scipy.ndimage.fourier_shift¶
-
scipy.ndimage.fourier_shift(input, shift, n=-1, axis=-1, output=None)[source]¶ Multi-dimensional fourier shift filter.
The array is multiplied with the fourier transform of a shift operation.
Parameters: input : array_like
The input array.
shift : float or sequence
n : int, optional
If n is negative (default), then the input is assumed to be the result of a complex fft. If n is larger than or equal to zero, the input is assumed to be the result of a real fft, and n gives the length of the array before transformation along the real transform direction.
axis : int, optional
The axis of the real transform.
output : ndarray, optional
If given, the result of shifting the input is placed in this array. None is returned in this case.
Returns: fourier_shift : ndarray or None
The shifted input. If output is given as a parameter, None is returned.
Examples
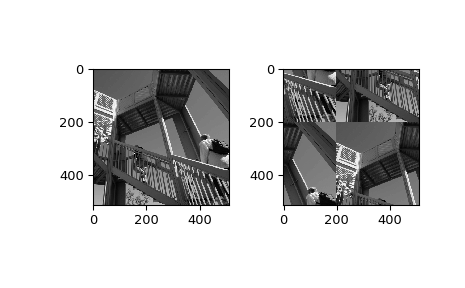
>>> from scipy import ndimage, misc >>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt >>> import numpy.fft >>> fig, (ax1, ax2) = plt.subplots(1, 2) >>> plt.gray() # show the filtered result in grayscale >>> ascent = misc.ascent() >>> input_ = numpy.fft.fft2(ascent) >>> result = ndimage.fourier_shift(input_, shift=200) >>> result = numpy.fft.ifft2(result) >>> ax1.imshow(ascent) >>> ax2.imshow(result.real) # the imaginary part is an artifact >>> plt.show()