Syntax:
compute ID group-ID gyration
Examples:
compute 1 molecule gyration
Description:
Define a computation that calculates the radius of gyration Rg of the group of atoms, including all effects due to atoms passing thru periodic boundaries.
Rg is a measure of the size of the group of atoms, and is computed by this formula
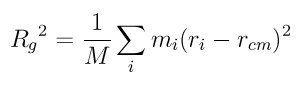
where M is the total mass of the group, Rcm is the center-of-mass position of the group, and the sum is over all atoms in the group.
A Rg tensor, stored as a 6-element vector, is also calculated by this compute. The formula for the components of the tensor is the same as the above formula, except that (Ri - Rcm)^2 is replaced by (Rix - Rcmx) * (Riy - Rcmy) for the xy component, etc. The 6 components of the vector are ordered xx, yy, zz, xy, xz, yz.
IMPORTANT NOTE: The coordinates of an atom contribute to Rg in "unwrapped" form, by using the image flags associated with each atom. See the dump custom command for a discussion of "unwrapped" coordinates. See the Atoms section of the read_data command for a discussion of image flags and how they are set for each atom. You can reset the image flags (e.g. to 0) before invoking this compute by using the set image command.
Output info:
This compute calculates a global scalar (Rg) and a global vector of length 6 (Rg tensor), which can be accessed by indices 1-6. These values can be used by any command that uses a global scalar value or vector values from a compute as input. See Section_howto 15 for an overview of LIGGGHTS(R)-PUBLIC output options.
The scalar and vector values calculated by this compute are "intensive". The scalar and vector values will be in distance units.
Restrictions: none
Related commands:
Default: none