---
comments: true
difficulty: 中等
edit_url: https://github.com/doocs/leetcode/edit/main/solution/1000-1099/1091.Shortest%20Path%20in%20Binary%20Matrix/README.md
rating: 1658
source: 第 141 场周赛 Q3
tags:
- 广度优先搜索
- 数组
- 矩阵
---
# [1091. 二进制矩阵中的最短路径](https://leetcode.cn/problems/shortest-path-in-binary-matrix)
[English Version](/solution/1000-1099/1091.Shortest%20Path%20in%20Binary%20Matrix/README_EN.md)
## 题目描述
给你一个 n x n 的二进制矩阵 grid 中,返回矩阵中最短 畅通路径 的长度。如果不存在这样的路径,返回 -1 。
二进制矩阵中的 畅通路径 是一条从 左上角 单元格(即,(0, 0))到 右下角 单元格(即,(n - 1, n - 1))的路径,该路径同时满足下述要求:
- 路径途经的所有单元格的值都是
0 。
- 路径中所有相邻的单元格应当在 8 个方向之一 上连通(即,相邻两单元之间彼此不同且共享一条边或者一个角)。
畅通路径的长度 是该路径途经的单元格总数。
示例 1:
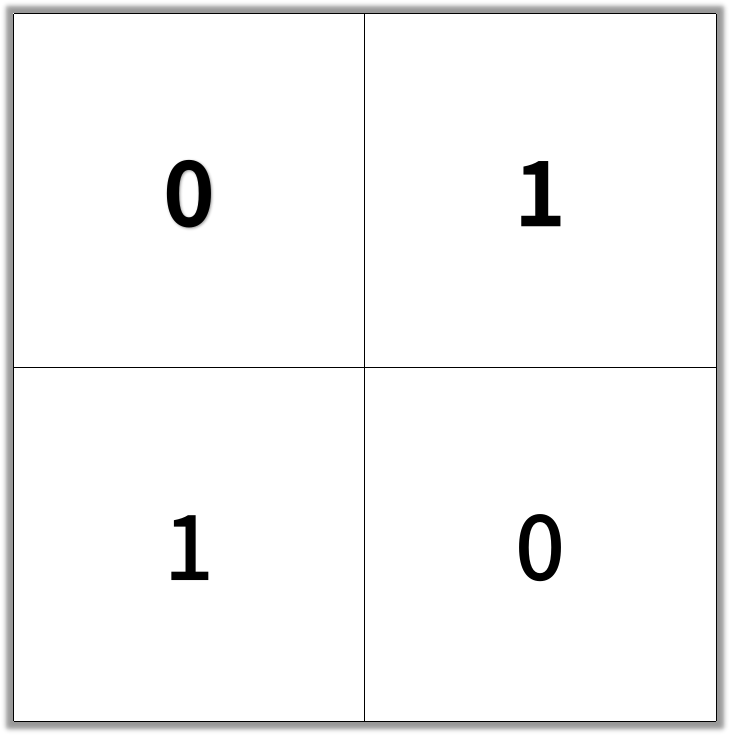
输入:grid = [[0,1],[1,0]]
输出:2
示例 2:
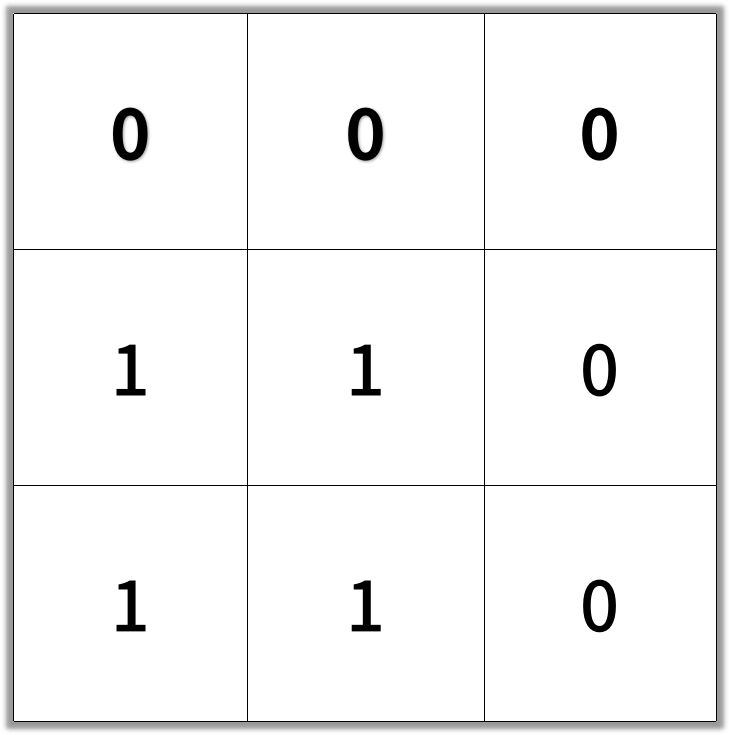
输入:grid = [[0,0,0],[1,1,0],[1,1,0]]
输出:4
示例 3:
输入:grid = [[1,0,0],[1,1,0],[1,1,0]]
输出:-1
提示:
n == grid.lengthn == grid[i].length1 <= n <= 100grid[i][j] 为 0 或 1
## 解法
### 方法一:BFS
根据题目描述,一条畅通路径是从左上角单元格 $(0, 0)$ 到右下角单元格 $(n - 1, n - 1)$ 的路径,且路径上所有单元格的值都是 $0$。
因此,如果左上角单元格 $(0, 0)$ 的值为 $1$,则不存在满足要求的路径,直接返回 $-1$。
否则,我们创建一个队列 $q$,将左上角单元格 $(0, 0)$ 加入队列,并且将其标记为已访问,即把 $grid[0][0]$ 的值置为 $1$,然后开始广度优先搜索。
在每一轮搜索中,我们每次取出队首节点 $(i, j)$,如果 $(i, j)$ 为右下角单元格 $(n - 1, n - 1)$,则路径长度为当前的搜索轮数,直接返回。否则,我们将当前节点的所有未被访问过的相邻节点加入队列,并且将它们标记为已访问。每一轮搜索结束后,我们将搜索轮数增加 $1$。然后继续执行上述过程,直到队列为空或者找到目标节点。
如果在搜索结束后,我们仍然没有到达右下角的节点,那么说明右下角的节点不可达,返回 $-1$。
时间复杂度 $O(n^2)$,空间复杂度 $O(n^2)$。其中 $n$ 是给定的二进制矩阵的边长。
#### Python3
```python
class Solution:
def shortestPathBinaryMatrix(self, grid: List[List[int]]) -> int:
if grid[0][0]:
return -1
n = len(grid)
grid[0][0] = 1
q = deque([(0, 0)])
ans = 1
while q:
for _ in range(len(q)):
i, j = q.popleft()
if i == j == n - 1:
return ans
for x in range(i - 1, i + 2):
for y in range(j - 1, j + 2):
if 0 <= x < n and 0 <= y < n and grid[x][y] == 0:
grid[x][y] = 1
q.append((x, y))
ans += 1
return -1
```
#### Java
```java
class Solution {
public int shortestPathBinaryMatrix(int[][] grid) {
if (grid[0][0] == 1) {
return -1;
}
int n = grid.length;
grid[0][0] = 1;
Deque q = new ArrayDeque<>();
q.offer(new int[] {0, 0});
for (int ans = 1; !q.isEmpty(); ++ans) {
for (int k = q.size(); k > 0; --k) {
var p = q.poll();
int i = p[0], j = p[1];
if (i == n - 1 && j == n - 1) {
return ans;
}
for (int x = i - 1; x <= i + 1; ++x) {
for (int y = j - 1; y <= j + 1; ++y) {
if (x >= 0 && x < n && y >= 0 && y < n && grid[x][y] == 0) {
grid[x][y] = 1;
q.offer(new int[] {x, y});
}
}
}
}
}
return -1;
}
}
```
#### C++
```cpp
class Solution {
public:
int shortestPathBinaryMatrix(vector>& grid) {
if (grid[0][0]) {
return -1;
}
int n = grid.size();
grid[0][0] = 1;
queue> q;
q.emplace(0, 0);
for (int ans = 1; !q.empty(); ++ans) {
for (int k = q.size(); k; --k) {
auto [i, j] = q.front();
q.pop();
if (i == n - 1 && j == n - 1) {
return ans;
}
for (int x = i - 1; x <= i + 1; ++x) {
for (int y = j - 1; y <= j + 1; ++y) {
if (x >= 0 && x < n && y >= 0 && y < n && !grid[x][y]) {
grid[x][y] = 1;
q.emplace(x, y);
}
}
}
}
}
return -1;
}
};
```
#### Go
```go
func shortestPathBinaryMatrix(grid [][]int) int {
if grid[0][0] == 1 {
return -1
}
n := len(grid)
grid[0][0] = 1
q := [][2]int{{0, 0}}
for ans := 1; len(q) > 0; ans++ {
for k := len(q); k > 0; k-- {
p := q[0]
i, j := p[0], p[1]
q = q[1:]
if i == n-1 && j == n-1 {
return ans
}
for x := i - 1; x <= i+1; x++ {
for y := j - 1; y <= j+1; y++ {
if x >= 0 && x < n && y >= 0 && y < n && grid[x][y] == 0 {
grid[x][y] = 1
q = append(q, [2]int{x, y})
}
}
}
}
}
return -1
}
```
#### TypeScript
```ts
function shortestPathBinaryMatrix(grid: number[][]): number {
if (grid[0][0]) {
return -1;
}
const max = grid.length - 1;
grid[0][0] = 1;
let q: number[][] = [[0, 0]];
for (let ans = 1; q.length > 0; ++ans) {
const nq: number[][] = [];
for (const [i, j] of q) {
if (i === max && j === max) {
return ans;
}
for (let x = i - 1; x <= i + 1; ++x) {
for (let y = j - 1; y <= j + 1; ++y) {
if (grid[x]?.[y] === 0) {
grid[x][y] = 1;
nq.push([x, y]);
}
}
}
}
q = nq;
}
return -1;
}
```
#### Rust
```rust
use std::collections::VecDeque;
impl Solution {
pub fn shortest_path_binary_matrix(mut grid: Vec>) -> i32 {
let n = grid.len();
let mut queue = VecDeque::new();
queue.push_back([0, 0]);
let mut res = 0;
while !queue.is_empty() {
res += 1;
for _ in 0..queue.len() {
let [i, j] = queue.pop_front().unwrap();
if grid[i][j] == 1 {
continue;
}
if i == n - 1 && j == n - 1 {
return res;
}
grid[i][j] = 1;
for x in -1..=1 {
for y in -1..=1 {
let x = x + (i as i32);
let y = y + (j as i32);
if x < 0 || x == (n as i32) || y < 0 || y == (n as i32) {
continue;
}
queue.push_back([x as usize, y as usize]);
}
}
}
}
-1
}
}
```

