# :skull_and_crossbones: SEMA :skull_and_crossbones: - ToolChain using Symbolic Execution for Malware Analysis.
```
██████ ▓█████ ███▄ ▄███▓ ▄▄▄
▒██ ▒ ▓█ ▀ ▓██▒▀█▀ ██▒▒████▄
░ ▓██▄ ▒███ ▓██ ▓██░▒██ ▀█▄
▒ ██▒▒▓█ ▄ ▒██ ▒██ ░██▄▄▄▄██
▒██████▒▒░▒████▒▒██▒ ░██▒ ▓█ ▓██▒
▒ ▒▓▒ ▒ ░░░ ▒░ ░░ ▒░ ░ ░ ▒▒ ▓▒█░
░ ░▒ ░ ░ ░ ░ ░░ ░ ░ ▒ ▒▒ ░
░ ░ ░ ░ ░ ░ ░ ▒
░ ░ ░ ░ ░ ░
```
# Table of Contents
1. [Architecture](#architecture)
- [Toolchain Architecture](#toolchain-architecture)
2. [Recommended Installation and Usage](#page_with_curl-recommended-installation-and-usage)
3. [Dockerhub Installation and Usage](#page_with_curl-dockerhub-installation)
4. [Pypi Installation and Usage](#page_with_curl-pypi-installation-and-usage)
5. [Credentials](#page_with_curl-credentials)
:page_with_curl: Architecture
====
### Toolchain architecture
Our toolchain is represented in the following figure and works as follows:
- A collection of labelled binaries from different malware families is collected and used as the input of the toolchain.
- **Angr**, a framework for symbolic execution, is used to execute binaries symbolically and extract execution traces. For this purpose, different heuristics have been developed to optimize symbolic execution.
- Several execution traces (i.e., API calls used and their arguments) corresponding to one binary are extracted with Angr and gathered together using several graph heuristics to construct a SCDG.
- These resulting SCDGs are then used as input to graph mining to extract common graphs between SCDGs of the same family and create a signature.
- Finally, when a new sample has to be classified, its SCDG is built and compared with SCDGs of known families using a simple similarity metric.
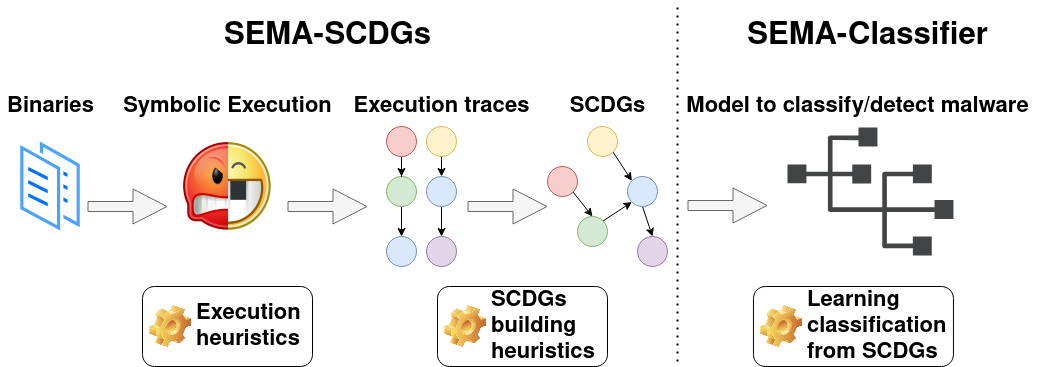
This repository contains a first version of a SCDG extractor. During the symbolic analysis of a binary, all system calls and their arguments found are recorded. After some stop conditions for symbolic analysis, a graph is built as follows: Nodes are system calls recorded, edges show that some arguments are shared between calls.
When a new sample has to be evaluated, its SCDG is first built as described previously. Then, `gspan` is applied to extract the biggest common subgraph and a similarity score is evaluated to decide if the graph is considered as part of the family or not. The similarity score `S` between graph `G'` and `G''` is computed as follows:
Since `G''` is a subgraph of `G'`, this is calculating how much `G'` appears in `G''`.
Another classifier we use is the Support Vector Machine (`SVM`) with INRIA graph kernel or the Weisfeiler-Lehman extension graph kernel.
A web application is available and is called SemaWebApp. It allows to manage the launch of experiments on SemaSCDG and/or SemaClassifier.
#### Main depencies:
* Python 3.8
* Docker >=26.1.3 , docker buildx, Docker Compose >=v2.27.0
* radare2
* libvirt-dev, libgraphviz-dev, wheel
#### Interesting links
- [Angr](https://angr.io/)
- [Bazaar Abuse](https://bazaar.abuse.ch/)
- [Docker Installation on Ubuntu](https://docs.docker.com/engine/install/ubuntu/)
#### Extracting database
To extract the database, use the following commands:
```bash
cd databases/Binaries
./extract_deploy_db.sh
```
Password for archive is "infected". Warning : it contains real samples of malwares.
#### Compressing database
To compress the database, use the following commands:
```bash
#To zip back the test database
cd databases/Binaries
./compress_db.sh
```
:page_with_curl: **Recommended installation and usage**
====
To install the entire toolchain, use the following command:
```bash
# Full installation (ubuntu)
make build-toolchain;
```
## How to use ?
### Using the web application
First launch the containers :
```bash
make run-toolchain
```
This will start the SCDG, the classifier, and the web app services. If you wish to use only the SCDG or only the classifier, refer to the specific sections below.
Wait for the containers to be up, then visit 127.0.0.1:5000 on your browser
See next sections for details about the different parameters.
#### Shut down
To leave the toolchain just press Ctrl+C then use
```bash
make stop-toolchain
```
To stop all docker containers.
If you want to remove all images :
```bash
docker rmi sema-web-app
docker rmi sema-scdg
docker rmi sema-classifier
```
### Use only SemaSCDG
To use only the SemaSCDG, first run the SCDG container with volumes like this:
```bash
docker run --rm --name="sema-scdg" -v ${PWD}/OutputFolder:/sema-scdg/application/database/SCDG -v ${PWD}/ConfigFolder:/sema-scdg/application/configs -v ${PWD}/InputFolder:/sema-scdg/application/database/Binaries -p 5001:5001 -it sema-scdg bash
```
In this command:
- The first volume corresponds to the output folder where the results will be put.
- The second volume corresponds to the folder containing the configuration files that will be passed to the docker.
- The third matches the folder containing the binaries that are going to be passed to the container.
Example taking the files already provided, being inside the sema_toolchain folder, run :
```bash
docker run --rm --name="sema-scdg" -v ${PWD}/database/SCDG:/sema-scdg/application/database/SCDG -v ${PWD}/sema_scdg/application/configs:/sema-scdg/application/configs -v ${PWD}/database/Binaries:/sema-scdg/application/database/Binaries -p 5001:5001 -it sema-scdg bash
```
If you want to be able to modify the code when the container is running, use
```bash
docker run --rm --name="sema-scdg" -v ${PWD}/database:/sema-scdg/application/database -v ${PWD}/sema_scdg/application:/sema-scdg/application -p 5001:5001 -it sema-scdg bash
```
To run experiments, run inside the container :
```bash
python3 SemaSCDG.py configs/config.ini
```
Or if you want to use pypy3:
```bash
pypy3 SemaSCDG.py configs/config.ini
```
#### Configuration files
The parameters are put in a configuration file : `configs/config.ini`. Feel free to modify it or create new configuration files to run different experiments.
The output of the SCDG are put into `database/SCDG/runs/` by default. If you are not using volumes and want to save some runs from the container to your host machine, use :
```bash
make save-scdg-runs ARGS=PATH
```
#### Parameters description
SCDG module arguments
```
expl_method:
DFS Depth First Search
BFS Breadth First Search
CDFS Coverage Depth-First Search Strategy (Default)
CBFS Coverage Breadth First Search
graph_output:
gs .GS format
json .JSON format
EMPTY if left empty then build on all available format
packing_type:
symbion Concolic unpacking method (linux | windows [in progress])
unipacker Emulation unpacking method (windows only)
SCDG exploration techniques parameters:
jump_it Number of iteration allowed for a symbolic loop (default : 3)
max_in_pause_stach Number of states allowed in pause stash (default : 200)
max_step Maximum number of steps allowed for a state (default : 50 000)
max_end_state Number of deadended state required to stop (default : 600)
max_simul_state Number of simultaneous states we explore with simulation manager (default : 5)
Binary parameters:
n_args Number of symbolic arguments given to the binary (default : 0)
loop_counter_concrete How many times a loop can loop (default : 10240)
count_block_enable Enable the count of visited blocks and instructions
sim_file Create SimFile
entry_addr Entry address of the binary
SCDG creation parameter:
min_size Minimum size required for a trace to be used in SCDG (default : 3)
disjoint_union Do we merge traces or use disjoint union ? (default : merge)
not_comp_args Do we compare arguments to add new nodes when building graph ? (default : comparison enabled)
three_edges Do we use the three-edges strategy ? (default : False)
not_ignore_zero Do we ignore zero when building graph ? (default : Discard zero)
keep_inter_SCDG Keep intermediate SCDG in file (default : False)
eval_time TODO
Global parameter:
concrete_target_is_local Use a local GDB server instead of using cuckoo (default : False)
print_syscall Print the syscall found
csv_file Name of the csv to save the experiment data
plugin_enable Enable the plugins set to true in the config.ini file
approximate Symbolic approximation
is_packed Is the binary packed ? (default : False, not yet supported)
timeout Timeout in seconds before ending extraction (default : 600)
string_resolve Do we try to resolv references of string (default : True)
log_level_sema Level of log of sema, can be INFO, DEBUG, WARNING, ERROR (default : INFO)
log_level_angr Level of log of angr, can be INFO, DEBUG, WARNING, ERROR (default : ERROR)
log_level_claripy Level of log of claripy, can be INFO, DEBUG, WARNING, ERROR (default : ERROR)
family Family of the malware (default : Unknown)
exp_dir Name of the directory to save SCDG extracted (default : Default)
binary_path Relative path to the binary or directory (has to be in the database folder)
fast_main Jump directly into the main function
Plugins:
plugin_env_var Enable the env_var plugin
plugin_locale_info Enable the locale_info plugin
plugin_resources Enable the resources plugin
plugin_widechar Enable the widechar plugin
plugin_registry Enable the registry plugin
plugin_atom Enable the atom plugin
plugin_thread Enable the thread plugin
plugin_track_command Enable the track_command plugin
plugin_ioc_report Enable the ioc_report plugin
plugin_hooks Enable the hooks plugin
```
**The binary path has to be a relative path to a binary beeing into the `database` directory**
To know the details of the angr options see [Angr documentation](https://docs.angr.io/en/latest/appendix/options.html)
You also have a script `MergeGspan.py` in `sema_scdg/application/helper` which could merge all `.gs` from a directory into only one file.
#### Run multiple experiments automatically
If you wish to run multiple experiments with different configuration files, the script `multiple_experiments.sh` is available and can be used inside the scdg container:
```bash
# To show usage
./multiple_experiments.sh -h
# Run example
./multiple_experiments.sh -m python3 -c configs/config1 configs/config2
```
#### Tests
To run the test, inside the docker container :
```bash
python3 scdg_tests.py test_data/config_test.ini
```
#### Tutorial
There is a jupyter notebook providing a tutorial on how to use the scdg. To launch it, inside the docker, run
```bash
jupyter notebook --ip=0.0.0.0 --port=5001 --no-browser --allow-root --IdentityProvider.token=''
```
and visit `http://127.0.0.1:5001/tree` on your browser. Go to `/Tutorial` and open the jupyter notebook.
### Use only SemaClassifier
Launch the container:
```bash
docker run --rm --name="sema-scdg" -v ${PWD}/InputFolder:/sema-classifier/application/database -it sema-classifier ../docker_startup.sh 1
```
Where the volume correspond to the folder containings the inputs that will be accessible by the container.
Then just run the script :
```
python3 SemaClassifier.py FOLDER/FILE
usage: update_readme_usage.py [-h] [--threshold THRESHOLD] [--biggest_subgraph BIGGEST_SUBGRAPH] [--support SUPPORT] [--ctimeout CTIMEOUT] [--epoch EPOCH] [--sepoch SEPOCH]
[--data_scale DATA_SCALE] [--vector_size VECTOR_SIZE] [--batch_size BATCH_SIZE] (--classification | --detection) (--wl | --inria | --dl | --gspan)
[--bancteian] [--delf] [--FeakerStealer] [--gandcrab] [--ircbot] [--lamer] [--nitol] [--RedLineStealer] [--sfone] [--sillyp2p] [--simbot]
[--Sodinokibi] [--sytro] [--upatre] [--wabot] [--RemcosRAT] [--verbose_classifier] [--train] [--nthread NTHREAD]
binaries
Classification module arguments
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
--classification By malware family
--detection Cleanware vs Malware
--wl TODO
--inria TODO
--dl TODO
--gspan TODOe
Global classifiers parameters:
--threshold THRESHOLD
Threshold used for the classifier [0..1] (default : 0.45)
Gspan options:
--biggest_subgraph BIGGEST_SUBGRAPH
Biggest subgraph consider for Gspan (default: 5)
--support SUPPORT Support used for the gpsan classifier [0..1] (default : 0.75)
--ctimeout CTIMEOUT Timeout for gspan classifier (default : 3sec)
Deep Learning options:
--epoch EPOCH Only for deep learning model: number of epoch (default: 5) Always 1 for FL model
--sepoch SEPOCH Only for deep learning model: starting epoch (default: 1)
--data_scale DATA_SCALE
Only for deep learning model: data scale value (default: 0.9)
--vector_size VECTOR_SIZE
Only for deep learning model: Size of the vector used (default: 4)
--batch_size BATCH_SIZE
Only for deep learning model: Batch size for the model (default: 1)
Malware familly:
--bancteian
--delf
--FeakerStealer
--gandcrab
--ircbot
--lamer
--nitol
--RedLineStealer
--sfone
--sillyp2p
--simbot
--Sodinokibi
--sytro
--upatre
--wabot
--RemcosRAT
Global parameter:
--verbose_classifier Verbose output during train/classification (default : False)
--train Launch training process, else classify/detect new sample with previously computed model
--nthread NTHREAD Number of thread used (default: max)
binaries Name of the folder containing binary'signatures to analyze (Default: output/save-SCDG/, only that for ToolChain)
```
#### Example
This will train models for input dataset
```bash
python3 SemaClassifier.py --train output/save-SCDG/
```
This will classify input dataset based on previously computed models
```bash
python3 SemaClassifier.py output/test-set/
```
#### Tests
To run the classifier tests, run inside the docker container:
```bash
python3 classifier_tests.py configs/config_test.ini
```
:page_with_curl: **Dockerhub installation**
====
## SemaSCDG
If you only need the SCDG part of the toolchain you can use :
```bash
make pull-scdg
```
To pull the docker image directly from dockerHub. Or visit `https://hub.docker.com/repository/docker/manonoreins/sema-scdg/tags`
Then use the same commands than in the recommended usage section
## SemaClassifier
If you only need the Classifier part of the toolchain you can use :
```bash
make pull-classifier
```
To pull the docker image directly from dockerHub. Or visit `https://hub.docker.com/repository/docker/manonoreins/sema-classifier/tags`
Then use the same commands than in the recommended usage section
:page_with_curl: **Pypi installation and usage**
====
It is also possible to use the toolchain without docker container by using the Pypi package to install dependencies.
```bash
pip install sema_toolchain
```
After cloning the git you can then use the toolchain without docker
Example :
```bash
python3 sema_scdg/application/SemaSCDG.py sema_scdg/application/configs/config.ini
```
#### Pypy3 usage
By default, pypy3 can be used to launch experiments inside the SCDG's docker container. If you wish to use it outside the container, make sure to install pypy3 :
```bash
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:pypy/ppa
sudo apt update
sudo apt install pypy3
```
Then install the dependecies on pypy3 :
```bash
pypy3 -m pip install -r /sema_scdg/requirements_pypy.txt
```
Then use pypy3 instead of python3 to launch experiments:
```bash
pypy3 sema_scdg/application/SemaSCDG.py sema_scdg/application/configs/config.ini
```
:page_with_curl: Credentials
====
Main authors of the projects:
* **Charles-Henry Bertrand Van Ouytsel** (UCLouvain)
* **Christophe Crochet** (UCLouvain)
* **Khanh Huu The Dam** (UCLouvain)
* **Oreins Manon** (UCLouvain)
Under the supervision and with the support of **Fabrizio Biondi** (Avast)
Under the supervision and with the support of our professor **Axel Legay** (UCLouvain) (:heart:)