{
"cells": [
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"execution": {
"iopub.execute_input": "2020-09-29T01:08:19.500487Z",
"iopub.status.busy": "2020-09-29T01:08:19.500061Z",
"iopub.status.idle": "2020-09-29T01:08:19.791026Z",
"shell.execute_reply": "2020-09-29T01:08:19.791536Z"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"import sys\n",
"import os\n",
"sys.path.append(os.environ.get('NOTEBOOK_ROOT'))\n",
"\n",
"%matplotlib inline \n",
"import matplotlib.pyplot as plt"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"\n",
"\n",
"# Coastline Classifier\n",
"This coastal boundary algorithm is used to classify a given pixel as either coastline or not coastline using a simple binary format like in the table before. \n",
"\n",
"
\n",
"\n",
"$\\begin{array}{|c|c|}\n",
"\\hline\n",
"1& Coastline \\\\ \\hline\n",
"0& Not Coastline \\\\ \\hline\n",
"\\end{array}$\n",
"\n",
"
\n",
"\n",
"\n",
"The algorithm makes a classification by examining surrounding pixels and making a determination based on how many pixels around it are water \n",
"\n",
"
\n",
"\n",
" \n",
" \n",
"
\n",
"\n",
"If the count of land pixels surrounding a pixel exceeds 5, then it's likely not coastline.\n",
"If the count of land pixels surrounding a pixel does not exceed 1, then it's likely not a coastline\n",
" \n",
"
\n",
"\n",
"$$\n",
"Classification(pixel) = \\begin{cases} \n",
" 1 & 2\\le count\\_water\\_surrounding(pixel) \\leq 5 \\\\\n",
" 0 & \n",
" \\end{cases}\n",
"$$\n",
"\n",
"
\n",
" \n",
" \n",
"### Counting by applying a convolutional kernel \n",
"\n",
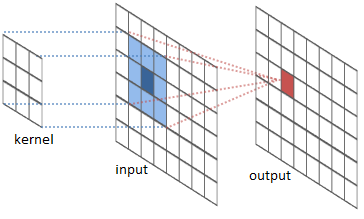
"A convolution applies a `kernel` to a point and it's surrounding pixels. Then maps the product to a new grid. \n",
" \n",
"\n",
"\n",
"\n",
"\n",
"\n",
"\n",
"\n",
"In the case of coastal boundary classification, A convolution the following kernel is applied to a grid of `water`, `not-water` pixels.\n",
"\n",
"
\n",
"\n",
"\n",
"$$ \n",
"Kernel =\n",
" \\begin{bmatrix}\n",
" 1 & 1 & 1\\\\\n",
" 1 & 0 & 1\\\\ \n",
" 1 & 1 & 1\\\\\n",
" \\end{bmatrix}\n",
"$$ \n",
" \n",
"
\n",
"There exist more complicated differential kernels that would also work( see [sobel operator](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sobel_operator)). \n",
"The one used in this notebooks operates on binary variables and is easier to work with and easy to debug. \n",
"\n",
"
\n",
"\n",
"# Index\n",
"\n",
"* [Import Dependencies and Connect to the Data Cube](#coastline_classifier_import)\n",
"* [Choose Platform and Product](#coastline_classifier_plat_prod)\n",
"* [Define the Extents of the Analysis](#coastline_classifier_define_extents)\n",
"* [Load Data from the Data Cube and Create a Composite](#coastline_classifier_retrieve_data)\n",
"* [Obtain Water Classifications and Coastal Change](#coastline_classifier_water_cls_and_coastal_change)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"## Import Dependencies and Connect to the Data Cube [▴](#coastline_classifier_top)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"execution": {
"iopub.execute_input": "2020-09-29T01:08:19.796824Z",
"iopub.status.busy": "2020-09-29T01:08:19.796393Z",
"iopub.status.idle": "2020-09-29T01:08:19.815219Z",
"shell.execute_reply": "2020-09-29T01:08:19.814767Z"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"import scipy.ndimage.filters as conv\n",
"import numpy as np\n",
"\n",
"def _coastline_classification(dataset, water_band='wofs'):\n",
" kern = np.array([[1, 1, 1], [1, 0.001, 1], [1, 1, 1]])\n",
" convolved = conv.convolve(dataset[water_band], kern, mode='constant') // 1\n",
"\n",
" ds = dataset.where(convolved > 0)\n",
" ds = ds.where(convolved < 6)\n",
" ds.wofs.values[~np.isnan(ds.wofs.values)] = 1\n",
" ds.wofs.values[np.isnan(ds.wofs.values)] = 0\n",
"\n",
" return ds.rename({\"wofs\": \"coastline\"})"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"execution": {
"iopub.execute_input": "2020-09-29T01:08:19.818573Z",
"iopub.status.busy": "2020-09-29T01:08:19.817878Z",
"iopub.status.idle": "2020-09-29T01:08:20.992414Z",
"shell.execute_reply": "2020-09-29T01:08:20.992871Z"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"from datacube.utils.aws import configure_s3_access\n",
"configure_s3_access(requester_pays=True)\n",
"\n",
"import datacube\n",
"dc = datacube.Datacube(app = \"Coastline classification\") "
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"## Choose Platform and Product [▴](#coastline_classifier_top)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"execution": {
"iopub.execute_input": "2020-09-29T01:08:20.996114Z",
"iopub.status.busy": "2020-09-29T01:08:20.995693Z",
"iopub.status.idle": "2020-09-29T01:08:20.997525Z",
"shell.execute_reply": "2020-09-29T01:08:20.997967Z"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"platform = 'LANDSAT_8'\n",
"product = 'ls8_usgs_sr_scene'\n",
"collection = 'c1'\n",
"level = 'l2'"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"## Define the Extents of the Analysis [▴](#coastline_classifier_top)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"West Africa is subject to considerable coastal erosion in some areas. The links listed below are references regarding coastal erosion in West Africa and coastal erosion in general. \n",
"\n",
"- World Bank WACA program brochure (2015) [- link](http://pubdocs.worldbank.org/en/622041448394069174/1606426-WACA-Brochure.pdf)\n",
"- USAID - Adapting to Coastal Climate Change (2009) - [- link](http://www.crc.uri.edu/download/CoastalAdaptationGuide.pdf) "
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"execution": {
"iopub.execute_input": "2020-09-29T01:08:21.001160Z",
"iopub.status.busy": "2020-09-29T01:08:21.000735Z",
"iopub.status.idle": "2020-09-29T01:08:21.002437Z",
"shell.execute_reply": "2020-09-29T01:08:21.002845Z"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"# Ghana\n",
"lon = (0.0520, 0.3458)\n",
"lat = (5.6581, 5.8113)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"**Visualize the selected area**"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"execution": {
"iopub.execute_input": "2020-09-29T01:08:21.006138Z",
"iopub.status.busy": "2020-09-29T01:08:21.005452Z",
"iopub.status.idle": "2020-09-29T01:08:21.187101Z",
"shell.execute_reply": "2020-09-29T01:08:21.186652Z"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"from utils.data_cube_utilities.dc_display_map import display_map\n",
"display_map(lat, lon)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"## Load Data from the Data Cube and Create a Composite [▴](#coastline_classifier_top)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"execution": {
"iopub.execute_input": "2020-09-29T01:08:21.194709Z",
"iopub.status.busy": "2020-09-29T01:08:21.194236Z",
"iopub.status.idle": "2020-09-29T01:08:21.196397Z",
"shell.execute_reply": "2020-09-29T01:08:21.195963Z"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"from datetime import datetime \n",
"\n",
"params = dict(platform=platform,\n",
" product=product,\n",
" time=(datetime(2013,1,1), datetime(2013,12,31)) ,\n",
" lon= lon,\n",
" lat= lat,\n",
" measurements = ['red', 'green', 'blue', 'nir', 'swir1', 'swir2', 'pixel_qa'],\n",
" dask_chunks={'time':1, 'latitude':1000, 'longitude':1000})"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"execution": {
"iopub.execute_input": "2020-09-29T01:08:21.208169Z",
"iopub.status.busy": "2020-09-29T01:08:21.207759Z",
"iopub.status.idle": "2020-09-29T01:08:23.659788Z",
"shell.execute_reply": "2020-09-29T01:08:23.660544Z"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"dataset = dc.load(**params).persist()"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"**Obtain the clean mask**"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"execution": {
"iopub.execute_input": "2020-09-29T01:08:23.665196Z",
"iopub.status.busy": "2020-09-29T01:08:23.664503Z",
"iopub.status.idle": "2020-09-29T01:08:23.831965Z",
"shell.execute_reply": "2020-09-29T01:08:23.832425Z"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"from utils.data_cube_utilities.clean_mask import landsat_clean_mask_full\n",
"\n",
"clean_mask = landsat_clean_mask_full(dc, dataset, product=product, platform=platform, \n",
" collection=collection, level=level).persist()"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"**Create a composite**"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"execution": {
"iopub.execute_input": "2020-09-29T01:08:23.844711Z",
"iopub.status.busy": "2020-09-29T01:08:23.844307Z",
"iopub.status.idle": "2020-09-29T01:08:26.890065Z",
"shell.execute_reply": "2020-09-29T01:08:26.889549Z"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"from utils.data_cube_utilities.dc_mosaic import create_median_mosaic\n",
"from utils.data_cube_utilities.dc_utilities import ignore_warnings\n",
"\n",
"composited_dataset = ignore_warnings(create_median_mosaic, dataset, clean_mask).persist()"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"**Visualize Composited imagery** "
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"execution": {
"iopub.execute_input": "2020-09-29T01:08:26.894079Z",
"iopub.status.busy": "2020-09-29T01:08:26.893361Z",
"iopub.status.idle": "2020-09-29T01:08:27.529927Z",
"shell.execute_reply": "2020-09-29T01:08:27.530366Z"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"from utils.data_cube_utilities.plotter_utils import figure_ratio\n",
"\n",
"composited_dataset.swir1.plot(cmap = \"Greys\", figsize = figure_ratio(dataset, fixed_width = 20))"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"## Obtain Water Classifications and Coastal Change [▴](#coastline_classifier_top)"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"execution": {
"iopub.execute_input": "2020-09-29T01:08:27.533792Z",
"iopub.status.busy": "2020-09-29T01:08:27.533308Z",
"iopub.status.idle": "2020-09-29T01:08:27.637893Z",
"shell.execute_reply": "2020-09-29T01:08:27.637388Z"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"from utils.data_cube_utilities.dc_water_classifier import wofs_classify\n",
"\n",
"water_classification = ignore_warnings(wofs_classify, composited_dataset, mosaic = True).persist()"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"execution": {
"iopub.execute_input": "2020-09-29T01:08:27.642637Z",
"iopub.status.busy": "2020-09-29T01:08:27.641966Z",
"iopub.status.idle": "2020-09-29T01:08:28.164455Z",
"shell.execute_reply": "2020-09-29T01:08:28.164902Z"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"water_classification.wofs.plot(cmap = \"Blues\", figsize = figure_ratio(dataset, fixed_width = 20))"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"metadata": {},
"source": [
"
"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"execution": {
"iopub.execute_input": "2020-09-29T01:08:28.168681Z",
"iopub.status.busy": "2020-09-29T01:08:28.168277Z",
"iopub.status.idle": "2020-09-29T01:08:28.193830Z",
"shell.execute_reply": "2020-09-29T01:08:28.194269Z"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"coast = _coastline_classification(water_classification, water_band='wofs').persist()"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"execution_count": null,
"metadata": {
"execution": {
"iopub.execute_input": "2020-09-29T01:08:28.198089Z",
"iopub.status.busy": "2020-09-29T01:08:28.197676Z",
"iopub.status.idle": "2020-09-29T01:08:28.731996Z",
"shell.execute_reply": "2020-09-29T01:08:28.732417Z"
}
},
"outputs": [],
"source": [
"coast.coastline.plot(cmap = \"Blues\", figsize = figure_ratio(dataset, fixed_width = 20))"
]
}
],
"metadata": {
"kernelspec": {
"display_name": "Python 3",
"language": "python",
"name": "python3"
},
"language_info": {
"codemirror_mode": {
"name": "ipython",
"version": 3
},
"file_extension": ".py",
"mimetype": "text/x-python",
"name": "python",
"nbconvert_exporter": "python",
"pygments_lexer": "ipython3",
"version": "3.6.9"
}
},
"nbformat": 4,
"nbformat_minor": 4
}