---
comments: true
difficulty: 困难
edit_url: https://github.com/doocs/leetcode/edit/main/solution/1100-1199/1168.Optimize%20Water%20Distribution%20in%20a%20Village/README.md
rating: 2069
source: 第 7 场双周赛 Q4
tags:
- 并查集
- 图
- 最小生成树
- 堆(优先队列)
---
# [1168. 水资源分配优化 🔒](https://leetcode.cn/problems/optimize-water-distribution-in-a-village)
[English Version](/solution/1100-1199/1168.Optimize%20Water%20Distribution%20in%20a%20Village/README_EN.md)
## 题目描述
村里面一共有 n 栋房子。我们希望通过建造水井和铺设管道来为所有房子供水。
对于每个房子 i,我们有两种可选的供水方案:一种是直接在房子内建造水井,成本为 wells[i - 1] (注意 -1 ,因为 索引从0开始 );另一种是从另一口井铺设管道引水,数组 pipes 给出了在房子间铺设管道的成本,其中每个 pipes[j] = [house1j, house2j, costj] 代表用管道将 house1j 和 house2j连接在一起的成本。连接是双向的。
请返回 为所有房子都供水的最低总成本 。
示例 1:
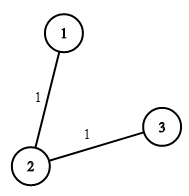
输入:n = 3, wells = [1,2,2], pipes = [[1,2,1],[2,3,1]]
输出:3
解释:
上图展示了铺设管道连接房屋的成本。
最好的策略是在第一个房子里建造水井(成本为 1),然后将其他房子铺设管道连起来(成本为 2),所以总成本为 3。
示例 2:
输入:n = 2, wells = [1,1], pipes = [[1,2,1]]
输出:2
解释:我们可以用以下三种方法中的一种来提供低成本的水:
选项1:
在1号房子里面建一口井,成本为1
在房子2内建造井,成本为1
总成本是2。
选项2:
在1号房子里面建一口井,成本为1
-花费1连接房子2和房子1。
总成本是2。
选项3:
在房子2内建造井,成本为1
-花费1连接房子1和房子2。
总成本是2。
注意,我们可以用cost 1或cost 2连接房子1和房子2,但我们总是选择最便宜的选项。
提示:
2 <= n <= 104wells.length == n0 <= wells[i] <= 1051 <= pipes.length <= 104pipes[j].length == 31 <= house1j, house2j <= n0 <= costj <= 105house1j != house2j
## 解法
### 方法一:Kruskal 算法(最小生成树)
我们假设有一个水井编号为 $0$,那么我们可以将每个房子与水井 $0$ 之间的连通性看作是一条边,每条边的权值为该房子建造水井的成本。同时,我们将每个房子之间的连通性也看作是一条边,每条边的权值为铺设管道的成本。这样一来,我们就可以将本题转化成求一张无向图的最小生成树的问题。
我们可以使用 Kruskal 算法求出无向图的最小生成树。我们先把水井 $0$ 与房子之间的一条边加入 $pipes$ 数组中,然后将 $pipes$ 数组按照边权值从小到大排序。随后,我们遍历每一条边,如果这条边连接了不同的连通分量,我们就选用这条边,并将对应连通分量合并。如果当前的连通分量恰好为 $1$,那么我们就找到了最小生成树,此时的答案即为当前边权值,我们将其返回即可。
时间复杂度 $O((m + n) \times \log (m + n))$,空间复杂度 $O(m + n)$。其中 $m$ 和 $n$ 分别是 $pipes$ 数组和 $wells$ 数组的长度。
#### Python3
```python
class Solution:
def minCostToSupplyWater(
self, n: int, wells: List[int], pipes: List[List[int]]
) -> int:
def find(x: int) -> int:
if p[x] != x:
p[x] = find(p[x])
return p[x]
for i, w in enumerate(wells, 1):
pipes.append([0, i, w])
pipes.sort(key=lambda x: x[2])
p = list(range(n + 1))
ans = 0
for a, b, c in pipes:
pa, pb = find(a), find(b)
if pa != pb:
p[pa] = pb
n -= 1
ans += c
if n == 0:
return ans
```
#### Java
```java
class Solution {
private int[] p;
public int minCostToSupplyWater(int n, int[] wells, int[][] pipes) {
int[][] nums = Arrays.copyOf(pipes, pipes.length + n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
nums[pipes.length + i] = new int[] {0, i + 1, wells[i]};
}
Arrays.sort(nums, (a, b) -> a[2] - b[2]);
p = new int[n + 1];
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
p[i] = i;
}
int ans = 0;
for (var x : nums) {
int a = x[0], b = x[1], c = x[2];
int pa = find(a), pb = find(b);
if (pa != pb) {
p[pa] = pb;
ans += c;
if (--n == 0) {
return ans;
}
}
}
return ans;
}
private int find(int x) {
if (p[x] != x) {
p[x] = find(p[x]);
}
return p[x];
}
}
```
#### C++
```cpp
class Solution {
public:
int minCostToSupplyWater(int n, vector& wells, vector>& pipes) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
pipes.push_back({0, i + 1, wells[i]});
}
sort(pipes.begin(), pipes.end(), [](const vector& a, const vector& b) {
return a[2] < b[2];
});
int p[n + 1];
iota(p, p + n + 1, 0);
function find = [&](int x) {
if (p[x] != x) {
p[x] = find(p[x]);
}
return p[x];
};
int ans = 0;
for (const auto& x : pipes) {
int pa = find(x[0]), pb = find(x[1]);
if (pa == pb) {
continue;
}
p[pa] = pb;
ans += x[2];
if (--n == 0) {
break;
}
}
return ans;
}
};
```
#### Go
```go
func minCostToSupplyWater(n int, wells []int, pipes [][]int) (ans int) {
for i, w := range wells {
pipes = append(pipes, []int{0, i + 1, w})
}
sort.Slice(pipes, func(i, j int) bool { return pipes[i][2] < pipes[j][2] })
p := make([]int, n+1)
for i := range p {
p[i] = i
}
var find func(int) int
find = func(x int) int {
if p[x] != x {
p[x] = find(p[x])
}
return p[x]
}
for _, x := range pipes {
pa, pb := find(x[0]), find(x[1])
if pa == pb {
continue
}
p[pa] = pb
ans += x[2]
n--
if n == 0 {
break
}
}
return
}
```
#### TypeScript
```ts
function minCostToSupplyWater(n: number, wells: number[], pipes: number[][]): number {
for (let i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
pipes.push([0, i + 1, wells[i]]);
}
pipes.sort((a, b) => a[2] - b[2]);
const p = Array(n + 1)
.fill(0)
.map((_, i) => i);
const find = (x: number): number => {
if (p[x] !== x) {
p[x] = find(p[x]);
}
return p[x];
};
let ans = 0;
for (const [a, b, c] of pipes) {
const pa = find(a);
const pb = find(b);
if (pa === pb) {
continue;
}
p[pa] = pb;
ans += c;
if (--n === 0) {
break;
}
}
return ans;
}
```
#### Rust
```rust
struct UnionFind {
p: Vec,
size: Vec,
}
impl UnionFind {
fn new(n: usize) -> Self {
let p: Vec = (0..n).collect();
let size = vec![1; n];
UnionFind { p, size }
}
fn find(&mut self, x: usize) -> usize {
if self.p[x] != x {
self.p[x] = self.find(self.p[x]);
}
self.p[x]
}
fn union(&mut self, a: usize, b: usize) -> bool {
let pa = self.find(a);
let pb = self.find(b);
if pa == pb {
false
} else if self.size[pa] > self.size[pb] {
self.p[pb] = pa;
self.size[pa] += self.size[pb];
true
} else {
self.p[pa] = pb;
self.size[pb] += self.size[pa];
true
}
}
}
impl Solution {
pub fn min_cost_to_supply_water(n: i32, wells: Vec, pipes: Vec>) -> i32 {
let n = n as usize;
let mut pipes = pipes;
for i in 0..n {
pipes.push(vec![0, (i + 1) as i32, wells[i]]);
}
pipes.sort_by(|a, b| a[2].cmp(&b[2]));
let mut uf = UnionFind::new(n + 1);
let mut ans = 0;
for pipe in pipes {
let a = pipe[0] as usize;
let b = pipe[1] as usize;
let c = pipe[2];
if uf.union(a, b) {
ans += c;
if n == 0 {
break;
}
}
}
ans
}
}
```
### 方法二
#### Python3
```python
class UnionFind:
__slots__ = ("p", "size")
def __init__(self, n):
self.p = list(range(n))
self.size = [1] * n
def find(self, x: int) -> int:
if self.p[x] != x:
self.p[x] = self.find(self.p[x])
return self.p[x]
def union(self, a: int, b: int) -> bool:
pa, pb = self.find(a), self.find(b)
if pa == pb:
return False
if self.size[pa] > self.size[pb]:
self.p[pb] = pa
self.size[pa] += self.size[pb]
else:
self.p[pa] = pb
self.size[pb] += self.size[pa]
return True
class Solution:
def minCostToSupplyWater(
self, n: int, wells: List[int], pipes: List[List[int]]
) -> int:
for i, w in enumerate(wells, 1):
pipes.append([0, i, w])
pipes.sort(key=lambda x: x[2])
uf = UnionFind(n + 1)
ans = 0
for a, b, c in pipes:
if uf.union(a, b):
ans += c
n -= 1
if n == 0:
return ans
```
#### Java
```java
class UnionFind {
private int[] p;
private int[] size;
public UnionFind(int n) {
p = new int[n];
size = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
p[i] = i;
size[i] = 1;
}
}
public int find(int x) {
if (p[x] != x) {
p[x] = find(p[x]);
}
return p[x];
}
public boolean union(int a, int b) {
int pa = find(a), pb = find(b);
if (pa == pb) {
return false;
}
if (size[pa] > size[pb]) {
p[pb] = pa;
size[pa] += size[pb];
} else {
p[pa] = pb;
size[pb] += size[pa];
}
return true;
}
}
class Solution {
public int minCostToSupplyWater(int n, int[] wells, int[][] pipes) {
int[][] nums = Arrays.copyOf(pipes, pipes.length + n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
nums[pipes.length + i] = new int[] {0, i + 1, wells[i]};
}
Arrays.sort(nums, (a, b) -> a[2] - b[2]);
UnionFind uf = new UnionFind(n + 1);
int ans = 0;
for (var x : nums) {
int a = x[0], b = x[1], c = x[2];
if (uf.union(a, b)) {
ans += c;
if (--n == 0) {
break;
}
}
}
return ans;
}
}
```
#### C++
```cpp
class UnionFind {
public:
UnionFind(int n) {
p = vector(n);
size = vector(n, 1);
iota(p.begin(), p.end(), 0);
}
bool unite(int a, int b) {
int pa = find(a), pb = find(b);
if (pa == pb) {
return false;
}
if (size[pa] > size[pb]) {
p[pb] = pa;
size[pa] += size[pb];
} else {
p[pa] = pb;
size[pb] += size[pa];
}
return true;
}
int find(int x) {
if (p[x] != x) {
p[x] = find(p[x]);
}
return p[x];
}
private:
vector p, size;
};
class Solution {
public:
int minCostToSupplyWater(int n, vector& wells, vector>& pipes) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
pipes.push_back({0, i + 1, wells[i]});
}
sort(pipes.begin(), pipes.end(), [](const vector& a, const vector& b) {
return a[2] < b[2];
});
UnionFind uf(n + 1);
int ans = 0;
for (const auto& x : pipes) {
if (uf.unite(x[0], x[1])) {
ans += x[2];
if (--n == 0) {
break;
}
}
}
return ans;
}
};
```
#### Go
```go
type unionFind struct {
p, size []int
}
func newUnionFind(n int) *unionFind {
p := make([]int, n)
size := make([]int, n)
for i := range p {
p[i] = i
size[i] = 1
}
return &unionFind{p, size}
}
func (uf *unionFind) find(x int) int {
if uf.p[x] != x {
uf.p[x] = uf.find(uf.p[x])
}
return uf.p[x]
}
func (uf *unionFind) union(a, b int) bool {
pa, pb := uf.find(a), uf.find(b)
if pa == pb {
return false
}
if uf.size[pa] > uf.size[pb] {
uf.p[pb] = pa
uf.size[pa] += uf.size[pb]
} else {
uf.p[pa] = pb
uf.size[pb] += uf.size[pa]
}
return true
}
func minCostToSupplyWater(n int, wells []int, pipes [][]int) (ans int) {
for i, w := range wells {
pipes = append(pipes, []int{0, i + 1, w})
}
sort.Slice(pipes, func(i, j int) bool { return pipes[i][2] < pipes[j][2] })
uf := newUnionFind(n + 1)
for _, x := range pipes {
if uf.union(x[0], x[1]) {
ans += x[2]
n--
if n == 0 {
break
}
}
}
return
}
```
#### TypeScript
```ts
class UnionFind {
private p: number[];
private size: number[];
constructor(n: number) {
this.p = Array(n)
.fill(0)
.map((_, i) => i);
this.size = Array(n).fill(1);
}
find(x: number): number {
if (this.p[x] !== x) {
this.p[x] = this.find(this.p[x]);
}
return this.p[x];
}
union(a: number, b: number): boolean {
const pa = this.find(a);
const pb = this.find(b);
if (pa === pb) {
return false;
}
if (this.size[pa] > this.size[pb]) {
this.p[pb] = pa;
this.size[pa] += this.size[pb];
} else {
this.p[pa] = pb;
this.size[pb] += this.size[pa];
}
return true;
}
}
function minCostToSupplyWater(n: number, wells: number[], pipes: number[][]): number {
for (let i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
pipes.push([0, i + 1, wells[i]]);
}
pipes.sort((a, b) => a[2] - b[2]);
const uf = new UnionFind(n + 1);
let ans = 0;
for (const [a, b, c] of pipes) {
if (uf.union(a, b)) {
ans += c;
if (--n === 0) {
break;
}
}
}
return ans;
}
```

