{
"cells": [
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"# Lecture 1: Probability and Counting\n",
"\n",
"## Stat 110, Prof. Joe Blitzstein, Harvard University\n",
"\n",
"\n",
"----"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"## Definitions\n",
"\n",
"We start with some basic definitions:\n",
"\n",
"#### Definition: sample space\n",
"\n",
"> A __sample space__ is the set of all possible outcomes of an experiment.\n",
"\n",
"\n",
"\n",
"#### Definition: event\n",
"\n",
"> An __event__ is a subset of the sample space.\n",
"\n",
"\n",
"#### Definition: naïve definition of probability\n",
"> Under the __naïve definition of probability__, the probability of a given event $A$ occurring is expressed as\n",
">\n",
"> \\begin\\{align\\}\n",
"> P(A) &= \\frac{ \\text{# favorable outcomes}}{\\text{# possible outcomes}}\n",
"> \\end\\{align\\}\n",
">\n",
"> assuming all outcomes are equally likely in a finite sample space.\n",
"\n",
"----"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"## Counting\n",
"\n",
"With the __multiplication rule__, if we have an experiment with $n_1$ possible outcomes; and we have a 2nd experiment with $n_2$ possible outcomes; ..., and for the rth experiment there are $n_r$ possible outcomes; then overall there are $n_1 n_2 ... n_r$ possible outcomes (product).\n",
"\n",
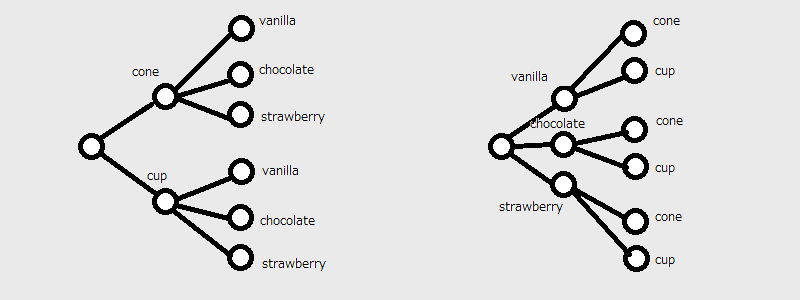
"Let's say you are ordering ice cream. You can either get a cone or a cup, and the ice cream comes in three flavors. The order of choice here does not matter, and the total number of choices is $2 \\times 3 = 3 \\times 2 = 6$. This can be represented with a very simple [probability tree][1].\n",
"\n",
"[1]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tree_diagram_(probability_theory)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
""
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"The __binomial coefficient__ is defined as \n",
"\n",
"\\begin{align}\n",
" \\binom{n}{k} =\n",
" \\begin{cases}\n",
" \\frac{n!}{(n-k)!k!} & \\quad \\text{if } 0 \\le k \\le n \\\\\n",
" 0 & \\quad \\text{if } k \\gt n\n",
" \\end{cases}\n",
"\\end{align}\n",
"\n",
"This expresses the number of ways you could choose a subset of size $k$ from $n$ items, where order doesn't matter.\n",
"\n",
"----"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"## Sampling\n",
"\n",
"Choose $k$ objects out of $n$\n",
"\n",
"| | ordered | unordered |\n",
"|-----------|:---------:|:-----------:|\n",
"| __w/ replacement__ | $n^k$ | ??? |\n",
"| __w/o replacement__ | $n(n-1)(n-2) \\ldots (n-k+1)$ | $\\binom{n}{k}$ |\n",
"\n",
"\n",
"* __ordered, w/ replacement__: there are $n$ choices for each $k$, so this follows from the multiplication rule.\n",
"* __ordered, w/out replacement__: there are $n$ choices for the 1st position; $n-1$ for the 2nd; $n-2$ for the 3rd; and $n-k+1$ for the $k$th.\n",
"* __unordered, w/ replacement__: ???\n",
"* __unordered, w/out replacement__: the binomial coefficient; think of choosing a hand from a deck of cards.\n",
"\n",
"Out of the 4 ways of choosing $k$ objects out of $n$, the case of __unordered, with replacement__ is perhaps not as clear-cut and easy to grasp as the other three. Move on to Lecture 2.\n",
"\n",
"-----"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"View [Lecture 1: Probability and Counting | Statistics 110](http://bit.ly/2vSEEeI) on YouTube."
]
}
],
"metadata": {
"kernelspec": {
"display_name": "Python 3",
"language": "python",
"name": "python3"
},
"language_info": {
"codemirror_mode": {
"name": "ipython",
"version": 3
},
"file_extension": ".py",
"mimetype": "text/x-python",
"name": "python",
"nbconvert_exporter": "python",
"pygments_lexer": "ipython3",
"version": "3.6.3"
}
},
"nbformat": 4,
"nbformat_minor": 1
}