# TINTOlib: Python Library to convert Tabular Data into Synthetic Images
[](https://github.com/oeg-upm/TINTOlib-Documentation/blob/main/LICENSE)
[](https://pypi.python.org/pypi/)
[](https://tintolib.readthedocs.io/en/latest/)
[](https://colab.research.google.com/github/oeg-upm/TINTOlib-Crash_Course/blob/main/Notebooks/Challenge/Regression_CNN.ipynb)
[](https://colab.research.google.com/github/oeg-upm/TINTOlib-Crash_Course/blob/main/Notebooks/Challenge/Regression_CNN%2BMLP.ipynb)
[](https://colab.research.google.com/github/oeg-upm/TINTOlib-Crash_Course/blob/main/Notebooks/Challenge/Regression_ViT.ipynb)
[](https://colab.research.google.com/github/oeg-upm/TINTOlib-Crash_Course/blob/main/Notebooks/Challenge/Regression_ViT%2BMLP.ipynb)
[](https://deepwiki.com/oeg-upm/TINTOlib)
[](https://pepy.tech/projects/tintolib)
## 🎉 New Free Course on Udemy! (Spanish) 🎉
**We’ve just launched a 100% free course on Udemy** about **using TINTOlib** and developing **Hybrid Neural Networks**.
Learn how to turn tabular data into synthetic images and apply CNNs, ViTs, and hybrid architectures like a pro.

---
### 📺 VideoTutorial Course (English/Spanish)
🎥 Prefer not to register on Udemy or looking for the English version of the course? No worries — you can follow the full course directly on GitHub!
This hands-on tutorial includes **bilingual videos (English/Spanish)** and **practical notebooks** to help you learn how to use **TINTOlib** with deep learning models like CNNs, ViTs, and hybrid architectures.

---
## 🧠 Overview
**TINTOlib** is a state-of-the-art Python library that transforms **tidy data** (also known as tabular data) into **synthetic images**, enabling the application of advanced deep learning techniques, including **Vision Transformers (ViTs)** and **Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs)**, to traditionally structured data. This transformation bridges the gap between tabular data and powerful vision-based machine learning models, unlocking new possibilities for tackling regression, classification, and other complex tasks.
---
## 🔎 Explore TINTOlib with DeepWiki
TINTOlib has a dedicated space on **[DeepWiki](https://deepwiki.com/oeg-upm/TINTOlib)**, where you can explore semantic documentation, relevant links, bibliography, and answers to frequently asked questions about its use and application.

---
## 📚 Features
- Input formats: **CSV** or Pandas DataFrame
- Designed for tidy data (**target column last**)
- Output: grayscale or RGB images from reduction and transformation methods
- Compatible with **Linux, Windows, macOS**
- Requires **Python 3.7+**
---
## 🧪 Methods
TINTOlib includes a variety of methods for generating synthetic images. Below is a summary of the supported methods and their hyperparameters:
| Methods | Class | Hyperparameters |
|:----------------------------------------------------------------:|:------------:|:-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------:|
| [TINTO](https://github.com/oeg-upm/TINTO) | `TINTO()` | `problem` `transformer` `verbose` `pixels` `algorithm` `blur` `submatrix` `amplification` `distance` `steps` `option` `times` `train_m` `zoom` `format` `cmap` `random_seed` |
| [IGTD](https://github.com/zhuyitan/igtd) | `IGTD()` | `problem` `transformer` `verbose` `scale` `fea_dist_method` `image_dist_method` `error` `max_step` `val_step` `switch_t` `min_gain` `zoom` `format` `cmap` `random_seed` |
| [REFINED](https://github.com/omidbazgirTTU/REFINED) | `REFINED()` | `problem` `transformer` `verbose` `hcIterations` `n_processors` `zoom` `format` `cmap` `random_seed` |
| [BarGraph](https://github.com/anuraganands/Non-image-data-classification-with-CNN/) | `BarGraph()` | `problem` `transformer` `verbose` `pixel_width` `gap` `zoom` |
| [DistanceMatrix](https://github.com/anuraganands/Non-image-data-classification-with-CNN/) | `DistanceMatrix()` | `problem` `transformer` `verbose` `zoom` |
| [Combination](https://github.com/anuraganands/Non-image-data-classification-with-CNN/) | `Combination()` | `problem` `transformer` `verbose` `zoom` |
| [SuperTML](https://github.com/GilesStrong/SuperTML_HiggsML_Test) | `SuperTML()` | `problem` `transformer` `verbose` `pixels` `feature_importance` `font_size` `random_seed` |
| [FeatureWrap](https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-319-70139-4_87) | `FeatureWrap()` | `problem` `transformer` `verbose` `size` `bins` `zoom` |
| [BIE](https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10278393) | `BIE()` | `problem` `transformer` `verbose` `precision` `zoom` |
| [Fotomics](https://github.com/VafaeeLab/Fotomics-Imagification) | `Fotomics()` | `image_dim` `problem` `transformer` `verbose` `outliers` `min_percentile` `max_percentile` `outliers_treatment` `assignment_method` `relocate` `algorithm_opt` `group_method` `zoom` `format` `cmap` `random_seed` |
| [DeepInsight](https://github.com/alok-ai-lab/pyDeepInsight) | `DeepInsight()` | `image_dim` `problem` `transformer` `verbose` `algorithm_rd` `assignment_method` `relocate` `algorithm_opt` `group_method` `zoom` `format` `cmap` `random_seed` |
---
## ⚠️ Platform-Specific Requirements for Certain Transformation Methods
Some transformation methods in TINTOlib have specific system requirements or limitations when used on platforms such as Google Colab, Windows, Linux, or macOS.
### REFINED
This method relies on `mpi4py`, which enables parallel computation using MPI (Message Passing Interface). However, `mpi4py` requires administrative permissions to utilize multiple processors, making it incompatible with platforms like Google Colab.
- **Linux**:
Ensure that the MPI environment is set up before installing `mpi4py`. Run the following commands:
```bash
sudo apt-get install python3
sudo apt install python3-pip
sudo apt install python3-mpi4py
```
Once MPI is installed:
```bash
pip install mpi4py
```
- **MacOS / Windows:** Direct installation is usually supported:
```bash
pip install mpi4py
```
### SuperTML
The **SuperTML** method generates text-based synthetic images and requires the **MS Sans Serif** font (or **Arial** as implemented in TINTOlib).
- On **Windows**, this font is typically available by default.
- On **Linux** and **macOS**, it must be installed manually to avoid rendering issues.
#### Font Installation
- **Linux**: Install Microsoft Core Fonts:
```bash
sudo apt install ttf-mscorefonts-installer
```
On **Google Colab**, installing additional fonts is not permitted due to administrative restrictions.
## 📄 Getting Started
- You can install TINTOlib using **[Pypi](https://pypi.org/project/TINTOlib/)**:
```bash
pip install TINTOlib
```
TINTOlib already includes all necessary dependencies, so there’s no need to install them individually.
However, if you prefer manual installation or want to explore the full environment:
- The repository includes a `requirements.txt` file listing the **core dependencies** required to use TINTOlib. You can directly run the **TINTOlib-example.ipynb** notebook located in the examples/ folder using the dependencies listed in `requirements.txt`.
- **Other notebooks**, which include training deep learning models on the generated images, require additional libraries. To run them, install the extended dependencies from `requirements-example.txt`:
---
## 🧩 Importing a Specific Model
- To use a specific image transformation model, import it directly. For example, to use **TINTO**:
```python
from TINTOlib.tinto import TINTO
```
- Create the model. If you don't set any hyperparameter, the model will use the default values, refer to the **[Models Section](#models)** or the **[TINTO Documentation](https://tintolib.readthedocs.io/en/latest/)**.
```python
model = TINTO(problem="supervised", blur=True)
```
---
## 🔧 Generating Synthetic Images
To generate synthetic images, use the following workflow with the `fit`, `transform`, and `fit_transform` methods:
**Parameters**:
- **data**: A path to a CSV file or a Pandas DataFrame (target column must be the last column).
- **folder**: Path to the folder where the synthetic images will be saved.
#### Sintaxis
1. The `fit` method trains the model on the tabular data and prepares it for image generation.
```python
model.fit(data)
```
2. The `transform` method generates and saves synthetic images in a specified folder. It requires the model to be fitted first.
```python
model.transform(data, folder)
```
3. The `fit_transform` method combines the training and image generation steps. It fits the model to the data and generates synthetic images in one step.
```python
model.fit_transform(data, folder)
```
#### Notes:
- **The model must be fitted** before using the `transform` method. If the model isn't fitted, a `RuntimeError` will be raised.
---
## 📚 Documentation
To get started with **TINTOlib**, a dedicated **[Crash Course Repository](https://github.com/oeg-upm/TINTOlib-Crash_Course)** is available. It includes videoturials, slides and Jupyter Notebooks that demonstrate how to apply state-of-the-art vision models like Vision Transformers (ViTs), Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) and Hybrid Neural Networks to problems.
For example, the following table shows a classic example of the [IRIS CSV dataset](https://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/datasets/iris) as it should look like for the run:
| sepal length | sepal width | petal length | petal width | target |
|--------------|-------------|--------------|-------------|--------|
| 4.9 | 3.0 | 1.4 | 0.2 | 1 |
| 7.0 | 3.2 | 4.7 | 1.4 | 2 |
| 6.3 | 3.3 | 6.0 | 2.5 | 3 |
- The following example shows how to execute TINTOlib using the TINTO method and then display the synthetic image generated for the first row:
```python
model = TINTO(problem="supervised", pixel=30, algorithm="t-SNE", steps=5, blur=True)
model.fit_transform("iris.csv", "synthetic_images")
```
---
## 🚀 Vision-based Neural Network Architectures
Using synthetic images, experiment with either vision models like CNNs or ViTs, and explore hybrid models. Below are the architectures that will be presented, and the ones you will modify and use during the session:
- **Synthetic images using CNN**
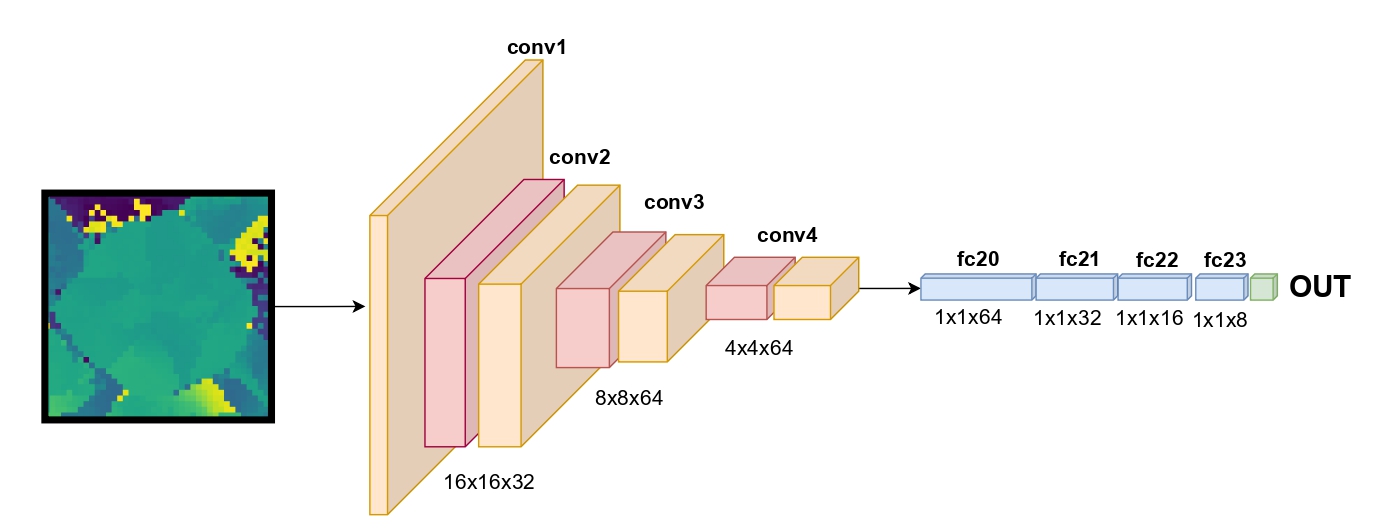
- **Synthetic images using Hybrid Neural Network with ViT (HyViT)**
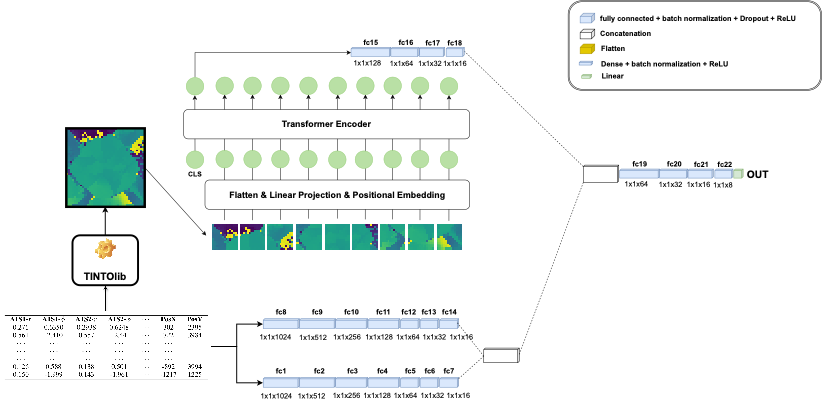
---
## 💬 More information
- For more detailed information, refer to the **[TINTOlib ReadTheDocs](https://tintolib.readthedocs.io/en/latest/)**.
- PyPI: **[PyPI](https://pypi.org/project/TINTOlib/)**.
---
## 📖 Citation
If you use TINTOlib in your research, please cite our paper en [SoftwareX journal](https://doi.org/10.1016/j.softx.2025.102444):
```bibtex
@article{LIU2025102444,
title = {TINTOlib: A Python library for transforming tabular data into synthetic images for deep neural networks},
journal = {SoftwareX},
volume = {32},
pages = {102444},
year = {2025},
issn = {2352-7110},
doi = {https://doi.org/10.1016/j.softx.2025.102444}
}
```
----
## 🧪 Citing TINTO Method:
If you used TINTO method with Hybrid Neural Networks in your work, please cite the **[IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing](https://doi.org/10.1109/JSTSP.2025.3555067)**:
```bib
@ARTICLE{10946146,
author={Castillo-Cara, Manuel and Martínez-Gómez, Jesus and Ballesteros-Jerez, Javier and García-Varea, Ismael and García-Castro, Raúl and Orozco-Barbosa, Luis},
journal={IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing},
title={MIMO-Based Indoor Localisation with Hybrid Neural Networks: Leveraging Synthetic Images from Tidy Data for Enhanced Deep Learning},
year={2025},
volume={},
number={},
pages={1-13},
keywords={Location awareness;Accuracy;Neural networks;Measurement;Deep learning;Complexity theory;Antennas;Antenna measurements;Base stations;Signal processing algorithms;Massive MIMO;Deep Learning;Hybrid Neural Network;Synthetic Images;Positioning;Indoor Localisation},
doi={10.1109/JSTSP.2025.3555067}}
```
If you used TINTO in your work, please cite the **[SoftwareX](https://doi.org/10.1016/j.softx.2023.101391)**:
```bib
@article{softwarex_TINTO,
title = {TINTO: Converting Tidy Data into Image for Classification with 2-Dimensional Convolutional Neural Networks},
journal = {SoftwareX},
author = {Manuel Castillo-Cara and Reewos Talla-Chumpitaz and Raúl García-Castro and Luis Orozco-Barbosa},
volume={22},
pages={101391},
year = {2023},
issn = {2352-7110},
doi = {https://doi.org/10.1016/j.softx.2023.101391}
}
```
---
## 🛡️ License
TINTOlib is available under the **[Apache License 2.0](https://github.com/oeg-upm/TINTOlib-Documentation/blob/main/LICENSE)**.
## 👥 Authors
- **[Manuel Castillo-Cara](https://github.com/manwestc)**
- **[Raúl García-Castro](https://github.com/rgcmme)**
- **[David González Fernández](https://github.com/DavidGonzalezFernandez)**
- **[Jiayun Liu](https://github.com/DCY1117)**
---
## 🏛️ Contributors




