# Union-Find 算法详解




**通知:算法可视化编辑器上线,[点击体验](https://labuladong.online/algo/intro/visualize/)!另外,建议你在我的 [网站](https://labuladong.online/algo/) 学习文章,体验更好。**
读完本文,你不仅学会了算法套路,还可以顺便解决如下题目:
| LeetCode | 力扣 | 难度 |
| :----: | :----: | :----: |
| [130. Surrounded Regions](https://leetcode.com/problems/surrounded-regions/) | [130. 被围绕的区域](https://leetcode.cn/problems/surrounded-regions/) | 🟠
| [323. Number of Connected Components in an Undirected Graph](https://leetcode.com/problems/number-of-connected-components-in-an-undirected-graph/)🔒 | [323. 无向图中连通分量的数目](https://leetcode.cn/problems/number-of-connected-components-in-an-undirected-graph/)🔒 | 🟠
| [990. Satisfiability of Equality Equations](https://leetcode.com/problems/satisfiability-of-equality-equations/) | [990. 等式方程的可满足性](https://leetcode.cn/problems/satisfiability-of-equality-equations/) | 🟠
**-----------**
记得我之前在讲 [图论算法基础](https://labuladong.online/algo/fname.html?fname=图) 时说图论相关的算法不会经常考,但最近被打脸了,因为一些读者和我反馈近期求职面试涉及很多图论相关的算法,可能是因为环境不好所以算法这块更卷了吧。
常见的图论算法我都已经写过了,这里按难度顺序列举一下:
1. [图论算法基础](https://labuladong.online/algo/fname.html?fname=图)
2. [二分图判定算法及应用](https://labuladong.online/algo/fname.html?fname=二分图)
3. [环检测/拓扑排序算法及应用](https://labuladong.online/algo/fname.html?fname=拓扑排序)
4. 并查集算法及应用(本文)
5. [Kruskal 最小生成树算法及应用](https://labuladong.online/algo/fname.html?fname=kruskal)
6. [Prim 最小生成树算法及应用](https://labuladong.online/algo/fname.html?fname=prim算法)
7. [Dijkstra 算法模板及应用](https://labuladong.online/algo/fname.html?fname=dijkstra算法)
并查集(Union-Find)算法是一个专门针对「动态连通性」的算法,我之前写过两次,因为这个算法的考察频率高,而且它也是最小生成树算法的前置知识,所以我整合了本文,争取一篇文章把这个算法讲明白。
首先,从什么是图的动态连通性开始讲。
### 一、动态连通性
简单说,动态连通性其实可以抽象成给一幅图连线。比如下面这幅图,总共有 10 个节点,他们互不相连,分别用 0~9 标记:
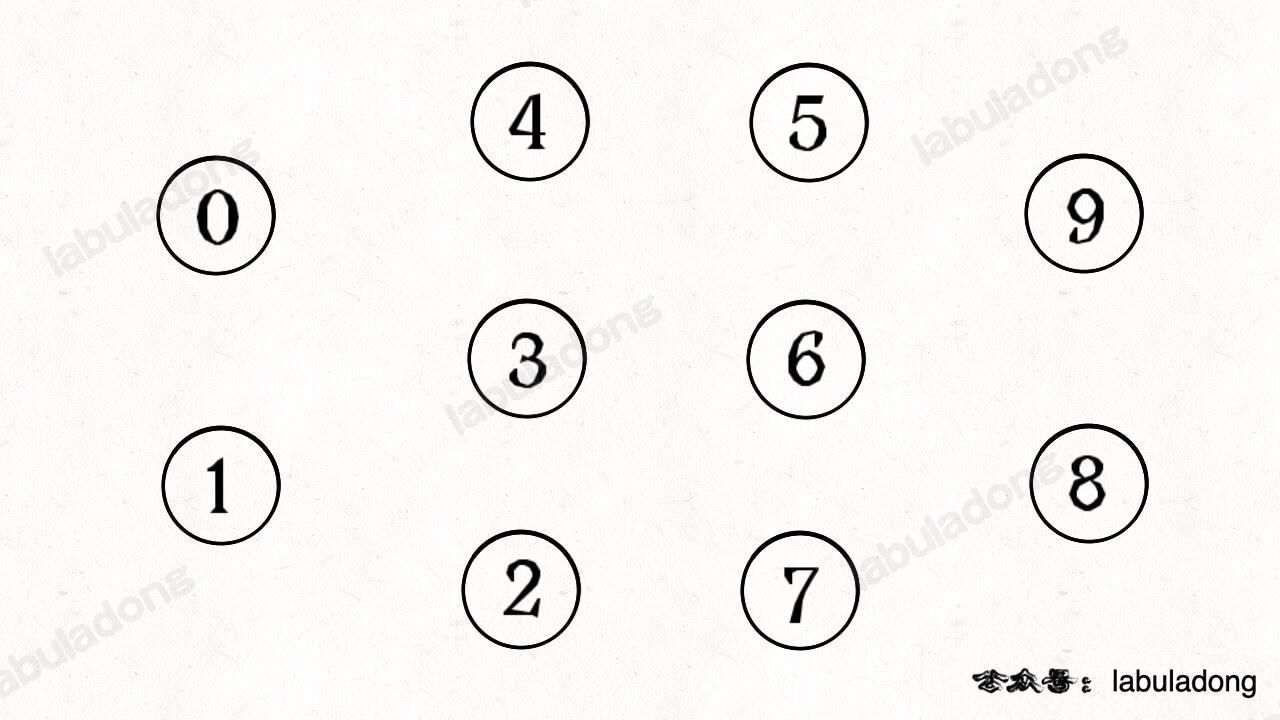
现在我们的 Union-Find 算法主要需要实现这两个 API:
```java
class UF {
/* 将 p 和 q 连接 */
public void union(int p, int q);
/* 判断 p 和 q 是否连通 */
public boolean connected(int p, int q);
/* 返回图中有多少个连通分量 */
public int count();
}
```
这里所说的「连通」是一种等价关系,也就是说具有如下三个性质:
1、自反性:节点 `p` 和 `p` 是连通的。
2、对称性:如果节点 `p` 和 `q` 连通,那么 `q` 和 `p` 也连通。
3、传递性:如果节点 `p` 和 `q` 连通,`q` 和 `r` 连通,那么 `p` 和 `r` 也连通。
比如说之前那幅图,0~9 任意两个**不同**的点都不连通,调用 `connected` 都会返回 false,连通分量为 10 个。
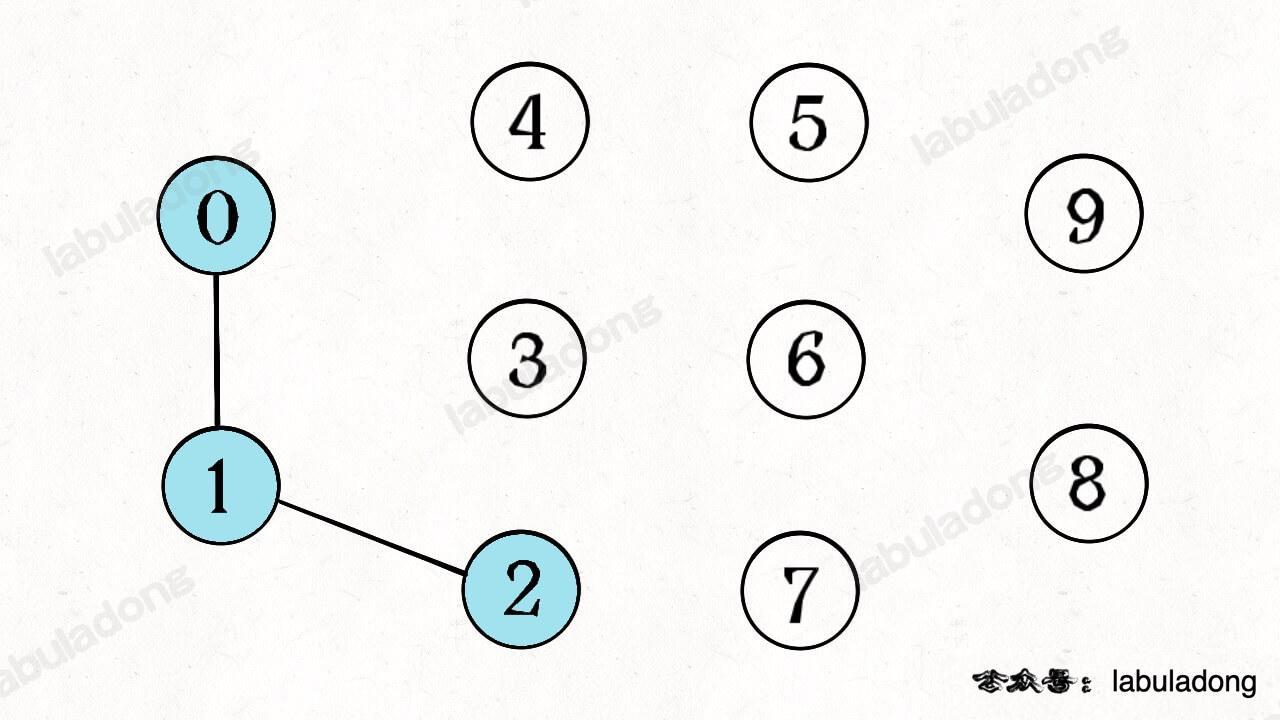
如果现在调用 `union(0, 1)`,那么 0 和 1 被连通,连通分量降为 9 个。
再调用 `union(1, 2)`,这时 0,1,2 都被连通,调用 `connected(0, 2)` 也会返回 true,连通分量变为 8 个。
判断这种「等价关系」非常实用,比如说编译器判断同一个变量的不同引用,比如社交网络中的朋友圈计算等等。
这样,你应该大概明白什么是动态连通性了,Union-Find 算法的关键就在于 `union` 和 `connected` 函数的效率。那么用什么模型来表示这幅图的连通状态呢?用什么数据结构来实现代码呢?
引用本文的文章
- [Dijkstra 算法模板及应用](https://labuladong.online/algo/fname.html?fname=dijkstra算法)
- [Kruskal 最小生成树算法](https://labuladong.online/algo/fname.html?fname=kruskal)
- [Prim 最小生成树算法](https://labuladong.online/algo/fname.html?fname=prim算法)
- [一文秒杀所有岛屿题目](https://labuladong.online/algo/fname.html?fname=岛屿题目)
- [二分图判定算法](https://labuladong.online/algo/fname.html?fname=二分图)
- [我的刷题心得:算法的本质](https://labuladong.online/algo/fname.html?fname=算法心得)
- [用算法打败算法](https://labuladong.online/algo/fname.html?fname=PDF中的算法)
引用本文的题目
安装 [我的 Chrome 刷题插件](https://labuladong.online/algo/intro/chrome/) 点开下列题目可直接查看解题思路:
| LeetCode | 力扣 |
| :----: | :----: |
| [1361. Validate Binary Tree Nodes](https://leetcode.com/problems/validate-binary-tree-nodes/?show=1) | [1361. 验证二叉树](https://leetcode.cn/problems/validate-binary-tree-nodes/?show=1) |
| [200. Number of Islands](https://leetcode.com/problems/number-of-islands/?show=1) | [200. 岛屿数量](https://leetcode.cn/problems/number-of-islands/?show=1) |
| [261. Graph Valid Tree](https://leetcode.com/problems/graph-valid-tree/?show=1)🔒 | [261. 以图判树](https://leetcode.cn/problems/graph-valid-tree/?show=1)🔒 |
| [310. Minimum Height Trees](https://leetcode.com/problems/minimum-height-trees/?show=1) | [310. 最小高度树](https://leetcode.cn/problems/minimum-height-trees/?show=1) |
| [368. Largest Divisible Subset](https://leetcode.com/problems/largest-divisible-subset/?show=1) | [368. 最大整除子集](https://leetcode.cn/problems/largest-divisible-subset/?show=1) |
| [582. Kill Process](https://leetcode.com/problems/kill-process/?show=1)🔒 | [582. 杀掉进程](https://leetcode.cn/problems/kill-process/?show=1)🔒 |
| [765. Couples Holding Hands](https://leetcode.com/problems/couples-holding-hands/?show=1) | [765. 情侣牵手](https://leetcode.cn/problems/couples-holding-hands/?show=1) |
| [947. Most Stones Removed with Same Row or Column](https://leetcode.com/problems/most-stones-removed-with-same-row-or-column/?show=1) | [947. 移除最多的同行或同列石头](https://leetcode.cn/problems/most-stones-removed-with-same-row-or-column/?show=1) |
**_____________**
本文为会员内容,请扫码关注公众号或 [点这里](https://labuladong.online/algo/fname.html?fname=UnionFind算法详解) 查看:

======其他语言代码======
### javascript
```js
class UF {
// 记录连通分量
count;
// 节点 x 的根节点是 parent[x]
parent;
constructor(n) {
// 一开始互不连通
this.count = n;
// 父节点指针初始指向自己
this.parent = new Array(n);
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++)
this.parent[i] = i;
}
/* 返回某个节点 x 的根节点 */
find(x) {
// 根节点的 parent[x] == x
while (this.parent[x] !== x)
x = this.parent[x];
return x;
}
/* 将 p 和 q 连接 */
union(p, q) {
// 如果某两个节点被连通,则让其中的(任意)
// 一个节点的根节点接到另一个节点的根节点上
let rootP = this.find(p);
let rootQ = this.find(q);
if (rootP === rootQ) return;
// 将两棵树合并为一棵
parent[rootP] = rootQ;
// parent[rootQ] = rootP 也一样
count--; // 两个分量合二为一
}
/* 判断 p 和 q 是否连通 */
connected(p, q) {
let rootP = this.find(p);
let rootQ = this.find(q);
return rootP === rootQ;
};
/* 返回图中有多少个连通分量 */
getCount() {
return this.count;
};
}
```
引入size属性,更好地平衡森林。
```js
class UF {
// 记录连通分量
count;
// 节点 x 的根节点是 parent[x]
parent;
// 记录树的“重量”
size;
constructor(n) {
// 一开始互不连通
this.count = n;
// 父节点指针初始指向自己
this.parent = new Array(n);
this.size = new Array(n);
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
this.parent[i] = i;
this.size[i] = 1;
}
}
/* 返回某个节点 x 的根节点 */
find(x) {
// 根节点的 parent[x] == x
while (this.parent[x] !== x) {
// 进行路径压缩
this.parent[x] = this.parent[this.parent[x]];
x = this.parent[x];
}
return x;
}
/* 将 p 和 q 连接 */
union(p, q) {
// 如果某两个节点被连通,则让其中的(任意)
// 一个节点的根节点接到另一个节点的根节点上
let rootP = this.find(p);
let rootQ = this.find(q);
if (rootP === rootQ) return;
// 小树接到大树下面,较平衡
if (this.size[rootP] > this.size[rootQ]) {
this.parent[rootQ] = rootP;
this.size[rootP] += this.size[rootQ];
} else {
this.parent[rootP] = rootQ;
this.size[rootQ] += this.size[rootP];
}
this.count--; // 两个分量合二为一
}
/* 判断 p 和 q 是否连通 */
connected(p, q) {
let rootP = this.find(p);
let rootQ = this.find(q);
return rootP === rootQ;
};
/* 返回图中有多少个连通分量 */
getCount() {
return this.count;
};
}
```



