str): Optional path to save CSV file with crop info.
extension (str): File extension of images to process (default: '.png').
scaleDownFactor_x (int): Factor to scale down the images for processing.
drop_width (int): Initial width of the drop to be detected. According to my experiment it is usually 150 in beginning and goes up to 450 for drops with surfactant.
tolerance_width (float): Tolerance width for drop detection (default: 1.13).
_morphologyEx (bool): Whether to apply morphologyEx operation on the image (default: False).
raises:
ValueError: If no images are found in the experiment folder.
ValueError: If the crop coordinates are invalid.
Example:
>>> Main("path/to/experiment", "path/to/save/cropped_images", "path/to/save/csv", extension='.png', scaleDownFactor_x=5, drop_width=300, tolerance_width=1.13)
returns:
None
"""
images = sorted(glob.glob(os.path.join(experiment, '*' + extension)))
if not images:
return
if not os.path.isdir(SaveAddress):
os.makedirs(SaveAddress, exist_ok=True)
if not os.path.isdir(SaveAddressCSV):
os.makedirs(SaveAddressCSV, exist_ok=True)
Detector = Detect()
try:
for image in images:
frame = cv2.imread(image)
_image = frame.copy()
if len(frame.shape) == 3:
frame = cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
if _morphologyEx:
frame = cv2.morphologyEx(frame, cv2.MORPH_CLOSE, kernel)
beginning, endpoint = detectionV2(image = frame,
scaleDownFactor = scaleDownFactor_x,
drop_width = drop_width)
drop_width = int (tolerance_width * (beginning - endpoint))
Detector.forward(image,
frame,
SaveAddress,
endpoint,
beginning,
tolerance_width)
Detector.Finish(SaveAddressCSV)
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error processing {experiment}: {e}")
Detector.CleanUp([SaveAddress, SaveAddressCSV])
def perfMeasure()-> None:
"""
Measure the performance of the drop detection algorithm.
This function is a placeholder for performance measurement logic.
args:
None: No arguments are required.
returns:
None: This function does not return any value.
 [detection_perf] Ran 1000 times
[detection_perf] Avg execution time: 0.000442 seconds
[detection_perf] Avg peak memory usage: 158.03 KiB
"""
import sys
import os
# Add the absolute path to the ./src folder
sys.path.append(os.path.abspath(os.path.join(os.path.dirname(__file__), '../../', 'Utils/Performance')))
# Now you can import normally
from Performance_mesurements import average_performance,measure_performance # type: ignore
@average_performance(runs=1_000)
def detection_perf(image: cv2.Mat|npt.NDArray[np.float64],scaleDownFactor: int):
vv = detect_drop(image,image.shape, show=False, scaleDownFactor_x=scaleDownFactor)
endpoint = walk_forward(vv)
beginning = backward(vv)
return beginning, endpoint
scaleDownFactor = 5
image_path = "src/PyThon/ContactAngle/DropDetection/doc/Long Drop.jpg"
image = cv2.imread(image_path)
beginning, endpoint = detection_perf(image, scaleDownFactor)
draw_bounds(image, beginning, endpoint,scaleDownFactor)
if __name__ == "__main__":
#%% Performance Measurement
# # Load the image
# scaleDownFactor = 5
# image_path = "src/PyThon/ContactAngle/DropDetection/doc/frame_002150.png"
# image = cv2.imread(image_path)
# # beginning, endpoint = detection_perf(image, scaleDownFactor)
# beginning, endpoint = detect_drop(image, image.shape, show=True, scaleDownFactor_x=scaleDownFactor)
# draw_bounds(image, beginning, endpoint, scaleDownFactor)
# perfMeasure()
#%% Running Main function for a single experiment/
# For the PINN drop coordinate system detection.
Main(experiment = '/media/d2u25/Dont/frames_Process_30/280/S3-SDS10_D/T110_06_0.005882541474',
SaveAddress = '/media/d2u25/Dont/frames_Process_30_PINN/280/S3-SDS10_D/T110_06_0.005882541474',
SaveAddressCSV = '/media/d2u25/Dont/frames_Process_30_PINN/280/S3-SDS10_D/T110_06_0.005882541474',
extension = '.png',
Detect = DetectEdgeSave)
[detection_perf] Ran 1000 times
[detection_perf] Avg execution time: 0.000442 seconds
[detection_perf] Avg peak memory usage: 158.03 KiB
"""
import sys
import os
# Add the absolute path to the ./src folder
sys.path.append(os.path.abspath(os.path.join(os.path.dirname(__file__), '../../', 'Utils/Performance')))
# Now you can import normally
from Performance_mesurements import average_performance,measure_performance # type: ignore
@average_performance(runs=1_000)
def detection_perf(image: cv2.Mat|npt.NDArray[np.float64],scaleDownFactor: int):
vv = detect_drop(image,image.shape, show=False, scaleDownFactor_x=scaleDownFactor)
endpoint = walk_forward(vv)
beginning = backward(vv)
return beginning, endpoint
scaleDownFactor = 5
image_path = "src/PyThon/ContactAngle/DropDetection/doc/Long Drop.jpg"
image = cv2.imread(image_path)
beginning, endpoint = detection_perf(image, scaleDownFactor)
draw_bounds(image, beginning, endpoint,scaleDownFactor)
if __name__ == "__main__":
#%% Performance Measurement
# # Load the image
# scaleDownFactor = 5
# image_path = "src/PyThon/ContactAngle/DropDetection/doc/frame_002150.png"
# image = cv2.imread(image_path)
# # beginning, endpoint = detection_perf(image, scaleDownFactor)
# beginning, endpoint = detect_drop(image, image.shape, show=True, scaleDownFactor_x=scaleDownFactor)
# draw_bounds(image, beginning, endpoint, scaleDownFactor)
# perfMeasure()
#%% Running Main function for a single experiment/
# For the PINN drop coordinate system detection.
Main(experiment = '/media/d2u25/Dont/frames_Process_30/280/S3-SDS10_D/T110_06_0.005882541474',
SaveAddress = '/media/d2u25/Dont/frames_Process_30_PINN/280/S3-SDS10_D/T110_06_0.005882541474',
SaveAddressCSV = '/media/d2u25/Dont/frames_Process_30_PINN/280/S3-SDS10_D/T110_06_0.005882541474',
extension = '.png',
Detect = DetectEdgeSave)