Examples > Analog I/O
Calibration
This example demonstrates one techinque for calibrating sensor input. The LaunchPad board takes sensor readings for five seconds during the startup, and tracks the highest and lowest values it gets. These sensor readings during the first five seconds of the sketch execution define the minimum and maximum of expected values for the readings taken during the loop.
Hardware Required
- LaunchPad board
- (1) LED
- (1) analog sensor (a photocell will do)
- (1) 10K ohm resistor
- (1) 220 ohm resistor
- breadboard
- hook-up wire
Relevant Groundwork
Analog sensor (e.g. potentiometer, light sensor) on analog input 3. LED on digital pin 2.
Circuit
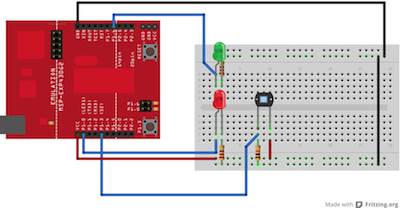
image developed using Fritzing. For more circuit examples, see the Fritzing project page
Connect an LED to digital pin 2 with a 220 ohm current limiting resistor. Connect a photocell to 3V and then to analog pin 3 with a 10K ohm resistor as a reference to ground.
Schematic
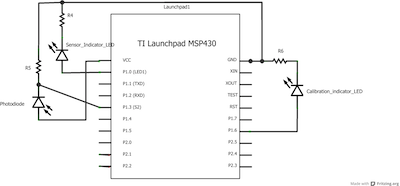
Code Explanation
Before the setup, you set initial values for the minimum and maximum like so:
int sensorMin = 1023; // minimum sensor value int sensorMax = 0; // maximum sensor value
These may seem backwards. Initially, you set the minimum high and read for anything lower than that, saving it as the new minimum. Likewise, you set the maximum low and read for anything higher as the new maximum, like so:
// calibrate during the first five seconds
while (millis() < 5000) {
sensorValue = analogRead(sensorPin);
// record the maximum sensor value
if (sensorValue > sensorMax) {
sensorMax = sensorValue;
}
// record the minimum sensor value
if (sensorValue < sensorMin) {
sensorMin = sensorValue;
}
}
This way, any further readings you take can be mapped to the range between this minimum and maximum like so:
// apply the calibration to the sensor reading sensorValue = map(sensorValue, sensorMin, sensorMax, 0, 255);
Code
Here's the whole program:
/*
Calibration
Demonstrates one technique for calibrating sensor input. The
sensor readings during the first five seconds of the sketch
execution define the minimum and maximum of expected values
attached to the sensor pin.
The sensor minimum and maximum initial values may seem backwards.
Initially, you set the minimum high and listen for anything
lower, saving it as the new minimum. Likewise, you set the
maximum low and listen for anything higher as the new maximum.
The circuit:
* Analog sensor (potentiometer will do) attached to analog input 0
* LED attached from digital pin 9 to ground
created 29 Oct 2008
By David A Mellis
modified 30 Aug 2011
By Tom Igoe
This example code is in the public domain.
*/
// These constants won't change:
const int sensorPin = A3; // pin that the sensor is attached to
const int ledPin = 2; // pin that the LED is attached to
// variables:
int sensorValue = 0; // the sensor value
int sensorMin = 1023; // minimum sensor value
int sensorMax = 0; // maximum sensor value
void setup() {
// turn on LED to signal the start of the calibration period:
pinMode(14, OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(14, HIGH);
// calibrate during the first five seconds
while (millis() < 5000) {
sensorValue = analogRead(sensorPin);
// record the maximum sensor value
if (sensorValue > sensorMax) {
sensorMax = sensorValue;
}
// record the minimum sensor value
if (sensorValue < sensorMin) {
sensorMin = sensorValue;
}
}
// signal the end of the calibration period
digitalWrite(14, LOW);
}
void loop() {
// read the sensor:
sensorValue = analogRead(sensorPin);
// apply the calibration to the sensor reading
sensorValue = map(sensorValue, sensorMin, sensorMax, 0, 255);
// in case the sensor value is outside the range seen during calibration
sensorValue = constrain(sensorValue, 0, 255);
// fade the LED using the calibrated value:
analogWrite(ledPin, sensorValue);
}
Working Video
(Insert Video Here)Try it out:
See Also:
- while()
- millis()
- constrain()
- map()
- If()
- AnalogInput - use a potentiometer to control the blinking of an LED
- AnalogInOutSerial - read an analog pin, map the result, and use that data to dim or brighten an LED
- Fade - use an analog input to fade an LED
- Smoothing - smooth multiple readings of an analog input
Corrections, suggestions, and new documentation should be posted to the Forum.
The text of the Energia reference is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 License. Energia reference is based on the Arduino reference. Code samples in the reference are released into the public domain.