# THIS DOCUMENT CONTAINS THE COMPLETE DOCUMENTATION FOR PLAYWRIGHT PYTHON.
# Getting started - Library
Getting started - Library
=========================
Installation[](#installation "Direct link to Installation")
------------------------------------------------------------
### Pip[](#pip "Direct link to Pip")
[](https://pypi.python.org/pypi/playwright/)
pip install --upgrade pippip install playwrightplaywright install
### Conda[](#conda "Direct link to Conda")
[](https://anaconda.org/Microsoft/playwright)
conda config --add channels conda-forgeconda config --add channels microsoftconda install playwrightplaywright install
These commands download the Playwright package and install browser binaries for Chromium, Firefox and WebKit. To modify this behavior see [installation parameters](/python/docs/browsers#install-browsers).
Usage[](#usage "Direct link to Usage")
---------------------------------------
Once installed, you can `import` Playwright in a Python script, and launch any of the 3 browsers (`chromium`, `firefox` and `webkit`).
from playwright.sync_api import sync_playwrightwith sync_playwright() as p: browser = p.chromium.launch() page = browser.new_page() page.goto("https://playwright.dev") print(page.title()) browser.close()
Playwright supports two variations of the API: synchronous and asynchronous. If your modern project uses [asyncio](https://docs.python.org/3/library/asyncio.html), you should use async API:
import asynciofrom playwright.async_api import async_playwrightasync def main(): async with async_playwright() as p: browser = await p.chromium.launch() page = await browser.new_page() await page.goto("https://playwright.dev") print(await page.title()) await browser.close()asyncio.run(main())
First script[](#first-script "Direct link to First script")
------------------------------------------------------------
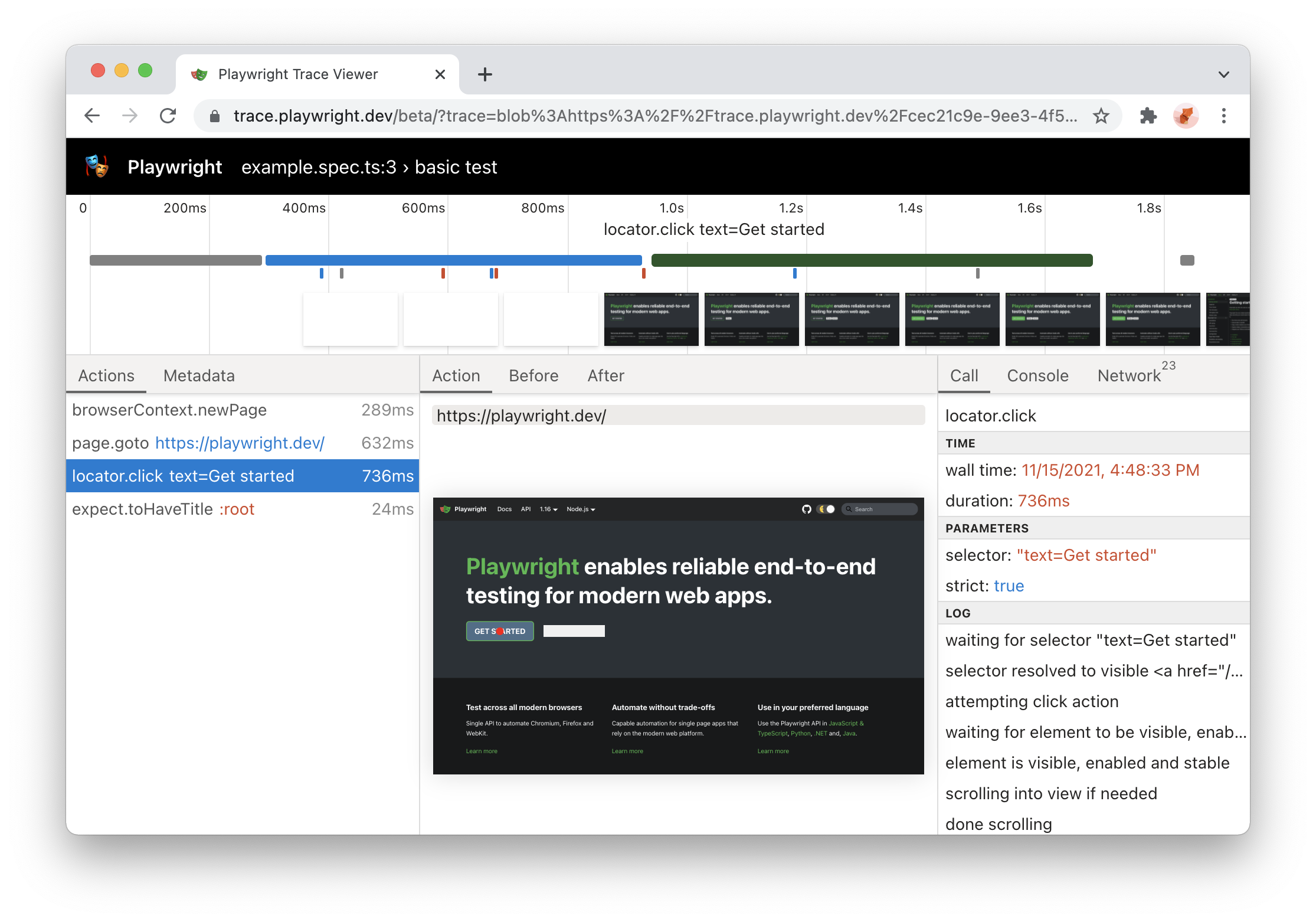
In our first script, we will navigate to `https://playwright.dev/` and take a screenshot in WebKit.
from playwright.sync_api import sync_playwrightwith sync_playwright() as p: browser = p.webkit.launch() page = browser.new_page() page.goto("https://playwright.dev/") page.screenshot(path="example.png") browser.close()
By default, Playwright runs the browsers in headless mode. To see the browser UI, set [headless](/python/docs/api/class-browsertype#browser-type-launch-option-headless) option to `False`. You can also use [slow\_mo](/python/docs/api/class-browsertype#browser-type-launch-option-slow-mo) to slow down execution. Learn more in the debugging tools [section](/python/docs/debug).
firefox.launch(headless=False, slow_mo=50)
Interactive mode (REPL)[](#interactive-mode-repl "Direct link to Interactive mode (REPL)")
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
You can launch the interactive python REPL:
python
and then launch Playwright within it for quick experimentation:
from playwright.sync_api import sync_playwrightplaywright = sync_playwright().start()# Use playwright.chromium, playwright.firefox or playwright.webkit# Pass headless=False to launch() to see the browser UIbrowser = playwright.chromium.launch()page = browser.new_page()page.goto("https://playwright.dev/")page.screenshot(path="example.png")browser.close()playwright.stop()
Async REPL such as `asyncio` REPL:
python -m asyncio
from playwright.async_api import async_playwrightplaywright = await async_playwright().start()browser = await playwright.chromium.launch()page = await browser.new_page()await page.goto("https://playwright.dev/")await page.screenshot(path="example.png")await browser.close()await playwright.stop()
Pyinstaller[](#pyinstaller "Direct link to Pyinstaller")
---------------------------------------------------------
You can use Playwright with [Pyinstaller](https://www.pyinstaller.org/) to create standalone executables.
main.py
from playwright.sync_api import sync_playwrightwith sync_playwright() as p: browser = p.chromium.launch() page = browser.new_page() page.goto("https://playwright.dev/") page.screenshot(path="example.png") browser.close()
If you want to bundle browsers with the executables:
* Bash
* PowerShell
* Batch
PLAYWRIGHT_BROWSERS_PATH=0 playwright install chromiumpyinstaller -F main.py
$env:PLAYWRIGHT_BROWSERS_PATH="0"playwright install chromiumpyinstaller -F main.py
set PLAYWRIGHT_BROWSERS_PATH=0playwright install chromiumpyinstaller -F main.py
note
Bundling the browsers with the executables will generate bigger binaries. It is recommended to only bundle the browsers you use.
Known issues[](#known-issues "Direct link to Known issues")
------------------------------------------------------------
### `time.sleep()` leads to outdated state[](#timesleep-leads-to-outdated-state "Direct link to timesleep-leads-to-outdated-state")
Most likely you don't need to wait manually, since Playwright has [auto-waiting](/python/docs/actionability). If you still rely on it, you should use `page.wait_for_timeout(5000)` instead of `time.sleep(5)` and it is better to not wait for a timeout at all, but sometimes it is useful for debugging. In these cases, use our wait (`wait_for_timeout`) method instead of the `time` module. This is because we internally rely on asynchronous operations and when using `time.sleep(5)` they can't get processed correctly.
### incompatible with `SelectorEventLoop` of `asyncio` on Windows[](#incompatible-with-selectoreventloop-of-asyncio-on-windows "Direct link to incompatible-with-selectoreventloop-of-asyncio-on-windows")
Playwright runs the driver in a subprocess, so it requires `ProactorEventLoop` of `asyncio` on Windows because `SelectorEventLoop` does not supports async subprocesses.
On Windows Python 3.7, Playwright sets the default event loop to `ProactorEventLoop` as it is default on Python 3.8+.
### Threading[](#threading "Direct link to Threading")
Playwright's API is not thread-safe. If you are using Playwright in a multi-threaded environment, you should create a playwright instance per thread. See [threading issue](https://github.com/microsoft/playwright-python/issues/623) for more details.
# Release notes
Release notes
=============
Version 1.58[](#version-158 "Direct link to Version 1.58")
-----------------------------------------------------------
### UI Mode and Trace Viewer Improvements[](#ui-mode-and-trace-viewer-improvements "Direct link to UI Mode and Trace Viewer Improvements")
* New 'system' theme option follows your OS dark/light mode preference
* Search functionality (Cmd/Ctrl+F) is now available in code editors
* Network details panel has been reorganized for better usability
* JSON responses are now automatically formatted for readability
Thanks to [@cpAdm](https://github.com/cpAdm) for contributing these improvements!
### Miscellaneous[](#miscellaneous "Direct link to Miscellaneous")
[browser\_type.connect\_over\_cdp()](/python/docs/api/class-browsertype#browser-type-connect-over-cdp) now accepts an `is_local` option. When set to `True`, it tells Playwright that it runs on the same host as the CDP server, enabling file system optimizations.
### Breaking Changes ⚠️[](#breaking-changes-️ "Direct link to Breaking Changes ⚠️")
* Removed `_react` and `_vue` selectors. See [locators guide](/python/docs/locators) for alternatives.
* Removed `:light` selector engine suffix. Use standard CSS selectors instead.
* Option `devtools` from [browser\_type.launch()](/python/docs/api/class-browsertype#browser-type-launch) has been removed. Use `args=['--auto-open-devtools-for-tabs']` instead.
* Removed macOS 13 support for WebKit. We recommend to upgrade your macOS version, or keep using an older Playwright version.
### Browser Versions[](#browser-versions "Direct link to Browser Versions")
* Chromium 145.0.7632.6
* Mozilla Firefox 146.0.1
* WebKit 26.0
This version was also tested against the following stable channels:
* Google Chrome 144
* Microsoft Edge 144
Version 1.57[](#version-157 "Direct link to Version 1.57")
-----------------------------------------------------------
### Chrome for Testing[](#chrome-for-testing "Direct link to Chrome for Testing")
Starting with this release, Playwright switches from Chromium, to using [Chrome for Testing](https://developer.chrome.com/blog/chrome-for-testing/) builds. Both headed and headless browsers are subject to this. Your tests should still be passing after upgrading to Playwright 1.57.
We're expecting no functional changes to come from this switch. The biggest change is the new icon and title in your toolbar.

If you still see an unexpected behaviour change, please [file an issue](https://github.com/microsoft/playwright/issues/new).
On Arm64 Linux, Playwright continues to use Chromium.
### Breaking Change[](#breaking-change "Direct link to Breaking Change")
After 3 years of being deprecated, we removed `page.accessibility` from our API. Please use other libraries such as [Axe](https://www.deque.com/axe/) if you need to test page accessibility. See our Node.js [guide](https://playwright.dev/docs/accessibility-testing) for integration with Axe.
### New APIs[](#new-apis "Direct link to New APIs")
* [worker.on("console")](/python/docs/api/class-worker#worker-event-console) event is emitted when JavaScript within the worker calls one of console API methods, e.g. console.log or console.dir. [worker.expect\_event()](/python/docs/api/class-worker#worker-wait-for-event) can be used to wait for it.
* [locator.description](/python/docs/api/class-locator#locator-description) returns locator description previously set with [locator.describe()](/python/docs/api/class-locator#locator-describe).
* New option [steps](/python/docs/api/class-locator#locator-click-option-steps) in [locator.click()](/python/docs/api/class-locator#locator-click) and [locator.drag\_to()](/python/docs/api/class-locator#locator-drag-to) that configures the number of `mousemove` events emitted while moving the mouse pointer to the target element.
* Network requests issued by [Service Workers](/python/docs/service-workers#network-events-and-routing) are now reported and can be routed through the [BrowserContext](/python/docs/api/class-browsercontext), only in Chromium. You can opt out using the `PLAYWRIGHT_DISABLE_SERVICE_WORKER_NETWORK` environment variable.
* Console messages from Service Workers are dispatched through [worker.on("console")](/python/docs/api/class-worker#worker-event-console). You can opt out of this using the `PLAYWRIGHT_DISABLE_SERVICE_WORKER_CONSOLE` environment variable.
### Browser Versions[](#browser-versions-1 "Direct link to Browser Versions")
* Chromium 143.0.7499.4
* Mozilla Firefox 144.0.2
* WebKit 26.0
Version 1.56[](#version-156 "Direct link to Version 1.56")
-----------------------------------------------------------
### New APIs[](#new-apis-1 "Direct link to New APIs")
* New methods [page.console\_messages()](/python/docs/api/class-page#page-console-messages) and [page.page\_errors()](/python/docs/api/class-page#page-page-errors) for retrieving the most recent console messages from the page
* New method [page.requests()](/python/docs/api/class-page#page-requests) for retrieving the most recent network requests from the page
### Breaking Changes[](#breaking-changes "Direct link to Breaking Changes")
* Event [browser\_context.on("backgroundpage")](/python/docs/api/class-browsercontext#browser-context-event-background-page) has been deprecated and will not be emitted. Method [browser\_context.background\_pages](/python/docs/api/class-browsercontext#browser-context-background-pages) will return an empty list
### Miscellaneous[](#miscellaneous-1 "Direct link to Miscellaneous")
* Aria snapshots render and compare `input` `placeholder`
### Browser Versions[](#browser-versions-2 "Direct link to Browser Versions")
* Chromium 141.0.7390.37
* Mozilla Firefox 142.0.1
* WebKit 26.0
Version 1.55[](#version-155 "Direct link to Version 1.55")
-----------------------------------------------------------
### Codegen[](#codegen "Direct link to Codegen")
* Automatic `to_be_visible()` assertions: Codegen can now generate automatic `to_be_visible()` assertions for common UI interactions. This feature can be enabled in the Codegen settings UI.
### Breaking Changes[](#breaking-changes-1 "Direct link to Breaking Changes")
* ⚠️ Dropped support for Chromium extension manifest v2.
### Miscellaneous[](#miscellaneous-2 "Direct link to Miscellaneous")
* Added support for Debian 13 "Trixie".
### Browser Versions[](#browser-versions-3 "Direct link to Browser Versions")
* Chromium 140.0.7339.16
* Mozilla Firefox 141.0
* WebKit 26.0
This version was also tested against the following stable channels:
* Google Chrome 139
* Microsoft Edge 139
Version 1.54[](#version-154 "Direct link to Version 1.54")
-----------------------------------------------------------
### Highlights[](#highlights "Direct link to Highlights")
* New cookie property `partition_key` in [browser\_context.cookies()](/python/docs/api/class-browsercontext#browser-context-cookies) and [browser\_context.add\_cookies()](/python/docs/api/class-browsercontext#browser-context-add-cookies). This property allows to save and restore partitioned cookies. See [CHIPS MDN article](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/Privacy/Guides/Privacy_sandbox/Partitioned_cookies) for more information. Note that browsers have different support and defaults for cookie partitioning.
* New option `--user-data-dir` in multiple commands. You can specify the same user data dir to reuse browsing state, like authentication, between sessions.
playwright codegen --user-data-dir=./user-data
* `playwright open` does not open the test recorder anymore. Use `playwright codegen` instead.
### Browser Versions[](#browser-versions-4 "Direct link to Browser Versions")
* Chromium 139.0.7258.5
* Mozilla Firefox 140.0.2
* WebKit 26.0
This version was also tested against the following stable channels:
* Google Chrome 140
* Microsoft Edge 140
Version 1.53[](#version-153 "Direct link to Version 1.53")
-----------------------------------------------------------
### Trace Viewer and HTML Reporter Updates[](#trace-viewer-and-html-reporter-updates "Direct link to Trace Viewer and HTML Reporter Updates")
* New Steps in Trace Viewer: 
* New method [locator.describe()](/python/docs/api/class-locator#locator-describe) to describe a locator. Used for trace viewer.
button = page.get_by_test_id("btn-sub").describe("Subscribe button")button.click()
* `python -m playwright install --list` will now list all installed browsers, versions and locations.
### Browser Versions[](#browser-versions-5 "Direct link to Browser Versions")
* Chromium 138.0.7204.4
* Mozilla Firefox 139.0
* WebKit 18.5
This version was also tested against the following stable channels:
* Google Chrome 137
* Microsoft Edge 137
Version 1.52[](#version-152 "Direct link to Version 1.52")
-----------------------------------------------------------
### Highlights[](#highlights-1 "Direct link to Highlights")
* New method [expect(locator).to\_contain\_class()](/python/docs/api/class-locatorassertions#locator-assertions-to-contain-class) to ergonomically assert individual class names on the element.
expect(page.get_by_role('listitem', name='Ship v1.52')).to_contain_class('done')
* [Aria Snapshots](/python/docs/aria-snapshots) got two new properties: [`/children`](/python/docs/aria-snapshots#strict-matching) for strict matching and `/url` for links.
expect(locator).to_match_aria_snapshot(""" - list - /children: equal - listitem: Feature A - listitem: - link "Feature B": - /url: "https://playwright.dev"""")
### Miscellaneous[](#miscellaneous-3 "Direct link to Miscellaneous")
* New option [max\_redirects](/python/docs/api/class-apirequest#api-request-new-context-option-max-redirects) in [api\_request.new\_context()](/python/docs/api/class-apirequest#api-request-new-context) to control the maximum number of redirects.
### Breaking Changes[](#breaking-changes-2 "Direct link to Breaking Changes")
* Glob URL patterns in methods like [page.route()](/python/docs/api/class-page#page-route) do not support `?` and `[]` anymore. We recommend using regular expressions instead.
* Method [route.continue\_()](/python/docs/api/class-route#route-continue) does not allow to override the `Cookie` header anymore. If a `Cookie` header is provided, it will be ignored, and the cookie will be loaded from the browser's cookie store. To set custom cookies, use [browser\_context.add\_cookies()](/python/docs/api/class-browsercontext#browser-context-add-cookies).
* macOS 13 is now deprecated and will no longer receive WebKit updates. Please upgrade to a more recent macOS version to continue benefiting from the latest WebKit improvements.
### Browser Versions[](#browser-versions-6 "Direct link to Browser Versions")
* Chromium 136.0.7103.25
* Mozilla Firefox 137.0
* WebKit 18.4
This version was also tested against the following stable channels:
* Google Chrome 135
* Microsoft Edge 135
Version 1.51[](#version-151 "Direct link to Version 1.51")
-----------------------------------------------------------
### Highlights[](#highlights-2 "Direct link to Highlights")
* New option [indexed\_db](/python/docs/api/class-browsercontext#browser-context-storage-state-option-indexed-db) for [browser\_context.storage\_state()](/python/docs/api/class-browsercontext#browser-context-storage-state) allows to save and restore IndexedDB contents. Useful when your application uses [IndexedDB API](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/IndexedDB_API) to store authentication tokens, like Firebase Authentication.
Here is an example following the [authentication guide](/python/docs/auth#reusing-signed-in-state):
# Save storage state into the file. Make sure to include IndexedDB.storage = await context.storage_state(path="state.json", indexed_db=True)# Create a new context with the saved storage state.context = await browser.new_context(storage_state="state.json")
* New option [visible](/python/docs/api/class-locator#locator-filter-option-visible) for [locator.filter()](/python/docs/api/class-locator#locator-filter) allows matching only visible elements.
# Ignore invisible todo items.todo_items = page.get_by_test_id("todo-item").filter(visible=True)# Check there are exactly 3 visible ones.await expect(todo_items).to_have_count(3)
* New option `contrast` for methods [page.emulate\_media()](/python/docs/api/class-page#page-emulate-media) and [browser.new\_context()](/python/docs/api/class-browser#browser-new-context) allows to emulate the `prefers-contrast` media feature.
* New option [fail\_on\_status\_code](/python/docs/api/class-apirequest#api-request-new-context-option-fail-on-status-code) makes all fetch requests made through the [APIRequestContext](/python/docs/api/class-apirequestcontext "APIRequestContext") throw on response codes other than 2xx and 3xx.
### Browser Versions[](#browser-versions-7 "Direct link to Browser Versions")
* Chromium 134.0.6998.35
* Mozilla Firefox 135.0
* WebKit 18.4
This version was also tested against the following stable channels:
* Google Chrome 133
* Microsoft Edge 133
Version 1.50[](#version-150 "Direct link to Version 1.50")
-----------------------------------------------------------
### Async Pytest Plugin[](#async-pytest-plugin "Direct link to Async Pytest Plugin")
* [Playwright's Pytest plugin](/python/docs/test-runners) now has support for [Async Fixtures](https://playwright.dev/python/docs/test-runners#async-fixtures).
### Miscellaneous[](#miscellaneous-4 "Direct link to Miscellaneous")
* Added method [expect(locator).to\_have\_accessible\_error\_message()](/python/docs/api/class-locatorassertions#locator-assertions-to-have-accessible-error-message) to assert the Locator points to an element with a given [aria errormessage](https://w3c.github.io/aria/#aria-errormessage).
### UI updates[](#ui-updates "Direct link to UI updates")
* New button in Codegen for picking elements to produce aria snapshots.
* Additional details (such as keys pressed) are now displayed alongside action API calls in traces.
* Display of `canvas` content in traces is error-prone. Display is now disabled by default, and can be enabled via the `Display canvas content` UI setting.
* `Call` and `Network` panels now display additional time information.
### Breaking[](#breaking "Direct link to Breaking")
* [expect(locator).to\_be\_editable()](/python/docs/api/class-locatorassertions#locator-assertions-to-be-editable) and [locator.is\_editable()](/python/docs/api/class-locator#locator-is-editable) now throw if the target element is not ``, or a number of other editable elements.
### Browser Versions[](#browser-versions-8 "Direct link to Browser Versions")
* Chromium 133.0.6943.16
* Mozilla Firefox 134.0
* WebKit 18.2
This version was also tested against the following stable channels:
* Google Chrome 132
* Microsoft Edge 132
Version 1.49[](#version-149 "Direct link to Version 1.49")
-----------------------------------------------------------
### Aria snapshots[](#aria-snapshots "Direct link to Aria snapshots")
New assertion [expect(locator).to\_match\_aria\_snapshot()](/python/docs/api/class-locatorassertions#locator-assertions-to-match-aria-snapshot) verifies page structure by comparing to an expected accessibility tree, represented as YAML.
page.goto("https://playwright.dev")expect(page.locator('body')).to_match_aria_snapshot(''' - banner: - heading /Playwright enables reliable/ [level=1] - link "Get started" - link "Star microsoft/playwright on GitHub" - main: - img "Browsers (Chromium, Firefox, WebKit)" - heading "Any browser • Any platform • One API"''')
You can generate this assertion with [Test Generator](/python/docs/codegen) or by calling [locator.aria\_snapshot()](/python/docs/api/class-locator#locator-aria-snapshot).
Learn more in the [aria snapshots guide](/python/docs/aria-snapshots).
### Tracing groups[](#tracing-groups "Direct link to Tracing groups")
New method [tracing.group()](/python/docs/api/class-tracing#tracing-group) allows you to visually group actions in the trace viewer.
# All actions between group and group_end# will be shown in the trace viewer as a group.page.context.tracing.group("Open Playwright.dev > API")page.goto("https://playwright.dev/")page.get_by_role("link", name="API").click()page.context.tracing.group_end()
### Breaking: `chrome` and `msedge` channels switch to new headless mode[](#breaking-chrome-and-msedge-channels-switch-to-new-headless-mode "Direct link to breaking-chrome-and-msedge-channels-switch-to-new-headless-mode")
This change affects you if you're using one of the following channels in your `playwright.config.ts`:
* `chrome`, `chrome-dev`, `chrome-beta`, or `chrome-canary`
* `msedge`, `msedge-dev`, `msedge-beta`, or `msedge-canary`
After updating to Playwright v1.49, run your test suite. If it still passes, you're good to go. If not, you will probably need to update your snapshots, and adapt some of your test code around PDF viewers and extensions. See [issue #33566](https://github.com/microsoft/playwright/issues/33566) for more details.
### Try new Chromium headless[](#try-new-chromium-headless "Direct link to Try new Chromium headless")
You can opt into the new headless mode by using `'chromium'` channel. As [official Chrome documentation puts it](https://developer.chrome.com/blog/chrome-headless-shell):
> New Headless on the other hand is the real Chrome browser, and is thus more authentic, reliable, and offers more features. This makes it more suitable for high-accuracy end-to-end web app testing or browser extension testing.
See [issue #33566](https://github.com/microsoft/playwright/issues/33566) for the list of possible breakages you could encounter and more details on Chromium headless. Please file an issue if you see any problems after opting in.
pytest test_login.py --browser-channel chromium
### Miscellaneous[](#miscellaneous-5 "Direct link to Miscellaneous")
* There will be no more updates for WebKit on Ubuntu 20.04 and Debian 11. We recommend updating your OS to a later version.
* `` elements inside a snapshot now draw a preview.
* Python 3.8 is not supported anymore.
### Browser Versions[](#browser-versions-9 "Direct link to Browser Versions")
* Chromium 131.0.6778.33
* Mozilla Firefox 132.0
* WebKit 18.2
This version was also tested against the following stable channels:
* Google Chrome 130
* Microsoft Edge 130
Version 1.48[](#version-148 "Direct link to Version 1.48")
-----------------------------------------------------------
### WebSocket routing[](#websocket-routing "Direct link to WebSocket routing")
New methods [page.route\_web\_socket()](/python/docs/api/class-page#page-route-web-socket) and [browser\_context.route\_web\_socket()](/python/docs/api/class-browsercontext#browser-context-route-web-socket) allow to intercept, modify and mock WebSocket connections initiated in the page. Below is a simple example that mocks WebSocket communication by responding to a `"request"` with a `"response"`.
def message_handler(ws: WebSocketRoute, message: Union[str, bytes]): if message == "request": ws.send("response")page.route_web_socket("/ws", lambda ws: ws.on_message( lambda message: message_handler(ws, message)))
See [WebSocketRoute](/python/docs/api/class-websocketroute "WebSocketRoute") for more details.
### UI updates[](#ui-updates-1 "Direct link to UI updates")
* New "copy" buttons for annotations and test location in the HTML report.
* Route method calls like [route.fulfill()](/python/docs/api/class-route#route-fulfill) are not shown in the report and trace viewer anymore. You can see which network requests were routed in the network tab instead.
* New "Copy as cURL" and "Copy as fetch" buttons for requests in the network tab.
### Miscellaneous[](#miscellaneous-6 "Direct link to Miscellaneous")
* New method [page.request\_gc()](/python/docs/api/class-page#page-request-gc) may help detect memory leaks.
* Requests made by [APIRequestContext](/python/docs/api/class-apirequestcontext "APIRequestContext") now record detailed timing and security information in the HAR.
### Browser Versions[](#browser-versions-10 "Direct link to Browser Versions")
* Chromium 130.0.6723.19
* Mozilla Firefox 130.0
* WebKit 18.0
This version was also tested against the following stable channels:
* Google Chrome 129
* Microsoft Edge 129
Version 1.47[](#version-147 "Direct link to Version 1.47")
-----------------------------------------------------------
### Network Tab improvements[](#network-tab-improvements "Direct link to Network Tab improvements")
The Network tab in the trace viewer has several nice improvements:
* filtering by asset type and URL
* better display of query string parameters
* preview of font assets

### Miscellaneous[](#miscellaneous-7 "Direct link to Miscellaneous")
* The `mcr.microsoft.com/playwright/python:v1.47.0` now serves a Playwright image based on Ubuntu 24.04 Noble. To use the 22.04 jammy-based image, please use `mcr.microsoft.com/playwright/python:v1.47.0-jammy` instead.
* The `:latest`/`:focal`/`:jammy` tag for Playwright Docker images is no longer being published. Pin to a specific version for better stability and reproducibility.
* TLS client certificates can now be passed from memory by passing [client\_certificates.cert](/python/docs/api/class-browser#browser-new-context-option-client-certificates) and [client\_certificates.key](/python/docs/api/class-browser#browser-new-context-option-client-certificates) as bytes instead of file paths.
* [no\_wait\_after](/python/docs/api/class-locator#locator-select-option-option-no-wait-after) in [locator.select\_option()](/python/docs/api/class-locator#locator-select-option) was deprecated.
* We've seen reports of WebGL in Webkit misbehaving on GitHub Actions `macos-13`. We recommend upgrading GitHub Actions to `macos-14`.
### Browser Versions[](#browser-versions-11 "Direct link to Browser Versions")
* Chromium 129.0.6668.29
* Mozilla Firefox 130.0
* WebKit 18.0
This version was also tested against the following stable channels:
* Google Chrome 128
* Microsoft Edge 128
Version 1.46[](#version-146 "Direct link to Version 1.46")
-----------------------------------------------------------
### TLS Client Certificates[](#tls-client-certificates "Direct link to TLS Client Certificates")
Playwright now allows to supply client-side certificates, so that server can verify them, as specified by TLS Client Authentication.
You can provide client certificates as a parameter of [browser.new\_context()](/python/docs/api/class-browser#browser-new-context) and [api\_request.new\_context()](/python/docs/api/class-apirequest#api-request-new-context). The following snippet sets up a client certificate for `https://example.com`:
context = browser.new_context( client_certificates=[ { "origin": "https://example.com", "certPath": "client-certificates/cert.pem", "keyPath": "client-certificates/key.pem", } ],)
### Trace Viewer Updates[](#trace-viewer-updates "Direct link to Trace Viewer Updates")
* Content of text attachments is now rendered inline in the attachments pane.
* New setting to show/hide routing actions like [route.continue\_()](/python/docs/api/class-route#route-continue).
* Request method and status are shown in the network details tab.
* New button to copy source file location to clipboard.
* Metadata pane now displays the `base_url`.
### Miscellaneous[](#miscellaneous-8 "Direct link to Miscellaneous")
* New `maxRetries` option in [api\_request\_context.fetch()](/python/docs/api/class-apirequestcontext#api-request-context-fetch) which retries on the `ECONNRESET` network error.
### Browser Versions[](#browser-versions-12 "Direct link to Browser Versions")
* Chromium 128.0.6613.18
* Mozilla Firefox 128.0
* WebKit 18.0
This version was also tested against the following stable channels:
* Google Chrome 127
* Microsoft Edge 127
Version 1.45[](#version-145 "Direct link to Version 1.45")
-----------------------------------------------------------
### Clock[](#clock "Direct link to Clock")
Utilizing the new [Clock](/python/docs/api/class-clock "Clock") API allows to manipulate and control time within tests to verify time-related behavior. This API covers many common scenarios, including:
* testing with predefined time;
* keeping consistent time and timers;
* monitoring inactivity;
* ticking through time manually.
# Initialize clock with some time before the test time and let the page load# naturally. `Date.now` will progress as the timers fire.page.clock.install(time=datetime.datetime(2024, 2, 2, 8, 0, 0))page.goto("http://localhost:3333")# Pretend that the user closed the laptop lid and opened it again at 10am.# Pause the time once reached that point.page.clock.pause_at(datetime.datetime(2024, 2, 2, 10, 0, 0))# Assert the page state.expect(page.get_by_test_id("current-time")).to_have_text("2/2/2024, 10:00:00 AM")# Close the laptop lid again and open it at 10:30am.page.clock.fast_forward("30:00")expect(page.get_by_test_id("current-time")).to_have_text("2/2/2024, 10:30:00 AM")
See [the clock guide](/python/docs/clock) for more details.
### Miscellaneous[](#miscellaneous-9 "Direct link to Miscellaneous")
* Method [locator.set\_input\_files()](/python/docs/api/class-locator#locator-set-input-files) now supports uploading a directory for ` Red Green Blue
element.select_option("Red")
### Miscellaneous[](#miscellaneous-11 "Direct link to Miscellaneous")
* Option `postData` in method [route.continue\_()](/python/docs/api/class-route#route-continue) now supports [Serializable](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/JSON/stringify#Description "Serializable") values.
### Browser Versions[](#browser-versions-29 "Direct link to Browser Versions")
* Chromium 109.0.5414.46
* Mozilla Firefox 107.0
* WebKit 16.4
This version was also tested against the following stable channels:
* Google Chrome 108
* Microsoft Edge 108
Version 1.28[](#version-128 "Direct link to Version 1.28")
-----------------------------------------------------------
### Playwright Tools[](#playwright-tools "Direct link to Playwright Tools")
* **Live Locators in CodeGen.** Generate a locator for any element on the page using "Explore" tool.

### New APIs[](#new-apis-12 "Direct link to New APIs")
* [locator.blur()](/python/docs/api/class-locator#locator-blur)
* [locator.clear()](/python/docs/api/class-locator#locator-clear)
### Browser Versions[](#browser-versions-30 "Direct link to Browser Versions")
* Chromium 108.0.5359.29
* Mozilla Firefox 106.0
* WebKit 16.4
This version was also tested against the following stable channels:
* Google Chrome 107
* Microsoft Edge 107
Version 1.27[](#version-127 "Direct link to Version 1.27")
-----------------------------------------------------------
### Locators[](#locators "Direct link to Locators")
With these new APIs writing locators is a joy:
* [page.get\_by\_text()](/python/docs/api/class-page#page-get-by-text) to locate by text content.
* [page.get\_by\_role()](/python/docs/api/class-page#page-get-by-role) to locate by [ARIA role](https://www.w3.org/TR/wai-aria-1.2/#roles), [ARIA attributes](https://www.w3.org/TR/wai-aria-1.2/#aria-attributes) and [accessible name](https://w3c.github.io/accname/#dfn-accessible-name).
* [page.get\_by\_label()](/python/docs/api/class-page#page-get-by-label) to locate a form control by associated label's text.
* [page.get\_by\_test\_id()](/python/docs/api/class-page#page-get-by-test-id) to locate an element based on its `data-testid` attribute (other attribute can be configured).
* [page.get\_by\_placeholder()](/python/docs/api/class-page#page-get-by-placeholder) to locate an input by placeholder.
* [page.get\_by\_alt\_text()](/python/docs/api/class-page#page-get-by-alt-text) to locate an element, usually image, by its text alternative.
* [page.get\_by\_title()](/python/docs/api/class-page#page-get-by-title) to locate an element by its title.
page.get_by_label("User Name").fill("John")page.get_by_label("Password").fill("secret-password")page.get_by_role("button", name="Sign in").click()expect(page.get_by_text("Welcome, John!")).to_be_visible()
All the same methods are also available on [Locator](/python/docs/api/class-locator "Locator"), [FrameLocator](/python/docs/api/class-framelocator "FrameLocator") and [Frame](/python/docs/api/class-frame "Frame") classes.
### Other highlights[](#other-highlights "Direct link to Other highlights")
* As announced in v1.25, Ubuntu 18 will not be supported as of Dec 2022. In addition to that, there will be no WebKit updates on Ubuntu 18 starting from the next Playwright release.
### Behavior Changes[](#behavior-changes "Direct link to Behavior Changes")
* [expect(locator).to\_have\_attribute()](/python/docs/api/class-locatorassertions#locator-assertions-to-have-attribute) with an empty value does not match missing attribute anymore. For example, the following snippet will succeed when `button` **does not** have a `disabled` attribute.
expect(page.get_by_role("button")).to_have_attribute("disabled", "")
### Browser Versions[](#browser-versions-31 "Direct link to Browser Versions")
* Chromium 107.0.5304.18
* Mozilla Firefox 105.0.1
* WebKit 16.0
This version was also tested against the following stable channels:
* Google Chrome 106
* Microsoft Edge 106
Version 1.26[](#version-126 "Direct link to Version 1.26")
-----------------------------------------------------------
### Assertions[](#assertions "Direct link to Assertions")
* New option `enabled` for [expect(locator).to\_be\_enabled()](/python/docs/api/class-locatorassertions#locator-assertions-to-be-enabled).
* [expect(locator).to\_have\_text()](/python/docs/api/class-locatorassertions#locator-assertions-to-have-text) now pierces open shadow roots.
* New option `editable` for [expect(locator).to\_be\_editable()](/python/docs/api/class-locatorassertions#locator-assertions-to-be-editable).
* New option `visible` for [expect(locator).to\_be\_visible()](/python/docs/api/class-locatorassertions#locator-assertions-to-be-visible).
### Other highlights[](#other-highlights-1 "Direct link to Other highlights")
* New option `max_redirects` for [api\_request\_context.get()](/python/docs/api/class-apirequestcontext#api-request-context-get) and others to limit redirect count.
* Python 3.11 is now supported.
### Behavior Change[](#behavior-change "Direct link to Behavior Change")
A bunch of Playwright APIs already support the `wait_until: "domcontentloaded"` option. For example:
page.goto("https://playwright.dev", wait_until="domcontentloaded")
Prior to 1.26, this would wait for all iframes to fire the `DOMContentLoaded` event.
To align with web specification, the `'domcontentloaded'` value only waits for the target frame to fire the `'DOMContentLoaded'` event. Use `wait_until="load"` to wait for all iframes.
### Browser Versions[](#browser-versions-32 "Direct link to Browser Versions")
* Chromium 106.0.5249.30
* Mozilla Firefox 104.0
* WebKit 16.0
This version was also tested against the following stable channels:
* Google Chrome 105
* Microsoft Edge 105
Version 1.25[](#version-125 "Direct link to Version 1.25")
-----------------------------------------------------------
### Announcements[](#announcements-1 "Direct link to Announcements")
* 🎁 We now ship Ubuntu 22.04 Jammy Jellyfish docker image: `mcr.microsoft.com/playwright/python:v1.34.0-jammy`.
* 🪦 This is the last release with macOS 10.15 support (deprecated as of 1.21).
* ⚠️ Ubuntu 18 is now deprecated and will not be supported as of Dec 2022.
### Browser Versions[](#browser-versions-33 "Direct link to Browser Versions")
* Chromium 105.0.5195.19
* Mozilla Firefox 103.0
* WebKit 16.0
This version was also tested against the following stable channels:
* Google Chrome 104
* Microsoft Edge 104
Version 1.24[](#version-124 "Direct link to Version 1.24")
-----------------------------------------------------------
### 🐂 Debian 11 Bullseye Support[](#-debian-11-bullseye-support "Direct link to 🐂 Debian 11 Bullseye Support")
Playwright now supports Debian 11 Bullseye on x86\_64 for Chromium, Firefox and WebKit. Let us know if you encounter any issues!
Linux support looks like this:
| | Ubuntu 20.04 | Ubuntu 22.04 | Debian 11 | :--- | :---: | :---: | :---: | :---: | | Chromium | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | | WebKit | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | | Firefox | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
### New introduction docs[](#new-introduction-docs "Direct link to New introduction docs")
We rewrote our Getting Started docs to be more end-to-end testing focused. Check them out on [playwright.dev](https://playwright.dev/python/docs/intro).
Version 1.23[](#version-123 "Direct link to Version 1.23")
-----------------------------------------------------------
### Network Replay[](#network-replay "Direct link to Network Replay")
Now you can record network traffic into a HAR file and re-use this traffic in your tests.
To record network into HAR file:
npx playwright open --save-har=github.har.zip https://github.com/microsoft
Alternatively, you can record HAR programmatically:
* Sync
* Async
context = browser.new_context(record_har_path="github.har.zip")# ... do stuff ...context.close()
context = await browser.new_context(record_har_path="github.har.zip")# ... do stuff ...await context.close()
Use the new methods [page.route\_from\_har()](/python/docs/api/class-page#page-route-from-har) or [browser\_context.route\_from\_har()](/python/docs/api/class-browsercontext#browser-context-route-from-har) to serve matching responses from the [HAR](http://www.softwareishard.com/blog/har-12-spec/) file:
* Sync
* Async
context.route_from_har("github.har.zip")
await context.route_from_har("github.har.zip")
Read more in [our documentation](/python/docs/mock#mocking-with-har-files).
### Advanced Routing[](#advanced-routing "Direct link to Advanced Routing")
You can now use [route.fallback()](/python/docs/api/class-route#route-fallback) to defer routing to other handlers.
Consider the following example:
* Sync
* Async
# Remove a header from all requestsdef remove_header_handler(route: Route) -> None: headers = route.request.all_headers() if "if-none-match" in headers: del headers["if-none-match"] route.fallback(headers=headers)page.route("**/*", remove_header_handler)# Abort all imagesdef abort_images_handler(route: Route) -> None: if route.request.resource_type == "image": route.abort() else: route.fallback()page.route("**/*", abort_images_handler)
# Remove a header from all requestsasync def remove_header_handler(route: Route) -> None: headers = await route.request.all_headers() if "if-none-match" in headers: del headers["if-none-match"] await route.fallback(headers=headers)await page.route("**/*", remove_header_handler)# Abort all imagesasync def abort_images_handler(route: Route) -> None: if route.request.resource_type == "image": await route.abort() else: await route.fallback()await page.route("**/*", abort_images_handler)
Note that the new methods [page.route\_from\_har()](/python/docs/api/class-page#page-route-from-har) and [browser\_context.route\_from\_har()](/python/docs/api/class-browsercontext#browser-context-route-from-har) also participate in routing and could be deferred to.
### Web-First Assertions Update[](#web-first-assertions-update "Direct link to Web-First Assertions Update")
* New method [expect(locator).to\_have\_values()](/python/docs/api/class-locatorassertions#locator-assertions-to-have-values) that asserts all selected values of `` element.
* Methods [expect(locator).to\_contain\_text()](/python/docs/api/class-locatorassertions#locator-assertions-to-contain-text) and [expect(locator).to\_have\_text()](/python/docs/api/class-locatorassertions#locator-assertions-to-have-text) now accept `ignore_case` option.
### Miscellaneous[](#miscellaneous-12 "Direct link to Miscellaneous")
* If there's a service worker that's in your way, you can now easily disable it with a new context option `service_workers`:
* Sync
* Async
context = browser.new_context(service_workers="block")page = context.new_page()
context = await browser.new_context(service_workers="block")page = await context.new_page()
* Using `.zip` path for `recordHar` context option automatically zips the resulting HAR:
* Sync
* Async
context = browser.new_context(record_har_path="github.har.zip")
context = await browser.new_context(record_har_path="github.har.zip")
* If you intend to edit HAR by hand, consider using the `"minimal"` HAR recording mode that only records information that is essential for replaying:
* Sync
* Async
context = browser.new_context(record_har_mode="minimal", record_har_path="har.har")
context = await browser.new_context(record_har_mode="minimal", record_har_path="har.har")
* Playwright now runs on Ubuntu 22 amd64 and Ubuntu 22 arm64.
Version 1.22[](#version-122 "Direct link to Version 1.22")
-----------------------------------------------------------
### Highlights[](#highlights-6 "Direct link to Highlights")
* Role selectors that allow selecting elements by their [ARIA role](https://www.w3.org/TR/wai-aria-1.2/#roles), [ARIA attributes](https://www.w3.org/TR/wai-aria-1.2/#aria-attributes) and [accessible name](https://w3c.github.io/accname/#dfn-accessible-name).
# Click a button with accessible name "log in"page.locator("role=button[name='log in']").click()
Read more in [our documentation](/python/docs/locators#locate-by-role).
* New [locator.filter()](/python/docs/api/class-locator#locator-filter) API to filter an existing locator
buttons = page.locator("role=button")# ...submit_button = buttons.filter(has_text="Submit")submit_button.click()
* Codegen now supports generating Pytest Tests

Version 1.21[](#version-121 "Direct link to Version 1.21")
-----------------------------------------------------------
### Highlights[](#highlights-7 "Direct link to Highlights")
* New role selectors that allow selecting elements by their [ARIA role](https://www.w3.org/TR/wai-aria-1.2/#roles), [ARIA attributes](https://www.w3.org/TR/wai-aria-1.2/#aria-attributes) and [accessible name](https://w3c.github.io/accname/#dfn-accessible-name).
* Sync
* Async
# Click a button with accessible name "log in"page.locator("role=button[name='log in']").click()
# Click a button with accessible name "log in"await page.locator("role=button[name='log in']").click()
Read more in [our documentation](/python/docs/locators#locate-by-role).
* New `scale` option in [page.screenshot()](/python/docs/api/class-page#page-screenshot) for smaller sized screenshots.
* New `caret` option in [page.screenshot()](/python/docs/api/class-page#page-screenshot) to control text caret. Defaults to `"hide"`.
### Behavior Changes[](#behavior-changes-1 "Direct link to Behavior Changes")
* The `mcr.microsoft.com/playwright` docker image no longer contains Python. Please use `mcr.microsoft.com/playwright/python` as a Playwright-ready docker image with pre-installed Python.
* Playwright now supports large file uploads (100s of MBs) via [locator.set\_input\_files()](/python/docs/api/class-locator#locator-set-input-files) API.
### Browser Versions[](#browser-versions-34 "Direct link to Browser Versions")
* Chromium 101.0.4951.26
* Mozilla Firefox 98.0.2
* WebKit 15.4
This version was also tested against the following stable channels:
* Google Chrome 100
* Microsoft Edge 100
Version 1.20[](#version-120 "Direct link to Version 1.20")
-----------------------------------------------------------
### Highlights[](#highlights-8 "Direct link to Highlights")
* New options for methods [page.screenshot()](/python/docs/api/class-page#page-screenshot), [locator.screenshot()](/python/docs/api/class-locator#locator-screenshot) and [element\_handle.screenshot()](/python/docs/api/class-elementhandle#element-handle-screenshot):
* Option `animations: "disabled"` rewinds all CSS animations and transitions to a consistent state
* Option `mask: Locator[]` masks given elements, overlaying them with pink `#FF00FF` boxes.
* [Trace Viewer](/python/docs/trace-viewer) now shows [API testing requests](/python/docs/api-testing).
* [locator.highlight()](/python/docs/api/class-locator#locator-highlight) visually reveals element(s) for easier debugging.
### Announcements[](#announcements-2 "Direct link to Announcements")
* We now ship a designated Python docker image `mcr.microsoft.com/playwright/python`. Please switch over to it if you use Python. This is the last release that includes Python inside our javascript `mcr.microsoft.com/playwright` docker image.
* v1.20 is the last release to receive WebKit update for macOS 10.15 Catalina. Please update macOS to keep using latest & greatest WebKit!
### Browser Versions[](#browser-versions-35 "Direct link to Browser Versions")
* Chromium 101.0.4921.0
* Mozilla Firefox 97.0.1
* WebKit 15.4
This version was also tested against the following stable channels:
* Google Chrome 99
* Microsoft Edge 99
Version 1.19[](#version-119 "Direct link to Version 1.19")
-----------------------------------------------------------
### Highlights[](#highlights-9 "Direct link to Highlights")
* Locator now supports a `has` option that makes sure it contains another locator inside:
* Sync
* Async
page.locator("article", has=page.locator(".highlight")).click()
await page.locator("article", has=page.locator(".highlight")).click()
Read more in [locator documentation](/python/docs/api/class-locator#locator-locator)
* New [locator.page](/python/docs/api/class-locator#locator-page)
* [page.screenshot()](/python/docs/api/class-page#page-screenshot) and [locator.screenshot()](/python/docs/api/class-locator#locator-screenshot) now automatically hide blinking caret
* Playwright Codegen now generates locators and frame locators
### Browser Versions[](#browser-versions-36 "Direct link to Browser Versions")
* Chromium 100.0.4863.0
* Mozilla Firefox 96.0.1
* WebKit 15.4
This version was also tested against the following stable channels:
* Google Chrome 98
* Microsoft Edge 98
Version 1.18[](#version-118 "Direct link to Version 1.18")
-----------------------------------------------------------
### API Testing[](#api-testing "Direct link to API Testing")
Playwright for Python 1.18 introduces new [API Testing](/python/docs/api/class-apirequestcontext) that lets you send requests to the server directly from Python! Now you can:
* test your server API
* prepare server side state before visiting the web application in a test
* validate server side post-conditions after running some actions in the browser
To do a request on behalf of Playwright's Page, use **new [page.request](/python/docs/api/class-page#page-request) API**:
* Sync
* Async
# Do a GET request on behalf of pageres = page.request.get("http://example.com/foo.json")
# Do a GET request on behalf of pageres = await page.request.get("http://example.com/foo.json")
Read more in [our documentation](/python/docs/api/class-apirequestcontext).
### Web-First Assertions[](#web-first-assertions "Direct link to Web-First Assertions")
Playwright for Python 1.18 introduces [Web-First Assertions](/python/docs/test-assertions).
Consider the following example:
* Sync
* Async
from playwright.sync_api import Page, expectdef test_status_becomes_submitted(page: Page) -> None: # .. page.locator("#submit-button").click() expect(page.locator(".status")).to_have_text("Submitted")
from playwright.async_api import Page, expectasync def test_status_becomes_submitted(page: Page) -> None: # .. await page.locator("#submit-button").click() await expect(page.locator(".status")).to_have_text("Submitted")
Playwright will be re-testing the node with the selector `.status` until fetched Node has the `"Submitted"` text. It will be re-fetching the node and checking it over and over, until the condition is met or until the timeout is reached. You can pass this timeout as an option.
Read more in [our documentation](/python/docs/test-assertions).
### Locator Improvements[](#locator-improvements "Direct link to Locator Improvements")
* [locator.drag\_to()](/python/docs/api/class-locator#locator-drag-to)
* Each locator can now be optionally filtered by the text it contains:
* Sync
* Async
page.locator("li", has_text="my item").locator("button").click()
await page.locator("li", has_text="my item").locator("button").click()
Read more in [locator documentation](/python/docs/api/class-locator#locator-locator)
### New APIs & changes[](#new-apis--changes "Direct link to New APIs & changes")
* [`accept_downloads`](/python/docs/api/class-browser#browser-new-context-option-accept-downloads) option now defaults to `True`.
* [`sources`](/python/docs/api/class-tracing#tracing-start-option-sources) option to embed sources into traces.
### Browser Versions[](#browser-versions-37 "Direct link to Browser Versions")
* Chromium 99.0.4812.0
* Mozilla Firefox 95.0
* WebKit 15.4
This version was also tested against the following stable channels:
* Google Chrome 97
* Microsoft Edge 97
Version 1.17[](#version-117 "Direct link to Version 1.17")
-----------------------------------------------------------
### Frame Locators[](#frame-locators "Direct link to Frame Locators")
Playwright 1.17 introduces [frame locators](/python/docs/api/class-framelocator) - a locator to the iframe on the page. Frame locators capture the logic sufficient to retrieve the `iframe` and then locate elements in that iframe. Frame locators are strict by default, will wait for `iframe` to appear and can be used in Web-First assertions.

Frame locators can be created with either [page.frame\_locator()](/python/docs/api/class-page#page-frame-locator) or [locator.frame\_locator()](/python/docs/api/class-locator#locator-frame-locator) method.
locator = page.frame_locator("my-frame").locator("text=Submit")locator.click()
Read more at [our documentation](/python/docs/api/class-framelocator).
### Trace Viewer Update[](#trace-viewer-update "Direct link to Trace Viewer Update")
Playwright Trace Viewer is now **available online** at [https://trace.playwright.dev](https://trace.playwright.dev)! Just drag-and-drop your `trace.zip` file to inspect its contents.
> **NOTE**: trace files are not uploaded anywhere; [trace.playwright.dev](https://trace.playwright.dev) is a [progressive web application](https://web.dev/progressive-web-apps/) that processes traces locally.
* Playwright Test traces now include sources by default (these could be turned off with tracing option)
* Trace Viewer now shows test name
* New trace metadata tab with browser details
* Snapshots now have URL bar
### HTML Report Update[](#html-report-update "Direct link to HTML Report Update")
* HTML report now supports dynamic filtering
* Report is now a **single static HTML file** that could be sent by e-mail or as a slack attachment.

### Ubuntu ARM64 support + more[](#ubuntu-arm64-support--more "Direct link to Ubuntu ARM64 support + more")
* Playwright now supports **Ubuntu 20.04 ARM64**. You can now run Playwright tests inside Docker on Apple M1 and on Raspberry Pi.
* You can now use Playwright to install stable version of Edge on Linux:
npx playwright install msedge
### New APIs[](#new-apis-13 "Direct link to New APIs")
* Tracing now supports a [`'title'`](/python/docs/api/class-tracing#tracing-start-option-title) option
* Page navigations support a new [`'commit'`](/python/docs/api/class-page#page-goto) waiting option
Version 1.16[](#version-116 "Direct link to Version 1.16")
-----------------------------------------------------------
### 🎭 Playwright Library[](#-playwright-library "Direct link to 🎭 Playwright Library")
#### `locator.wait_for`[](#locatorwait_for "Direct link to locatorwait_for")
Wait for a locator to resolve to a single element with a given state. Defaults to the `state: 'visible'`.
Comes especially handy when working with lists:
order_sent = page.locator("#order-sent")order_sent.wait_for()
Read more about [locator.wait\_for()](/python/docs/api/class-locator#locator-wait-for).
### Docker support for Arm64[](#docker-support-for-arm64 "Direct link to Docker support for Arm64")
Playwright Docker image is now published for Arm64 so it can be used on Apple Silicon.
Read more about [Docker integration](/python/docs/docker).
### 🎭 Playwright Trace Viewer[](#-playwright-trace-viewer "Direct link to 🎭 Playwright Trace Viewer")
* run trace viewer with `npx playwright show-trace` and drop trace files to the trace viewer PWA
* better visual attribution of action targets
Read more about [Trace Viewer](/python/docs/trace-viewer).
### Browser Versions[](#browser-versions-38 "Direct link to Browser Versions")
* Chromium 97.0.4666.0
* Mozilla Firefox 93.0
* WebKit 15.4
This version of Playwright was also tested against the following stable channels:
* Google Chrome 94
* Microsoft Edge 94
Version 1.15[](#version-115 "Direct link to Version 1.15")
-----------------------------------------------------------
### 🖱️ Mouse Wheel[](#️-mouse-wheel "Direct link to 🖱️ Mouse Wheel")
By using [mouse.wheel()](/python/docs/api/class-mouse#mouse-wheel) you are now able to scroll vertically or horizontally.
### 📜 New Headers API[](#-new-headers-api "Direct link to 📜 New Headers API")
Previously it was not possible to get multiple header values of a response. This is now possible and additional helper functions are available:
* [request.all\_headers()](/python/docs/api/class-request#request-all-headers)
* [request.headers\_array()](/python/docs/api/class-request#request-headers-array)
* [request.header\_value()](/python/docs/api/class-request#request-header-value)
* [response.all\_headers()](/python/docs/api/class-response#response-all-headers)
* [response.headers\_array()](/python/docs/api/class-response#response-headers-array)
* [response.header\_value()](/python/docs/api/class-response#response-header-value)
* [response.header\_values()](/python/docs/api/class-response#response-header-values)
### 🌈 Forced-Colors emulation[](#-forced-colors-emulation "Direct link to 🌈 Forced-Colors emulation")
Its now possible to emulate the `forced-colors` CSS media feature by passing it in the [browser.new\_context()](/python/docs/api/class-browser#browser-new-context) or calling [page.emulate\_media()](/python/docs/api/class-page#page-emulate-media).
### New APIs[](#new-apis-14 "Direct link to New APIs")
* [page.route()](/python/docs/api/class-page#page-route) accepts new `times` option to specify how many times this route should be matched.
* [page.set\_checked()](/python/docs/api/class-page#page-set-checked) and [locator.set\_checked()](/python/docs/api/class-locator#locator-set-checked) were introduced to set the checked state of a checkbox.
* [request.sizes()](/python/docs/api/class-request#request-sizes) Returns resource size information for given http request.
* [tracing.start\_chunk()](/python/docs/api/class-tracing#tracing-start-chunk) - Start a new trace chunk.
* [tracing.stop\_chunk()](/python/docs/api/class-tracing#tracing-stop-chunk) - Stops a new trace chunk.
### Browser Versions[](#browser-versions-39 "Direct link to Browser Versions")
* Chromium 96.0.4641.0
* Mozilla Firefox 92.0
* WebKit 15.0
Version 1.14[](#version-114 "Direct link to Version 1.14")
-----------------------------------------------------------
#### ⚡️ New "strict" mode[](#️-new-strict-mode "Direct link to ⚡️ New \"strict\" mode")
Selector ambiguity is a common problem in automation testing. **"strict" mode** ensures that your selector points to a single element and throws otherwise.
Pass `strict=true` into your action calls to opt in.
# This will throw if you have more than one button!page.click("button", strict=True)
#### 📍 New [**Locators API**](/python/docs/api/class-locator)[](#-new-locators-api "Direct link to -new-locators-api")
Locator represents a view to the element(s) on the page. It captures the logic sufficient to retrieve the element at any given moment.
The difference between the [Locator](/python/docs/api/class-locator) and [ElementHandle](/python/docs/api/class-elementhandle) is that the latter points to a particular element, while [Locator](/python/docs/api/class-locator) captures the logic of how to retrieve that element.
Also, locators are **"strict" by default**!
locator = page.locator("button")locator.click()
Learn more in the [documentation](/python/docs/api/class-locator).
#### 🧩 Experimental [**React**](/python/docs/other-locators#react-locator) and [**Vue**](/python/docs/other-locators#vue-locator) selector engines[](#-experimental-react-and-vue-selector-engines "Direct link to -experimental-react-and-vue-selector-engines")
React and Vue selectors allow selecting elements by its component name and/or property values. The syntax is very similar to [attribute selectors](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/CSS/Attribute_selectors) and supports all attribute selector operators.
page.locator("_react=SubmitButton[enabled=true]").click()page.locator("_vue=submit-button[enabled=true]").click()
Learn more in the [react selectors documentation](/python/docs/other-locators#react-locator) and the [vue selectors documentation](/python/docs/other-locators#vue-locator).
#### ✨ New [**`nth`**](/python/docs/other-locators#n-th-element-locator) and [**`visible`**](/python/docs/other-locators#css-matching-only-visible-elements) selector engines[](#-new-nth-and-visible-selector-engines "Direct link to -new-nth-and-visible-selector-engines")
* [`nth`](/python/docs/other-locators#n-th-element-locator) selector engine is equivalent to the `:nth-match` pseudo class, but could be combined with other selector engines.
* [`visible`](/python/docs/other-locators#css-matching-only-visible-elements) selector engine is equivalent to the `:visible` pseudo class, but could be combined with other selector engines.
# select the first button among all buttonsbutton.click("button >> nth=0")# or if you are using locators, you can use first, nth() and lastpage.locator("button").first.click()# click a visible buttonbutton.click("button >> visible=true")
### Browser Versions[](#browser-versions-40 "Direct link to Browser Versions")
* Chromium 94.0.4595.0
* Mozilla Firefox 91.0
* WebKit 15.0
Version 1.13[](#version-113 "Direct link to Version 1.13")
-----------------------------------------------------------
#### Playwright[](#playwright "Direct link to Playwright")
* **🖖 Programmatic drag-and-drop support** via the [page.drag\_and\_drop()](/python/docs/api/class-page#page-drag-and-drop) API.
* **🔎 Enhanced HAR** with body sizes for requests and responses. Use via `recordHar` option in [browser.new\_context()](/python/docs/api/class-browser#browser-new-context).
#### Tools[](#tools "Direct link to Tools")
* Playwright Trace Viewer now shows parameters, returned values and `console.log()` calls.
#### New and Overhauled Guides[](#new-and-overhauled-guides "Direct link to New and Overhauled Guides")
* [Intro](/python/docs/intro)
* [Authentication](/python/docs/auth)
* [Chrome Extensions](/python/docs/chrome-extensions)
#### Browser Versions[](#browser-versions-41 "Direct link to Browser Versions")
* Chromium 93.0.4576.0
* Mozilla Firefox 90.0
* WebKit 14.2
#### New Playwright APIs[](#new-playwright-apis "Direct link to New Playwright APIs")
* new `baseURL` option in [browser.new\_context()](/python/docs/api/class-browser#browser-new-context) and [browser.new\_page()](/python/docs/api/class-browser#browser-new-page)
* [response.security\_details()](/python/docs/api/class-response#response-security-details) and [response.server\_addr()](/python/docs/api/class-response#response-server-addr)
* [page.drag\_and\_drop()](/python/docs/api/class-page#page-drag-and-drop) and [frame.drag\_and\_drop()](/python/docs/api/class-frame#frame-drag-and-drop)
* [download.cancel()](/python/docs/api/class-download#download-cancel)
* [page.input\_value()](/python/docs/api/class-page#page-input-value), [frame.input\_value()](/python/docs/api/class-frame#frame-input-value) and [element\_handle.input\_value()](/python/docs/api/class-elementhandle#element-handle-input-value)
* new `force` option in [page.fill()](/python/docs/api/class-page#page-fill), [frame.fill()](/python/docs/api/class-frame#frame-fill), and [element\_handle.fill()](/python/docs/api/class-elementhandle#element-handle-fill)
* new `force` option in [page.select\_option()](/python/docs/api/class-page#page-select-option), [frame.select\_option()](/python/docs/api/class-frame#frame-select-option), and [element\_handle.select\_option()](/python/docs/api/class-elementhandle#element-handle-select-option)
Version 1.12[](#version-112 "Direct link to Version 1.12")
-----------------------------------------------------------
#### 🧟♂️ Introducing Playwright Trace Viewer[](#️-introducing-playwright-trace-viewer "Direct link to 🧟♂️ Introducing Playwright Trace Viewer")
[Playwright Trace Viewer](/python/docs/trace-viewer) is a new GUI tool that helps exploring recorded Playwright traces after the script ran. Playwright traces let you examine:
* page DOM before and after each Playwright action
* page rendering before and after each Playwright action
* browser network during script execution
Traces are recorded using the new [browser\_context.tracing](/python/docs/api/class-browsercontext#browser-context-tracing) API:
browser = chromium.launch()context = browser.new_context()# Start tracing before creating / navigating a page.context.tracing.start(screenshots=True, snapshots=True)page.goto("https://playwright.dev")# Stop tracing and export it into a zip archive.context.tracing.stop(path = "trace.zip")
Traces are examined later with the Playwright CLI:
playwright show-trace trace.zip
That will open the following GUI:

👉 Read more in [trace viewer documentation](/python/docs/trace-viewer).
#### Browser Versions[](#browser-versions-42 "Direct link to Browser Versions")
* Chromium 93.0.4530.0
* Mozilla Firefox 89.0
* WebKit 14.2
This version of Playwright was also tested against the following stable channels:
* Google Chrome 91
* Microsoft Edge 91
#### New APIs[](#new-apis-15 "Direct link to New APIs")
* `reducedMotion` option in [page.emulate\_media()](/python/docs/api/class-page#page-emulate-media), [browser\_type.launch\_persistent\_context()](/python/docs/api/class-browsertype#browser-type-launch-persistent-context), [browser.new\_context()](/python/docs/api/class-browser#browser-new-context) and [browser.new\_page()](/python/docs/api/class-browser#browser-new-page)
* [browser\_context.on("request")](/python/docs/api/class-browsercontext#browser-context-event-request)
* [browser\_context.on("requestfailed")](/python/docs/api/class-browsercontext#browser-context-event-request-failed)
* [browser\_context.on("requestfinished")](/python/docs/api/class-browsercontext#browser-context-event-request-finished)
* [browser\_context.on("response")](/python/docs/api/class-browsercontext#browser-context-event-response)
* `tracesDir` option in [browser\_type.launch()](/python/docs/api/class-browsertype#browser-type-launch) and [browser\_type.launch\_persistent\_context()](/python/docs/api/class-browsertype#browser-type-launch-persistent-context)
* new [browser\_context.tracing](/python/docs/api/class-browsercontext#browser-context-tracing) API namespace
* new [download.page](/python/docs/api/class-download#download-page) method
Version 1.11[](#version-111 "Direct link to Version 1.11")
-----------------------------------------------------------
🎥 New video: [Playwright: A New Test Automation Framework for the Modern Web](https://youtu.be/_Jla6DyuEu4) ([slides](https://docs.google.com/presentation/d/1xFhZIJrdHkVe2CuMKOrni92HoG2SWslo0DhJJQMR1DI/edit?usp=sharing))
* We talked about Playwright
* Showed engineering work behind the scenes
* Did live demos with new features ✨
* **Special thanks** to [applitools](http://applitools.com/) for hosting the event and inviting us!
#### Browser Versions[](#browser-versions-43 "Direct link to Browser Versions")
* Chromium 92.0.4498.0
* Mozilla Firefox 89.0b6
* WebKit 14.2
#### New APIs[](#new-apis-16 "Direct link to New APIs")
* support for **async predicates** across the API in methods such as [page.expect\_request()](/python/docs/api/class-page#page-wait-for-request) and others
* new **emulation devices**: Galaxy S8, Galaxy S9+, Galaxy Tab S4, Pixel 3, Pixel 4
* new methods:
* [page.wait\_for\_url()](/python/docs/api/class-page#page-wait-for-url) to await navigations to URL
* [video.delete()](/python/docs/api/class-video#video-delete) and [video.save\_as()](/python/docs/api/class-video#video-save-as) to manage screen recording
* new options:
* `screen` option in the [browser.new\_context()](/python/docs/api/class-browser#browser-new-context) method to emulate `window.screen` dimensions
* `position` option in [page.check()](/python/docs/api/class-page#page-check) and [page.uncheck()](/python/docs/api/class-page#page-uncheck) methods
* `trial` option to dry-run actions in [page.check()](/python/docs/api/class-page#page-check), [page.uncheck()](/python/docs/api/class-page#page-uncheck), [page.click()](/python/docs/api/class-page#page-click), [page.dblclick()](/python/docs/api/class-page#page-dblclick), [page.hover()](/python/docs/api/class-page#page-hover) and [page.tap()](/python/docs/api/class-page#page-tap)
Version 1.10[](#version-110 "Direct link to Version 1.10")
-----------------------------------------------------------
* [Playwright for Java v1.10](https://github.com/microsoft/playwright-java) is **now stable**!
* Run Playwright against **Google Chrome** and **Microsoft Edge** stable channels with the [new channels API](/python/docs/browsers).
* Chromium screenshots are **fast** on Mac & Windows.
#### Bundled Browser Versions[](#bundled-browser-versions "Direct link to Bundled Browser Versions")
* Chromium 90.0.4430.0
* Mozilla Firefox 87.0b10
* WebKit 14.2
This version of Playwright was also tested against the following stable channels:
* Google Chrome 89
* Microsoft Edge 89
#### New APIs[](#new-apis-17 "Direct link to New APIs")
* [browser\_type.launch()](/python/docs/api/class-browsertype#browser-type-launch) now accepts the new `'channel'` option. Read more in [our documentation](/python/docs/browsers).
Version 1.9[](#version-19 "Direct link to Version 1.9")
--------------------------------------------------------
* [Playwright Inspector](/python/docs/debug) is a **new GUI tool** to author and debug your tests.
* **Line-by-line debugging** of your Playwright scripts, with play, pause and step-through.
* Author new scripts by **recording user actions**.
* **Generate element selectors** for your script by hovering over elements.
* Set the `PWDEBUG=1` environment variable to launch the Inspector
* **Pause script execution** with [page.pause()](/python/docs/api/class-page#page-pause) in headed mode. Pausing the page launches [Playwright Inspector](/python/docs/debug) for debugging.
* **New has-text pseudo-class** for CSS selectors. `:has-text("example")` matches any element containing `"example"` somewhere inside, possibly in a child or a descendant element. See [more examples](/python/docs/other-locators#css-matching-by-text).
* **Page dialogs are now auto-dismissed** during execution, unless a listener for `dialog` event is configured. [Learn more](/python/docs/dialogs) about this.
* [Playwright for Python](https://github.com/microsoft/playwright-python) is **now stable** with an idiomatic snake case API and pre-built [Docker image](/python/docs/docker) to run tests in CI/CD.
#### Browser Versions[](#browser-versions-44 "Direct link to Browser Versions")
* Chromium 90.0.4421.0
* Mozilla Firefox 86.0b10
* WebKit 14.1
#### New APIs[](#new-apis-18 "Direct link to New APIs")
* [page.pause()](/python/docs/api/class-page#page-pause).
Version 1.8[](#version-18 "Direct link to Version 1.8")
--------------------------------------------------------
* [Selecting elements based on layout](/python/docs/other-locators#css-matching-elements-based-on-layout) with `:left-of()`, `:right-of()`, `:above()` and `:below()`.
* Playwright now includes command line interface, former playwright-cli.
playwright --help
* [page.select\_option()](/python/docs/api/class-page#page-select-option) now waits for the options to be present.
* New methods to [assert element state](/python/docs/actionability#assertions) like [page.is\_editable()](/python/docs/api/class-page#page-is-editable).
#### New APIs[](#new-apis-19 "Direct link to New APIs")
* [element\_handle.is\_checked()](/python/docs/api/class-elementhandle#element-handle-is-checked).
* [element\_handle.is\_disabled()](/python/docs/api/class-elementhandle#element-handle-is-disabled).
* [element\_handle.is\_editable()](/python/docs/api/class-elementhandle#element-handle-is-editable).
* [element\_handle.is\_enabled()](/python/docs/api/class-elementhandle#element-handle-is-enabled).
* [element\_handle.is\_hidden()](/python/docs/api/class-elementhandle#element-handle-is-hidden).
* [element\_handle.is\_visible()](/python/docs/api/class-elementhandle#element-handle-is-visible).
* [page.is\_checked()](/python/docs/api/class-page#page-is-checked).
* [page.is\_disabled()](/python/docs/api/class-page#page-is-disabled).
* [page.is\_editable()](/python/docs/api/class-page#page-is-editable).
* [page.is\_enabled()](/python/docs/api/class-page#page-is-enabled).
* [page.is\_hidden()](/python/docs/api/class-page#page-is-hidden).
* [page.is\_visible()](/python/docs/api/class-page#page-is-visible).
* New option `'editable'` in [element\_handle.wait\_for\_element\_state()](/python/docs/api/class-elementhandle#element-handle-wait-for-element-state).
#### Browser Versions[](#browser-versions-45 "Direct link to Browser Versions")
* Chromium 90.0.4392.0
* Mozilla Firefox 85.0b5
* WebKit 14.1
Version 1.7[](#version-17 "Direct link to Version 1.7")
--------------------------------------------------------
* **New Java SDK**: [Playwright for Java](https://github.com/microsoft/playwright-java) is now on par with [JavaScript](https://github.com/microsoft/playwright), [Python](https://github.com/microsoft/playwright-python) and [.NET bindings](https://github.com/microsoft/playwright-dotnet).
* **Browser storage API**: New convenience APIs to save and load browser storage state (cookies, local storage) to simplify automation scenarios with authentication.
* **New CSS selectors**: We heard your feedback for more flexible selectors and have revamped the selectors implementation. Playwright 1.7 introduces [new CSS extensions](/python/docs/other-locators#css-locator) and there's more coming soon.
* **New website**: The docs website at [playwright.dev](https://playwright.dev/) has been updated and is now built with [Docusaurus](https://v2.docusaurus.io/).
* **Support for Apple Silicon**: Playwright browser binaries for WebKit and Chromium are now built for Apple Silicon.
#### New APIs[](#new-apis-20 "Direct link to New APIs")
* [browser\_context.storage\_state()](/python/docs/api/class-browsercontext#browser-context-storage-state) to get current state for later reuse.
* `storageState` option in [browser.new\_context()](/python/docs/api/class-browser#browser-new-context) and [browser.new\_page()](/python/docs/api/class-browser#browser-new-page) to setup browser context state.
#### Browser Versions[](#browser-versions-46 "Direct link to Browser Versions")
* Chromium 89.0.4344.0
* Mozilla Firefox 84.0b9
* WebKit 14.1
# Supported languages
Supported languages
===================
Introduction[](#introduction "Direct link to Introduction")
------------------------------------------------------------
Playwright is available in multiple languages that share the same underlying implementation. All core features for automating the browser are supported in all languages, while testing ecosystem integration is different. Pick the language based on your experience, familiarity with its testing ecosystem and your project constraints. For the best experience pick the test runner that we recommend for each language.
JavaScript and TypeScript[](#javascript-and-typescript "Direct link to JavaScript and TypeScript")
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Playwright for Node.js comes with its own [test runner](https://playwright.dev/docs/running-tests) that provides great parallelization mechanism, screenshot assertions, html reporter, automatic tracing etc.
* [Documentation](https://playwright.dev/docs/intro)
* [GitHub repo](https://github.com/microsoft/playwright)
Python[](#python "Direct link to Python")
------------------------------------------
Playwright [Pytest plugin](https://playwright.dev/python/docs/test-runners) is the recommended way to run end-to-end tests. It provides context isolation, running it on multiple browser configurations and more out of the box.
* [Documentation](https://playwright.dev/python/docs/intro)
* [GitHub repo](https://github.com/microsoft/playwright-python)
Java[](#java "Direct link to Java")
------------------------------------
You can choose any testing framework such as JUnit or TestNG based on your project requirements.
* [Documentation](https://playwright.dev/java/docs/intro)
* [GitHub repo](https://github.com/microsoft/playwright-java)
.NET[](#net "Direct link to .NET")
-----------------------------------
Playwright for .NET comes with MSTest, NUnit, xUnit, and xUnit v3 [base classes](https://playwright.dev/dotnet/docs/test-runners) for writing end-to-end tests.
* [Documentation](https://playwright.dev/dotnet/docs/intro)
* [GitHub repo](https://github.com/microsoft/playwright-dotnet)
# Installation
Installation
============
Introduction[](#introduction "Direct link to Introduction")
------------------------------------------------------------
Playwright was created specifically to accommodate the needs of end-to-end testing. Playwright supports all modern rendering engines including Chromium, WebKit, and Firefox. Test on Windows, Linux, and macOS, locally or on CI, headless or headed with native mobile emulation.
The [Playwright library](/python/docs/library) can be used as a general purpose browser automation tool, providing a powerful set of APIs to automate web applications, for both sync and async Python.
This introduction describes the Playwright Pytest plugin, which is the recommended way to write end-to-end tests.
**You will learn**
* [How to install Playwright Pytest](/python/docs/intro#installing-playwright-pytest)
* [How to run the example test](/python/docs/intro#running-the-example-test)
Installing Playwright Pytest[](#installing-playwright-pytest "Direct link to Installing Playwright Pytest")
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Playwright recommends using the official [Playwright Pytest plugin](/python/docs/test-runners) to write end-to-end tests. It provides context isolation, running it on multiple browser configurations out of the box.
Get started by installing Playwright and running the example test to see it in action.
* PyPI
* Anaconda
Install the [Pytest plugin](https://pypi.org/project/pytest-playwright/):
pip install pytest-playwright
Install the [Pytest plugin](https://anaconda.org/Microsoft/pytest-playwright):
conda config --add channels conda-forgeconda config --add channels microsoftconda install pytest-playwright
Install the required browsers:
playwright install
Add Example Test[](#add-example-test "Direct link to Add Example Test")
------------------------------------------------------------------------
Create a file that follows the `test_` prefix convention, such as `test_example.py`, inside the current working directory or in a sub-directory with the code below. Make sure your test name also follows the `test_` prefix convention.
test\_example.py
import refrom playwright.sync_api import Page, expectdef test_has_title(page: Page): page.goto("https://playwright.dev/") # Expect a title "to contain" a substring. expect(page).to_have_title(re.compile("Playwright"))def test_get_started_link(page: Page): page.goto("https://playwright.dev/") # Click the get started link. page.get_by_role("link", name="Get started").click() # Expects page to have a heading with the name of Installation. expect(page.get_by_role("heading", name="Installation")).to_be_visible()
Running the Example Test[](#running-the-example-test "Direct link to Running the Example Test")
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
By default tests will be run on chromium. This can be configured via the [CLI options](/python/docs/running-tests). Tests are run in headless mode meaning no browser UI will open up when running the tests. Results of the tests and test logs will be shown in the terminal.
pytest
Updating Playwright[](#updating-playwright "Direct link to Updating Playwright")
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
To update Playwright to the latest version run the following command:
pip install pytest-playwright playwright -U
System requirements[](#system-requirements "Direct link to System requirements")
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
* Python 3.8 or higher.
* Windows 11+, Windows Server 2019+ or Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL).
* macOS 14 Ventura, or later.
* Debian 12, Debian 13, Ubuntu 22.04, Ubuntu 24.04, on x86-64 and arm64 architecture.
What's next[](#whats-next "Direct link to What's next")
--------------------------------------------------------
* [Write tests using web first assertions, page fixtures and locators](/python/docs/writing-tests)
* [Run single test, multiple tests, headed mode](/python/docs/running-tests)
* [Generate tests with Codegen](/python/docs/codegen)
* [See a trace of your tests](/python/docs/trace-viewer-intro)
# Writing tests
Writing tests
=============
Introduction[](#introduction "Direct link to Introduction")
------------------------------------------------------------
Playwright tests are simple, they
* **perform actions**, and
* **assert the state** against expectations.
There is no need to wait for anything prior to performing an action: Playwright automatically waits for the wide range of [actionability](/python/docs/actionability) checks to pass prior to performing each action.
There is also no need to deal with the race conditions when performing the checks - Playwright assertions are designed in a way that they describe the expectations that need to be eventually met.
That's it! These design choices allow Playwright users to forget about flaky timeouts and racy checks in their tests altogether.
**You will learn**
* [How to write the first test](/python/docs/writing-tests#first-test)
* [How to perform actions](/python/docs/writing-tests#actions)
* [How to use assertions](/python/docs/writing-tests#assertions)
* [How tests run in isolation](/python/docs/writing-tests#test-isolation)
* [How to use test hooks](/python/docs/writing-tests#using-fixtures)
First test[](#first-test "Direct link to First test")
------------------------------------------------------
Take a look at the following example to see how to write a test. Note how the file name follows the `test_` prefix convention as well as each test name.
test\_example.py
import refrom playwright.sync_api import Page, expectdef test_has_title(page: Page): page.goto("https://playwright.dev/") # Expect a title "to contain" a substring. expect(page).to_have_title(re.compile("Playwright"))def test_get_started_link(page: Page): page.goto("https://playwright.dev/") # Click the get started link. page.get_by_role("link", name="Get started").click() # Expects page to have a heading with the name of Installation. expect(page.get_by_role("heading", name="Installation")).to_be_visible()
Actions[](#actions "Direct link to Actions")
---------------------------------------------
### Navigation[](#navigation "Direct link to Navigation")
Most of the tests will start with navigating page to the URL. After that, test will be able to interact with the page elements.
page.goto("https://playwright.dev/")
Playwright will wait for page to reach the load state prior to moving forward. Learn more about the [page.goto()](/python/docs/api/class-page#page-goto) options.
### Interactions[](#interactions "Direct link to Interactions")
Performing actions starts with locating the elements. Playwright uses [Locators API](/python/docs/locators) for that. Locators represent a way to find element(s) on the page at any moment, learn more about the [different types](/python/docs/locators) of locators available. Playwright will wait for the element to be [actionable](/python/docs/actionability) prior to performing the action, so there is no need to wait for it to become available.
# Create a locator.get_started = page.get_by_role("link", name="Get started")# Click it.get_started.click()
In most cases, it'll be written in one line:
page.get_by_role("link", name="Get started").click()
### Basic actions[](#basic-actions "Direct link to Basic actions")
This is the list of the most popular Playwright actions. Note that there are many more, so make sure to check the [Locator API](/python/docs/api/class-locator) section to learn more about them.
Action
Description
[locator.check()](/python/docs/api/class-locator#locator-check)
Check the input checkbox
[locator.click()](/python/docs/api/class-locator#locator-click)
Click the element
[locator.uncheck()](/python/docs/api/class-locator#locator-uncheck)
Uncheck the input checkbox
[locator.hover()](/python/docs/api/class-locator#locator-hover)
Hover mouse over the element
[locator.fill()](/python/docs/api/class-locator#locator-fill)
Fill the form field, input text
[locator.focus()](/python/docs/api/class-locator#locator-focus)
Focus the element
[locator.press()](/python/docs/api/class-locator#locator-press)
Press single key
[locator.set\_input\_files()](/python/docs/api/class-locator#locator-set-input-files)
Pick files to upload
[locator.select\_option()](/python/docs/api/class-locator#locator-select-option)
Select option in the drop down
Assertions[](#assertions "Direct link to Assertions")
------------------------------------------------------
Playwright includes [assertions](/python/docs/test-assertions) that will wait until the expected condition is met. Using these assertions allows making the tests non-flaky and resilient. For example, this code will wait until the page gets the title containing "Playwright":
import refrom playwright.sync_api import expectexpect(page).to_have_title(re.compile("Playwright"))
Here is the list of the most popular async assertions. Note that there are [many more](/python/docs/test-assertions) to get familiar with:
Assertion
Description
[expect(locator).to\_be\_checked()](/python/docs/api/class-locatorassertions#locator-assertions-to-be-checked)
Checkbox is checked
[expect(locator).to\_be\_enabled()](/python/docs/api/class-locatorassertions#locator-assertions-to-be-enabled)
Control is enabled
[expect(locator).to\_be\_visible()](/python/docs/api/class-locatorassertions#locator-assertions-to-be-visible)
Element is visible
[expect(locator).to\_contain\_text()](/python/docs/api/class-locatorassertions#locator-assertions-to-contain-text)
Element contains text
[expect(locator).to\_have\_attribute()](/python/docs/api/class-locatorassertions#locator-assertions-to-have-attribute)
Element has attribute
[expect(locator).to\_have\_count()](/python/docs/api/class-locatorassertions#locator-assertions-to-have-count)
List of elements has given length
[expect(locator).to\_have\_text()](/python/docs/api/class-locatorassertions#locator-assertions-to-have-text)
Element matches text
[expect(locator).to\_have\_value()](/python/docs/api/class-locatorassertions#locator-assertions-to-have-value)
Input element has value
[expect(page).to\_have\_title()](/python/docs/api/class-pageassertions#page-assertions-to-have-title)
Page has title
[expect(page).to\_have\_url()](/python/docs/api/class-pageassertions#page-assertions-to-have-url)
Page has URL
### Test isolation[](#test-isolation "Direct link to Test isolation")
The Playwright Pytest plugin is based on the concept of test fixtures such as the [built in page fixture](/python/docs/test-runners), which is passed into your test. Pages are [isolated between tests due to the Browser Context](/python/docs/browser-contexts), which is equivalent to a brand new browser profile, where every test gets a fresh environment, even when multiple tests run in a single Browser.
test\_example.py
from playwright.sync_api import Pagedef test_example_test(page: Page): pass # "page" belongs to an isolated BrowserContext, created for this specific test.def test_another_test(page: Page): pass # "page" in this second test is completely isolated from the first test.
### Using fixtures[](#using-fixtures "Direct link to Using fixtures")
You can use various [fixtures](https://docs.pytest.org/en/6.2.x/fixture.html#autouse-fixtures-fixtures-you-don-t-have-to-request) to execute code before or after your tests and to share objects between them. A `function` scoped fixture e.g. with autouse behaves like a beforeEach/afterEach. And a `module` scoped fixture with autouse behaves like a beforeAll/afterAll which runs before all and after all the tests.
test\_example.py
import pytestfrom playwright.sync_api import Page, expect@pytest.fixture(scope="function", autouse=True)def before_each_after_each(page: Page): print("before the test runs") # Go to the starting url before each test. page.goto("https://playwright.dev/") yield print("after the test runs")def test_main_navigation(page: Page): # Assertions use the expect API. expect(page).to_have_url("https://playwright.dev/")
What's next[](#whats-next "Direct link to What's next")
--------------------------------------------------------
* [Run single test, multiple tests, headed mode](/python/docs/running-tests)
* [Generate tests with Codegen](/python/docs/codegen-intro)
* [See a trace of your tests](/python/docs/trace-viewer-intro)
* [Run tests on CI with GitHub Actions](/python/docs/ci-intro)
# Generating tests
Generating tests
================
Introduction[](#introduction "Direct link to Introduction")
------------------------------------------------------------
Playwright can generate tests automatically, providing a quick way to get started with testing. Codegen opens a browser window for interaction and the Playwright Inspector for recording, copying, and managing your generated tests.
**You will learn**
* [How to record a test](/python/docs/codegen#recording-a-test)
* [How to generate locators](/python/docs/codegen#generating-locators)
Running Codegen[](#running-codegen "Direct link to Running Codegen")
---------------------------------------------------------------------
Use the `codegen` command to run the test generator followed by the URL of the website you want to generate tests for. The URL is optional and can be added directly in the browser window if omitted.
playwright codegen demo.playwright.dev/todomvc
### Recording a test[](#recording-a-test "Direct link to Recording a test")
Run `codegen` and perform actions in the browser. Playwright generates code for your interactions automatically. Codegen analyzes the rendered page and recommends the best locator, prioritizing role, text, and test id locators. When multiple elements match a locator, the generator improves it to uniquely identify the target element, reducing test failures and flakiness.
With the test generator you can record:
* Actions like click or fill by interacting with the page
* Assertions by clicking a toolbar icon, then clicking a page element to assert against. You can choose:
* `'assert visibility'` to assert that an element is visible
* `'assert text'` to assert that an element contains specific text
* `'assert value'` to assert that an element has a specific value

###### [](#-1 "Direct link to -1")
When you finish interacting with the page, press the `'record'` button to stop recording and use the `'copy'` button to copy the generated code to your editor.
Use the `'clear'` button to clear the code and start recording again. Once finished, close the Playwright Inspector window or stop the terminal command.
To learn more about generating tests, check out our detailed guide on [Codegen](/python/docs/codegen).
### Generating locators[](#generating-locators "Direct link to Generating locators")
You can generate [locators](/python/docs/locators) with the test generator.
* Press the `'Record'` button to stop recording and the `'Pick Locator'` button will appear
* Click the `'Pick Locator'` button and hover over elements in the browser window to see the locator highlighted underneath each element
* Click the element you want to locate and the code for that locator will appear in the locator playground next to the Pick Locator button
* Edit the locator in the locator playground to fine-tune it and see the matching element highlighted in the browser window
* Use the copy button to copy the locator and paste it into your code
###### [](#-2 "Direct link to -2")

### Emulation[](#emulation "Direct link to Emulation")
You can generate tests using emulation for specific viewports, devices, color schemes, geolocation, language, or timezone. The test generator can also preserve authenticated state. Check out the [Test Generator](/python/docs/codegen#emulation) guide to learn more.
What's Next[](#whats-next "Direct link to What's Next")
--------------------------------------------------------
* [See a trace of your tests](/python/docs/trace-viewer-intro)
# Running and debugging tests
Running and debugging tests
===========================
Introduction[](#introduction "Direct link to Introduction")
------------------------------------------------------------
You can run a single test, a set of tests or all tests. Tests can be run on one browser or multiple browsers by using the `--browser` flag. By default, tests are run in a headless manner, meaning no browser window will be opened while running the tests and results will be seen in the terminal. If you prefer, you can run your tests in headed mode by using the `--headed` CLI argument.
**You will learn**
* [How to run tests from the command line](/python/docs/running-tests#command-line)
* [How to debug tests](/python/docs/running-tests#debugging-tests)
Running tests[](#running-tests "Direct link to Running tests")
---------------------------------------------------------------
### Command Line[](#command-line "Direct link to Command Line")
To run your tests, use the `pytest` command. This will run your tests on the Chromium browser by default. Tests run in headless mode by default meaning no browser window will be opened while running the tests and results will be seen in the terminal.
pytest
### Run tests in headed mode[](#run-tests-in-headed-mode "Direct link to Run tests in headed mode")
To run your tests in headed mode, use the `--headed` flag. This will open up a browser window while running your tests and once finished the browser window will close.
pytest --headed
### Run tests on different browsers[](#run-tests-on-different-browsers "Direct link to Run tests on different browsers")
To specify which browser you would like to run your tests on, use the `--browser` flag followed by the name of the browser.
pytest --browser webkit
To specify multiple browsers to run your tests on, use the `--browser` flag multiple times followed by the name of each browser.
pytest --browser webkit --browser firefox
### Run specific tests[](#run-specific-tests "Direct link to Run specific tests")
To run a single test file, pass in the name of the test file that you want to run.
pytest test_login.py
To run a set of test files, pass in the names of the test files that you want to run.
pytest tests/test_todo_page.py tests/test_landing_page.py
To run a specific test, pass in the function name of the test you want to run.
pytest -k test_add_a_todo_item
### Run tests in parallel[](#run-tests-in-parallel "Direct link to Run tests in parallel")
To run your tests in parallel, use the `--numprocesses` flag followed by the number of processes you would like to run your tests on. We recommend half of logical CPU cores.
pytest --numprocesses 2
(This assumes `pytest-xdist` is installed. For more information see [here](/python/docs/test-runners#parallelism-running-multiple-tests-at-once).)
For more information, see [Playwright Pytest usage](/python/docs/test-runners) or the Pytest documentation for [general CLI usage](https://docs.pytest.org/en/stable/usage.html).
Debugging tests[](#debugging-tests "Direct link to Debugging tests")
---------------------------------------------------------------------
Since Playwright runs in Python, you can debug it with your debugger of choice, e.g., with the [Python extension](https://code.visualstudio.com/docs/python/python-tutorial) in Visual Studio Code. Playwright comes with the Playwright Inspector which allows you to step through Playwright API calls, see their debug logs and explore [locators](/python/docs/locators).
To debug all tests, run the following command.
* Bash
* PowerShell
* Batch
PWDEBUG=1 pytest -s
$env:PWDEBUG=1pytest -s
set PWDEBUG=1pytest -s
To debug one test file, run the command followed by the name of the test file that you want to debug.
* Bash
* PowerShell
* Batch
PWDEBUG=1 pytest -s test_example.py
$env:PWDEBUG=1pytest -s test_example.py
set PWDEBUG=1pytest -s test_example.py
To debug a specific test, add `-k` followed by the name of the test that you want to debug.
* Bash
* PowerShell
* Batch
PWDEBUG=1 pytest -s -k test_get_started_link
$env:PWDEBUG=1pytest -s -k test_get_started_link
set PWDEBUG=1pytest -s -k test_get_started_link
This command will open up a Browser window as well as the Playwright Inspector. You can use the step over button at the top of the inspector to step through your test. Or press the play button to run your test from start to finish. Once the test has finished, the browser window will close.
While debugging you can use the Pick Locator button to select an element on the page and see the locator that Playwright would use to find that element. You can also edit the locator and see it highlighting live on the Browser window. Use the Copy Locator button to copy the locator to your clipboard and then paste it into your test.
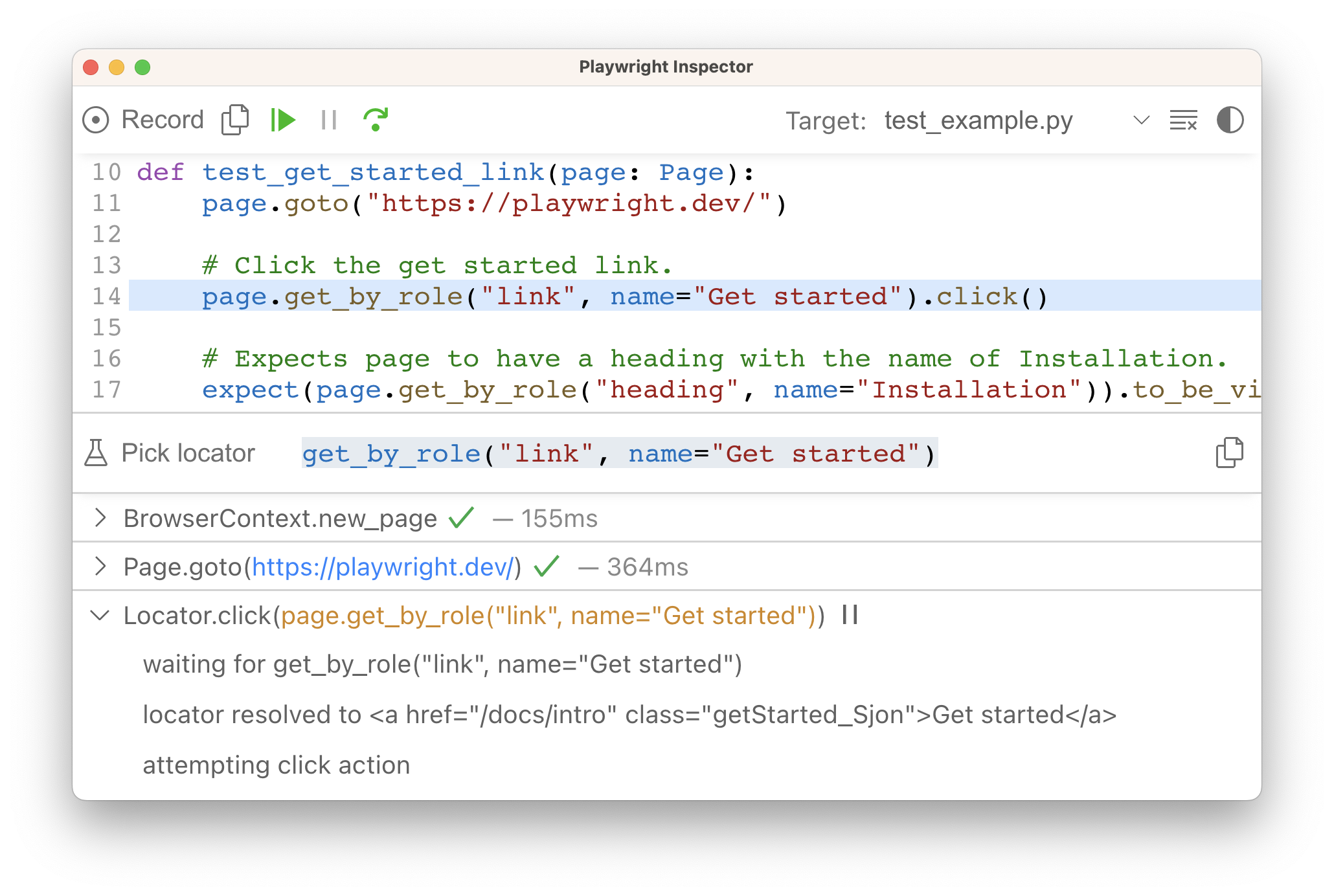
Check out our [debugging guide](/python/docs/debug) to learn more about the [Playwright Inspector](/python/docs/debug#playwright-inspector) as well as debugging with [Browser Developer tools](/python/docs/debug#browser-developer-tools).
What's next[](#whats-next "Direct link to What's next")
--------------------------------------------------------
* [Generate tests with Codegen](/python/docs/codegen)
* [See a trace of your tests](/python/docs/trace-viewer-intro)
* [Run your tests on CI with GitHub Actions](/python/docs/ci-intro)
# Trace viewer
Trace viewer
============
Introduction[](#introduction "Direct link to Introduction")
------------------------------------------------------------
Playwright Trace Viewer is a GUI tool that lets you explore recorded Playwright traces of your tests meaning you can go back and forward though each action of your test and visually see what was happening during each action.
**You will learn**
* How to record a trace
* How to open the trace viewer
Recording a trace[](#recording-a-trace "Direct link to Recording a trace")
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
Traces can be recorded by running your tests with the `--tracing` flag.
pytest --tracing on
Options for tracing are:
* `on`: Record trace for each test
* `off`: Do not record trace. (default)
* `retain-on-failure`: Record trace for each test, but remove all traces from successful test runs.
This will record the trace and place it into the file named `trace.zip` in your `test-results` directory.
If you are not using Pytest, click here to learn how to record traces.
* Sync
* Async
browser = chromium.launch()context = browser.new_context()# Start tracing before creating / navigating a page.context.tracing.start(screenshots=True, snapshots=True, sources=True)page = context.new_page()page.goto("https://playwright.dev")# Stop tracing and export it into a zip archive.context.tracing.stop(path = "trace.zip")
browser = await chromium.launch()context = await browser.new_context()# Start tracing before creating / navigating a page.await context.tracing.start(screenshots=True, snapshots=True, sources=True)page = await context.new_page()await page.goto("https://playwright.dev")# Stop tracing and export it into a zip archive.await context.tracing.stop(path = "trace.zip")
Opening the trace[](#opening-the-trace "Direct link to Opening the trace")
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
You can open the saved trace using the Playwright CLI or in your browser on [`trace.playwright.dev`](https://trace.playwright.dev). Make sure to add the full path to where your trace's zip file is located. Once opened you can click on each action or use the timeline to see the state of the page before and after each action. You can also inspect the log, source and network during each step of the test. The trace viewer creates a DOM snapshot so you can fully interact with it, open devtools etc.
playwright show-trace trace.zip

To learn more check out our detailed guide on [Trace Viewer](/python/docs/trace-viewer).
What's next[](#whats-next "Direct link to What's next")
--------------------------------------------------------
* [Run tests on CI with GitHub Actions](/python/docs/ci-intro)
* [Learn more about Trace Viewer](/python/docs/trace-viewer)
# Setting up CI
Setting up CI
=============
Introduction[](#introduction "Direct link to Introduction")
------------------------------------------------------------
Playwright tests can be run on any CI provider. In this section we cover running tests on GitHub using GitHub Actions. If you would like to see how to configure other CI providers, check out our detailed [doc on Continuous Integration](/python/docs/ci).
#### You will learn[](#you-will-learn "Direct link to You will learn")
* [How to set up GitHub Actions](/python/docs/ci-intro#setting-up-github-actions)
* [How to view test logs](/python/docs/ci-intro#viewing-test-logs)
* [How to view the trace](/python/docs/ci-intro#viewing-the-trace)
Setting up GitHub Actions[](#setting-up-github-actions "Direct link to Setting up GitHub Actions")
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
To add a [GitHub Actions](https://docs.github.com/en/actions) file, first create `.github/workflows` folder and inside it add a `playwright.yml` file containing the example code below so that your tests run on each push and pull request for the main/master branch.
.github/workflows/playwright.yml
name: Playwright Testson: push: branches: [ main, master ] pull_request: branches: [ main, master ]jobs: test: timeout-minutes: 60 runs-on: ubuntu-latest steps: - uses: actions/checkout@v5 - name: Set up Python uses: actions/setup-python@v6 with: python-version: '3.13' - name: Install dependencies run: | python -m pip install --upgrade pip pip install -r requirements.txt - name: Ensure browsers are installed run: python -m playwright install --with-deps - name: Run your tests run: pytest --tracing=retain-on-failure - uses: actions/upload-artifact@v4 if: ${{ !cancelled() }} with: name: playwright-traces path: test-results/
To learn more about this, see ["Understanding GitHub Actions"](https://docs.github.com/en/actions/learn-github-actions/understanding-github-actions).
Looking at the list of steps in `jobs.test.steps`, you can see that the workflow performs these steps:
1. Clone your repository
2. Install language dependencies
3. Install project dependencies and build
4. Install Playwright Browsers
5. Run tests
Create a Repo and Push to GitHub[](#create-a-repo-and-push-to-github "Direct link to Create a Repo and Push to GitHub")
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Once you have your [GitHub Actions workflow](#setting-up-github-actions) setup, then all you need to do is [Create a repo on GitHub](https://docs.github.com/en/get-started/quickstart/create-a-repo) or push your code to an existing repository. Follow the instructions on GitHub and don't forget to [initialize a git repository](https://github.com/git-guides/git-init) using the `git init` command so you can [add](https://github.com/git-guides/git-add), [commit](https://github.com/git-guides/git-commit), and [push](https://github.com/git-guides/git-push) your code.
Opening the Workflows[](#opening-the-workflows "Direct link to Opening the Workflows")
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Click on the **Actions** tab to see the workflows. Here you see if your tests have passed or failed.
###### [](#-1 "Direct link to -1")
Viewing Test Logs[](#viewing-test-logs "Direct link to Viewing Test Logs")
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
Clicking on the workflow run shows you all the actions that GitHub performed and clicking on **Run Playwright tests** shows the error messages, what was expected and what was received as well as the call log.
###### [](#-2 "Direct link to -2")

Viewing the Trace[](#viewing-the-trace "Direct link to Viewing the Trace")
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
[trace.playwright.dev](https://trace.playwright.dev) is a statically hosted variant of the Trace Viewer. You can upload trace files using drag and drop.

Properly handling Secrets[](#properly-handling-secrets "Direct link to Properly handling Secrets")
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Artifacts like trace files or console logs contain information about your test execution. They can contain sensitive data like user credentials for a test user, access tokens to a staging backend, testing source code, or sometimes even your application source code. Treat these files just as carefully as you treat that sensitive data. If you upload reports and traces as part of your CI workflow, make sure that you only upload them to trusted artifact stores, or that you encrypt the files before upload. The same is true for sharing artifacts with team members: Use a trusted file share or encrypt the files before sharing.
What's Next[](#whats-next "Direct link to What's Next")
--------------------------------------------------------
* [Learn how to use Locators](/python/docs/locators)
* [Learn how to perform Actions](/python/docs/input)
* [Learn how to write Assertions](/python/docs/test-assertions)
* [Learn more about the Trace Viewer](/python/docs/trace-viewer)
* [Learn more ways of running tests on GitHub Actions](/python/docs/ci#github-actions)
* [Learn more about running tests on other CI providers](/python/docs/ci)
# Pytest Plugin Reference
Pytest Plugin Reference
=======================
Introduction[](#introduction "Direct link to Introduction")
------------------------------------------------------------
Playwright provides a [Pytest](https://docs.pytest.org/en/stable/) plugin to write end-to-end tests. To get started with it, refer to the [getting started guide](/python/docs/intro).
Usage[](#usage "Direct link to Usage")
---------------------------------------
To run your tests, use [Pytest](https://docs.pytest.org/en/stable/) CLI.
pytest --browser webkit --headed
If you want to add the CLI arguments automatically without specifying them, you can use the [pytest.ini](https://docs.pytest.org/en/stable/reference.html#ini-options-ref) file:
# content of pytest.ini[pytest]# Run firefox with UIaddopts = --headed --browser firefox
CLI arguments[](#cli-arguments "Direct link to CLI arguments")
---------------------------------------------------------------
Note that CLI arguments are only applied to the default `browser`, `context` and `page` fixtures. If you create a browser, a context or a page with the API call like [browser.new\_context()](/python/docs/api/class-browser#browser-new-context), the CLI arguments are not applied.
* `--headed`: Run tests in headed mode (default: headless).
* `--browser`: Run tests in a different browser `chromium`, `firefox`, or `webkit`. It can be specified multiple times (default: `chromium`).
* `--browser-channel` [Browser channel](/python/docs/browsers) to be used.
* `--slowmo` Slows down Playwright operations by the specified amount of milliseconds. Useful so that you can see what is going on (default: 0).
* `--device` [Device](/python/docs/emulation) to be emulated.
* `--output` Directory for artifacts produced by tests (default: `test-results`).
* `--tracing` Whether to record a [trace](/python/docs/trace-viewer) for each test. `on`, `off`, or `retain-on-failure` (default: `off`).
* `--video` Whether to record video for each test. `on`, `off`, or `retain-on-failure` (default: `off`).
* `--screenshot` Whether to automatically capture a screenshot after each test. `on`, `off`, or `only-on-failure` (default: `off`).
* `--full-page-screenshot` Whether to take a full page screenshot on failure. By default, only the viewport is captured. Requires `--screenshot` to be enabled (default: `off`).
Fixtures[](#fixtures "Direct link to Fixtures")
------------------------------------------------
This plugin configures Playwright-specific [fixtures for pytest](https://docs.pytest.org/en/latest/fixture.html). To use these fixtures, use the fixture name as an argument to the test function.
def test_my_app_is_working(fixture_name): pass # Test using fixture_name # ...
**Function scope**: These fixtures are created when requested in a test function and destroyed when the test ends.
* `context`: New [browser context](/python/docs/browser-contexts) for a test.
* `page`: New [browser page](/python/docs/pages) for a test.
* `new_context`: Allows creating different [browser contexts](/python/docs/browser-contexts) for a test. Useful for multi-user scenarios. Accepts the same parameters as [browser.new\_context()](/python/docs/api/class-browser#browser-new-context).
**Session scope**: These fixtures are created when requested in a test function and destroyed when all tests end.
* `playwright`: [Playwright](/python/docs/api/class-playwright) instance.
* `browser_type`: [BrowserType](/python/docs/api/class-browsertype) instance of the current browser.
* `browser`: [Browser](/python/docs/api/class-browser) instance launched by Playwright.
* `browser_name`: Browser name as string.
* `browser_channel`: Browser channel as string.
* `is_chromium`, `is_webkit`, `is_firefox`: Booleans for the respective browser types.
**Customizing fixture options**: For `browser` and `context` fixtures, use the following fixtures to define custom launch options.
* `browser_type_launch_args`: Override launch arguments for [browser\_type.launch()](/python/docs/api/class-browsertype#browser-type-launch). It should return a Dict.
* `browser_context_args`: Override the options for [browser.new\_context()](/python/docs/api/class-browser#browser-new-context). It should return a Dict.
* `connect_options`: Connect to an existing browser via WebSocket endpoint. It should return a Dict with [browser\_type.connect()](/python/docs/api/class-browsertype#browser-type-connect) options.
Its also possible to override the context options ([browser.new\_context()](/python/docs/api/class-browser#browser-new-context)) for a single test by using the `browser_context_args` marker:
import pytest@pytest.mark.browser_context_args(timezone_id="Europe/Berlin", locale="en-GB")def test_browser_context_args(page): assert page.evaluate("window.navigator.userAgent") == "Europe/Berlin" assert page.evaluate("window.navigator.languages") == ["de-DE"]
Parallelism: Running Multiple Tests at Once[](#parallelism-running-multiple-tests-at-once "Direct link to Parallelism: Running Multiple Tests at Once")
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
If your tests are running on a machine with a lot of CPUs, you can speed up the overall execution time of your test suite by using [`pytest-xdist`](https://pypi.org/project/pytest-xdist/) to run multiple tests at once:
# install dependencypip install pytest-xdist# use the --numprocesses flagpytest --numprocesses auto
Depending on the hardware and nature of your tests, you can set `numprocesses` to be anywhere from `2` to the number of CPUs on the machine. If set too high, you may notice unexpected behavior.
See [Running Tests](/python/docs/running-tests) for general information on `pytest` options.
Examples[](#examples "Direct link to Examples")
------------------------------------------------
### Configure typings for auto-completion[](#configure-typings-for-auto-completion "Direct link to Configure typings for auto-completion")
test\_my\_application.py
from playwright.sync_api import Pagedef test_visit_admin_dashboard(page: Page): page.goto("/admin") # ...
If you're using VSCode with Pylance, these types can be inferred by enabling the `python.testing.pytestEnabled` setting so you don't need the type annotation.
### Using multiple contexts[](#using-multiple-contexts "Direct link to Using multiple contexts")
In order to simulate multiple users, you can create multiple [`BrowserContext`](/python/docs/browser-contexts) instances.
test\_my\_application.py
from playwright.sync_api import Page, BrowserContextfrom pytest_playwright.pytest_playwright import CreateContextCallbackdef test_foo(page: Page, new_context: CreateContextCallback) -> None: page.goto("https://example.com") context = new_context() page2 = context.new_page() # page and page2 are in different contexts
### Skip test by browser[](#skip-test-by-browser "Direct link to Skip test by browser")
test\_my\_application.py
import pytest@pytest.mark.skip_browser("firefox")def test_visit_example(page): page.goto("https://example.com") # ...
### Run on a specific browser[](#run-on-a-specific-browser "Direct link to Run on a specific browser")
conftest.py
import pytest@pytest.mark.only_browser("chromium")def test_visit_example(page): page.goto("https://example.com") # ...
### Run with a custom browser channel like Google Chrome or Microsoft Edge[](#run-with-a-custom-browser-channel-like-google-chrome-or-microsoft-edge "Direct link to Run with a custom browser channel like Google Chrome or Microsoft Edge")
pytest --browser-channel chrome
test\_my\_application.py
def test_example(page): page.goto("https://example.com")
### Configure base-url[](#configure-base-url "Direct link to Configure base-url")
Start Pytest with the `base-url` argument. The [`pytest-base-url`](https://github.com/pytest-dev/pytest-base-url) plugin is used for that which allows you to set the base url from the config, CLI arg or as a fixture.
pytest --base-url http://localhost:8080
test\_my\_application.py
def test_visit_example(page): page.goto("/admin") # -> Will result in http://localhost:8080/admin
### Ignore HTTPS errors[](#ignore-https-errors "Direct link to Ignore HTTPS errors")
conftest.py
import pytest@pytest.fixture(scope="session")def browser_context_args(browser_context_args): return { **browser_context_args, "ignore_https_errors": True }
### Use custom viewport size[](#use-custom-viewport-size "Direct link to Use custom viewport size")
conftest.py
import pytest@pytest.fixture(scope="session")def browser_context_args(browser_context_args): return { **browser_context_args, "viewport": { "width": 1920, "height": 1080, } }
### Device emulation / BrowserContext option overrides[](#device-emulation--browsercontext-option-overrides "Direct link to Device emulation / BrowserContext option overrides")
conftest.py
import pytest@pytest.fixture(scope="session")def browser_context_args(browser_context_args, playwright): iphone_11 = playwright.devices['iPhone 11 Pro'] return { **browser_context_args, **iphone_11, }
Or via the CLI `--device="iPhone 11 Pro"`
### Connect to remote browsers[](#connect-to-remote-browsers "Direct link to Connect to remote browsers")
conftest.py
import pytest@pytest.fixture(scope="session")def connect_options(): return { "wsEndpoint": "ws://localhost:8080/ws" }
### Using with `unittest.TestCase`[](#using-with-unittesttestcase "Direct link to using-with-unittesttestcase")
See the following example for using it with `unittest.TestCase`. This has a limitation, that only a single browser can be specified and no matrix of multiple browsers gets generated when specifying multiple.
import pytestimport unittestfrom playwright.sync_api import Pageclass MyTest(unittest.TestCase): @pytest.fixture(autouse=True) def setup(self, page: Page): self.page = page def test_foobar(self): self.page.goto("https://microsoft.com") self.page.locator("#foobar").click() assert self.page.evaluate("1 + 1") == 2
Debugging[](#debugging "Direct link to Debugging")
---------------------------------------------------
### Use with pdb[](#use-with-pdb "Direct link to Use with pdb")
Use the `breakpoint()` statement in your test code to pause execution and get a [pdb](https://docs.python.org/3/library/pdb.html) REPL.
def test_bing_is_working(page): page.goto("https://bing.com") breakpoint() # ...
Deploy to CI[](#deploy-to-ci "Direct link to Deploy to CI")
------------------------------------------------------------
See the [guides for CI providers](/python/docs/ci) to deploy your tests to CI/CD.
Async Fixtures[](#async-fixtures "Direct link to Async Fixtures")
------------------------------------------------------------------
To use async fixtures, install [`pytest-playwright-asyncio`](https://pypi.org/project/pytest-playwright-asyncio/).
Ensure you are using `pytest-asyncio>=0.26.0` and set [`asyncio_default_test_loop_scope = session`](https://pytest-asyncio.readthedocs.io/en/v0.26.0/how-to-guides/change_default_test_loop.html) in your configuration (`pytest.ini/pyproject.toml/setup.cfg`).
import pytestfrom playwright.async_api import Page@pytest.mark.asyncio(loop_scope="session")async def test_foo(page: Page): await page.goto("https://github.com") # ...
# Actions
Actions
=======
Introduction[](#introduction "Direct link to Introduction")
------------------------------------------------------------
Playwright can interact with HTML Input elements such as text inputs, checkboxes, radio buttons, select options, mouse clicks, type characters, keys and shortcuts as well as upload files and focus elements.
Text input[](#text-input "Direct link to Text input")
------------------------------------------------------
Using [locator.fill()](/python/docs/api/class-locator#locator-fill) is the easiest way to fill out the form fields. It focuses the element and triggers an `input` event with the entered text. It works for `