| k-Wave Toolbox |
 
|
| On this page… |
|---|
|
Running simulations using the C++ code Reloading the output data into MATLAB |
This example demonstrates how to use the C++ versions of kspaceFirstOrder3D. Before use, the appropriate C++ codes must be downloaded from http://www.k-wave.org/download.php and placed in the binaries folder of the toolbox.
MATLAB is a very powerful environment for scientific computing. It interfaces with a number of highly-optimised matrix and maths libraries, and can be programmed using relatively simple syntax. User written MATLAB code is also highly portable across operating systems and computer platforms. The portability comes from MATLAB being an interpreted language. This means the code is analysed and executed line by line as the program runs, without needing to be compiled into machine code in advance. In most situations, this means the k-Wave Toolbox works straight out of the (virtual) box on any computer installed with MATLAB.
The downside of MATLAB being an interpreted language is that it can be difficult to optimise user code. Within the main time loop of the k-Wave simulation functions, the code consists primarily of FFTs and element-wise matrix operations like multiplication and addition. Executing these tasks involves a large number of memory operations for relatively few compute operations. For example, to multiply two matrices together element by element, the individual matrix elements are transferred from main memory to cache in blocks, multiplied together using the CPU, and then the results transferred back to main memory. If the matrix elements were already stored in cache, the multiplication would be an order of magnitude faster. However, because the lines of code in MATLAB are executed independently, there is no way in MATLAB to fuse together multiple operations to maximise the temporal and spatial locality of the data.
For simulations using small grid sizes, the compute times are short enough that the drawbacks of MATLAB being an interpreted language are not a concern. However, for simulations using large grid sizes (for example, 512 by 512 by 512), the compute times in MATLAB can stretch into tens of hours. To reduce these compute times, k-Wave also includes optimised versions of kspaceFirstOrder3D written in C++ . The code for desktop computers and servers is called kspaceFirstOrder3D-OMP. This is optimised for shared memory computer architectures, including machines with multiple CPUs based on a non-uniform memory access (NUMA) design. The code for NVIDIA graphics processing units (GPUs) is called kspaceFirstOrder3D-CUDA.
The C++ code has been designed as a standalone application that can be used completely independently of MATLAB. This is important when using computers and servers that do not have MATLAB support. For this reason, simulation data must be transferred between MATLAB and the C++ code using external input and output files. These files are stored using the Hierarchical Data Format HDF5. The input file defines the properties of the grid, medium, source, and sensor in the same way as the input files passed to the MATLAB code. The output file contains the recorded simulation data along with performance statistics like the compute time and memory usage. A more detailed discussion of the file format and properties is given in the k-Wave manual.
Although the required input file may be created using C++ or any programming language that supports HDF5, for most users it will be easiest to use the MATLAB function kspaceFirstOrder3D to create the input matrices and save them to disk in the required format (note, this requires MATLAB 2011a or later). The HDF5 input file is automatically generated by adding the flag 'SaveToDisk' and a filename (or pathname and filename) to the optional input arguments as shown below. When this flag is given, the MATLAB code runs the preprocessing steps, saves the input parameters to disk, and then aborts without running the actual simulation (set example_number = 1 within the example m-file).
% save input files to disk filename = 'example_input.h5'; kspaceFirstOrder3D(kgrid, medium, source, sensor, 'SaveToDisk', filename);
After saving the input data, the compiled C++ code kspaceFirstOrder3D-OMP can be called from a terminal window or the command prompt. The code requires two command line parameters to specify the input and output files, in addition to a number of optional parameters and flags (a full list is given in the k-Wave manual). For example, assuming the input file is located in a root folder called data, in Linux, the C++ code can be run from a terminal window using the syntax
./kspaceFirstOrder3D-OMP -i /data/example_input.h5 -o /data/example_output.h5
Similarly, in Windows, the C++ code can be run from the command prompt using the syntax
kspaceFirstOrder3D-OMP.exe -i C:\data\example_input.h5 -o C:\data\example_output.h5
By default, the time varying pressure at the grid points specified by the sensor mask are recorded during the simulation. When using the MATLAB code, it is possible to control the acoustic variables that are recorded during the simulation by setting the value of sensor.record. For the C++ code, the same behaviour is achieved using additional command line parameters (a full list is given in the k-Wave manual). For example, the final pressure field and the particle velocity can be recorded using the syntax
./kspaceFirstOrder3D-OMP -i /data/example_input.h5 -o /data/example_output.h5 --p_final --p_maxAs the code runs, status updates and computational parameters are printed to the command line.
--------------------------------
kspaceFirstOrder3D-OMP v1.1
--------------------------------
Number of CPU threads: 8
Domain dims: [ 256, 128, 64]
Simulation time steps: 1200
--------------------------------
........ Initialization ........
Memory allocation ..........Done
Data loading................Done
Elapsed time: 0.06s
--------------------------------
.......... Computation .........
FFT plans creation..........Done
Pre-processing phase........Done
Current memory in use: 203MB
Elapsed time: 1.05s
-------------------------------------------------------------
....................... Simulation ..........................
Progress...ElapsedTime........TimeToGo......TimeOfTermination
0% 0.139s 83.209s 12/02/14 09:33:20
5% 4.173s 77.919s 12/02/14 09:33:18
10% 8.309s 74.099s 12/02/14 09:33:19
15% 12.653s 71.234s 12/02/14 09:33:20
20% 17.366s 69.102s 12/02/14 09:33:23
25% 21.973s 65.338s 12/02/14 09:33:24
30% 26.465s 61.508s 12/02/14 09:33:24
35% 31.593s 58.244s 12/02/14 09:33:26
40% 36.173s 54.071s 12/02/14 09:33:27
45% 40.353s 48.989s 12/02/14 09:33:25
50% 44.740s 44.443s 12/02/14 09:33:25
55% 48.872s 39.718s 12/02/14 09:33:25
60% 52.912s 35.152s 12/02/14 09:33:25
65% 57.318s 30.638s 12/02/14 09:33:24
70% 61.657s 26.215s 12/02/14 09:33:24
75% 66.055s 21.823s 12/02/14 09:33:24
80% 70.324s 17.489s 12/02/14 09:33:24
85% 75.571s 13.249s 12/02/14 09:33:25
90% 80.071s 8.732s 12/02/14 09:33:25
95% 84.736s 4.304s 12/02/14 09:33:25
-------------------------------------------------------------
Elapsed time: 88.73s
-------------------------------------------------------------
Post-processing phase.......Done
Elapsed time: 0.24s
--------------------------------
............ Summary ...........
Peak memory in use: 205MB
Total execution time: 90.28s
--------------------------------
End of computation
--------------------------------
After the C++ code has executed, the output files can be reloaded into MATLAB using the function h5read (set example_number = 2 within the example m-file, ensuring that the path to the output file is correct). The variables stored in the HDF5 output file have the identical names to the MATLAB code. For example, for a simulation run with the --p_final and --p_max flags, equivalent to setting sensor.record = {'p_final', 'p_max'}, the output data can be loaded into MATLAB as shown below.
% load output data from the C++ simulation
sensor_data.p_final = h5read('example_output.h5', '/p_final');
sensor_data.p_max = h5read('example_output.h5', '/p_max');
For the simulation in the example file, the source is a square piston driven by a continuous wave, and the medium has a heterogeneous inclusion in the beam path. The expected output from the simulation is shown below.
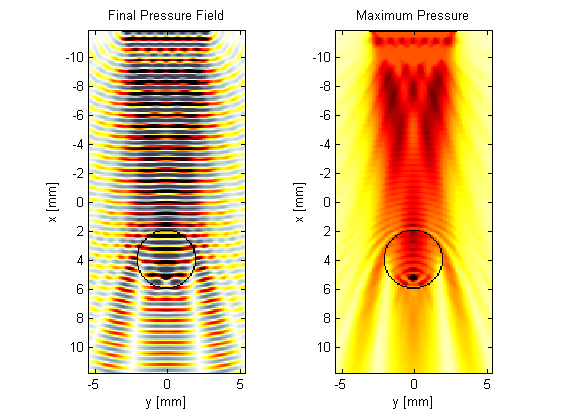
Note, not all simulation options are currently supported by the C++ code. The sensor mask must be given as a binary matrix or a list of cuboid corners (Cartesian sensor masks are not supported), and all display parameters are ignored as the C++ code does not have a graphical output. Moreover, if using a Transducer as the sensor (e.g., as used in the Simulating B-mode Ultrasound Images Example), the returned sensor data will be different to the MATLAB code. This is because the C++ code returns the time series recorded at each grid point, rather than averaged across each physical sensor element. The C++ sensor data can be converted to the MATLAB format using the combine_sensor_data method of the kWaveTransducer class.
sensor_data = transducer.combine_sensor_data(sensor_data)
In addition to calling the C++ code from a terminal or command window, it is also possible to run the C++ code directly from MATLAB. To run the code blindly, calls to kspaceFirstOrder3D can be directly substituted with calls to kspaceFirstOrder3DC without any other changes (set example_number = 3 within the example m-file). This function automatically adds the 'SaveToDisk' flag, calls kspaceFirstOrder3D to create the input variables, calls the C++ code using the computer command, reloads the output variables from disk using h5read, then deletes the input and output files. This is useful when running MATLAB interactively. The disadvantage of running the C++ code from within MATLAB is the additional memory footprint of having many variables allocated in memory twice, as well as the overhead of running MATLAB.
In addition to the CPU code, k-Wave also includes an optimised C++/CUDA code for running simulations on graphics processing units (GPUs). The code is called kspaceFirstOrder3D-CUDA and is used in the identical way to kspaceFirstOrder3D-OMP. The code requires a CUDA-enabled NVIDIA GPU with a minimum compute capability of 1.3 and a recent NVIDIA driver. To run the code directly from MATLAB, calls to kspaceFirstOrder3D can be directly substituted with calls to kspaceFirstOrder3DG (set example_number = 4 within the example m-file).
 |
Using the C++ Code | Saving Input Files In Parts |  |
© 2009-2014 Bradley Treeby and Ben Cox.