# MLOps Zoomcamp Course Project (cohorts 2023)
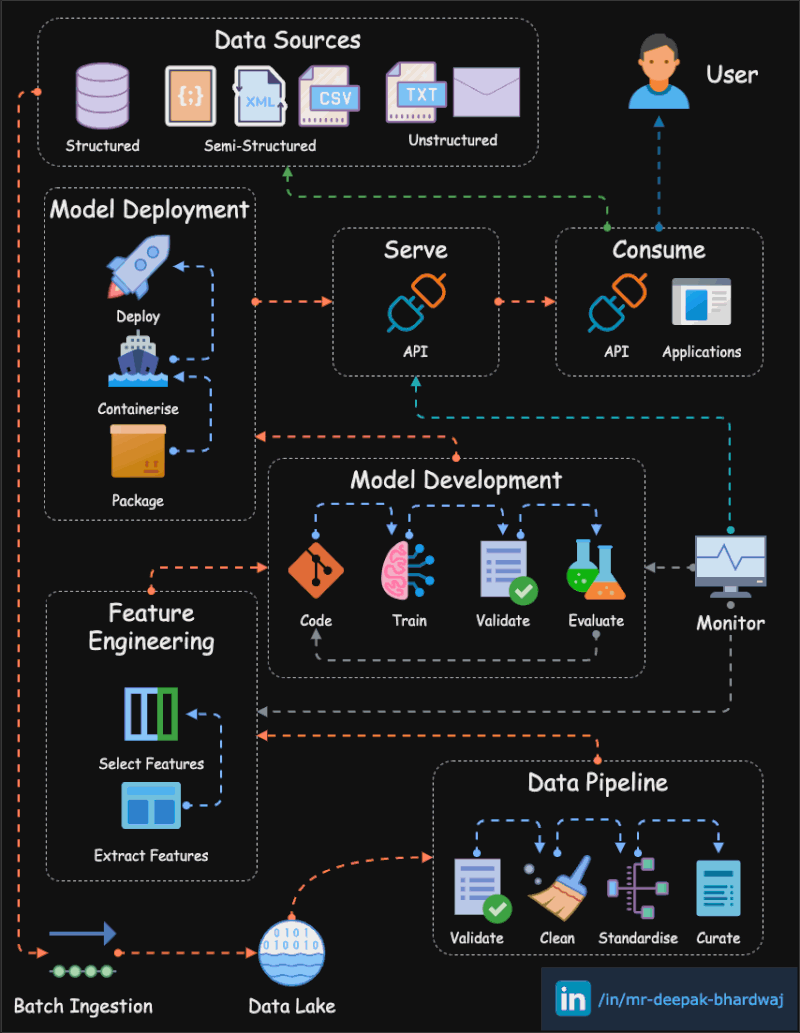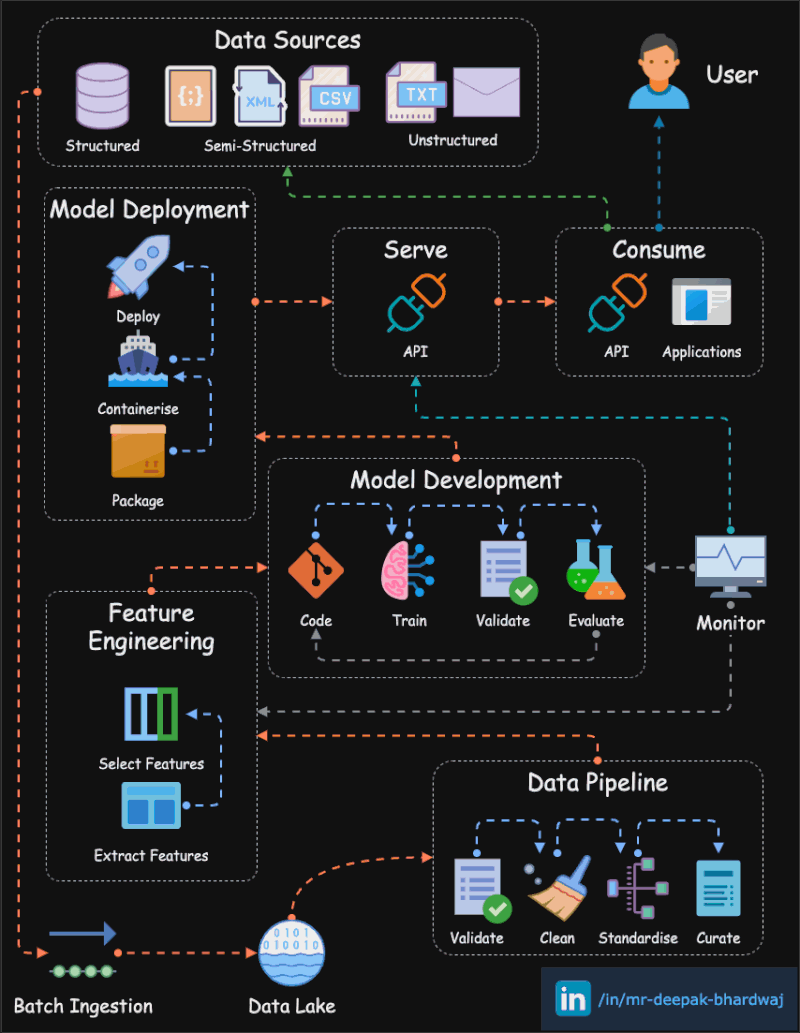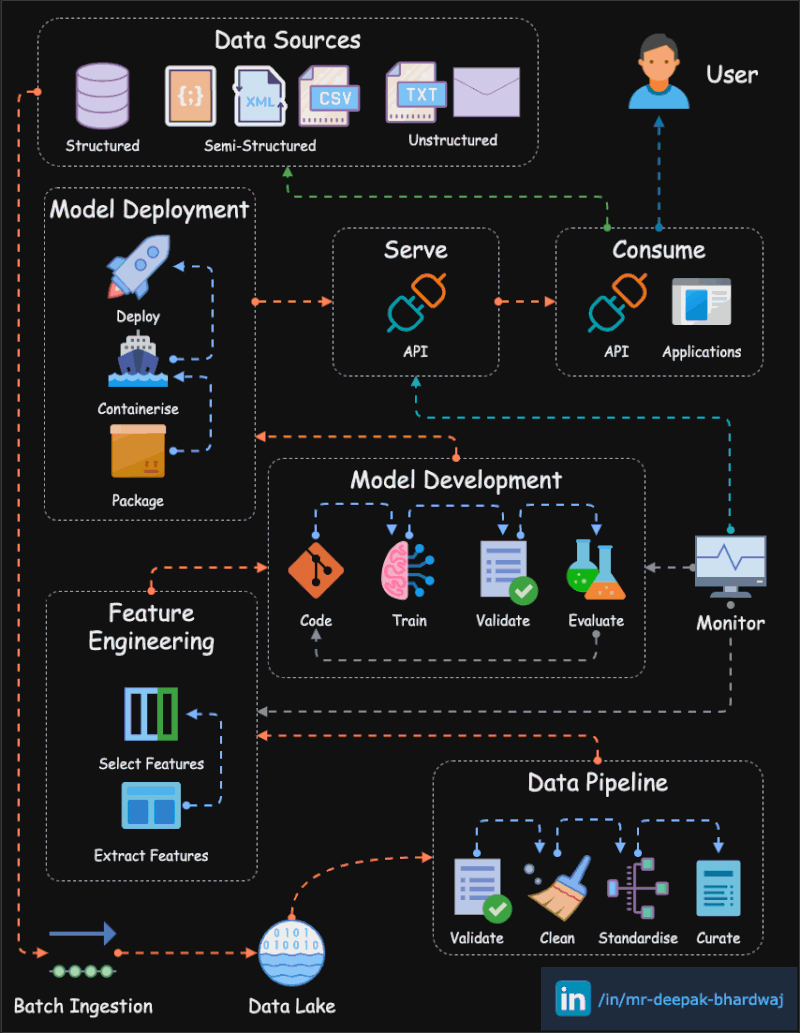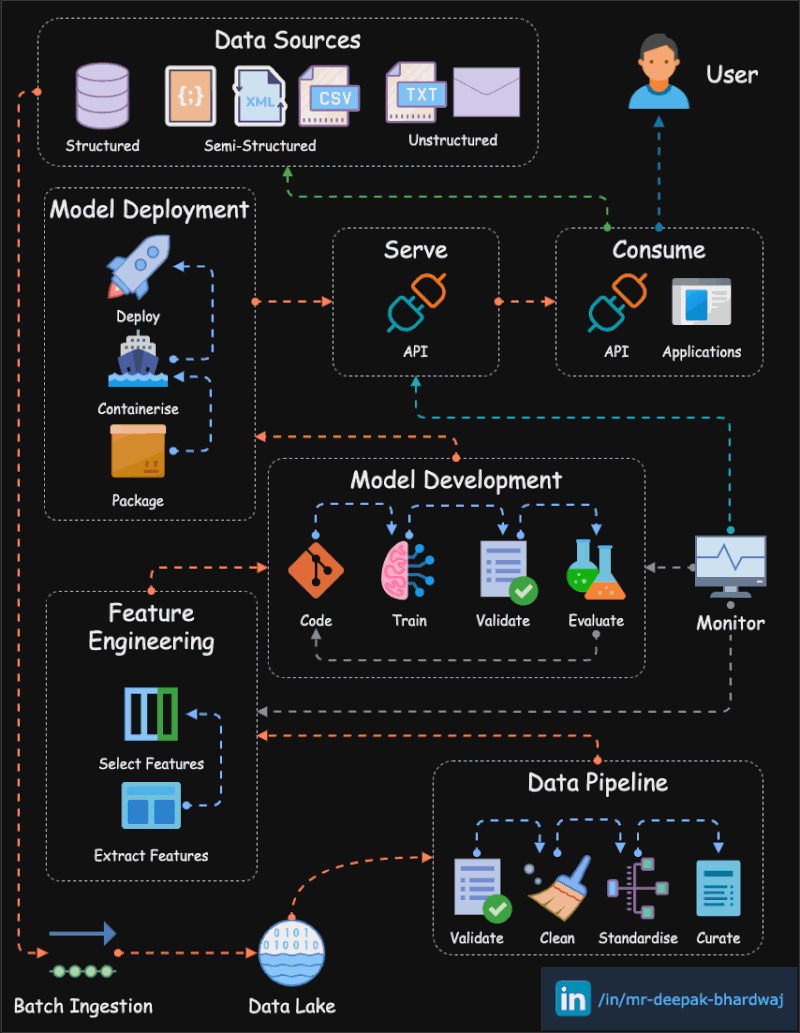
## Project Title: Passenger Ride Cost Estimation in Washington DC
## Problem Statement:
In this MLOps zoomcamp e-course capstone project, I aim to tackle the challenge of estimating the cost for passengers taking regular taxi rides from one location to another within Washington, DC, along with nearby areas in Virginia and Maryland. Leveraging the Washington, DC taxi rides dataset, which comprises historical records of taxi rides throughout all 2018 calendar months, I will build a predictive model to provide accurate fare estimates. To ensure the model's accuracy and reliability, I will validate and test it using the first six calendar months' data from 2019. The dataset contains comprehensive information on taxi rides that occurred within the boundaries of the DC-area. The dataset can be accessed through the provided [download link](https://opendata.dc.gov/search?categories=transportation&q=taxi&type=document%20link). I will be tasked with employing MLOps techniques and methodologies learned throughout the course to streamline the development, deployment, and monitoring of the machine learning model. By successfully addressing this problem, we can enhance the taxi service experience for both drivers and passengers while demonstrating the practical application of MLOps principles in real-world scenarios.
## Technologies:
- Cloud: AWS
- Experiment tracking tools: MLFlow
- Workflow orchestration: Prefect
- Monitoring: Evidently (metrics calculation) & Grafana (data vizualisation)
- CI/CD: Github actions
- Infrastructure as code (IaC): Terraform
- Model training: Linear Regression, Lasso, XGBoost
- Model tuning: Hyperopt
- Model deployment: REST API (Flask)
- Containerization: Docker
- Dependency management: Pipenv
## Data Inputs and Outputs
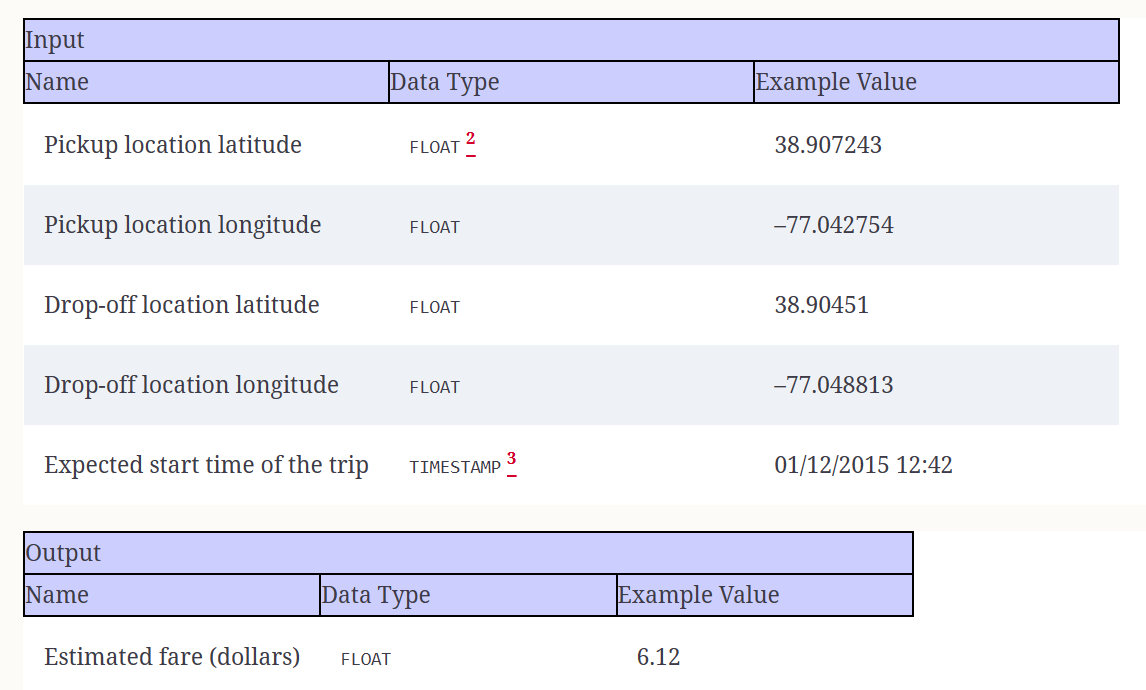
The ML model for estimating trip fare takes latitude and longitude coordinates as inputs, which correspond to the pickup and drop-off locations of a taxi ride in Washington, DC. These coordinates are then utilized by the ML model to predict the trip fare accurately. The service does not require human-readable addresses for geocoding; instead, it expects direct latitude and longitude values. To interact with the service after the deployment of the ML model into production, users can use a mobile application where they can visually drop pins on a map to specify the pickup and drop-off locations. Alternatively, users may have the option to use geocoding features from services like Google Maps as an alternative input method for specifying locations.
## Model Training
The ML model training pipeline is fully explained and demonstrated in the [ml_train README](ml_train/README.md) file
## Model Serving
The ML model serving pipeline is fully explained and demonstrated in the [ml_serve README](ml_serve/README.md) file
## Model Deployment
The ML model deployment work is fully explained and demonstrated in the [ml_deploy README](ml_deploy/README.md) file
## Model Monitoring
The ML model monitoring proceeses and dashboard are fully explained and demonstrated in the [ml_monitor README](ml_monitor/README.md) file
## CICD (GitHub Actions)
The CICD (GitHub Actions) workflow is fully explained and demonstrated in the [workflows README](.github/workflows/README.md) file
## Infrastructure as Code (Terraform)
The Infrastructure as Code (Terraform) configurations are fully explained and demonstrated in the [infrastructure README](infrastructure/README.md) file

