Packaging Units Feature Overview 

MCMulti-currency MLMulti-language MSMulti-store
Unit of measure that is used as packaging for a product is referred to as packaging unit. A shop can sell the same product in different packaging units, for example apples can be sold as an "Item", a "Bag" of apples or a "Pallet" of apples. The "bag", "pallet", "box" etc. are referred to as packaging unit types. The packaging unit types can be created and managed in the Administration Interface.
Each packaging unit is defined on an abstract product level and is represented by one product variant, for example:
| Abstract Product | Concrete Product / Variant | Packaging Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Apple | "An apple" | Item |
| Apple | "Bag of apples" | Bag |
| Apple | "Pallet of apples" | Palett |
Each packaging unit has a certain amount of products inside it by default (default amount). The shop owner can choose whether the packaging unit, for example a bag, has a separate stock or shares stock with the contained item. In our example, the different product variants have their own SKU and price, but they represent the same physical product in the warehouse. To share the information about availability among these variants, we use the concept of a leading product.
The leading product represents relation between abstract and concrete product and holds the availability. A group of products in a packaging unit, that has a leading product holding the availability, is called a product packaging unit group.
However leading products are not always relevant. Packaging units that represent a package of items which quantity can not be changed, do not need a leading product. In this case, availability of the packaged items themselves, not individual items in the package, matters. Such packaged products actually behave like normal abstract products for which customers might have a possibility to select applicable sales units (see Measurement Units per Product to learn about product sales units).
Basically, when a packaging unit does not use the leading product, it means that the stock is disjoined.
For example, if there is a leading product in the product abstract with 3 packagings, where 1 of the packages "has no lead product", it means that the 2 other packages actually consume the same product when you buy them. But the 3rd packaging (which does not use the leading product) is completely independent from stock perspective, it only depends on its own stock.
To reflect availability of a leading product for a packaging unit and to define how the calculation of the availability works, has_lead_product attribute is used.
Example:
| Use leading product | Abstract product | Concrete product/ Variant | Packaging unit |
Current concrete availability |
Derived availability | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lead product | Irrelevant | Apple | "An apple" | Item | 100 | 100 |
| Packaging unit | Yes | Apple | "Bag of apples" | Bag | never out of stock | FLOOR ((Same as "An apple") / default_amount) |
| Packaging unit | No | Apple | "Palette of apples" | >Palette | never out of stock | never out of stock |
| Packaging unit | No | Apple | "Special boxed apples" | Special box | 5 | 5 |
| Packaging unit | Yes | Apple | "Gift wrapping apples" | Gift wrap | 10 | MIN ( FLOOR ((Same as "An apple") / default_amount) ; current concrete availability ) |
The shop owner can define various sales units for the packaging units. For example, for a chocolate bar, the base unit could be set to item, and the sales units could be box, packet or gift box with variable or fixed amount of chocolate bars in them.
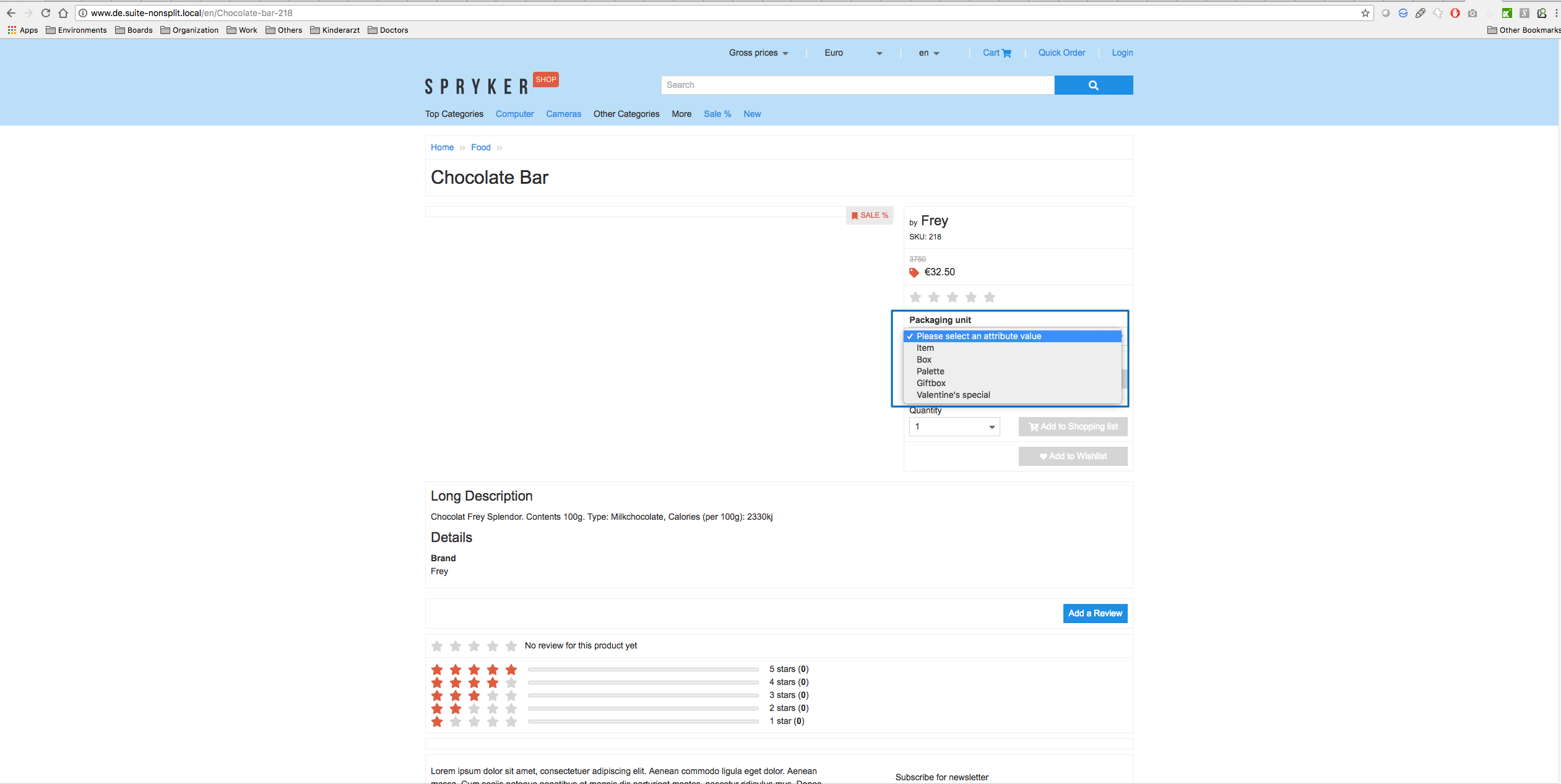
Read on to learn about the product packaging unit amount options.
Product Packaging Unit Amount
A packaging unit usually contains multiple items of a product. For instance a "Bag of apples" can contain 10, 20, 40... apples. This information is called the amount of a packaging unit. It is always related to the leading product of the product packaging unit group. Therefore, the amounts apply only when leading product is used, otherwise they do not make sense.
The packaging unit amount can be:
| Packaging Unit Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Default (default_amount) | Default amount of items that customer can buy.
Customer can buy 40 apples. Also, this value is used for calculating price when custom amount is provided. The Amount field in the web shop is pre-filled with a value set in default_amount. |
| Variable (is_variable=true) | Customer can buy any number of that item (respecting the amount restrictions). In case of a variable amount the price is adjusted by the formula: (Price) * (Customer Input) / (Default Amount). |
| Fixed (is_variable=false) | Customer can buy a pre-determined, fixed amount of items. When is_variable is set to "false", all amount_* values are set as NULL. When the amount is non-variable the customer can still see the default amount, but can not change it.
However, if a product has sales unit set for it, the customer is able to select a different sales unit for the amount, which will adjust the displayed amount according to that sales unit. See Measurement Units per Product to learn about product sales units. |
| Interval amount (amount_interval) | Interval of amounts that a customer can buy.
For instance you can only buy 40, 80, 120, ... but not 45. The interval is shifted by the minimum value (e.g: minimum = 5, interval = 3; valid values: 5, 8, 11, ...). Only relevant if is_variable=true. If the amount is set as variable, by default, the interval amount is set to 1. |
| Minimum amount (amount_minimum) | Minimum amount that a customer can buy.
For instance you cannot buy less than 1 apple. Only relevant if is_variable=true. If the amount is set as variable, by default, the minimum amount equals the interval amount. |
|
Maximum amount (amount_maximum) |
Maximum amount that a customer can buy.
For instance you cannot buy more than 10 apples. Only relevant if is_variable=true. |
The schema below shows relations between products, packaging units, their types and amounts:
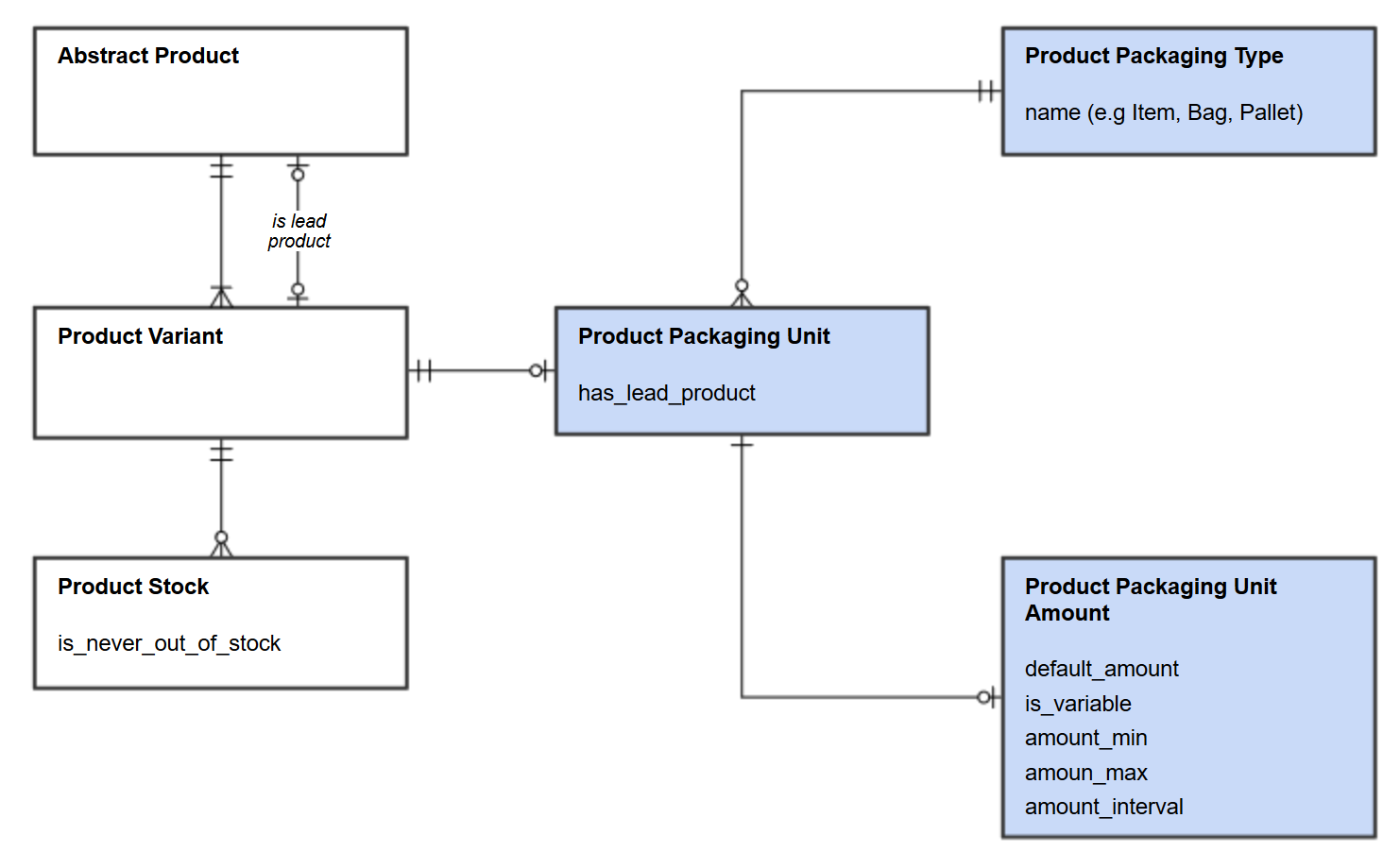
All packaging units having leading products, have a base unit of measure and can also have various sales units reflecting the amount of items in the packaging units.
For example, a packaging unit "bag" can be set to have "item" as base unit and might also have "kg" and "g" as sales units (see Measurement Units per Product to learn about base and sales units for products).
The amount of items contained in a sales unit is referred to as sales unit amount. If a customer chooses a sales unit amount, which is in between 2 available amounts (due to amount restriction settings), he/she is suggested to select a higher or lower amount.
If there is no lower/higher amount available, the user is suggested to buy just a higher/lower amount respectively.
The following figure shows an example of how quantities and amounts appear in the web-shop:
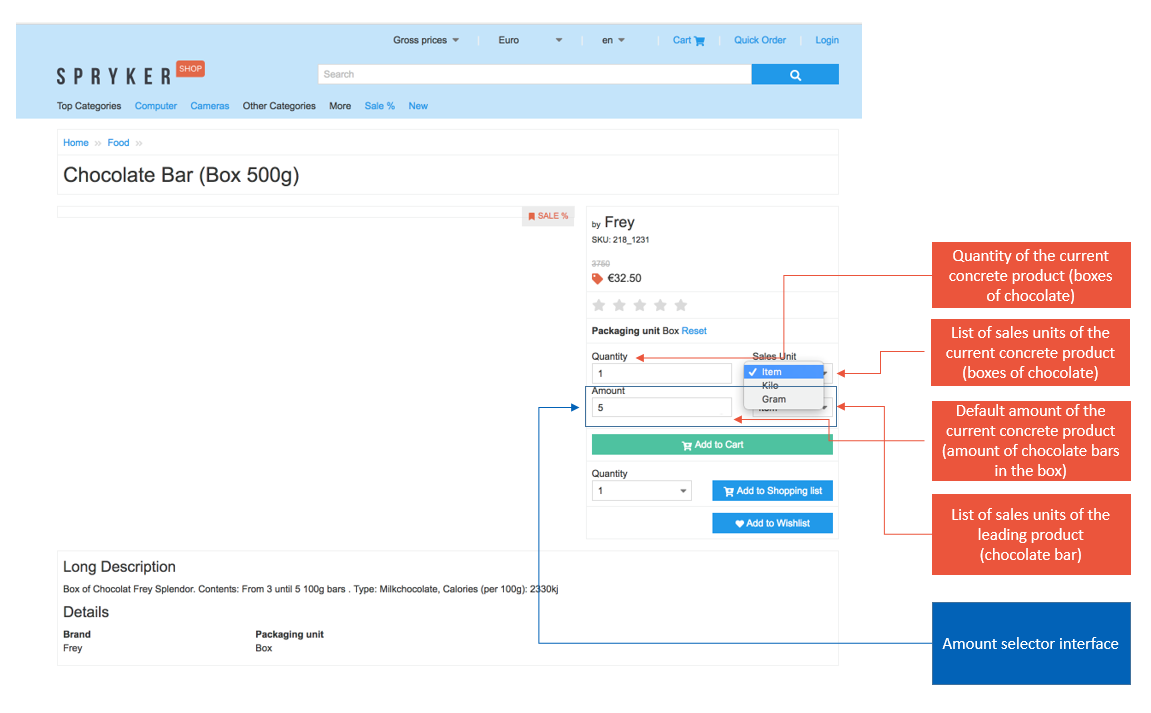
In this example:
- The chocolate bar is an abstract product with various packaging units (product concretes).
- The leading product for this product's packaging units has been set to "chocolate bar".
A customer can select product packaging unit types and quantity for it.
- Also, besides the base unit "item", the chocolate bar is set to have sales units as well - kilograms and grams.
It means that if customer wants to buy a box of chocolates and wants to see how many kilograms or grams there will be in the box, he/she can select a respective sales unit.
- Moreover, since the chocolate box is not a leading product (however a leading product is used and the amount has been set to be variable) the amount selector is available as well.
Meaning it is also possible to select the packaging unit amount and sales units of the leading product. In our example, the Amount field has been pre-filled with 5, since the default value for "box" has been set to 5.
When the very same item is added to cart with a different amount of sales units or with the same amount but a different sales unit, then the item appears in the cart in form of separate items.
Meaning it will be one sales order containing multiple order items.
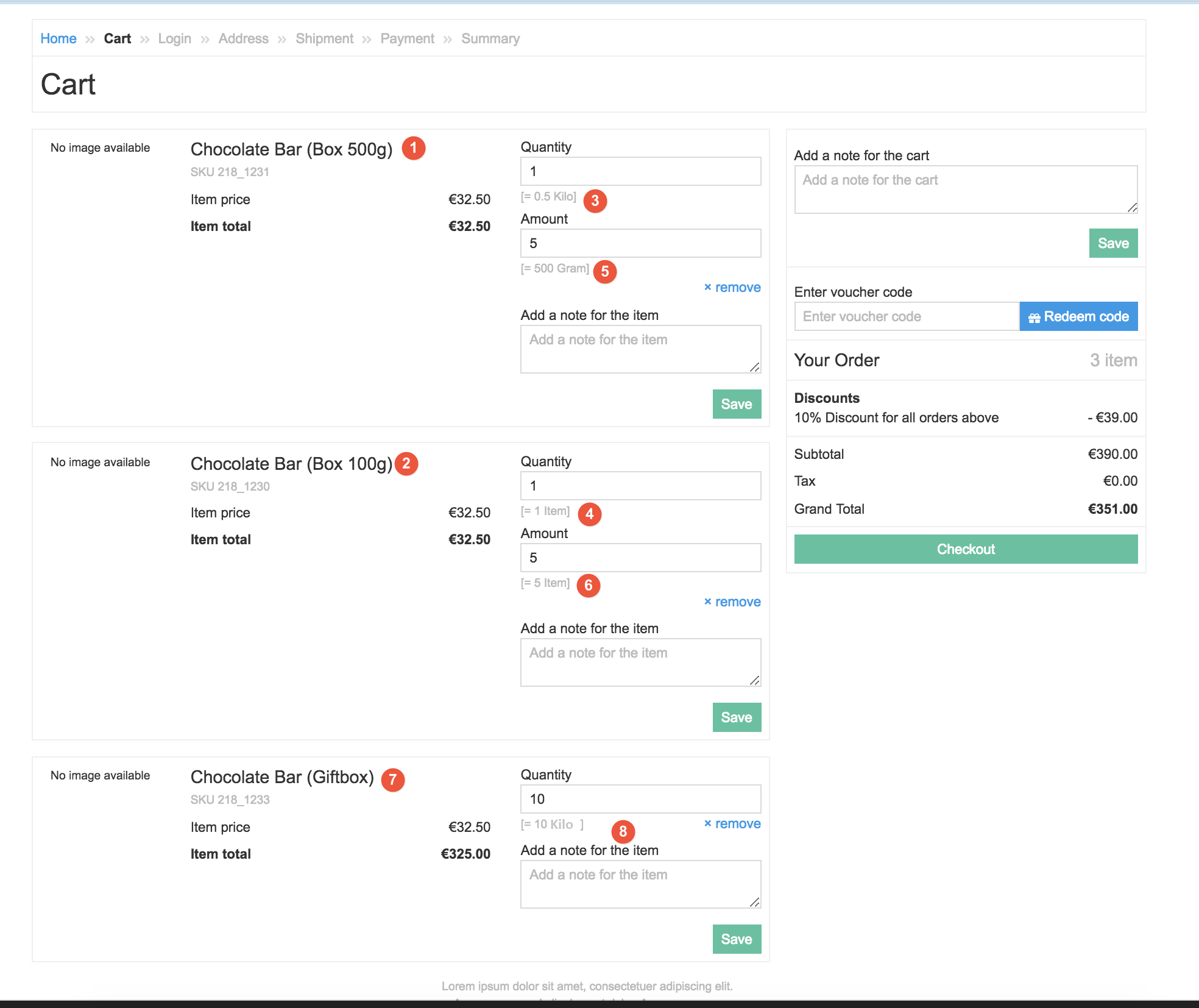
The figure below shows how one and the same item bought in different sales units and packaging units appears in the cart.
In our example, the following conditions are met:
- We put different packaging units into the cart: box of chocolates with 500g and 100g. (
 and
and  respectively)
respectively) - The products have different sales units: 0.5kg vs 1 item (
 and
and  respectively).
respectively). - Amount has different sales units: 1st uses grams, 2nd uses items. (
 and
and  respectively)
respectively) - The third product with packaging unit (giftbox with chocolate bars
 ) has no amount (
) has no amount ( ).
).
Packaging Units Import
The shop owner can import packaging unit information and types. However it should be kept in mind, that packaging unit type import should happen first, otherwise you won't be able to import packaging units if the types don't exist yet.
Importing Packaging Unit Types
To extend the list of the packaging unit types available by default (box, bag, palette etc.), the shop administrator can import more packaging unit types into the system. The .csv file for import must have name field populated.
To import packaging units types from ProductPackagingUnitDataImport/data/import/product_packaging_unit.csv file, run
console data:import product-packaging-unit-typeOr, if you want to import packaging units types from your file, indicate a path to it:
console data:import product-packaging-unit-type -f path_to_file.csvThe imported packaging unit types will appear in the spy_product_packaging_unit_type DB table.
Importing Packaging Units Information
The shop owner can import product packaging unit information via a .csv file, specifically, he/she can:
- Define a packaging unit for a specific product concrete by populating concrete_sku and packaging_unit_type_name fields.
Both fields are required.
- Decide if the packaging unit uses the lead product stock by setting 1 or 0 for has_lead_product field.
The default value is 0.
- Define a lead product in is_lead_product field. If is_lead_product is set as 1, no spy_product_packaging_unit_amount record is created, i.e. default_amount, is_variable, amount_* columns are ignored. Also, when is_lead_product is set as 1, has_lead_product is to be 0.
The default value of the is_lead_product field is 0.
- Set amount restrictions (is_variable=1) when product is not a lead product.
By default, is_variable, amount_min, amount_max, amount_interval are set to 0.
To import packaging units information from ProductPackagingUnitDataImport/data/import/product_packaging_unit.csv file, run
console data:import product-packaging-unitOr, if you want to import packaging unit data from your file, indicate a path to it:
console data:import product-packaging-unit -f path_to_file.csvThe import will populate spy_product_packaging_unit, spy_product_packaging_unit_amount and spy_product_packaging_lead_product, spy_product_packaging_unit_amount tables with the respective data.
The packaging units information is saved in Storage after import: in the Administration Interface, under Maintenace-Storage menu, there ar Redis keys: product_abstract_packaging:{redis_key_suffix_column}
In the current implementation each packaging unit and lead product has to define sales units. It's enough to define the default "item" as base unit for the abstract and to define also "item" as one and the only sales unit for both the lead product and all related packaging units.
Current Constraints
- In the Spryker Commerce OS you cannot define packaging units for products. Currently, they are imported to the database manually.
- We strive to shift all business logic to our backend, however, with Packaging Units, calculations are performed on Yves.
- On the shopping cart as well as the shopping list page, products do not have a dropdown to change the packaging units. You can select a packaging unit on the product details page only.
- A shopper cannot reorder the items with the selected packaging units as they are not added automatically. They should be added manually on the product details page.
- In the Quick Order form and search widget, the products use the default packaging units that cannot be changed. Flexible packaging units are not supported on the Quick Order page.
Example: You have a product in your shop - a pen. And there exists a packaging unit for a pen - a box with a minimum amount of 5 items in it up to the maximum amount of 50 pens available. Every shopper can define the necessary amount of pens that will be included in the box and order several such boxes. But on the Quick Order page, if the customer adds a pen with the packaging unit 'box', the box consisting of minimum 5 items will be added by default.
Last review date: Jul 08, 2019