给你一个大小为 m x n 的迷宫 maze ,以及球的初始位置 start 和目的地 destination ,其中 start = [startrow, startcol] 且 destination = [destinationrow, destinationcol] 。请你判断球能否在目的地停下:如果可以,返回 true ;否则,返回 false 。
你可以 假定迷宫的边缘都是墙壁(参考示例)。
示例 1:
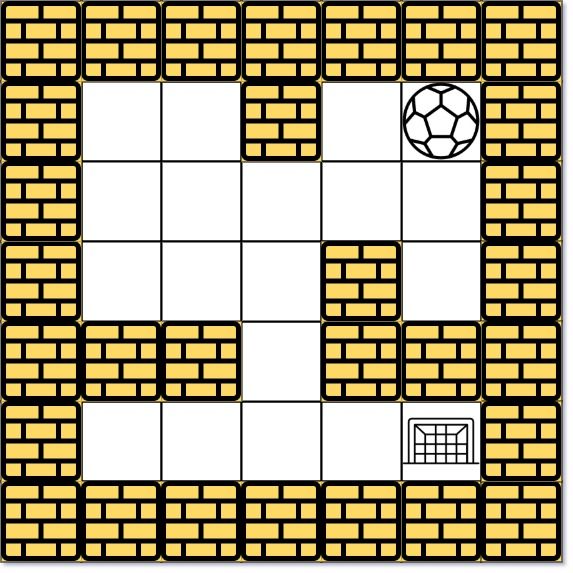
输入:maze = [[0,0,1,0,0],[0,0,0,0,0],[0,0,0,1,0],[1,1,0,1,1],[0,0,0,0,0]], start = [0,4], destination = [4,4] 输出:true 解释:一种可能的路径是 : 左 -> 下 -> 左 -> 下 -> 右 -> 下 -> 右。
示例 2:
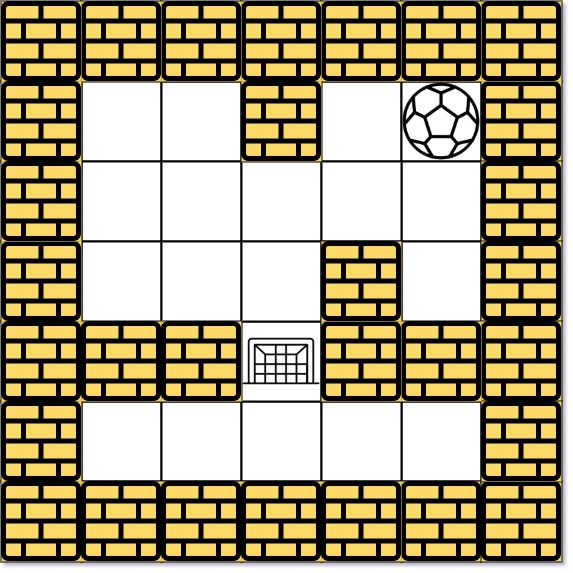
输入:maze = [[0,0,1,0,0],[0,0,0,0,0],[0,0,0,1,0],[1,1,0,1,1],[0,0,0,0,0]], start = [0,4], destination = [3,2] 输出:false 解释:不存在能够使球停在目的地的路径。注意,球可以经过目的地,但无法在那里停驻。
示例 3:
输入:maze = [[0,0,0,0,0],[1,1,0,0,1],[0,0,0,0,0],[0,1,0,0,1],[0,1,0,0,0]], start = [4,3], destination = [0,1] 输出:false
提示:
m == maze.lengthn == maze[i].length1 <= m, n <= 100maze[i][j]is0or1.start.length == 2destination.length == 20 <= startrow, destinationrow < m0 <= startcol, destinationcol < n- 球和目的地都在空地上,且初始时它们不在同一位置
- 迷宫 至少包括 2 块空地