# ACEBench: Who Wins the Match Point in Tool Usage?
📃 Paper
· 🏆 Leaderboard (Continuously Updated)
English | [中文](README_CN.md)
## 📚 Content
- [1\. Abstract](#abstract)
- [2\. Benchmark Statistics](#statistics)
- [3\. Leaderboard](#leaderboard)
- [4\. Setup](#setup)
- [5\. Data](#data)
- [6\. Inference](#inference)
- [6.1\. Inference Script](#open_source_inference)
- [6.2\. Inference Examples](#openai_inference)
- [7\. Evaluation](#evaluation)
- [Citation](#citation)
---
## 🛠️ Updates [[Back to Top]](#content)
### [2025.10.29]
1 We have corrected the possible answers in the normal_atom_enum_9, normal_atom_number_17, and normal_atom_list_34 datasets.
## 📘 1\. Abstract [[Back to Top]](#content)
Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated significant potential in decision-making and reasoning, particularly when integrated with various tools to effectively solve complex problems. However, existing benchmarks for evaluating LLMs' tool usage face several limitations: (1) limited evaluation scenarios, often lacking assessments in real multi-turn dialogue contexts; (2) narrow evaluation dimensions, with insufficient detailed assessments of how LLMs use tools; and (3) reliance on LLMs or real API executions for evaluation, which introduces significant overhead. To address these challenges, we introduce ACEBench, a comprehensive benchmark for assessing tool usage in LLMs. ACEBench categorizes data into three primary types based on evaluation methodology: Normal, Special, and Agent. "Normal" evaluates tool usage in basic scenarios; "Special" evaluates tool usage in situations with ambiguous or incomplete instructions; "Agent" evaluates tool usage through multi-agent interactions to simulate real-world, multi-turn dialogues. We conducted extensive experiments using ACEBench, analyzing various LLMs in-depth and providing a more granular examination of error causes across different data types.
---
## 📊 2.Benchmark Data Analysis [[Back to Top]](#content)
### **Domain of APIs**
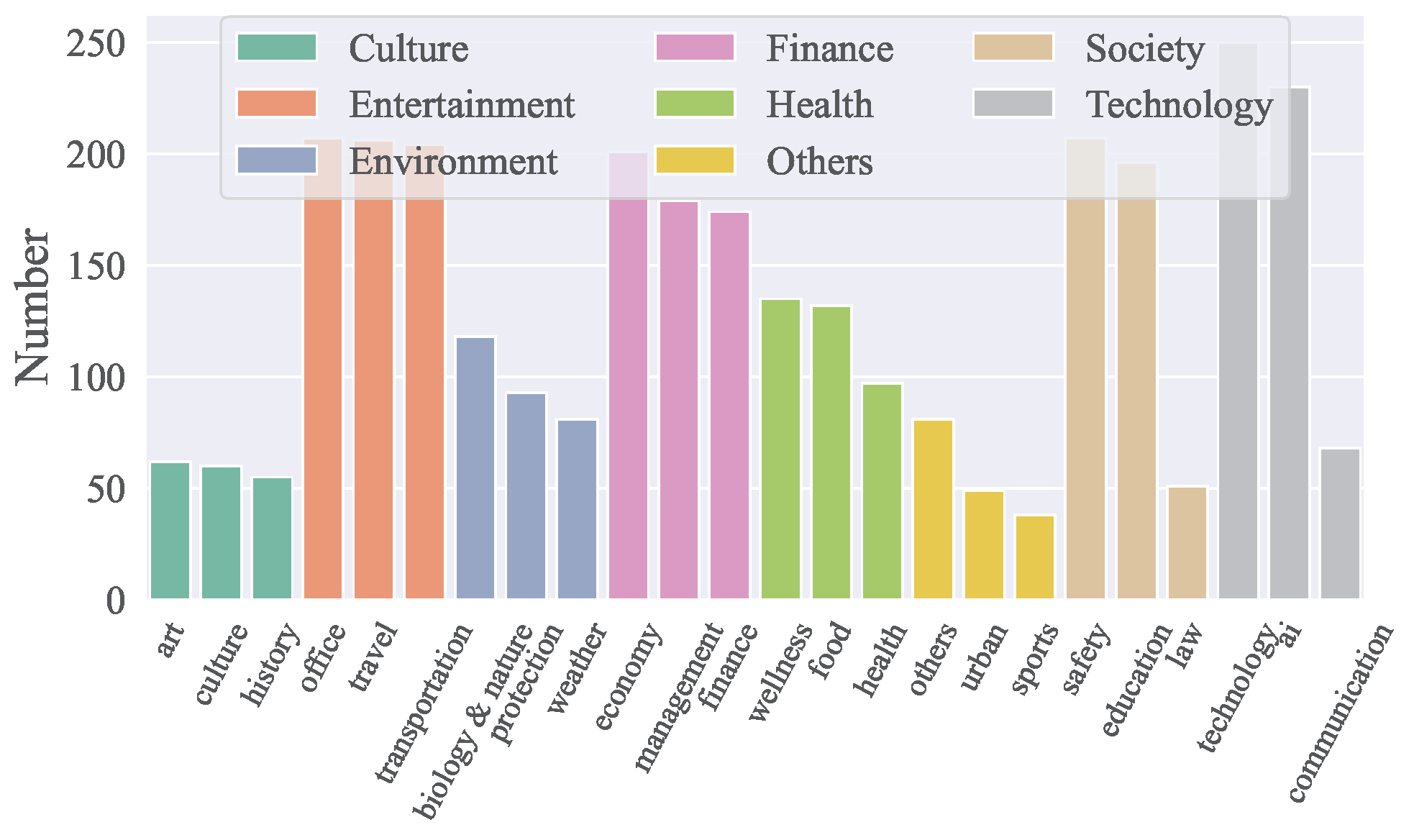
- ACEBench covers **8 major domains** and **68 sub-domains**, including technology, finance, entertainment, society, health, culture, environment, and more.
- It includes a total of **4,538 APIs** in both Chinese and English.
- The distribution of APIs across domains is visualized in the figure below:
### **Data Composition**
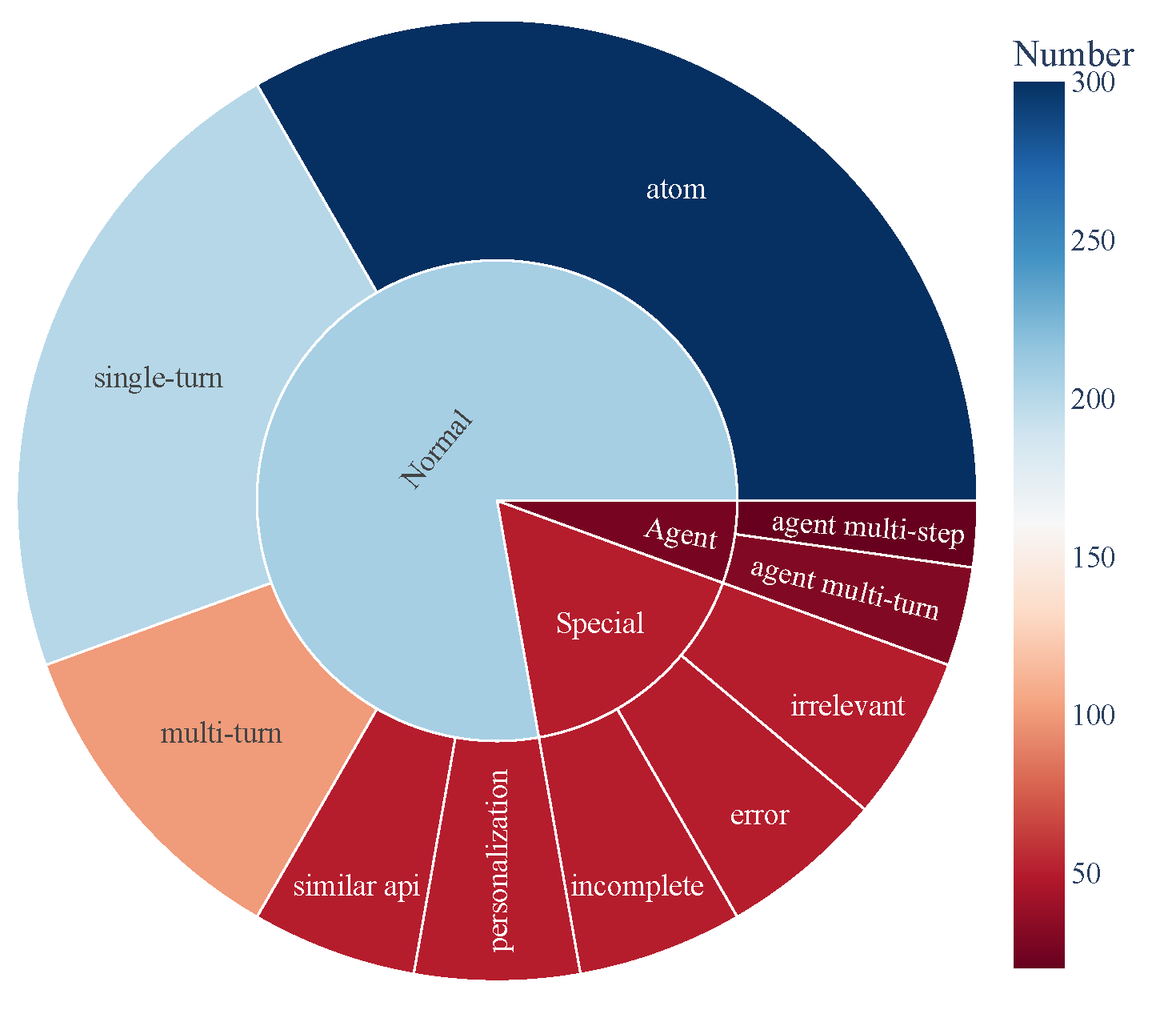
- ACEBench consists of three main categories of test samples:
- **Normal**: Basic tool-use scenarios.
- **Agent**: Multi-turn interactions involving users and environments.
- **Special**: Complex scenarios requiring multiple steps or handling infeasible tool calls.
- The data composition is visualized below, showcasing the comprehensive coverage of tool-use capabilities:
## 🏆 3\. Leaderboard [[Back to Top]](#content)
| Model | normal | special | agent | overall |
| ------------------------------------- | ------ | ------- | ----- | ------- |
| **close-source model** |
| gpt-4o-2024-11-20 | 0.927 | 0.933 | 0.715 | 0.896 |
| gpt-4-turbo-2024-04-09 | 0.917 | 0.913 | 0.725 | 0.886 |
| qwen-max | 0.887 | 0.740 | 0.685 | 0.817 |
| o1-preview | 0.830 | 0.793 | 0.735 | 0.806 |
| deepseek-chat | 0.926 | 0.733 | 0.350 | 0.785 |
| gpt-4o-mini-2024-07-18 | 0.834 | 0.813 | 0.390 | 0.760 |
| claude-3-5-sonnet-20241022 | 0.835 | 0.820 | 0.350 | 0.756 |
| gemini-1.5-pro | 0.822 | 0.800 | 0.250 | 0.728 |
| o1-mini | 0.774 | 0.673 | 0.610 | 0.722 |
| doubao-pro-32k | 0.750 | 0.593 | 0.235 | 0.628 |
| **open-source model** |
| Qwen2.5-Coder-32B-Instruct-local | 0.908 | 0.813 | 0.715 | 0.853 |
| Qwen2.5-32B-Instruct-local | 0.852 | 0.747 | 0.690 | 0.799 |
| Qwen2.5-72B-Instruct-local | 0.873 | 0.773 | 0.525 | 0.793 |
| Qwen2.5-Coder-14B-Instruct-local | 0.868 | 0.647 | 0.525 | 0.756 |
| Qwen2.5-14B-Instruct-local | 0.790 | 0.540 | 0.250 | 0.640 |
| Llama-3.1-70B-Instruct-local | 0.753 | 0.473 | 0.435 | 0.629 |
| Qwen2.5-7B-Instruct-local | 0.759 | 0.447 | 0.125 | 0.578 |
| DeepSeek-Coder-V2-Lite-Instruct-local | 0.688 | 0.413 | 0.015 | 0.511 |
| Qwen2.5-Coder-7B-Instruct-local | 0.735 | 0.193 | 0.125 | 0.496 |
| watt-tool-8B-local | 0.763 | 0.100 | 0.040 | 0.474 |
| ToolACE-8B-local | 0.782 | 0.013 | 0.040 | 0.462 |
| Hammer2.1-7b-local | 0.627 | 0.260 | 0.185 | 0.461 |
| Meta-Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct-local | 0.450 | 0.267 | 0.040 | 0.338 |
| Qwen2.5-Coder-3B-Instruct-local | 0.495 | 0.100 | 0.065 | 0.323 |
| Phi-3-mini-128k-instruct-local | 0.389 | 0.253 | 0.015 | 0.295 |
| Qwen2.5-3B-Instruct-local | 0.408 | 0.127 | 0.065 | 0.280 |
| Llama-3.2-3B-Instruct-local | 0.327 | 0.100 | 0.000 | 0.216 |
| xLAM-7b-r-local | 0.187 | 0.013 | 0.075 | 0.123 |
| Hammer2.1-3b-local | 0.118 | 0.013 | 0.015 | 0.074 |
---
## 🛠️ 4\. Setup [[Back to Top]](#content)
Execute the following command to install the required dependencies for inference and evaluation:
```bash
pip install -r requirements.txt
```
---
## 🗂️ 5\. Data [[Back to Top]](#content)
All data is stored in the data_all directory, divided into English and Chinese parts, which are located in the data_en and data_zh folders respectively. Each folder contains multiple JSON files, named in the format data_{category}.json, where category represents the type of data.
```
data_all/
├── possible_answer_en/
│ ├── data_{normal}.json
│ ├── data_{special}.json
│ ├── data_{agent}.json
├── possible_answer_zh/
│ ├── data_{normal}.json
│ ├── data_{special}.json
│ ├── data_{agent}.json
...
```
## 🧠 6\. Inference [[Back to Top]](#content)
### 6.1 Inference Script
To run inference with cmodels, use the `generate.py` script. This script supports various models, categories, and languages.
### Basic Usage
```bash
python generate.py --model --model_path
--category --language
```
Arguments:
- `--model`: Specifies the model to use for inference.
- `--model_path`: Specifies the local path to the model (only for open-source models).
- `--category`: Defines the category of tasks or datasets to evaluate. Available categories can be found in eval_checker/eval_checker_constant.py.
- `--language`: Specifies the language of the input/output. Supported languages: "en" (English), "zh" (Chinese)
### 6.2\. Inference Examples
for closed-source model
```bash
python generate.py --model qwen-max --category test_all --language zh
```
for local model
```bash
python generate.py --model Qwen2.5-3B-Instruct-local --model-path /mnt/nas/ckpt/Qwen2.5-3B-Instruct --category test_all --language zh
```
### 6.3\. Precautions
* Before running the program, ensure that the environment variable .env file is correctly configured. To invoke OpenAI, you need to use the external network. Configure the environment variables https_proxy and http_proxy. To use the gemini model, you need to use the Japanese proxy.
* The model to be evaluated needs to be mapped in model_inference/inference_map.py. The model invoked through OpenAI can be added to the APIModelInference list, and the customized inference model can be added to the CommonInference list. The name of a local model ends with -local.
* To add a customized evaluation model, add the model class to model_dict by referring to model_inference/model_infer.py.
* Evaluate the open-source model on Hugging Face. You are advised to use LLaMA-Factory to combine LoRA weights and then infer.
## 📈 7. Evaluation [[Back to Top]](#content)
To evaluate the performance of the models, use the `eval_main.py` script. This script supports various evaluation metrics and can be used for both open-source and closed-source models.
### Basic Usage
```bash
python eval_main.py --model --category --language
```
## 📄 Citation
If you find our paper and resources useful, please consider citing our paper:
```bibtex
@article{chen2025acebench,
title={ACEBench: Who Wins the Match Point in Tool Learning?},
author={Chen, Chen and Hao, Xinlong and Liu, Weiwen and Huang, Xu and Zeng, Xingshan and Yu, Shuai and Li, Dexun and Wang, Shuai and Gan, Weinan and Huang, Yuefeng and others},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2501.12851},
year={2025}
}
```


