# OpenAPI Specification Support (formerly Swagger)
API Platform natively support the [OpenAPI](https://www.openapis.org/) API specification format.

Watch the OpenAPI screencast
The specification of the API is available at the `/docs.json` path.
By default, OpenAPI v3 is used.
You can also get an OpenAPI v3-compliant version thanks to the `spec_version` query parameter: `/docs.json?spec_version=3`
It also integrates a customized version of [Swagger UI](https://swagger.io/swagger-ui/) and [ReDoc](https://rebilly.github.io/ReDoc/), some nice tools to display the
API documentation in a user friendly way.
## Using the OpenAPI Command
You can also dump an OpenAPI specification for your API.
OpenAPI, JSON format:
```console
docker compose exec php \
bin/console api:openapi:export
```
OpenAPI, YAML format:
```console
docker compose exec php \
bin/console api:openapi:export --yaml
```
Create a file containing the specification:
```console
docker compose exec php \
bin/console api:openapi:export --output=swagger_docs.json
```
If you want to use the old OpenAPI v2 (Swagger) JSON format, use:
```console
docker compose exec php \
bin/console api:swagger:export
```
## Overriding the OpenAPI Specification
Symfony allows to [decorate services](https://symfony.com/doc/current/service_container/service_decoration.html), here we
need to decorate `api_platform.openapi.factory`.
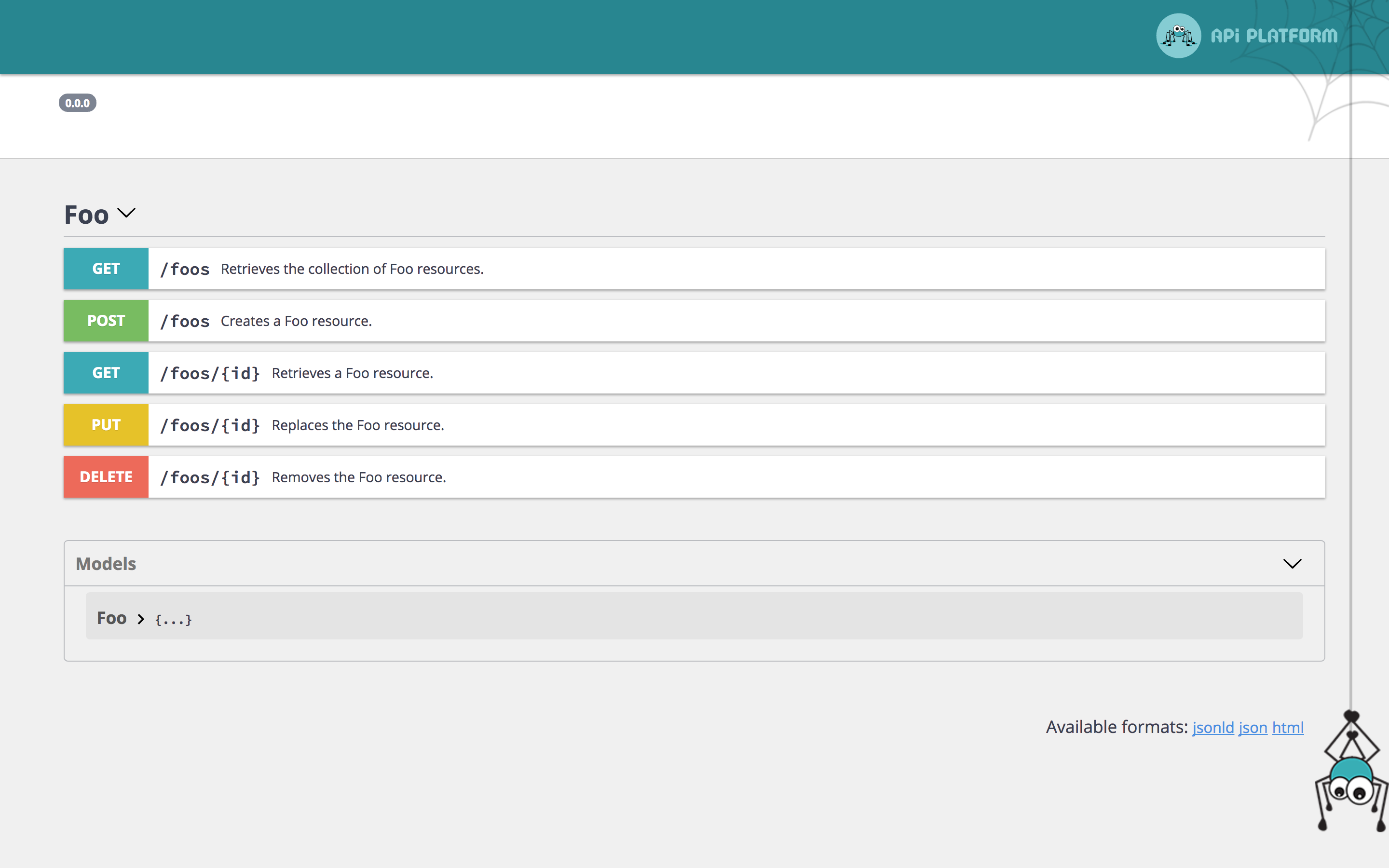
In the following example, we will see how to override the title of the Swagger documentation and add a custom filter for
the `GET` operation of `/foos` path.
```yaml
# api/config/services.yaml
App\OpenApi\OpenApiFactory:
decorates: 'api_platform.openapi.factory'
arguments: [ '@App\OpenApi\OpenApiFactory.inner' ]
autoconfigure: false
```
```php
decorated = $decorated;
}
public function __invoke(array $context = []): OpenApi
{
$openApi = $this->decorated->__invoke($context);
$pathItem = $openApi->getPaths()->getPath('/api/grumpy_pizzas/{id}');
$operation = $pathItem->getGet();
$openApi->getPaths()->addPath('/api/grumpy_pizzas/{id}', $pathItem->withGet(
$operation->withParameters(array_merge(
$operation->getParameters(),
[new Model\Parameter('fields', 'query', 'Fields to remove of the output')]
))
));
$openApi = $openApi->withInfo((new Model\Info('New Title', 'v2', 'Description of my custom API'))->withExtensionProperty('info-key', 'Info value'));
$openApi = $openApi->withExtensionProperty('key', 'Custom x-key value');
$openApi = $openApi->withExtensionProperty('x-value', 'Custom x-value value');
return $openApi;
}
}
```
The impact on the swagger-ui is the following:

## Using the OpenAPI and Swagger Contexts
Sometimes you may want to change the information included in your OpenAPI documentation.
The following configuration will give you total control over your OpenAPI definitions:
```php
'string',
'enum' => ['one', 'two'],
'example' => 'one'
]
)]
public string $name;
#[ORM\Column(type: "datetime")]
#[Assert\DateTime]
#[ApiProperty(
openapiContext: [
'type' => 'string',
'format' => 'date-time'
]
)]
public $timestamp;
// ...
}
```
```yaml
# api/config/api_platform/resources.yaml
resources:
App\Entity\Product:
properties:
name:
attributes:
openapi_context:
type: string
enum: ['one', 'two']
example: one
timestamp:
attributes:
openapi_context:
type: string
format: date-time
```
```xml
type
one
two
one
string
date-time
```
This will produce the following Swagger documentation:
```json
"components": {
"schemas": {
"GrumpyPizza:jsonld": {
"type": "object",
"description": "",
"properties": {
"@context": {
"readOnly": true,
"type": "string"
},
"@id": {
"readOnly": true,
"type": "string"
},
"@type": {
"readOnly": true,
"type": "string"
},
"timestamp": {
"type": "string",
"format": "date-time"
},
"id": {
"readOnly": true,
"type": "integer"
},
"name": {
"type": "string",
"enum": [
"one",
"two"
],
"example": "one"
}
}
}
}
}
```
To pass a context to the OpenAPI **v2** generator, use the `swaggerContext` attribute (notice the prefix: `swagger` instead of `openapi`).
## Changing the Name of a Definition
API Platform generates a definition name based on the serializer `groups` defined
in the (`de`)`normalizationContext`. It's possible to override the name
thanks to the `swagger_definition_name` option:
```php
use ApiPlatform\Metadata\ApiResource;
use ApiPlatform\Metadata\Post;
#[ApiResource]
#[Post(denormalizationContext: ['groups' => ['user:read'], 'swagger_definition_name' => 'Read'])]
class User
{
// ...
}
```
It's also possible to re-use the (`de`)`normalizationContext`:
```php
use ApiPlatform\Metadata\ApiResource;
use ApiPlatform\Metadata\Post;
#[ApiResource]
#[Post(denormalizationContext: [User::API_WRITE])]
class User
{
const API_WRITE = [
'groups' => ['user:read'],
'swagger_definition_name' => 'Read',
];
}
```
## Changing Operations in the OpenAPI Documentation
You also have full control over both built-in and custom operations documentation.
```php
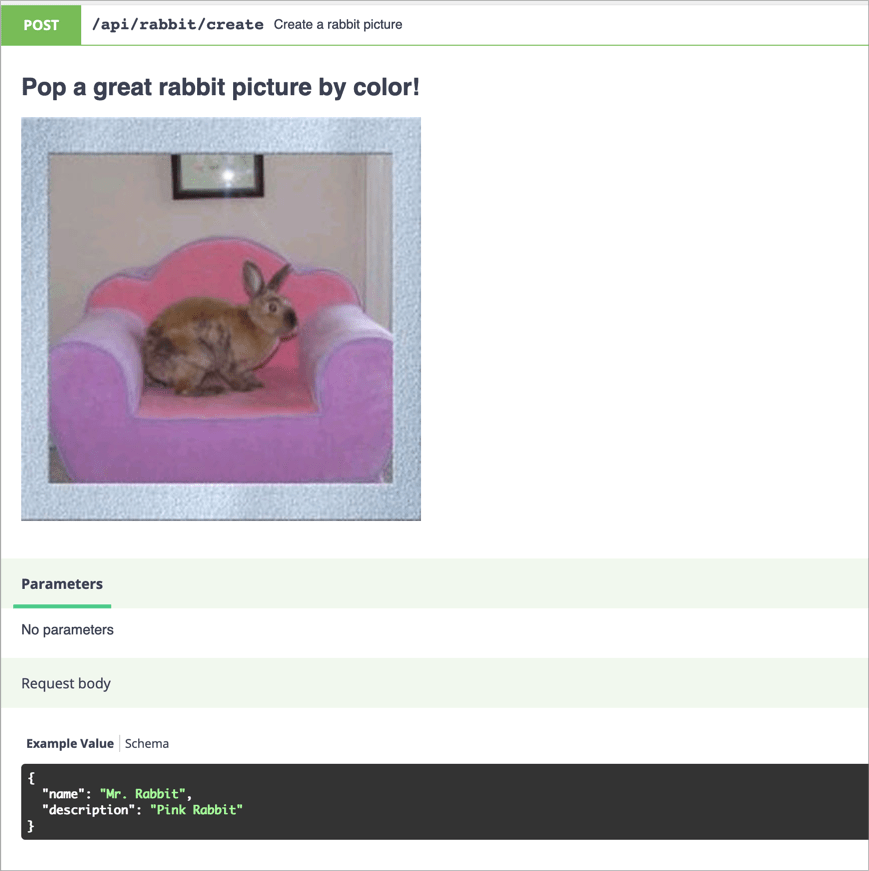
'Create a rabbit picture',
'description' => '# Pop a great rabbit picture by color!\n\n',
'requestBody' => [
'content' => [
'application/json' => [
'schema' => [
'type' => 'object',
'properties' => [
'name' => ['type' => 'string'],
'description' => ['type' => 'string']
]
],
'example' => [
'name' => 'Mr. Rabbit',
'description' => 'Pink Rabbit'
]
]
]
]
]
)]
class Rabbit
{
// ...
}
```
```yaml
resources:
App\Entity\Rabbit:
operations:
create_rabbit:
class: ApiPlatform\Metadata\Post
path: '/rabbit/create'
controller: App\Controller\RandomRabbit
openapiContext:
summary: Random rabbit picture
description: >
# Pop a great rabbit picture by color!

requestBody:
content:
application/json:
schema:
type: object
properties:
name: { type: string }
description: { type: string }
example:
name: Mr. Rabbit
description: Pink rabbit
```
```xml
Create a rabbit picture
# Pop a great rabbit picture by color!!

object
string
string
```
## Disabling Swagger UI or ReDoc
To disable Swagger UI (ReDoc will be shown by default):
```yaml
# api/config/packages/api_platform.yaml
api_platform:
# ...
enable_swagger_ui: false
```
To disable ReDoc:
```yaml
# api/config/packages/api_platform.yaml
api_platform:
# ...
enable_re_doc: false
```
## Changing the Location of Swagger UI
By default, the Swagger UI is available at the API location (when the HTML format is asked) and at the route `/docs`.
You may want to change its route and/or disable it at the API location.
### Changing the Route
Manually register the Swagger UI controller:
```yaml
# app/config/routes.yaml
api_doc:
path: /api_documentation
controller: api_platform.swagger.action.ui
```
Change `/api_documentation` to the URI you wish Swagger UI to be accessible on.
### Disabling Swagger UI at the API Location
To disable the Swagger UI at the API location, disable both Swagger UI and ReDoc:
```yaml
# api/config/packages/api_platform.yaml
api_platform:
# ...
enable_swagger_ui: false
enable_re_doc: false
```
If you have manually registered the Swagger UI controller, the Swagger UI will still be accessible at the route you have chosen.
## Using a custom Asset Package in Swagger UI
Sometimes you may want to use a different [Asset Package](https://symfony.com/doc/current/reference/configuration/framework.html#packages) for the Swagger UI.
In this way you'll have more fine-grained control over the asset URL generations.
This is useful i.e. if you want to use different base path, base URL or asset versioning strategy.
Specify a custom asset package name:
```yaml
# config/packages/api_platform.yaml
api_platform:
asset_package: 'api_platform'
```
Set or override asset properties per package:
```yaml
# config/packages/framework.yaml
framework:
# ...
assets:
base_path: '/custom_base_path' # the default
packages:
api_platform:
base_path: '/'
```
## Overriding the UI Template
As described [in the Symfony documentation](https://symfony.com/doc/current/templating/overriding.html), it's possible to override the Twig template that loads Swagger UI and renders the documentation:
```twig
{# templates/bundles/ApiPlatformBundle/SwaggerUi/index.html.twig #}
{% if title %}{{ title }} {% endif %}My custom template
{# ... #}
```
You may want to copy the [one shipped with API Platform](https://github.com/api-platform/core/blob/main/src/Symfony/Bundle/Resources/views/SwaggerUi/index.html.twig) and customize it.
## Compatibility Layer with Amazon API Gateway
[AWS API Gateway](https://aws.amazon.com/api-gateway/) supports OpenAPI partially, but it [requires some changes](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/apigateway/latest/developerguide/api-gateway-known-issues.html).
API Platform provides a way to be compatible with Amazon API Gateway.
To enable API Gateway compatibility on your OpenAPI docs, add `api_gateway=true` as query parameter: `http://www.example.com/docs.json?api_gateway=true`.
The flag `--api-gateway` is also available through the command-line.
## OAuth
If you implemented OAuth on your API, you should configure OpenApi's authorization using API Platform's configuration:
```yaml
api_platform:
oauth:
# To enable or disable oauth.
enabled: false
# The oauth client id.
clientId: ''
# The oauth client secret.
clientSecret: ''
# The oauth type.
type: 'oauth2'
# The oauth flow grant type.
flow: 'application'
# The oauth token url.
tokenUrl: '/oauth/v2/token'
# The oauth authentication url.
authorizationUrl: '/oauth/v2/auth'
# The oauth scopes.
scopes: []
```
Note that `clientId` and `clientSecret` are being used by the SwaggerUI if enabled.
## Info Object
The [info object](https://swagger.io/specification/#info-object) provides metadata about the API like licensing information or a contact. You can specify this information using API Platform's configuration:
```yaml
api_platform:
# The title of the API.
title: 'API title'
# The description of the API.
description: 'API description'
# The version of the API.
version: '0.0.0'
openapi:
# The contact information for the exposed API.
contact:
# The identifying name of the contact person/organization.
name:
# The URL pointing to the contact information. MUST be in the format of a URL.
url:
# The email address of the contact person/organization. MUST be in the format of an email address.
email:
# A URL to the Terms of Service for the API. MUST be in the format of a URL.
termsOfService:
# The license information for the exposed API.
license:
# The license name used for the API.
name:
# URL to the license used for the API. MUST be in the format of a URL.
url:
```
