---
comments: true
difficulty: 中等
edit_url: https://github.com/doocs/leetcode/edit/main/solution/0300-0399/0308.Range%20Sum%20Query%202D%20-%20Mutable/README.md
tags:
- 设计
- 树状数组
- 线段树
- 数组
- 矩阵
---
# [308. 二维区域和检索 - 矩阵可修改 🔒](https://leetcode.cn/problems/range-sum-query-2d-mutable)
[English Version](/solution/0300-0399/0308.Range%20Sum%20Query%202D%20-%20Mutable/README_EN.md)
## 题目描述
给你一个二维矩阵 matrix ,处理以下类型的多个查询:
- 更新
matrix 中单元格的值。
- 计算由 左上角
(row1, col1) 和 右下角 (row2, col2) 定义的 matrix 内矩阵元素的 和。
实现 NumMatrix 类:
NumMatrix(int[][] matrix) 用整数矩阵 matrix 初始化对象。void update(int row, int col, int val) 更新 matrix[row][col] 的值到 val 。int sumRegion(int row1, int col1, int row2, int col2) 返回矩阵 matrix 中指定矩形区域元素的 和 ,该区域由 左上角 (row1, col1) 和 右下角 (row2, col2) 界定。
示例 1:
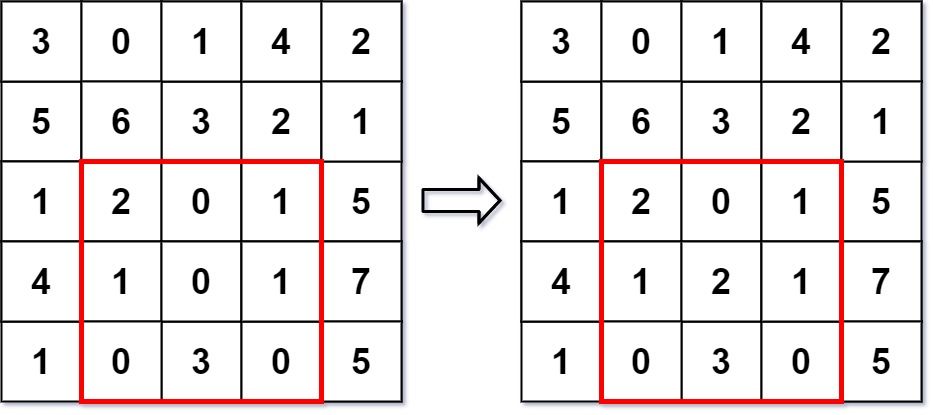
输入
["NumMatrix", "sumRegion", "update", "sumRegion"]
[[[[3, 0, 1, 4, 2], [5, 6, 3, 2, 1], [1, 2, 0, 1, 5], [4, 1, 0, 1, 7], [1, 0, 3, 0, 5]]], [2, 1, 4, 3], [3, 2, 2], [2, 1, 4, 3]]
输出
[null, 8, null, 10]
解释
NumMatrix numMatrix = new NumMatrix([[3, 0, 1, 4, 2], [5, 6, 3, 2, 1], [1, 2, 0, 1, 5], [4, 1, 0, 1, 7], [1, 0, 3, 0, 5]]);
numMatrix.sumRegion(2, 1, 4, 3); // 返回 8 (即, 左侧红色矩形的和)
numMatrix.update(3, 2, 2); // 矩阵从左图变为右图
numMatrix.sumRegion(2, 1, 4, 3); // 返回 10 (即,右侧红色矩形的和)
提示:
m == matrix.lengthn == matrix[i].length1 <= m, n <= 200-1000 <= matrix[i][j] <= 10000 <= row < m0 <= col < n-1000 <= val <= 10000 <= row1 <= row2 < m0 <= col1 <= col2 < n- 最多调用
5000 次 sumRegion 和 update 方法
## 解法
### 方法一:树状数组
树状数组,也称作“二叉索引树”(Binary Indexed Tree)或 Fenwick 树。 它可以高效地实现如下两个操作:
1. **单点更新** `update(x, delta)`: 把序列 x 位置的数加上一个值 delta;
1. **前缀和查询** `query(x)`:查询序列 `[1,...x]` 区间的区间和,即位置 x 的前缀和。
这两个操作的时间复杂度均为 $O(\log n)$。
对于本题,可以构建二维树状数组。
#### Python3
```python
class BinaryIndexedTree:
def __init__(self, n):
self.n = n
self.c = [0] * (n + 1)
@staticmethod
def lowbit(x):
return x & -x
def update(self, x, delta):
while x <= self.n:
self.c[x] += delta
x += BinaryIndexedTree.lowbit(x)
def query(self, x):
s = 0
while x > 0:
s += self.c[x]
x -= BinaryIndexedTree.lowbit(x)
return s
class NumMatrix:
def __init__(self, matrix: List[List[int]]):
self.trees = []
n = len(matrix[0])
for row in matrix:
tree = BinaryIndexedTree(n)
for j, v in enumerate(row):
tree.update(j + 1, v)
self.trees.append(tree)
def update(self, row: int, col: int, val: int) -> None:
tree = self.trees[row]
prev = tree.query(col + 1) - tree.query(col)
tree.update(col + 1, val - prev)
def sumRegion(self, row1: int, col1: int, row2: int, col2: int) -> int:
return sum(
tree.query(col2 + 1) - tree.query(col1)
for tree in self.trees[row1 : row2 + 1]
)
# Your NumMatrix object will be instantiated and called as such:
# obj = NumMatrix(matrix)
# obj.update(row,col,val)
# param_2 = obj.sumRegion(row1,col1,row2,col2)
```
#### Java
```java
class BinaryIndexedTree {
private int n;
private int[] c;
public BinaryIndexedTree(int n) {
this.n = n;
c = new int[n + 1];
}
public void update(int x, int delta) {
while (x <= n) {
c[x] += delta;
x += lowbit(x);
}
}
public int query(int x) {
int s = 0;
while (x > 0) {
s += c[x];
x -= lowbit(x);
}
return s;
}
public static int lowbit(int x) {
return x & -x;
}
}
class NumMatrix {
private BinaryIndexedTree[] trees;
public NumMatrix(int[][] matrix) {
int m = matrix.length;
int n = matrix[0].length;
trees = new BinaryIndexedTree[m];
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
BinaryIndexedTree tree = new BinaryIndexedTree(n);
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
tree.update(j + 1, matrix[i][j]);
}
trees[i] = tree;
}
}
public void update(int row, int col, int val) {
BinaryIndexedTree tree = trees[row];
int prev = tree.query(col + 1) - tree.query(col);
tree.update(col + 1, val - prev);
}
public int sumRegion(int row1, int col1, int row2, int col2) {
int s = 0;
for (int i = row1; i <= row2; ++i) {
BinaryIndexedTree tree = trees[i];
s += tree.query(col2 + 1) - tree.query(col1);
}
return s;
}
}
/**
* Your NumMatrix object will be instantiated and called as such:
* NumMatrix obj = new NumMatrix(matrix);
* obj.update(row,col,val);
* int param_2 = obj.sumRegion(row1,col1,row2,col2);
*/
```
#### C++
```cpp
class BinaryIndexedTree {
public:
int n;
vector c;
BinaryIndexedTree(int _n)
: n(_n)
, c(_n + 1) {}
void update(int x, int delta) {
while (x <= n) {
c[x] += delta;
x += lowbit(x);
}
}
int query(int x) {
int s = 0;
while (x > 0) {
s += c[x];
x -= lowbit(x);
}
return s;
}
int lowbit(int x) {
return x & -x;
}
};
class NumMatrix {
public:
vector trees;
NumMatrix(vector>& matrix) {
int m = matrix.size();
int n = matrix[0].size();
trees.resize(m);
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
BinaryIndexedTree* tree = new BinaryIndexedTree(n);
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) tree->update(j + 1, matrix[i][j]);
trees[i] = tree;
}
}
void update(int row, int col, int val) {
BinaryIndexedTree* tree = trees[row];
int prev = tree->query(col + 1) - tree->query(col);
tree->update(col + 1, val - prev);
}
int sumRegion(int row1, int col1, int row2, int col2) {
int s = 0;
for (int i = row1; i <= row2; ++i) {
BinaryIndexedTree* tree = trees[i];
s += tree->query(col2 + 1) - tree->query(col1);
}
return s;
}
};
/**
* Your NumMatrix object will be instantiated and called as such:
* NumMatrix* obj = new NumMatrix(matrix);
* obj->update(row,col,val);
* int param_2 = obj->sumRegion(row1,col1,row2,col2);
*/
```
#### Go
```go
type BinaryIndexedTree struct {
n int
c []int
}
func newBinaryIndexedTree(n int) *BinaryIndexedTree {
c := make([]int, n+1)
return &BinaryIndexedTree{n, c}
}
func (this *BinaryIndexedTree) lowbit(x int) int {
return x & -x
}
func (this *BinaryIndexedTree) update(x, delta int) {
for x <= this.n {
this.c[x] += delta
x += this.lowbit(x)
}
}
func (this *BinaryIndexedTree) query(x int) int {
s := 0
for x > 0 {
s += this.c[x]
x -= this.lowbit(x)
}
return s
}
type NumMatrix struct {
trees []*BinaryIndexedTree
}
func Constructor(matrix [][]int) NumMatrix {
n := len(matrix[0])
var trees []*BinaryIndexedTree
for _, row := range matrix {
tree := newBinaryIndexedTree(n)
for j, v := range row {
tree.update(j+1, v)
}
trees = append(trees, tree)
}
return NumMatrix{trees}
}
func (this *NumMatrix) Update(row int, col int, val int) {
tree := this.trees[row]
prev := tree.query(col+1) - tree.query(col)
tree.update(col+1, val-prev)
}
func (this *NumMatrix) SumRegion(row1 int, col1 int, row2 int, col2 int) int {
s := 0
for i := row1; i <= row2; i++ {
tree := this.trees[i]
s += tree.query(col2+1) - tree.query(col1)
}
return s
}
/**
* Your NumMatrix object will be instantiated and called as such:
* obj := Constructor(matrix);
* obj.Update(row,col,val);
* param_2 := obj.SumRegion(row1,col1,row2,col2);
*/
```
### 方法二:线段树
线段树将整个区间分割为多个不连续的子区间,子区间的数量不超过 `log(width)`。更新某个元素的值,只需要更新 `log(width)` 个区间,并且这些区间都包含在一个包含该元素的大区间内。
- 线段树的每个节点代表一个区间;
- 线段树具有唯一的根节点,代表的区间是整个统计范围,如 `[1, N]`;
- 线段树的每个叶子节点代表一个长度为 1 的元区间 `[x, x]`;
- 对于每个内部节点 `[l, r]`,它的左儿子是 `[l, mid]`,右儿子是 `[mid + 1, r]`, 其中 `mid = ⌊(l + r) / 2⌋` (即向下取整)。
#### Python3
```python
class Node:
def __init__(self):
self.l = 0
self.r = 0
self.v = 0
class SegmentTree:
def __init__(self, nums):
n = len(nums)
self.nums = nums
self.tr = [Node() for _ in range(4 * n)]
self.build(1, 1, n)
def build(self, u, l, r):
self.tr[u].l = l
self.tr[u].r = r
if l == r:
self.tr[u].v = self.nums[l - 1]
return
mid = (l + r) >> 1
self.build(u << 1, l, mid)
self.build(u << 1 | 1, mid + 1, r)
self.pushup(u)
def modify(self, u, x, v):
if self.tr[u].l == x and self.tr[u].r == x:
self.tr[u].v = v
return
mid = (self.tr[u].l + self.tr[u].r) >> 1
if x <= mid:
self.modify(u << 1, x, v)
else:
self.modify(u << 1 | 1, x, v)
self.pushup(u)
def query(self, u, l, r):
if self.tr[u].l >= l and self.tr[u].r <= r:
return self.tr[u].v
mid = (self.tr[u].l + self.tr[u].r) >> 1
v = 0
if l <= mid:
v += self.query(u << 1, l, r)
if r > mid:
v += self.query(u << 1 | 1, l, r)
return v
def pushup(self, u):
self.tr[u].v = self.tr[u << 1].v + self.tr[u << 1 | 1].v
class NumMatrix:
def __init__(self, matrix: List[List[int]]):
self.trees = [SegmentTree(row) for row in matrix]
def update(self, row: int, col: int, val: int) -> None:
tree = self.trees[row]
tree.modify(1, col + 1, val)
def sumRegion(self, row1: int, col1: int, row2: int, col2: int) -> int:
return sum(
self.trees[row].query(1, col1 + 1, col2 + 1)
for row in range(row1, row2 + 1)
)
# Your NumMatrix object will be instantiated and called as such:
# obj = NumMatrix(matrix)
# obj.update(row,col,val)
# param_2 = obj.sumRegion(row1,col1,row2,col2)
```
#### Java
```java
class Node {
int l;
int r;
int v;
}
class SegmentTree {
private Node[] tr;
private int[] nums;
public SegmentTree(int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length;
tr = new Node[n << 2];
this.nums = nums;
for (int i = 0; i < tr.length; ++i) {
tr[i] = new Node();
}
build(1, 1, n);
}
public void build(int u, int l, int r) {
tr[u].l = l;
tr[u].r = r;
if (l == r) {
tr[u].v = nums[l - 1];
return;
}
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
build(u << 1, l, mid);
build(u << 1 | 1, mid + 1, r);
pushup(u);
}
public void modify(int u, int x, int v) {
if (tr[u].l == x && tr[u].r == x) {
tr[u].v = v;
return;
}
int mid = (tr[u].l + tr[u].r) >> 1;
if (x <= mid) {
modify(u << 1, x, v);
} else {
modify(u << 1 | 1, x, v);
}
pushup(u);
}
public void pushup(int u) {
tr[u].v = tr[u << 1].v + tr[u << 1 | 1].v;
}
public int query(int u, int l, int r) {
if (tr[u].l >= l && tr[u].r <= r) {
return tr[u].v;
}
int mid = (tr[u].l + tr[u].r) >> 1;
int v = 0;
if (l <= mid) {
v += query(u << 1, l, r);
}
if (r > mid) {
v += query(u << 1 | 1, l, r);
}
return v;
}
}
class NumMatrix {
private SegmentTree[] trees;
public NumMatrix(int[][] matrix) {
int m = matrix.length;
trees = new SegmentTree[m];
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
trees[i] = new SegmentTree(matrix[i]);
}
}
public void update(int row, int col, int val) {
SegmentTree tree = trees[row];
tree.modify(1, col + 1, val);
}
public int sumRegion(int row1, int col1, int row2, int col2) {
int s = 0;
for (int row = row1; row <= row2; ++row) {
SegmentTree tree = trees[row];
s += tree.query(1, col1 + 1, col2 + 1);
}
return s;
}
}
/**
* Your NumMatrix object will be instantiated and called as such:
* NumMatrix obj = new NumMatrix(matrix);
* obj.update(row,col,val);
* int param_2 = obj.sumRegion(row1,col1,row2,col2);
*/
```
#### C++
```cpp
class Node {
public:
int l;
int r;
int v;
};
class SegmentTree {
public:
vector tr;
vector nums;
SegmentTree(vector& nums) {
int n = nums.size();
tr.resize(n << 2);
this->nums = nums;
for (int i = 0; i < tr.size(); ++i) tr[i] = new Node();
build(1, 1, n);
}
void build(int u, int l, int r) {
tr[u]->l = l;
tr[u]->r = r;
if (l == r) {
tr[u]->v = nums[l - 1];
return;
}
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
build(u << 1, l, mid);
build(u << 1 | 1, mid + 1, r);
pushup(u);
}
void modify(int u, int x, int v) {
if (tr[u]->l == x && tr[u]->r == x) {
tr[u]->v = v;
return;
}
int mid = (tr[u]->l + tr[u]->r) >> 1;
if (x <= mid)
modify(u << 1, x, v);
else
modify(u << 1 | 1, x, v);
pushup(u);
}
int query(int u, int l, int r) {
if (tr[u]->l >= l && tr[u]->r <= r) return tr[u]->v;
int mid = (tr[u]->l + tr[u]->r) >> 1;
int v = 0;
if (l <= mid) v += query(u << 1, l, r);
if (r > mid) v += query(u << 1 | 1, l, r);
return v;
}
void pushup(int u) {
tr[u]->v = tr[u << 1]->v + tr[u << 1 | 1]->v;
}
};
class NumMatrix {
public:
vector trees;
NumMatrix(vector>& matrix) {
int m = matrix.size();
trees.resize(m);
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) trees[i] = new SegmentTree(matrix[i]);
}
void update(int row, int col, int val) {
SegmentTree* tree = trees[row];
tree->modify(1, col + 1, val);
}
int sumRegion(int row1, int col1, int row2, int col2) {
int s = 0;
for (int row = row1; row <= row2; ++row) s += trees[row]->query(1, col1 + 1, col2 + 1);
return s;
}
};
/**
* Your NumMatrix object will be instantiated and called as such:
* NumMatrix* obj = new NumMatrix(matrix);
* obj->update(row,col,val);
* int param_2 = obj->sumRegion(row1,col1,row2,col2);
*/
```
