| k-Wave Toolbox |
 
|
Shift time series to and from staggered temporal grid
data = timeShift(data, dt) data = timeShift(data, dt, true) data = timeShift(data, dt, false)
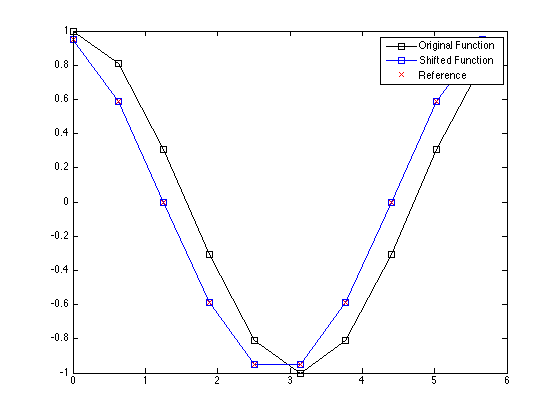
timeShift shifts an input time series (or 2D array of time series) to and from a staggered temporal grid using Fourier interpolation. If the input data is defined as a 2D array of time series, the temporal shift is performed along the second dimension assuming that the array is indexed as (n, t). This function can be used to shift the acoustic particle velocity recorded by the first-order simulation functions to the regular (non-staggered) temporal grid. An example of shifting a discretely sampled cosine is given below.
dt = pi/5;
t = 0:dt:(2*pi - dt);
y = cos(t);
y_shift = timeShift(y, dt);
y_ref = cos(t + dt/2);
plot(t, y, 'k-s', t, y_shift, 'b-s', t, y_ref, 'rx');
legend('Original Function', 'Shifted Function', 'Reference');
|
1D or 2D input data, for 2D input data, the time shift is performed along the second dimension |
|
time step [s] |
|
Boolean controlling whether the time series is shifted forward or backward in time (default = |
|
shifted time series |
gradientSpect, kspaceFirstOrder1D, kspaceFirstOrder2D, kspaceFirstOrder3D, pstdElastic2D, pstdElastic3D
 |
stackedPlot | toneBurst |  |
© 2009-2014 Bradley Treeby and Ben Cox.