model_type/model_name pairs = described for each model separately here
Examples:
pair_style gran model hooke tangential history pair_style gran model hertz tangential history rolling_friction cdt pair_style gran model hertz tangential no_history cohesion sjkr
General description:
The gran styles use the following formula for the frictional force between two granular particles, when the distance r between two particles of radii Ri and Rj is less than their contact distance d = Ri + Rj. Typically, there is no force between the particles when r > d.
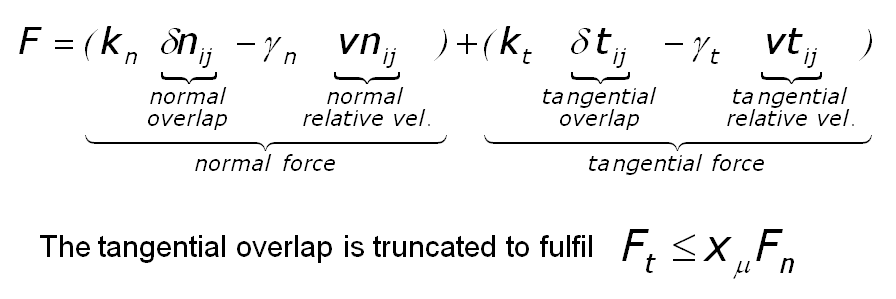
The quantities in the equations are as follows:
- delta_n = d - r = overlap distance of 2 particles
- k_n = elastic constant for normal contact
- k_t = elastic constant for tangential contact
- gamma_n = viscoelastic damping constant for normal contact
- gamma_t = viscoelastic damping constant for tangential contact
- delta_t = tangential displacement vector between 2 spherical particles
In the first term is the normal force between the two particles and the second term is the tangential force. The normal force has 2 terms, a contact force and a damping force. The tangential force also has 2 terms: a shear force and a damping force. The shear force is a "history" effect that accounts for the tangential displacement ("tangential overlap") between the particles for the duration of the time they are in contact.
The concrete implementation for k_n, k_t, gamma_n, gamma_t and the shear history depend on the concrete models as chosen by the user. They are described on separate doc pages here
Also, other models may add additional forces or torques on the particles, such as cohesive or rolling friction forces. These are also described on separate doc pages here
IMPORTANT NOTE: The order of model keywords is important, you have to stick to the order as outlined in the "Syntax" section of this doc page.
General comments:
For granular styles there are no additional coefficients to set for each pair of atom types via the pair_coeff command. All settings are global and are made via the pair_style command. However you must still use the pair_coeff for all pairs of granular atom types. For example the command
pair_coeff * *
should be used if all atoms in the simulation interact via a granular potential (i.e. one of the pair styles above is used). If a granular potential is used as a sub-style of pair_style hybrid, then specific atom types can be used in the pair_coeff command to determine which atoms interact via a granular potential.
Mixing, shift, table, tail correction, restart, rRESPA info:
The pair_modify mix, shift, table, and tail options are not relevant for granular pair styles.
These pair styles write their information to binary restart files, so a pair_style command does not need to be specified in an input script that reads a restart file.
IMPORTANT NOTE: The material properties are not written to restart files! Thus, if you restart a simulation, you have to re-define them (by using the fixes mentioned above).
These pair styles can only be used via the pair keyword of the run_style respa command. They do not support the inner, middle, outer keywords.
Restrictions:
These pair styles require that atoms store torque and angular velocity (omega) as defined by the atom_style. They also require a per-particle radius is stored. The sphere or granular atom style does all of this.
This pair style requires you to use the communicate vel yes option so that velocites are stored by ghost atoms.
Only unit system that are self-consistent (si, cgs, lj) can be used with this pair style.
Related commands:
pair_coeff Models for use with this command are described here
Default:
model = 'hertz' tangential = 'off' rolling_friction = 'off' cohesion = 'off' surface = 'default'