# 经典数组技巧:前缀和数组




**通知:算法可视化编辑器上线,[点击体验](https://labuladong.online/algo/intro/visualize/)!另外,建议你在我的 [网站](https://labuladong.online/algo/) 学习文章,体验更好。**
读完本文,你不仅学会了算法套路,还可以顺便解决如下题目:
| LeetCode | 力扣 | 难度 |
| :----: | :----: | :----: |
| [303. Range Sum Query - Immutable](https://leetcode.com/problems/range-sum-query-immutable/) | [303. 区域和检索 - 数组不可变](https://leetcode.cn/problems/range-sum-query-immutable/) | 🟢
| [304. Range Sum Query 2D - Immutable](https://leetcode.com/problems/range-sum-query-2d-immutable/) | [304. 二维区域和检索 - 矩阵不可变](https://leetcode.cn/problems/range-sum-query-2d-immutable/) | 🟠
| - | [剑指 Offer II 013. 二维子矩阵的和](https://leetcode.cn/problems/O4NDxx/) | 🟠
**-----------**
> tip:本文有视频版:[前缀和/差分数组技巧精讲](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1NY4y1J7xQ/)。建议关注我的 B 站账号,我会用视频领读的方式带大家学习那些稍有难度的算法技巧。
前缀和技巧适用于快速、频繁地计算一个索引区间内的元素之和。
### 一维数组中的前缀和
先看一道例题,力扣第 303 题「区域和检索 - 数组不可变」,让你计算数组区间内元素的和,这是一道标准的前缀和问题:
题目要求你实现这样一个类:
```java
class NumArray {
public NumArray(int[] nums) {}
/* 查询闭区间 [left, right] 的累加和 */
public int sumRange(int left, int right) {}
}
```
`sumRange` 函数需要计算并返回一个索引区间之内的元素和,没学过前缀和的人可能写出如下代码:
```java
class NumArray {
private int[] nums;
public NumArray(int[] nums) {
this.nums = nums;
}
public int sumRange(int left, int right) {
int res = 0;
for (int i = left; i <= right; i++) {
res += nums[i];
}
return res;
}
}
```
这样,可以达到效果,但是效率很差,因为 `sumRange` 方法会被频繁调用,而它的时间复杂度是 `O(N)`,其中 `N` 代表 `nums` 数组的长度。
这道题的最优解法是使用前缀和技巧,将 `sumRange` 函数的时间复杂度降为 `O(1)`,说白了就是不要在 `sumRange` 里面用 for 循环,咋整?
直接看代码实现:
```java
class NumArray {
// 前缀和数组
private int[] preSum;
/* 输入一个数组,构造前缀和 */
public NumArray(int[] nums) {
// preSum[0] = 0,便于计算累加和
preSum = new int[nums.length + 1];
// 计算 nums 的累加和
for (int i = 1; i < preSum.length; i++) {
preSum[i] = preSum[i - 1] + nums[i - 1];
}
}
/* 查询闭区间 [left, right] 的累加和 */
public int sumRange(int left, int right) {
return preSum[right + 1] - preSum[left];
}
}
```
核心思路是我们 new 一个新的数组 `preSum` 出来,`preSum[i]` 记录 `nums[0..i-1]` 的累加和,看图 10 = 3 + 5 + 2:
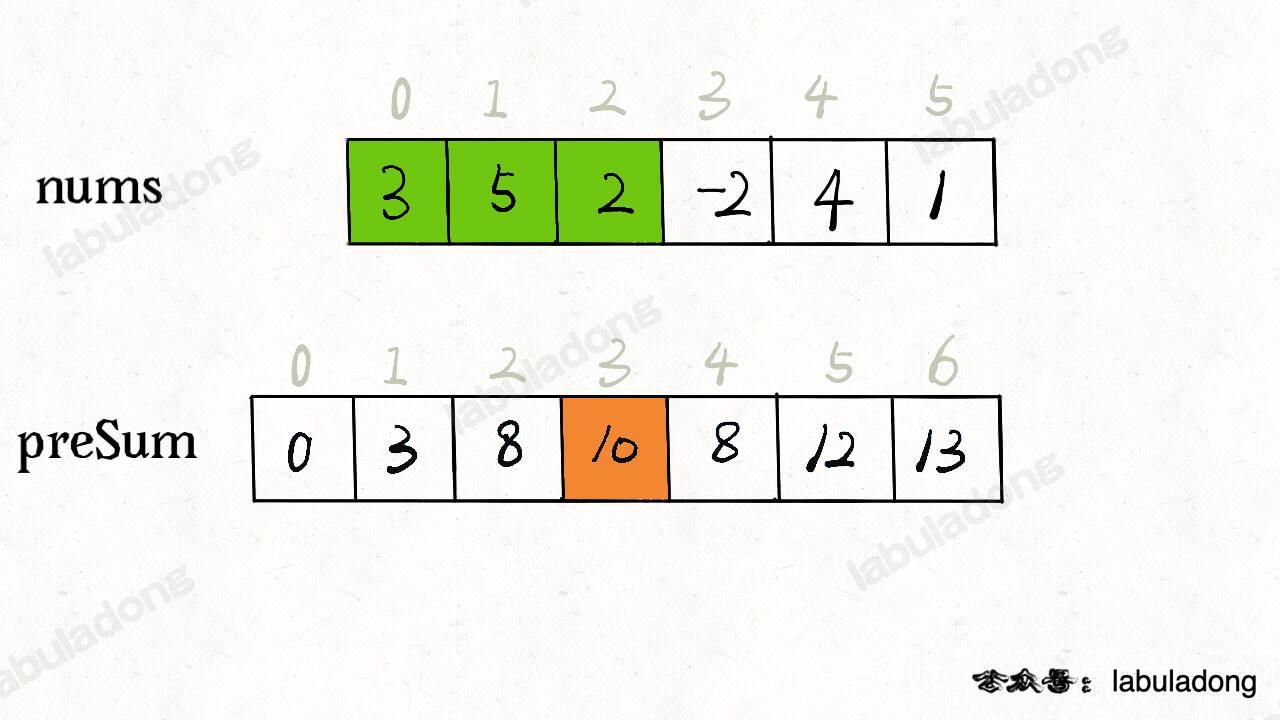
看这个 `preSum` 数组,如果我想求索引区间 `[1, 4]` 内的所有元素之和,就可以通过 `preSum[5] - preSum[1]` 得出。
这样,`sumRange` 函数仅仅需要做一次减法运算,避免了每次进行 for 循环调用,最坏时间复杂度为常数 `O(1)`。
这个技巧在生活中运用也挺广泛的,比方说,你们班上有若干同学,每个同学有一个期末考试的成绩(满分 100 分),那么请你实现一个 API,输入任意一个分数段,返回有多少同学的成绩在这个分数段内。
那么,你可以先通过计数排序的方式计算每个分数具体有多少个同学,然后利用前缀和技巧来实现分数段查询的 API:
```java
int[] scores; // 存储着所有同学的分数
// 试卷满分 100 分
int[] count = new int[100 + 1]
// 记录每个分数有几个同学
for (int score : scores)
count[score]++
// 构造前缀和
for (int i = 1; i < count.length; i++)
count[i] = count[i] + count[i-1];
// 利用 count 这个前缀和数组进行分数段查询
```
接下来,我们看一看前缀和思路在二维数组中如何运用。
### 二维矩阵中的前缀和
这是力扣第 304 题「二维区域和检索 - 矩阵不可变」,其实和上一题类似,上一题是让你计算子数组的元素之和,这道题让你计算二维矩阵中子矩阵的元素之和:
比如说输入的 `matrix` 如下图:
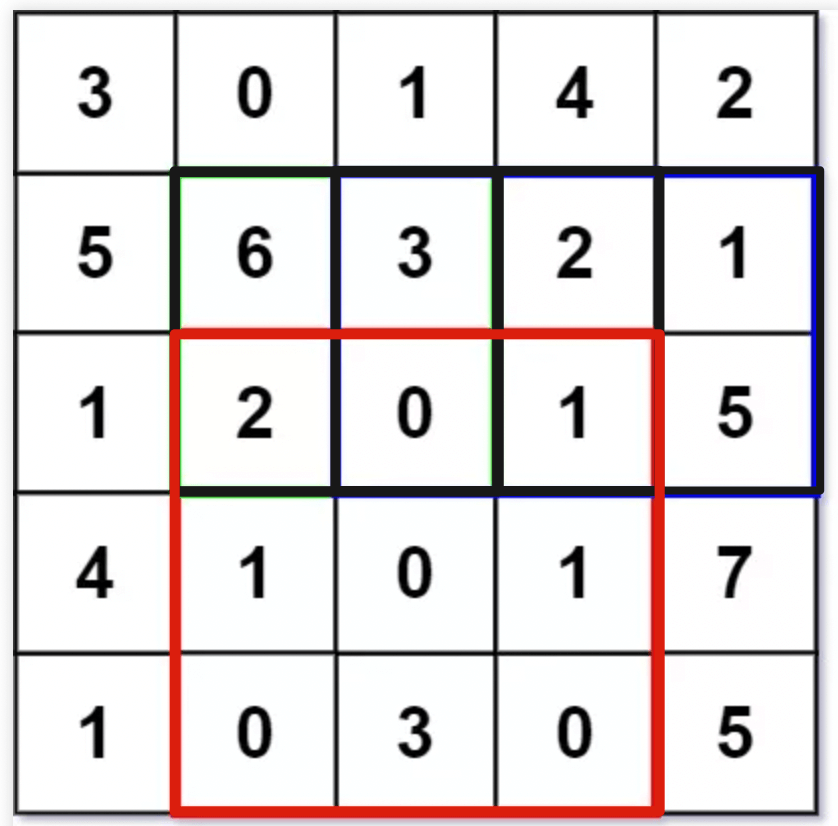
按照题目要求,矩阵左上角为坐标原点 `(0, 0)`,那么 `sumRegion([2,1,4,3])` 就是图中红色的子矩阵,你需要返回该子矩阵的元素和 8。
当然,你可以用一个嵌套 for 循环去遍历这个矩阵,但这样的话 `sumRegion` 函数的时间复杂度就高了,你算法的格局就低了。
注意任意子矩阵的元素和可以转化成它周边几个大矩阵的元素和的运算:
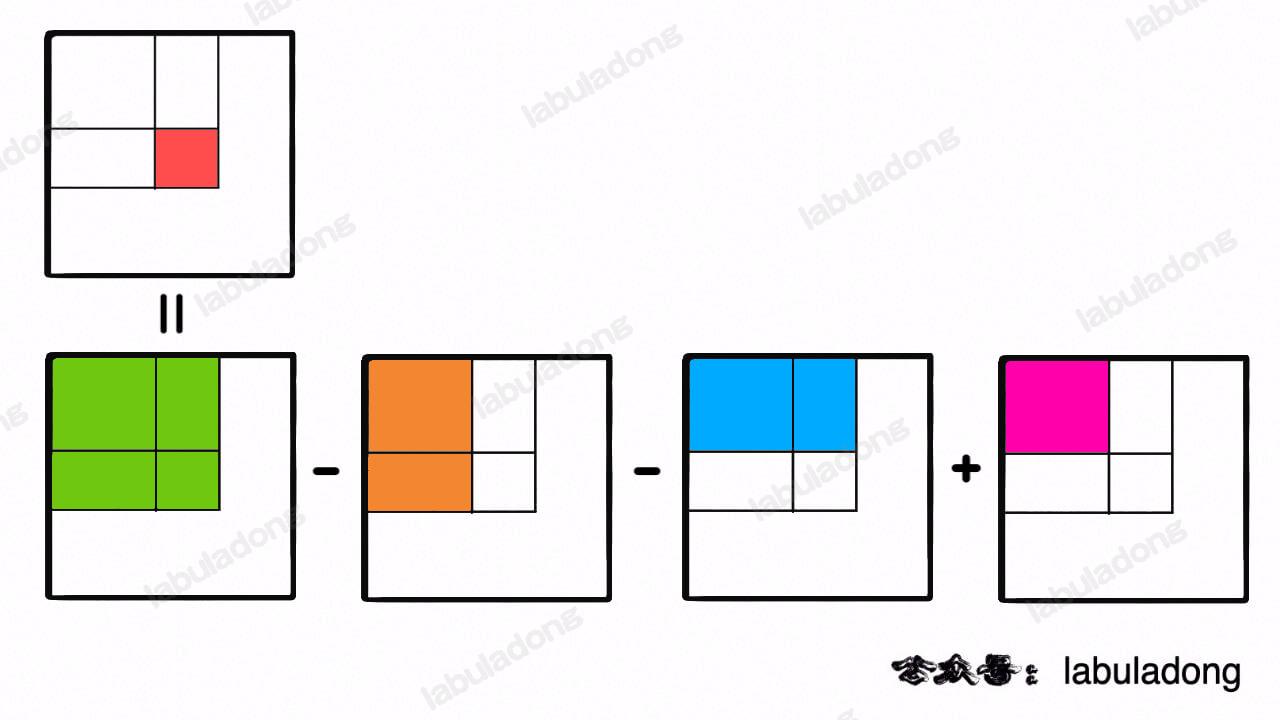
而这四个大矩阵有一个共同的特点,就是左上角都是 `(0, 0)` 原点。
那么做这道题更好的思路和一维数组中的前缀和是非常类似的,我们可以维护一个二维 `preSum` 数组,专门记录以原点为顶点的矩阵的元素之和,就可以用几次加减运算算出任何一个子矩阵的元素和:
```java
class NumMatrix {
// 定义:preSum[i][j] 记录 matrix 中子矩阵 [0, 0, i-1, j-1] 的元素和
private int[][] preSum;
public NumMatrix(int[][] matrix) {
int m = matrix.length, n = matrix[0].length;
if (m == 0 || n == 0) return;
// 构造前缀和矩阵
preSum = new int[m + 1][n + 1];
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
// 计算每个矩阵 [0, 0, i, j] 的元素和
preSum[i][j] = preSum[i-1][j] + preSum[i][j-1] + matrix[i - 1][j - 1] - preSum[i-1][j-1];
}
}
}
// 计算子矩阵 [x1, y1, x2, y2] 的元素和
public int sumRegion(int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2) {
// 目标矩阵之和由四个相邻矩阵运算获得
return preSum[x2+1][y2+1] - preSum[x1][y2+1] - preSum[x2+1][y1] + preSum[x1][y1];
}
}
```
这样,`sumRegion` 函数的时间复杂度也用前缀和技巧优化到了 O(1),这是典型的「空间换时间」思路。
前缀和技巧就讲到这里,应该说这个算法技巧是会者不难难者不会,实际运用中还是要多培养自己的思维灵活性,做到一眼看出题目是一个前缀和问题。
除了本文举例的基本用法,前缀和数组经常和其他数据结构或算法技巧相结合,我会在 [前缀和技巧高频习题](https://labuladong.online/algo/fname.html?fname=前缀和习题) 中举例讲解。
引用本文的文章
- [二维数组的花式遍历技巧](https://labuladong.online/algo/fname.html?fname=花式遍历)
- [动态规划设计:最大子数组](https://labuladong.online/algo/fname.html?fname=最大子数组)
- [小而美的算法技巧:差分数组](https://labuladong.online/algo/fname.html?fname=差分技巧)
- [带权重的随机选择算法](https://labuladong.online/algo/fname.html?fname=随机权重)
- [归并排序详解及应用](https://labuladong.online/algo/fname.html?fname=归并排序)
- [我的刷题心得:算法的本质](https://labuladong.online/algo/fname.html?fname=算法心得)
- [本站简介](https://labuladong.online/algo/fname.html?fname=home)
引用本文的题目
安装 [我的 Chrome 刷题插件](https://labuladong.online/algo/intro/chrome/) 点开下列题目可直接查看解题思路:
| LeetCode | 力扣 |
| :----: | :----: |
| [1314. Matrix Block Sum](https://leetcode.com/problems/matrix-block-sum/?show=1) | [1314. 矩阵区域和](https://leetcode.cn/problems/matrix-block-sum/?show=1) |
| [1352. Product of the Last K Numbers](https://leetcode.com/problems/product-of-the-last-k-numbers/?show=1) | [1352. 最后 K 个数的乘积](https://leetcode.cn/problems/product-of-the-last-k-numbers/?show=1) |
| [238. Product of Array Except Self](https://leetcode.com/problems/product-of-array-except-self/?show=1) | [238. 除自身以外数组的乘积](https://leetcode.cn/problems/product-of-array-except-self/?show=1) |
| [325. Maximum Size Subarray Sum Equals k](https://leetcode.com/problems/maximum-size-subarray-sum-equals-k/?show=1)🔒 | [325. 和等于 k 的最长子数组长度](https://leetcode.cn/problems/maximum-size-subarray-sum-equals-k/?show=1)🔒 |
| [327. Count of Range Sum](https://leetcode.com/problems/count-of-range-sum/?show=1) | [327. 区间和的个数](https://leetcode.cn/problems/count-of-range-sum/?show=1) |
| [437. Path Sum III](https://leetcode.com/problems/path-sum-iii/?show=1) | [437. 路径总和 III](https://leetcode.cn/problems/path-sum-iii/?show=1) |
| [523. Continuous Subarray Sum](https://leetcode.com/problems/continuous-subarray-sum/?show=1) | [523. 连续的子数组和](https://leetcode.cn/problems/continuous-subarray-sum/?show=1) |
| [525. Contiguous Array](https://leetcode.com/problems/contiguous-array/?show=1) | [525. 连续数组](https://leetcode.cn/problems/contiguous-array/?show=1) |
| [560. Subarray Sum Equals K](https://leetcode.com/problems/subarray-sum-equals-k/?show=1) | [560. 和为 K 的子数组](https://leetcode.cn/problems/subarray-sum-equals-k/?show=1) |
| [724. Find Pivot Index](https://leetcode.com/problems/find-pivot-index/?show=1) | [724. 寻找数组的中心下标](https://leetcode.cn/problems/find-pivot-index/?show=1) |
| [862. Shortest Subarray with Sum at Least K](https://leetcode.com/problems/shortest-subarray-with-sum-at-least-k/?show=1) | [862. 和至少为 K 的最短子数组](https://leetcode.cn/problems/shortest-subarray-with-sum-at-least-k/?show=1) |
| [918. Maximum Sum Circular Subarray](https://leetcode.com/problems/maximum-sum-circular-subarray/?show=1) | [918. 环形子数组的最大和](https://leetcode.cn/problems/maximum-sum-circular-subarray/?show=1) |
| [974. Subarray Sums Divisible by K](https://leetcode.com/problems/subarray-sums-divisible-by-k/?show=1) | [974. 和可被 K 整除的子数组](https://leetcode.cn/problems/subarray-sums-divisible-by-k/?show=1) |
| - | [剑指 Offer 57 - II. 和为s的连续正数序列](https://leetcode.cn/problems/he-wei-sde-lian-xu-zheng-shu-xu-lie-lcof/?show=1) |
| - | [剑指 Offer II 010. 和为 k 的子数组](https://leetcode.cn/problems/QTMn0o/?show=1) |
| - | [剑指 Offer II 011. 0 和 1 个数相同的子数组](https://leetcode.cn/problems/A1NYOS/?show=1) |
| - | [剑指 Offer II 012. 左右两边子数组的和相等](https://leetcode.cn/problems/tvdfij/?show=1) |
| - | [剑指 Offer II 013. 二维子矩阵的和](https://leetcode.cn/problems/O4NDxx/?show=1) |
| - | [剑指 Offer II 050. 向下的路径节点之和](https://leetcode.cn/problems/6eUYwP/?show=1) |
**_____________**
**《labuladong 的算法笔记》已经出版,关注公众号查看详情;后台回复「**全家桶**」可下载配套 PDF 和刷题全家桶**:

======其他语言代码======
[560.和为K的子数组](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/subarray-sum-equals-k)
### javascript
[560.和为K的子数组](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/subarray-sum-equals-k)
```js
/**
* @param {number[]} nums
* @param {number} k
* @return {number}
*/
let subarraySum = function (nums, k) {
let n = nums.length;
// 构造前缀和
let sum = new Array(n + 1);
sum[0] = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
sum[i + 1] = sum[i] + nums[i];
}
let ans = 0;
// 穷举所有子数组
for (let i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for (let j = 0; j < i; j++)
// sum of nums[j..i-1]
if (sum[i] - sum[j] === k)
ans++;
return ans;
}
```
优化一下。
```js
/**
* @param {number[]} nums
* @param {number} k
* @return {number}
*/
let subarraySum = function (nums, k) {
let n = nums.length;
// map:前缀和 -> 该前缀和出现的次数
let preSum = new Map();
// base case
preSum.set(0, 1);
let ans = 0, sum0_i = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
sum0_i += nums[i];
// 这是我们想找的前缀和 nums[0..j]
let sum0_j = sum0_i - k;
// 如果前面有这个前缀和,则直接更新答案
if (preSum.has(sum0_j))
ans += preSum.get(sum0_j);
// 把前缀和 nums[0..i] 加入并记录出现次数
if (preSum.has(sum0_i)) {
preSum.set(sum0_i,
preSum.get(sum0_i) + 1);
} else {
preSum.set(sum0_i, 1);
}
}
return ans;
}
```



