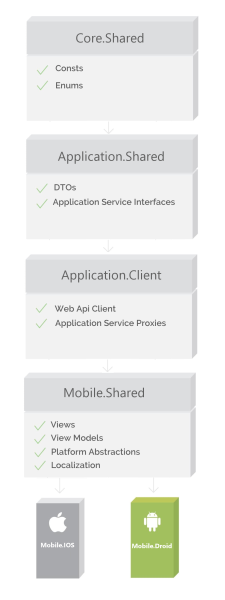
Xamarin Architecture
Xamarin is a cross-platform UI toolkit that allows developers to efficiently
create native cross platform user interface layouts.
This document is intended to show how to setup a Xamarin development environment
and introduce existing features and user interfaces on Asp.Net Zero Xamarin platform.
For an overview of the Xamarin installation and setup practices see
Xamarin.Forms Requirements and
Installation.
For an overview of the Asp.Net Zero getting started see
Asp.Net Zero Getting Started. The Asp.Net Zero
Xamarin is only available for ASP.NET Core included Angular UI and Mvc UI.
Following tools are needed in order to develop ASP.NET Zero Xamarin:
Asp.Net Zero Xamarin applications can be written for the following operating systems:
You should have the latest Android SDK Tools and Android API platform installed. You can update to the latest versions using the Android SDK Manager.
Additionally, the target/compile version for Android projects must be set to Use latest installed platform. However the minimum version can be set to API 15 so you can continue to support devices that use Android 4.0.3 and newer.
These values are set in the Project Options:
Project Options > Application > Application Properties

You can use Visual Studio for Mac to develop Xamarin.Forms apps on OS X El Capitan (10.11) or newer. To develop iOS apps, it is recommended having at least the iOS 10 SDK and Xcode latest installed.
Xamarin.Forms apps for iOS and Android can be built on any Windows installation that supports Xamarin development. A networked Mac is required for iOS development.
After you download your project, you will see 3 types of solutions;
For Xamarin development, you can open .Mobile.sln.

Xamarin Architecture
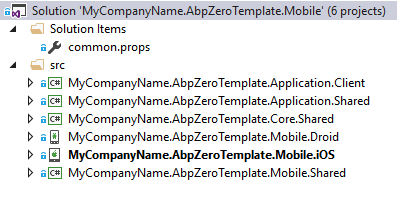
Mobile Solution
There are 6 projects in the mobile solution:
To start debugging Xamarin app you need to configure host settings. You can use
either Web.Mvc or Web.Host to feed the Xamarin app.
Open Windows Command Prompt. Go to the folder where your Web.Host or Web.Mvc csproj
file is located.
Then run the commands below to start hosting your Web Api.
SET ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENT=Development
SET ASPNETCORE_URLS=http://*:22742
dotnet run
In order to every time write these lines, you can download the batch file below and run it to host your web api.
Download Start-Host.zip
After you successfully run the host or mvc project you will see the output as below;
Host started successfully:
Mvc started successfully:
We have successfully started host. Now we can configure Xamarin app to connect this host.
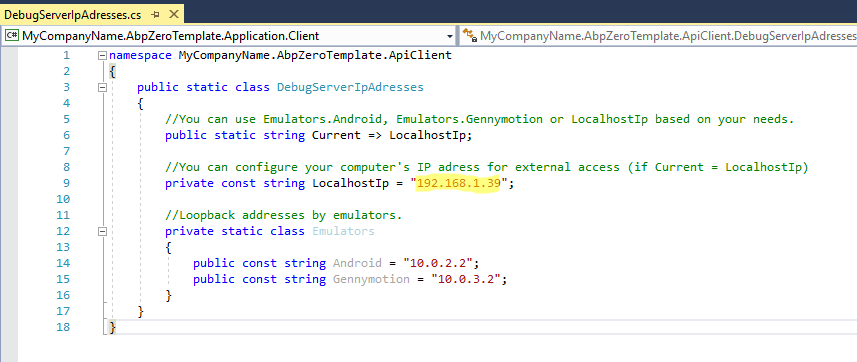
To start debugging you need to change the IP address in DebugServerIpAddresses
class. In the below screen you see the IP address 192.168.1.39, this is the IP of
host computer. If you host Web.Mvc or Web.Host from your computer then change this
IP with your computer's LAN IP.
If you host Web.Mvc or Web.Host from another computer then you have to change this
IP address with that computer's IP address.
Info If you are using an emulator and the emulator is running on the same computer with host, you have to use loopback IP addresses. Eg: Android emulator loopback IP address is 10.0.2.2
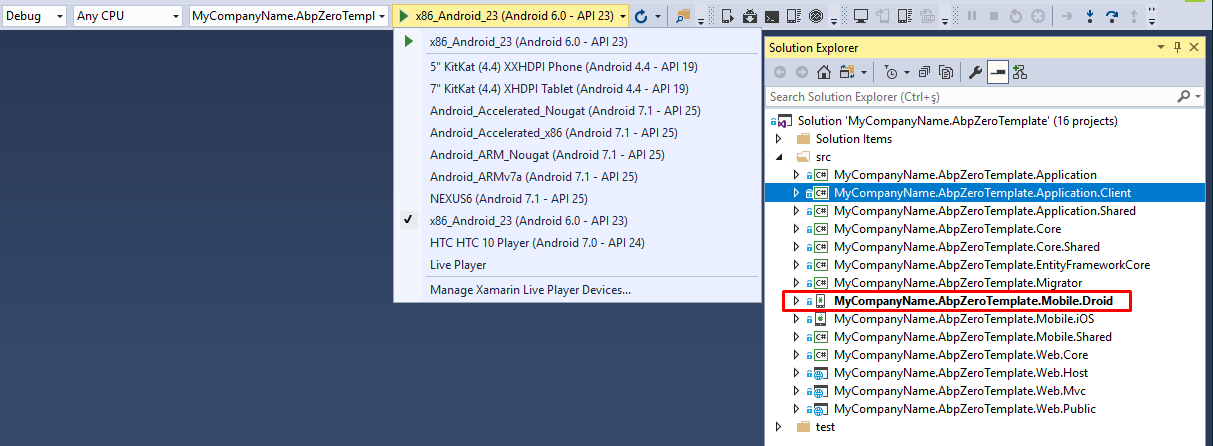
There are a few installation steps and configuration details required to install Xamarin.Android. It's highly recommended you to read the Xamarin Android Setup and Deployment document for necessary setups.
After successful setup, set *.Mobile.Droid as startup project. Choose an Android emulator from list and press start button.
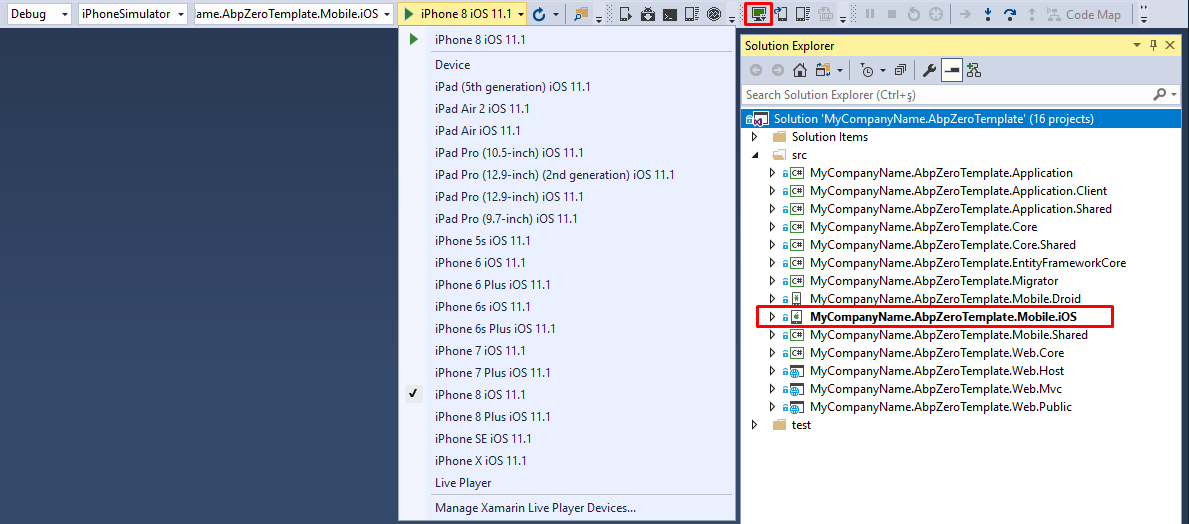
There are a few requirements that must be adhered to when developing for iOS in Visual Studio. A Mac is required to compile IPA files. Applications cannot be deployed to a device without Apple's certificates and code-signing tools. Also, the iOS simulator can be used only on a Mac.
There are a number of configuration options available to debug IOS app. It's
highly recommended you to read the
Xamarin IOS Getting started document to build an iOS application and debug
using a networked Mac to host Apple's compiler and simulator.
After you successfully configure and connect to a Mac, choose an iPhone simulator from list and press start button.
Xamarin Live Player currently does not support some of the key features. Thus Asp.Net Zero Xamarin application cannot be debugged on Xamarin Live Player. Further information read Xamarin Live Player limitations.
LiveXAML is a Xaml previewer runs while you are debugging your application. Whenever you save any XAML file, it automatically updates the running application. LiveXAML is a paid product. If you want to purchase LiveXAML, Asp.Net Zero customers get %30 discount.
A key component of building cross-platform applications is being able to share code across various platform-specific projects. Asp.Net Zero Xamarin is using Xamarin.Forms to maximize code sharing between two end platforms (IOS & Android). It is expected to write shared codes in Mobile.Shared project so that it will be used in both IOS and Android. If you need platform specific development then try to use class abstractions in shared project and implement/extend in end platforms.
Xamarin Android project has a very basic structure. Asp.Net Zero adds or modifies these files in the default project;
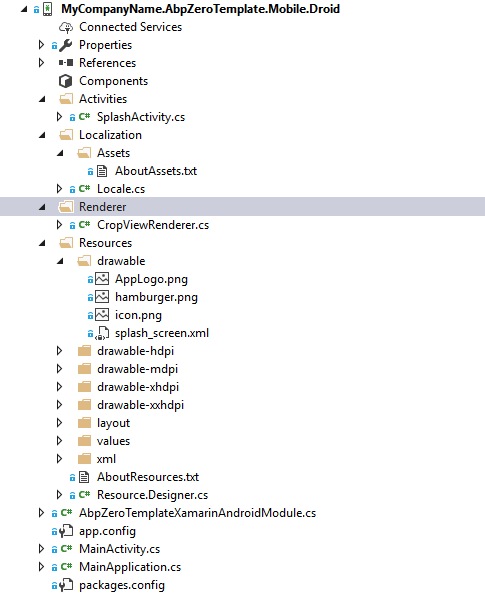
Android Project Structure
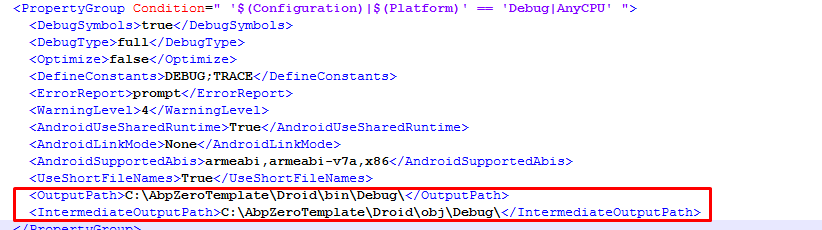
Asp.Net Zero Xamarin changed the output path (bin) and intermediate output path (obj) of Android project to be shorter. The main reason of this is avoiding "Path too long exception" while compiling project. If you want to modify it, you can open Mobile.iOS.csproj in notepad and find replace all occurrences of OutputPath and IntermediateOutputPath tags.
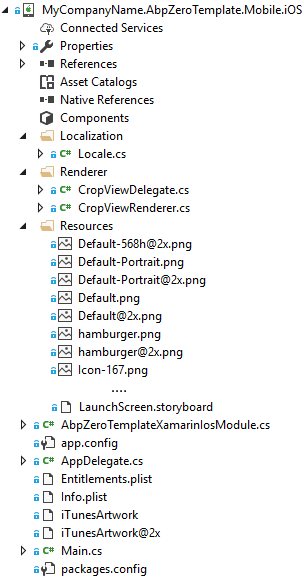
IOS Structure
Xamarin IOS project has a very simple structure. Asp.Net Zero adds or modifies these files in the default project;
Shared project is a special type of project that can be used across disparate CLI platforms including Mobile.iOS and Mobile.Android. That's why it's not been targeted to a specific framework version but targeted Netstandard 2.0. Shared code project should only reference assemblies that are available across all platforms. Shared project should implement as much non-UI functionality as is possible.
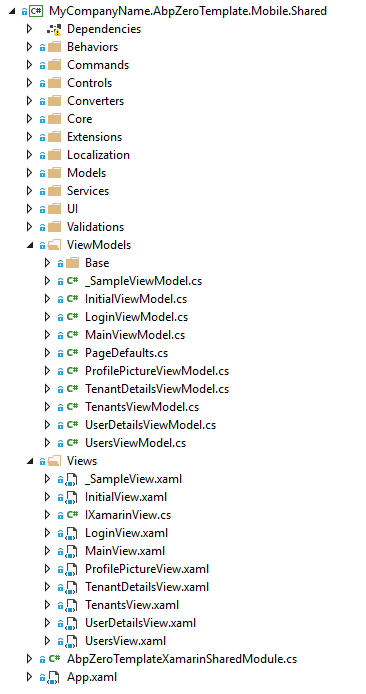
Shared Project Structure
Mobile.Shared project consists of fundamentals of a Xamarin application like Behaviors, Commands, Controls, Converters, Extensions, Views and ViewModels.
The Model-View-ViewModel (MVVM) architectural pattern is used in the shared project. The pattern enforces a separation between three software layers the XAML user interface, stored in Views folder; the underlying data are stored in Models folder; and an intermediary between the View and the Model, are stored in ViewModels folder. The View and the ViewModel are often connected through data bindings defined in the XAML file. The BindingContext for the View is always an instance of the ViewModel.
Asp.Net Zero has a built-in feature that binds View with ViewModel. BindingContext for a view is automatically set when AutoWireViewModel flag set to true in xaml. There's a naming convention between ViewModels and Views. A xaml filename must end with View postfix and the binding context of the xaml filename must end with ViewModel postfix. For example if xaml filename is ProductView.xaml the corresponding view model filename must be ProductViewModel.cs.
<ContentPage
...
base:ViewManager.AutoWireViewModel="true"
...>
There's an empty sample view called _SampleView.xaml and binding context _SampleViewModel.cs. You can copy paste and rename these empty templates to add a new blank page.
Asp.Net Zero Xamarin uses Asp.Net Boilerplate Framework's dependency injection system. Therefore it uses Castle Windsor as an Inversion of Control container. To resolve dependencies; you can use constructor or property injection, beside there's a shortcut class called DependencyResolver, which can be used to resolve dependencies as well. Asp.Net Boilerplate provides ITransientDependency and ISingletonDependency interfaces as a shortcut to register classes. See Asp.Net Boilerplate Dependency Injection
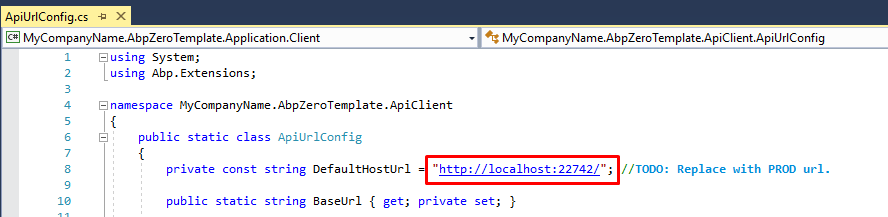
AbpApiClient class is used to communicate with host. In this class, FlurlClient is used as http client. The host address DefaultHostUrl is stored in ApiUrlConfig class. Before publishing application you need to change this address with your production host server address. In development time, it's important to change LocalhostIp as your computer's LAN IP in DebugServerIpAdresses.cs.
WebRequestExecuter class handles http web requests in a safe manner. When the request fails, it handles different types of exceptions. So if it's a timeout exception, it asks user to retry the same request. Or if it's a user friendly exception thrown by ABP it shows an alert and so on... You have to write a success and a fail callback to handle the result. In fail callback, the exception can be retrieved and in success callback result of the request can be retrieved.
SetBusyAsync method is in the base class of View Models in XamarinViewModel class. Whenever a long lasting operation is required it should be wrapped with SetBusyAsync method in view model so that user can see a busy indicator.
Navigation service implementation is done in NavigationService class. It's initialized in App.xaml.cs OnStart() method. If user is not signed in LoginView is shown as initial view, if user is already signed in then MainView is shown. MainView is NavigationPage, pages from menu are opened as detail page. In navigation service you can use these methods;
All exceptions are globally handled in ExceptionHandler class, LogException() method. Subscription to app wide unhandled exceptions is done in MainActivity class for Android and in AppDelegate class for IOS. However be aware that when an unhandled exception occurs, typically Android will be destroying the process. So there's not a lot can be done on the Android side, but your Xamarin code should still be able to work. So you can log the error message with a third party tool like HockeyApp Crash Reporting. Beside it's advised to keep a breakpoint in LogException() method. This is useful to see the exception before app crashes.
InitialView is a transition page that checks whether user has any granted menu permission or not. If user has no permissions then an info message will be shown on the screen. But if user has at least one granted menu permission, it is automatically being navigated to the first authorized menu item. InitialView is being created in MainView.xaml.
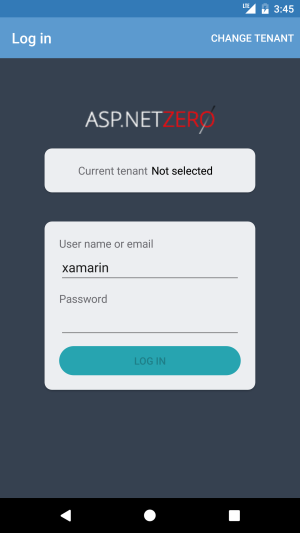
When user enters credentials AccessTokenManager authenticates user, stores access token in memory. For authentication needed Api calls, this token is being added to the request as bearer token. There's a timer in AccessTokenManager class that renews token before it expires. If an error occurs while communicating with host, client tries to reconnect within an exponentiation increasing time. After successful login user credentials are stored in device. This is for auto login (password is stored as encrypted). User information is being set in ApplicationContext so if current logon account information is needed it can be retrieved with injecting IApplicationContext.
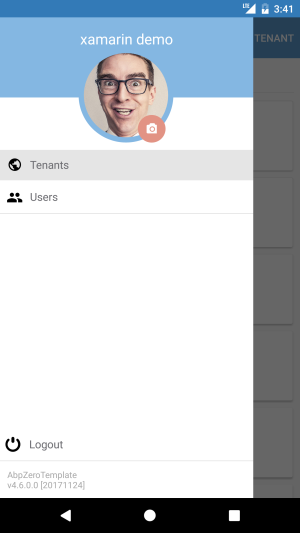
MainView is responsible for navigation service. Xamarin.Forms provides a number of different page navigation experiences, Asp.Net Zero Xamarin uses MasterDetailPage. The Xamarin.Forms MasterDetailPage is a page that manages two pages of related information a master page that presents items, and a detail page that presents details about items on the master page. When user taps hamburger menu icon, a popover is shown with menu items, logout button and profile picture. User profile picture is shown as circle image that uses ImageCirclePlugin. There is camera icon on the bottom right of the image. The icon button is implemented with Xamarin.Plugins.Iconize. When user taps the camera icon a dialog is shown to ask user whether choosing an image from gallery or taking a photo. After image retrieved, it's being routed to CropView. After cropping or rotating process, image is being sent to server.
Menu items are stored in MenuProvider class. A menu item is shown if only user has granted required permission. The menu items are being created in MainViewModel class with BuildMenuItems() method. A new menu item can be added directly to MenuProvider class.
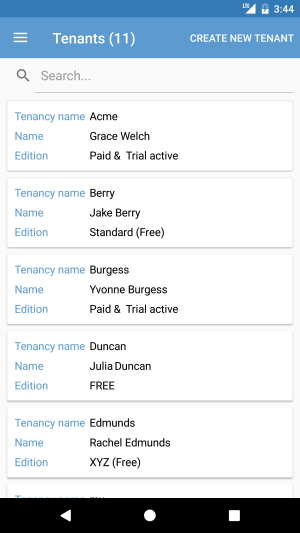
This page is shown if only user is a tenant owner. Page lists all tenants with a list view. There is HideableToolbarItem to create a new tenant. This toolbar item is extended control of a toolbar item that can be hidden if user has no tenant creation permission. The view model of this page is TenantsViewModel class. There is a search bar on the top that filters tenants on keypress. A limited information is shown in the list view item template. When user taps any item it navigates to the TenantDetailsView with the selected tenant object.
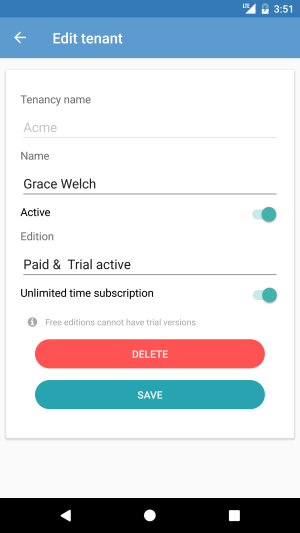
This page shows information about the selected tenant. Selected tenant model is being retrieved with navigationData object in InitializeAsync(object navigationData). There are action buttons on the bottom of the page which can be hidden if user has no permission. The permission is checked with an extension in xaml like below;
IsVisible="{extensions:HasPermission Text={x:Static permission:PermissionKey.TenantEdit}}"
Checking permission in c# classes can be done with IPermissionService class. It can be injected to the class and usage is like below;
_permissionService.HasPermission(PermissionKey.TenantDelete)
Before sending the tenant object to server, it's being validated with DataAnnotationsValidator class. If any validation error occurs, a warning is being shown to user. After tenant object is saved or deleted, tenants page is being refreshed by MessagingCenter class. See Xamarin MessasingCenter. Lastly TenantDetailsView is being popped with GoBackAsync() method of NavigationService.
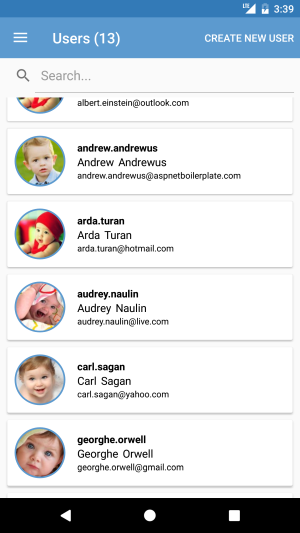
This page lists users of the tenant or tenant owner. It is only shown if the user has permission to this page. Same as tenants view, there's a search bar and a new user creation toolbar item. Profile pictures of users are shown in circle image view using Xam.Plugins.Forms.ImageCircle library. When a user is being tapped, it's navigated to UserDetailsView with the selected user.
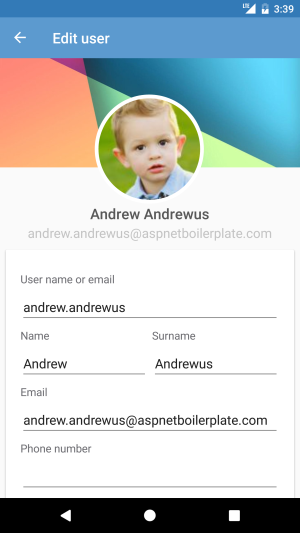
This page shows information about the selected user. If the logon user has no permission to edit then action buttons will be hidden and all inputs will be readonly. This is done in xaml with the following code;
IsEnabled="{extensions:HasPermission Text={x:Static permission:PermissionKey.UserEdit}}"

This is for viewing user profile picture in full screen mode. When user taps the profile picture thumbnail, this view is being shown.
If you want to publish your application to the related application store you can read the Xamarin official guides;
List of libraries are used to build ASP.NET Zero Xamarin project;