---
execute:
echo: true
message: false
warning: false
fig-format: "svg"
format:
revealjs:
highlight-style: a11y-dark
reference-location: margin
theme: lecture_styles.scss
controls: true
controls-tutorial: true
slide-number: true
code-link: true
chalkboard: true
incremental: false
smaller: true
preview-links: true
code-line-numbers: true
code-annotations: hover
history: false
progress: true
link-external-icon: true
pointer:
color: "#b18eb1"
revealjs-plugins:
- pointer
---
```{r}
#| echo: false
#| cache: false
require(downlit)
require(xml2)
require(tidyverse)
```
## {#title-slide data-menu-title="Workflow & Reproducibility" background="#1e4655" background-image="../../images/csss-logo.png" background-position="center top 5%" background-size="50%"}
[Workflow & Reproducibility]{.custom-title}
[CS&SS 508 • Lecture 3]{.custom-subtitle}
[{{< var lectures.three >}}]{.custom-subtitle2}
[Victoria Sass]{.custom-subtitle3}
# Roadmap{.section-title background-color="#99a486"}
---
:::: {.columns}
::: {.column width="50%"}
### Last time, we learned:
* The `tidyverse`
* Basics of `ggplot2`
* Advanced features of `ggplot2`
* Extensions of `ggplot2`
:::
::: {.column width="50%"}
::: {.fragment}
### Today, we will cover:
* Code Style
* Workflow
* Reproducibility
* Useful Base `R`
:::
:::
::::
# Code Style{.section-title background-color="#99a486"}
## Disclaimer
There are honestly no hard, fast rules about what is **the** *correct code*. You can produce all styles of code that will run and get you your desired results.
. . .
However, the following recommendations are made with these truths in mind:
::: {.incremental}
* Using a consistent style cuts down on the decisions you have to make, therefore allowing you to focus your attention on the substance of your code
* This makes code easier to write and your overall process more efficient!
* Easy-to-read code is faster-read-code: both for any collaborators you may have and also future-you.
* This is particularly helpful when scanning code in order to troubleshoot an error
:::
. . .
You can read more about the specific style we're using in this class [here](https://style.tidyverse.org/).
## Naming Objects
It's good practice to name objects (and oftentimes variables) using only lowercase letters, numbers, and `_` (to separate words).
. . .
Remember to give them descriptive names, even if that means they're longer.
. . .
If you have many related variables, try and be consistent with your naming convention.
* A common prefix is preferable to a common suffix due to RStudio's autocomplete feature.
```{r}
#| eval: false
# Code goal:
short_flights <- flights |>
filter(air_time < 60)
# Code foul:
SHORTFLIGHTS <- flights |>
filter(air_time < 60)
```
## Spacing
For readability you'll want to put spaces around all mathematical operators^[except for `^`] (i.e. `+`, `-`, `==`, `<`, etc.) as well as the assignment operator (`<-`).
```{r}
#| eval: false
# Code goals:
z <- (a + b)^2 / d
mean(x, na.rm = TRUE)
# Code foul:
z<-( a+b ) ^ 2/d
mean (x ,na.rm=TRUE)
```
. . .
To make code easier to skim quickly it's alright to add extra space for better alignment.
```{r}
#| eval: false
flights |>
mutate(
speed = distance / air_time,
dep_hour = dep_time %/% 100,
dep_minute = dep_time %% 100
)
```
## Pipes
As you begin to use more functions, sequentially, it can start to get unclear what's happening when, and to what.
```{r}
#| eval: false
median(sqrt(log(mean(gapminder$pop))))
```
. . .
With nested functions, like those above, you need to read the order of operations inside out, which is a bit awkward. It becomes even more confusing the more function calls you have, especially when they have multiple arguments each.
. . .
**Enter the pipe^[A component of programming which allows us to break a problem into a number of steps, each of which is straightforward and easy to understand.]:** `|>`
Pipes read "left to right" which is much more intuitive!
```{r}
#| eval: false
gapminder$pop |> mean() |> log() |> sqrt() |> median()
```
::: {.incremental}
* The above code takes what's on the left-hand side of `|>` and gives it as the first **unnamed** argument to the first function (`mean()`).
* The result of that function call is then "piped" to the first **unnamed** argument of the second function (`log()`)...
:::
## Pipes
As you can see, pipes allow us to "chain" many function calls together easily.
\
. . .
The so-called "native pipe" (i.e. built into base `R`) is relatively new. Before this, the pipe was a function from the `magrittr` package that looks like this: `%>%`.
\
. . .
This latter version continues to work but has a different functionality than the new, native pipe.
## `%>%` versus `|>` {.smaller}
[Most importantly, while both the `magrittr` pipe and the native pipe take the LHS (left-hand side) and "pipe" it to the RHS (right-hand side), they operate differently when it comes to explicitly specifying which argument of the RHS to pipe the LHS into.]{style="font-size: 85%;"}
. . .
```{r}
a <- c("Z", NA, "C", "G", "A")
```
. . .
:::: {.columns}
::: {.column width="50%"}
#### `%>%` (`magrittr` pipe)
```{r}
#| eval: false
a %>% gsub(pattern = 'A', # <1>
replacement = '-',
x = .) # <2>
```
1. `gsub` looks for a regular expression `pattern` (more on this in [Week 7](https://vsass.github.io/CSSS508/Lectures/Lecture7/CSSS508_Lecture7_index.html)) within the specified character vector `x`, and substitutes it with the specified `replacement` value.
2. By default, both pipes will pass the LHS to the first argument of the function on the RHS. If you need to pass the LHS to a different argument, i.e. the second, or third, etc., you need to explicitly tell the pipe which argument to pass it to. The placeholder for `%>%` is `.` (a period)
\
[Each of these examples returns:]{style="font-size: 85%;"}
```{r}
#| echo: false
a |> gsub('A','-', x = _)
```
:::
::: {.column width="50%"}
#### `|>` (native `R` pipe)
```{r}
#| eval: false
a |> gsub('A', # <3>
'-', # <3>
x = _) # <3>
a |> gsub(pattern = 'A', # <4>
replacement = '-') # <4>
a |> (\(placeholder) # <5>
gsub('A', # <5>
'-', # <5>
x = placeholder))() # <5>
```
3. `_` is the placeholder for `|>`
4. Leaving the "piped" argument as the only unnamed argument also works
5. Using an anonymous function call allows you to be explicit while specifying your own placeholder
:::
::::
::: aside
You can read more about the differences between `|>` and `%>%` [here](https://www.tidyverse.org/blog/2023/04/base-vs-magrittr-pipe/#-vs) and anonymous functions [here](http://adv-r.had.co.nz/Functional-programming.html#anonymous-functions). Code above comes from responses to [this stackoverflow post](https://stackoverflow.com/questions/70598384/piping-second-or-higher-argument-in-native-pipe).
:::
## Pipes
Some good syntax practices:
::: {.incremental}
* You should always put a space before `|>` and it should usually be the last thing on a line.
* New functions should be on a new line, indented 2 spaces (RStudio will automatically do this for you if you hit return after a pipe)
* Named arguments within a function should also get their own line
:::
```{r}
#| eval: false
# code goals
flights |>
group_by(tailnum) |>
summarize(
delay = mean(arr_delay, na.rm = TRUE),
n = n()
)
# code fouls
flights |> group_by(tailnum) |>
summarize(delay = mean(arr_delay, na.rm = TRUE), n = n())
```
## Selecting the native pipe
The `|>` is recommended over `%>%` simply because it's much simpler to use and it's always available (`%>%` relied on the `magrittr` package which was a dependency of `tidyverse` packages).
. . .
You'll need to specify to `R` that you want to enable its usage by going to *Tools* > *Global Options* > *Code*. Within the "Editing" Tab there is an option to "Use native pipe operator, `|>`". Check it! {{< fa check >}}
:::: {.columns}
::: {.column width="62%"}
{fig-align="left" width=110%}
:::
::: {.column width="38%"}
::: {.callout-note icon=false}
## {{< fa keyboard >}} Keyboard Shortcut
To insert a pipe (with spaces) quickly:
***Ctrl+Shift+M*** (Windows & Linux OS)
***Shift+Command+M*** (Mac)
:::
:::
::::
## Other Formatting Options
:::: {.columns}
::: {.column width="40%"}
There are some other useful formatting options I'd suggest setting globally and others you can specify to your preferences.
#### Suggested:
* Highlight Function Calls
* Enable preview of colors\
* Rainbow parentheses
:::
::: {.column width="60%"}
{fig-align="center"}
:::
::::
## Other Formatting Options
:::: {.columns}
::: {.column width="40%"}
There are some other useful formatting options I'd suggest setting globally and others you can specify to your preferences.
#### Suggested:
* [Highlight Function Calls]{.highlight-tableaured}
* Enable preview of colors\
* Rainbow parentheses
{fig-align="center"}
:::
::: {.column width="60%"}
{fig-align="center"}
:::
::::
## Other Formatting Options
:::: {.columns}
::: {.column width="40%"}
There are some other useful formatting options I'd suggest setting globally and others you can specify to your preferences.
#### Suggested:
* Highlight Function Calls
* [Enable preview of colors]{.highlight-tableaured}
* Rainbow parentheses
{fig-align="center" width=55%}
:::
::: {.column width="60%"}
{fig-align="center"}
:::
::::
## Other Formatting Options
:::: {.columns}
::: {.column width="40%"}
There are some other useful formatting options I'd suggest setting globally and others you can specify to your preferences.
#### Suggested:
* Highlight Function Calls
* Enable preview of colors
* [Rainbow parentheses]{.highlight-tableaured}
{fig-align="center" width=75%}
:::
::: {.column width="60%"}
{fig-align="center"}
:::
::::
## Other Formatting Options
:::: {.columns}
::: {.column width="40%"}
There are some other useful formatting options I'd suggest setting globally and others you can specify to your preferences.
#### Up to you:
* Code highlight style
:::
::: {.column width="60%"}
:::
::::
## Other Formatting Options
:::: {.columns}
::: {.column width="40%"}
There are some other useful formatting options I'd suggest setting globally and others you can specify to your preferences.
#### Up to you:
* Pane layout
:::
::: {.column width="60%"}
:::
::::
## Other Formatting Options
:::: {.columns}
::: {.column width="40%"}
There are some other useful formatting options I'd suggest setting globally and others you can specify to your preferences.
#### Up to you:
* Markdown options
* Output preview
* Inline output
:::
::: {.column width="60%"}
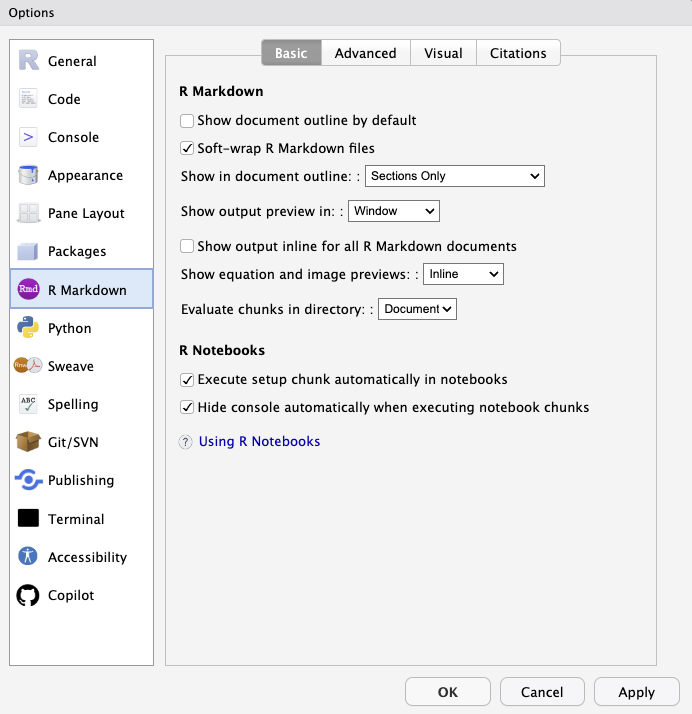
:::
::::
## Styling existing code
Imagine you've inherited a bunch of code from someone else and NOTHING is styled in the `tidyverse` way you've become accustomed. Or, you've dabbled in `R` before and you have some old code that is all over the place, with respect to styling.
. . .
Thanks to Lorenz Walthert there's a package for that! Using the [`styler` package](https://styler.r-lib.org/index.html) you can automatically apply the [`tidyverse` style guide](https://style.tidyverse.org/) standards to various filetypes (.R, .qmd, .Rmd, etc.) or even entire projects.
. . .
Have a style or variation of the `tidyverse` style that you prefer? You can specify that in the package as well. Use the keyboard shortcut *Cmd*/*Ctl* + *Shift* + *P* and search for "styler" to see all the options available.
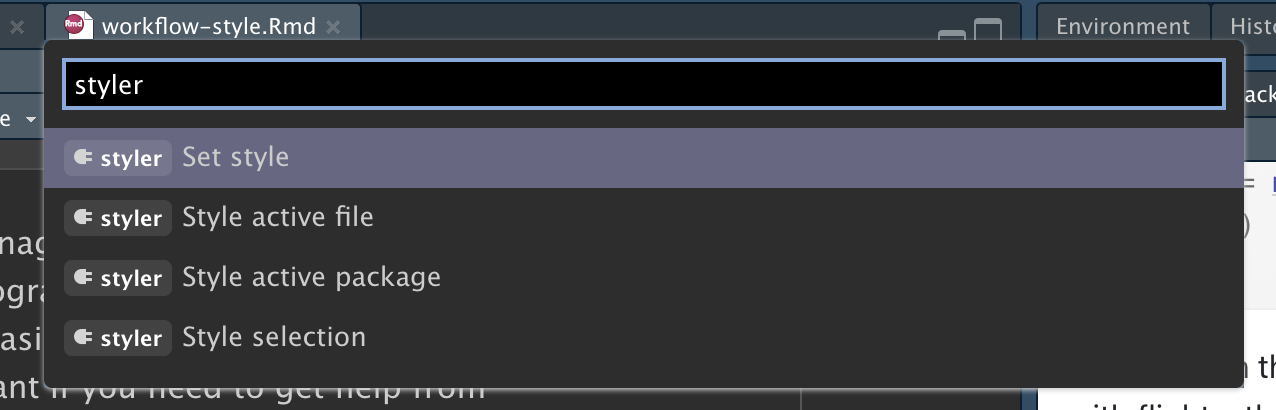{width=70% fig-align="center"}
# Workflow{.section-title background-color="#99a486"}
## .R scripts
We've been working with Quarto documents but you'll sometimes simply want to use an R script, which is basically an entire file that is just a code chunk.
. . .
::: {.panel-tabset}
### Why would you prefer an .R file over a .qmd file?
* You just need to run code, without the need for accompanying text output and plots in the same document. Examples include:
* Reading in and cleaning/manipulating your data before analysis
* Writing functions you'll use throughout your project
* Getting descriptive statistics/making descriptive plots of data
* Running models and generating tables/plots of their results
### When might you use a .qmd file?
* Homework assignments (like for this class) that require you to show code, describe your process for arriving at your solution, and include any results (i.e. tables, statistics, visualizations)
* Academic articles
* Presentations for class, conferences, talks, etc.
* Theses/dissertations
* Interactive visualizations (i.e. widgets)
* Building your own website
:::
## File naming
File names should:
. . .
* be machine readable: avoid spaces, symbols, and special characters. Don’t rely on case sensitivity to distinguish files.
* be human readable: use file names to describe what’s in the file.
* play well with default ordering: start file names with numbers so that alphabetical sorting puts them in the order they get used.
## Organization and Portability
Organizing research projects is something you either do accidentally — and badly — or purposefully with some upfront labor.
. . .
Uniform organization makes switching between or revisiting projects easier.
. . .
::: {.panel-tabset}
### Good Example directory
:::: {.columns}
::: {.column width="50%"}
```
project/
readme.md
data/
derived/
data_processed.RData
raw/
data_core.csv
data_supplementary.csv
docs/
paper_asa.qmd
paper_journal.qmd
syntax/
01-functions.R
02-cleaning.R
03_merging.R
04-exploratory.R
05-models.R
06-visualizations.R
visuals/
descriptive.png
heatmap.png
predicted_probabilities.png
```
:::
::: {.column width="50%"}
::: {.incremental .small1}
1. There is a clear hierarchy
* Written content is in `docs`
* Code is in `syntax`
* Data is in `data`
* Visualizations are in `visuals`
* The `readme.md` describes the project
2. Naming is uniform
* All lower case
* Words separated by underscores
3. Names are self-descriptive
4. Numbering scripts makes it clear in which order they should be run.
:::
:::
::::
### Bad Example directory
:::: {.columns}
::: {.column width="40%"}
```
alternative model.R
code for exploratory analysis.r
finalreport.qmd
FinalReport.qmd
fig 1.png
Figure_02.png
model_first_try.R
run-first.r
temp.txt
```
:::
::: {.column width="60%"}
::: {.incremental}
* Ordering of the files is unclear
* Inconsistent naming is confusing (which final report is THE final report?)
* Non-descriptive naming means more work for you in trying to decipher its contents
:::
:::
::::
:::
## Working directory
Your **working directory** is where `R` will look for any files that you ask it to load and where it'll put anything you ask it to save. It is literally just a folder somewhere on your computer or the remote server/cloud you're working within.
. . .
You can ask `R` what your current working directory is by running `getwd()` (`get` `w`orking `d`irectory).
. . .
```{r}
getwd()
```
You can see above that this lecture was created in a lecture-specific folder within a lectures folder, in a directory for this class, which is in a folder called `GitHub` on the Desktop of my laptop.
. . .
While you can *technically* set your working directory using `setwd()` (`set` `w`orking `d`irectory) and giving `R` a filepath, in the name of reproducible research DO NOT DO THIS! I strongly advise an alternative: **RStudio Projects**.
## Projects
A "project" is RStudio's built-in organizational support system which keeps all the files associated with a given project (i.e. data, R scripts, figures, results) together in one directory.
. . .
Creating a new project quite basically creates a new folder in a place that you specify. But it also does a few of other extremely useful things:
::: {.incremental}
* Creates a `.Rproj` file which tracks your command history and all the files in your project folder.
* Contains all the files needed to reproduce your work
* i.e. you can send a project folder to someone and they will be able to run it on their local machine
* Facilitates version control with built-in git/GitHub connection *(more on this later in the course)*
:::
## Creating an RStudio Project
:::: {.columns}
::: {.column width="65%"}
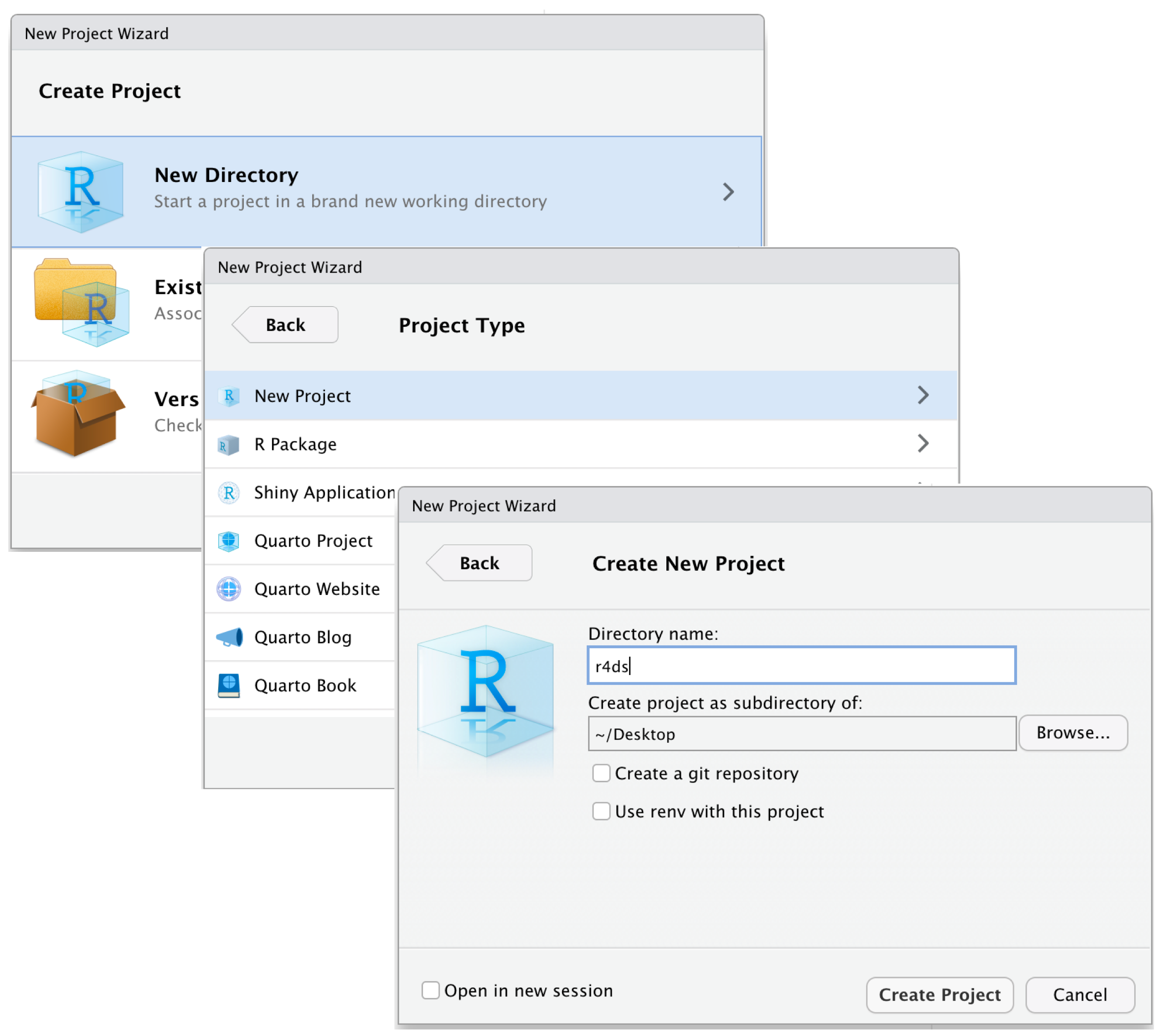{fig-align="center"}
:::
::: {.column width="35%"}
You can create a project by clicking
* *File* > *New Project...*
* {.absolute top=200} in the upper-left corner of RStudio
* the dropdown menu in the upper-right corner of RStudio and selecting *New Project...*
:::
::::
## Workflow versus Product
To summarize Jenny Bryan, [one should **separate workflow** (i.e. your personal tastes and habits) **from product** (i.e. the logic and output that is the essence of your project).](https://www.tidyverse.org/articles/2017/12/workflow-vs-script/)
. . .
:::: {.columns}
::: {.column width="50%"}
### Workflow
* The software you use to write your code (e.g. R/RStudio)
* The location you store a project
* The specific computer you use
* The code you ran earlier or typed into your console
:::
::: {.column width="50%"}
### Product
* The raw data
* The code that operates on your raw data
* The packages you use
* The output files or documents
:::
::::
. . .
Each data analysis (*or course using R*) should be organized as a [**project**]{.highlight-tableaured}.
* Projects *should NOT modify anything outside of the project* nor need to be modified by someone else (or future you) to run.
* **Projects *should be independent of your workflow*.**
## Portability
For research to be reproducible, it must also be *portable*. Portable software operates *independently of workflow*.
::: {.panel-tabset}
### **Do Not:**
* Use `setwd()`.
* Use *absolute paths* except for *fixed, immovable sources* (secure data).
+ `read_csv("C:/my_project/data/my_data.csv")`
* Use `install.packages()` in `R` script or .qmd files.
* Use `rm(list=ls())` anywhere but your console.
### **Do:**
:::: {.columns}
::: {.column width="50%"}
* Use RStudio projects (or the [`here` package](https://github.com/jennybc/here_here)) to set directories.
* Use *relative paths* to load and save files:
+ `read_csv("./data/my_data.csv")`
* Load all required packages using `library()`.
* Clear your workspace when closing RStudio.
+ Set *Tools > Global Options... > Save workspace...* to **Never**
:::
::: {.column width="50%"}
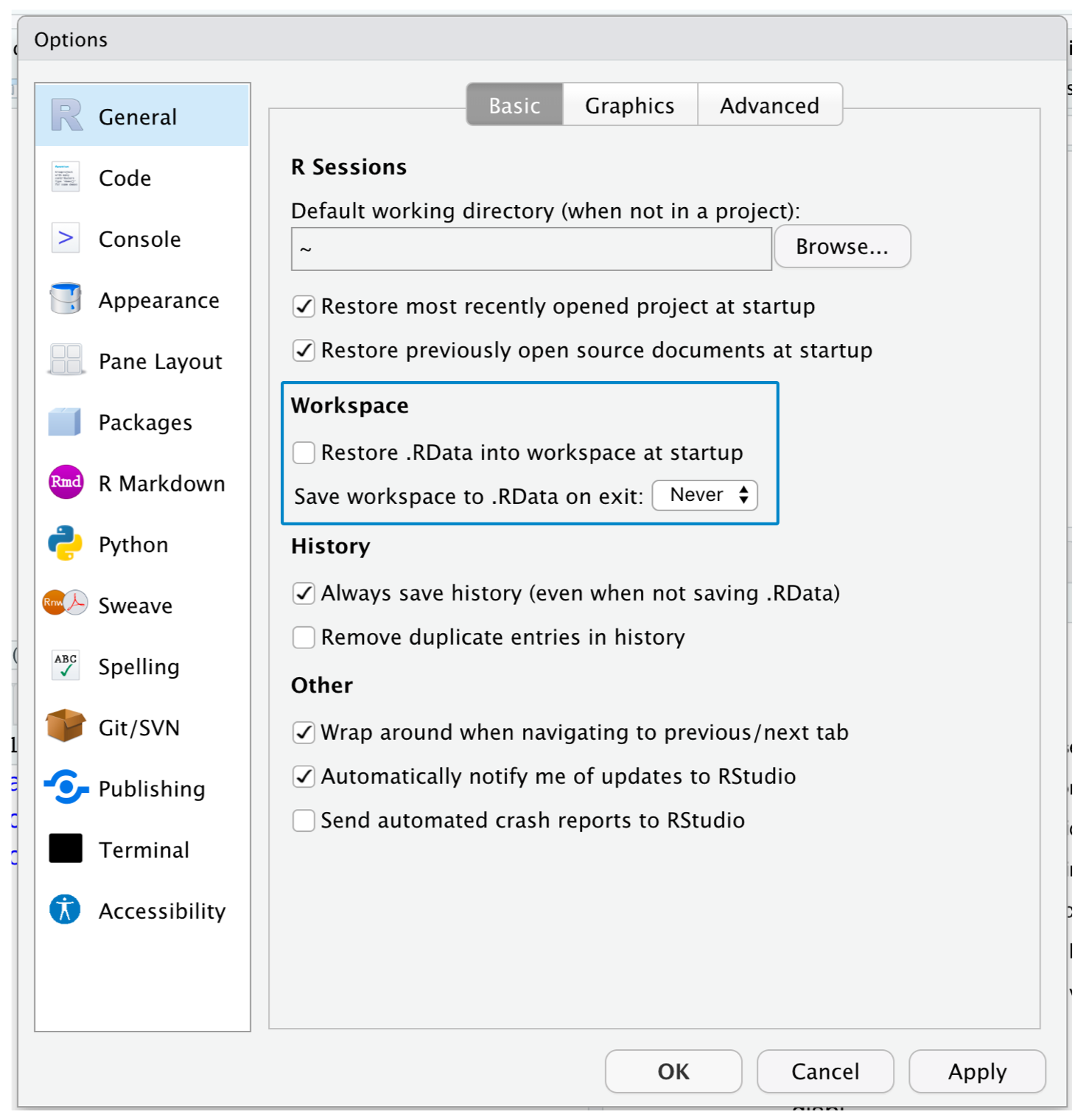{.absolute right=10 bottom=10 height=75%}
:::
::::
:::
## PSA: `setwd()` and `rm(list=ls())`
. . .
::: {.callout-warning icon=false}
## {{< fa triangle-exclamation >}} `setwd()`
Setting your working directory using `setwd()` makes it impossible for your project to be replicated by anyone but you, and only on the exact same computer on which it was created.
:::
. . .
::: {.callout-important icon=false}
## {{< fa circle-exclamation >}} `rm(list=ls())`
Make sure not to expect `rm(list=ls())` to give you a fresh `R` session. It may feel that way when all the objects in your global environment disappear but there are a host of dependencies (i.e. loaded packages, options set to non-defaults, the working directory) that have not changed. Your script will still be vulnerable to those settings unless you start a fresh `R` session.
:::
## File paths
A file path specifies the location of a file in a computer’s file system structure. They can be used to locate files and web resources. Some important things to note:
::: {.incremental}
* For file systems, each level in the hierarchy is a directory
* For URLs, each level in the hierarchy is a page.
* A path is a string of characters which specifies a unique location in a directory or page hierarchy.
* Different sections of the path are separated by a path separator, such as a forward slash (`/`).
* These different sections represent the separate directories or pages in the hierarchy.
* In Unix-based operating systems, such as Linux or macOS, the path separator is a forward slash (`/`).
* In Windows, the path separator is a back slash (`\`).
* URLs follow a standard format that always uses a forward slash (`/`) as the path separator regardless of the operating system.
:::
## Absolute Versus Relative Paths
::: {.panel-tabset}
### Absolute
Specifies the location of a file from the root directory in the file system structure. They are also called “full file paths” or “full paths.”
```{r}
#| eval: false
"/Users/victoriasass/Desktop/GitHub/CSSS508/Lectures/Lecture3/CSSS508_Lecture3.qmd"
```
:::{.fragment}
In Linux, the `~` is commonly used to represent a user's home directory, i.e.:
```{r}
#| eval: false
"~/Desktop/GitHub/CSSS508/Lectures/Lecture3/CSSS508_Lecture3.qmd"
```
:::
### Relative
Specifies the location of a file in the same folder or on the same server. In other words, a relative file path specifies a location of a file that is relative to the current directory.
```{r}
#| eval: false
"./CSSS508_Lecture3.qmd"` or `"CSSS508_Lecture3.qmd"
```
::: {.fragment}
Relative file paths use a dot notation at the start of the path, followed by a path separator and the location of the file.
* A single dot (`.`) indicates the current directory (as shown above)
* A double dot (`..`) indicates the parent directory.
:::
::: {.fragment}
For example, if I wanted to reference the syllabus (which is in the main project folder `CSSS508`) from my current folder `Lecture3` I would write:
```{r}
#| eval: false
"../../syllabus.qmd"
```
:::
:::
## Paths and Projects
When you work in an RStudio Project your *working directory* is the project folder.
. . .
If you are working on a `R` script or qmd file in a subfolder of this project, the working directory of that file will be its subfolder (not the project folder.
. . .
Keep this in mind when you're writing code and testing it interactively! Your current working directory will be the project folder when running code interactively even if you're writing code for a qmd that has a subfolder as the working directory.
::: aside
This is only relevant when using file paths (obviously). The most common uses of file paths in an `R` script or qmd is to read in or write data, and to save plots and tables.
:::
## Divide and Conquer
Often you do not want to include all code for a project in one `.qmd` file:
* The code takes too long to knit.
* The file is so long it is difficult to read.
. . .
There are two ways to deal with this:
1. Use separate `.R` scripts or `.qmd` files which save results from complicated parts of a project, then load these results in the main `.qmd` file.
+ This is good for loading and cleaning large data.
+ Also for running slow models.
. . .
2. Use `source()` to run external `.R` scripts when the `.qmd` renders
+ This can be used to run large files that aren't impractically slow.
+ Also good for loading project-specific functions.
## The Way of Many Files
I find it beneficial to break projects into *many* files:
* Scripts with specialized functions.
* Scripts to load and clean each set of variables.
* Scripts to run each set of models and make tables and plots.
* A main .qmd that runs some or all of these to reproduce the entire project.
. . .
Splitting up a project carries benefits:
* Once a portion of the project is done and in its own file, *it is out of your way.*
* If you need to make changes, you don't need to search through huge files.
* Entire sections of the project can be added or removed quickly (e.g. converted to an appendix of an article)
* **It is the only way to build a proper *pipeline* for a project. **
## Pipelines
Professional researchers and teams design projects as a **pipeline**.
. . .
A **pipeline** is a series of consecutive processing elements (scripts and functions in R).
. . .
Each stage of a pipeline...
1. Has clearly defined inputs and outputs
2. Does not modify its inputs.
3. Produces the exact same output every time it is re-run.
. . .
This means...
1. When you modify one stage, you only need to rerun *subsequent stages*.
2. Different people can work on each stage.
3. Problems are isolated within stages.
4. You can depict your project as a *directed graph* of **dependencies**.
## Example Pipeline
Every stage (oval) has an unambiguous input and output. Everything that precedes a given stage is a **dependency** — something required to run it.

::: aside
Note: [`targets` is a great package for managing R research pipelines.](https://docs.ropensci.org/targets/)
:::
# Lab 3 {.section-title background-color="#99a486"}
## {data-menu-title="Lab Exercises"}
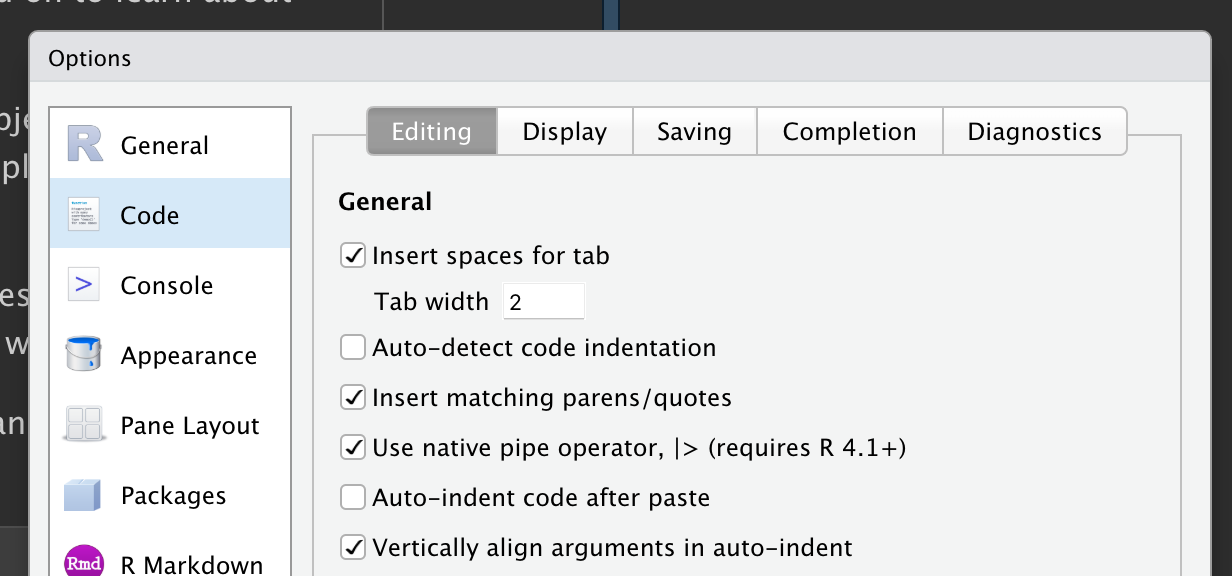
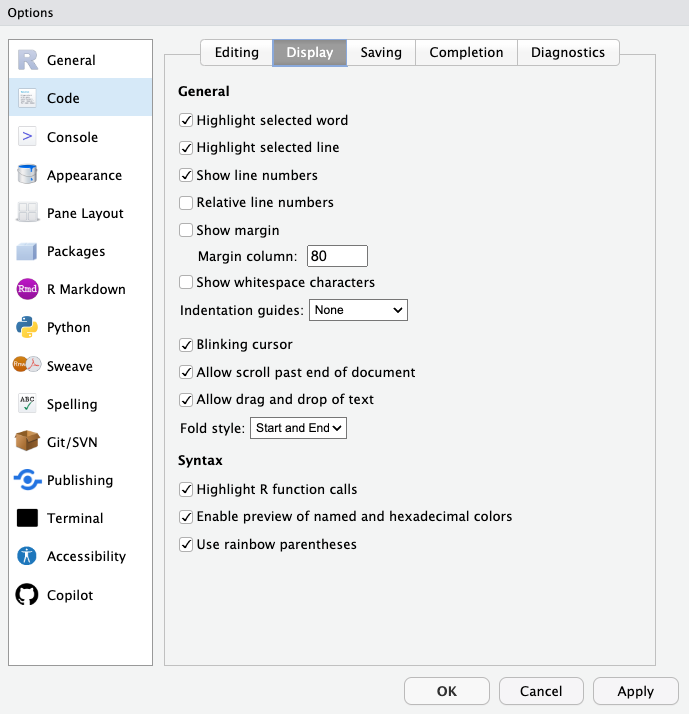
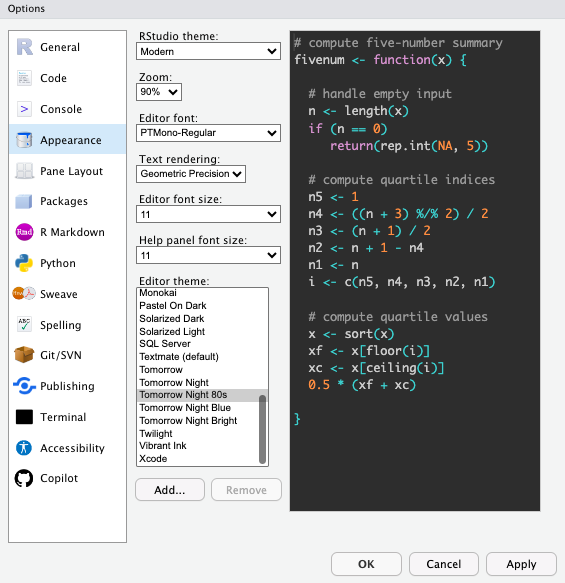
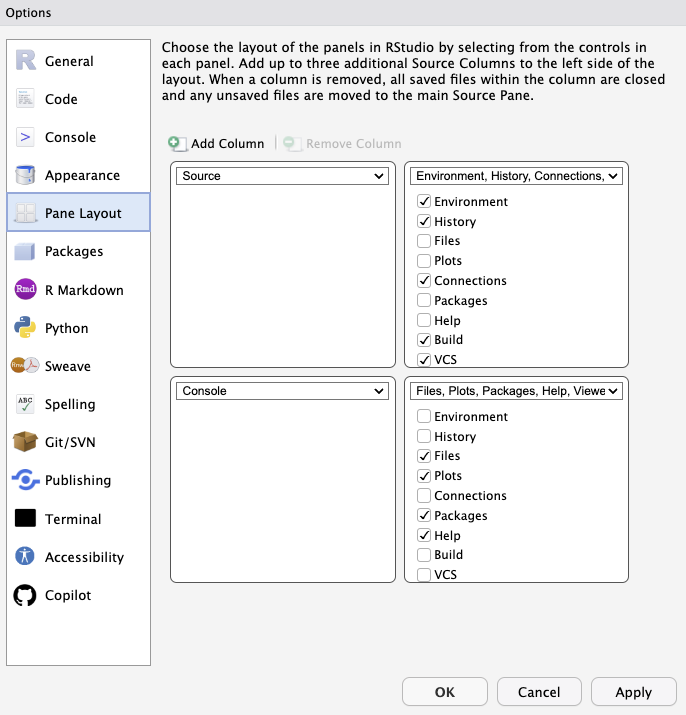
1. If you haven't already, go to *Tools* > *Global Options* and adjust your settings (i.e. *General*, *Code* > *Editing*, and *Code* > *Display*) to those recommended in the lecture and any others that you'd like to change (i.e. *Appearance*, *Pane Layout*, or *R Markdown*)
2. Restyle the following pipelines following the guidelines discussed in lecture:
```{r}
#| eval: false
flights|>filter(dest=="IAH")|>group_by(year,month,day)|>summarize(n=n(),
delay=mean(arr_delay,na.rm=TRUE))|>filter(n>10)
flights|>filter(carrier=="UA",dest%in%c("IAH","HOU"),sched_dep_time>
0900,sched_arr_time<2000)|>group_by(flight)|>summarize(delay=mean(
arr_delay,na.rm=TRUE),cancelled=sum(is.na(arr_delay)),n=n())|>filter(n>10)
```
3. Press *Option* + *Shift* + *K* / *Alt* + *Shift* + *K*. What happens? How can you get to the same place using the menus?
4. Tweak each of the following R commands so that they run correctly:
```{r}
#| eval: false
libary(todyverse)
ggplot(dTA = mpg) +
geom_point(maping = aes(x = displ y = hwy)) +
geom_smooth(method = "lm)
```
5. What might be a good way to organize your homework assignments for this class?
## Solution: 1. Adjust settings
{fig-align="center" width=50%}
## Solution: 1. Adjust settings
{fig-align="center" width=50%}
## Solution: 1. Adjust settings
{fig-align="center" width=50%}
## Solution: 1. Adjust settings
{fig-align="center" width=50%}
## Solution: 1. Adjust settings
{fig-align="center" width=50%}
## Solution: 1. Adjust settings
{fig-align="center" width=50%}
## Solution: 2. Readable code style
::: {.fragment .semi-fade-out fragment-index=1}
```{r}
#| eval: false
flights|>filter(dest=="IAH")|>group_by(year,month,day)|>summarize(n=n(),
delay=mean(arr_delay,na.rm=TRUE))|>filter(n>10)
flights|>filter(carrier=="UA",dest%in%c("IAH","HOU"),sched_dep_time>
0900,sched_arr_time<2000)|>group_by(flight)|>summarize(delay=mean(
arr_delay,na.rm=TRUE),cancelled=sum(is.na(arr_delay)),n=n())|>filter(n>10)
```
:::
::: {.fragment .fade-in fragment-index=1}
```{r}
#| eval: false
flights |>
filter(dest == "IAH") |>
group_by(year, month, day) |>
summarize(
n = n(),
delay = mean(arr_delay, na.rm = TRUE)
) |>
filter(n > 10)
flights |>
filter(carrier == "UA", dest %in% c("IAH", "HOU"),
sched_dep_time > 0900, sched_arr_time < 2000) |>
group_by(flight) |>
summarize(
delay = mean(arr_delay, na.rm = TRUE),
cancelled = sum(is.na(arr_delay)),
n = n()
) |>
filter(n > 10)
```
:::
## Solution: 3. *Option* + *Shift* + *K* / *Alt* + *Shift* + *K*
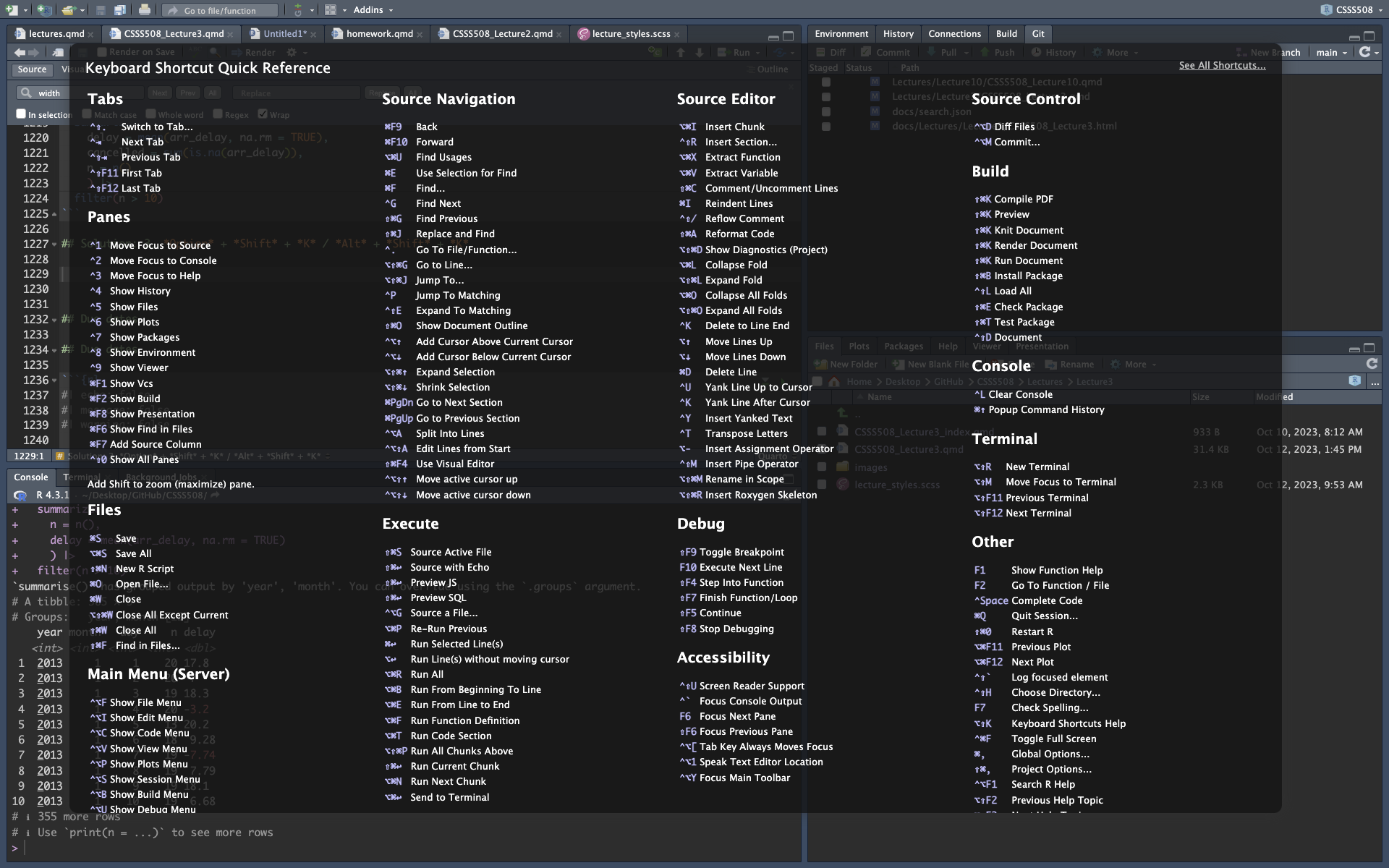{fig-align="center" width=80%}
::: aside
You can find the same quick reference pop-up by clicking *Tools* > *Keyboard Shortcuts Help*.
:::
## Solution: 4. Keyboard shortcut
::: {.fragment .semi-fade-out fragment-index=1}
```{r}
#| eval: false
libary(todyverse)
ggplot(dTA = mpg) +
geom_point(maping = aes(x = displ y = hwy)) +
geom_smooth(method = "lm)
```
:::
\
::: {.fragment .fade-in fragment-index=1}
```{r}
#| eval: false
libary(tidyverse)
ggplot(data = mpg,
mapping = aes(x = displ, y = hwy)) +
geom_point() +
geom_smooth(method = "lm")
```
:::
## Solution: 5. Organizing a class
:::: {.columns}
::: {.column width="50%"}
::: {.incremental}
1. Create a folder for this class on a computer/system that gets backed up regularly
2. Either the class itself is an RStudio project or each homework assignment subfolder is a separate project
3. Everything within each homework assignment project gets saved into that specific folder (or a subfolder of that folder)
4. Anything required for each homework assignment (e.g. downloaded data) is saved into its project-specific folder
:::
:::
::: {.column width="50%"}
::: {.fragment}
```
CSSS508/
Homeworks/
HW1/
homework1.qmd
homework1.html
HW2/
homework2.qmd
homework2.html
HW3/
homework3.qmd
homework3.html
HW4/
homework4.qmd
homework4.html
data.csv
HW5/
homework5.qmd
homework5.html
data/
data_raw.csv
data_processed.Rdata
HW6/
HW7/
HW8/
HW9/
```
:::
:::
::::
# Break!{.section-title background-color="#1e4655"}
# Reproducible Research{.section-title background-color="#99a486"}
## Why Reproducibility?
Reproducibility is not *replication*.
* **Replication** is running a new study to show if and how results of a prior study hold.
* **Reproducibility** is about rerunning *the same study* and getting the *same results*.
. . .
Reproducible studies can still be *wrong*... and in fact reproducibility makes proving a study wrong *much easier*.
. . .
\
Reproducibility means:
* Transparent research practices.
* Minimal barriers to verifying your results.
. . .
*Any study that isn't reproducible can only be trusted on faith.*
## Reproducibility Definitions
Reproducibility comes in three forms (Stodden 2014):
::: {.incremental}
1. **Empirical:** Repeatability in data collection.
2. **Statistical:** Verification with alternate methods of inference.
3. **Computational:** Reproducibility in cleaning, organizing, and presenting data and results.
:::
. . .
R is particularly well suited to enabling **computational reproducibility**^[ Python is equally well suited. Julia is an option as well.].
. . .
They will not fix flawed research design, nor offer a remedy for improper application of statistical methods.
Those are the difficult, non-automatable things you want skills in.
## Computational Reproducibility
Elements of computational reproducibility:
. . .
* Shared data
+ Researchers need your original data to verify and replicate your work.
. . .
* Shared code
+ Your code must be shared to make decisions transparent.
. . .
* Documentation
+ The operation of code should be either self-documenting or have written descriptions to make its use clear.
. . .
* Version Control^[We'll come back to this on the last week of class.]
+ Documents the research process.
+ Prevents losing work and facilitates sharing.
## Levels of Reproducibility
For academic papers, degrees of reproducibility vary:
::: {.incremental}
0. "Read the article"
1. Shared data with documentation
2. Shared data and all code
3. Interactive document^[A .qmd is one such example.]
4. Research compendium^[Usually contains all code, data, documentation, and outputs related to the project, allowing others to reproduce your analyses.]
5. Docker compendium^[A research compendium that includes a Dockerfile or container image so the full computational environment can be recreated, regardless of machine setup.]: Self-contained ecosystem
:::
## Interactive Documents
Interactive documents — like Quarto docs — combine code and text together into a self-contained document.
* Load and process data
* Run models
* Generate tables and plots in-line with text
* In-text values automatically filled in
. . .
Interactive documents allow a reader to examine your computational methods within the document itself; in effect, they are self-documenting.
. . .
By re-running the code, they reproduce your results on demand.
. . .
Common Platforms:
* **R:** Quarto
* **Python:** Jupyter Notebooks
# Useful Base R {.section-title background-color="#99a486"}
## Selecting from vectors with `[`
:::: {.columns}
::: {.column width="40%"}
Given a vector^[This is an example of a *named* vector, where each element is given a name (LHS) associated with its value (RHS).] of values:
```{r}
x <- c(a = "one",
b = NA,
c = "two",
d = "three",
e = "four",
f = NA,
g = NA,
h = "five")
```
:::
::: {.column width="60%"}
You can select from the vector
::: {.fragment}
```{r}
#| output-location: fragment
x[c(3, 1, 5)] # <1>
```
1. With positive integers
:::
::: {.fragment}
```{r}
#| output-location: fragment
x[c(3, 1, 1, 5, 3)] # <2>
```
2. Even repeated values
:::
::: {.fragment}
```{r}
#| output-location: fragment
x[c(-2, -6, -7)] # <3>
```
3. With negative integers (removes these elements from the vector)
:::
::: {.fragment}
```{r}
#| output-location: fragment
x[!is.na(x)] # <4>
```
4. With a logical vector
:::
::: {.fragment}
```{r}
#| output-location: fragment
x[c("c", "h")] # <5>
```
5. Or with a named vector
:::
:::
::::
## Selecting from dataframes with `[`
You can select rows and columns from dataframes with `df[rows, cols]`.
:::: {.columns}
::: {.column width="40%"}
```{r}
#| output-location: fragment
df <- tibble(
x = 1:3,
y = c("a", "e", "f"),
z = runif(3) # <1>
)
df
```
1. defaults: `min = 0`, `max = 1`
:::
::: {.column width="60%"}
::: {.fragment}
```{r}
#| output-location: fragment
df[1, 2] # <2>
```
2. Select first row and second column
:::
::: {.fragment}
```{r}
#| output-location: fragment
df[, c("x" , "y")] # <3>
```
3. Select all rows and columns `x` and `y`
:::
::: {.fragment}
```{r}
#| output-location: fragment
df[df$x > 1, ] # <4>
```
4. Select rows based on a logical condition (more on this in [Week 4](https://vsass.github.io/CSSS508/Lectures/Lecture4/CSSS508_Lecture4_index.html)), i.e. where rows of `x` are greater than 1 and all columns
:::
:::
::::
## `data.frame()` vs. `tibble()`
[Tibbles are the tidyverse version of a base `R` dataframe. Usually you can use them interchangably without issue but they have slightly different behavior that's important to know about when indexing in this way.]{style="font-size: 85%;"}
. . .
:::: {.columns}
::: {.column width="50%"}
[If `df` is a data.frame, then `df[, cols]` will return a vector if `col` selects a single column and a data frame if it selects more than one column.]{style="font-size: 85%;"}
```{r}
#| output-location: fragment
df1 <- data.frame(x = 1:3)
df1[, "x"]
```
:::
::: {.column width="50%"}
[If `df` is a tibble, then `[` will always return a tibble.]{style="font-size: 85%;"}
```{r}
#| output-location: fragment
df2 <- tibble(x = 1:3)
df2[, "x"]
```
:::
::::
. . .
\
[One way to avoid this ambiguity with `data.frames` is to explicitly specify `drop = FALSE`:]{style="font-size: 85%;"}
```{r}
#| output-location: fragment
df1[, "x" , drop = FALSE]
```
## Selecting from dataframes with `[[` and `$`
`[`, which selects many elements, is paired with `[[` and `$`, which extract a single element.
:::: {.columns}
::: {.column width="40%"}
```{r}
#| output-location: fragment
tb <- tibble(
x = 1:4,
y = c(10, 4, 1, 21)
)
tb
```
:::
::: {.column width="60%"}
::: {.fragment}
`[[` can access by position or by name:
```{r}
#| output-location: fragment
tb[[1]] # <1>
```
1. By position
:::
::: {.fragment}
```{r}
#| output-location: fragment
tb[["x"]] # <2>
```
2. By name
:::
::: {.fragment}
```{r}
#| output-location: fragment
tb$x # <3>
```
3. `$` is specialized for access by name
:::
::: {.fragment}
They can also be used to create new columns.
```{r}
#| output-location: fragment
tb$z <- tb$x + tb$y
tb
```
:::
:::
::::
## Getting Help {{< fa scroll >}} {.scrollable}
One of the most difficult things as a beginner in `R` (or any language tbh) is not always knowing what to ask to solve your issue. Being in this class is a great first step! Some other useful tools:
:::{.incremental}
* **Google**
+ Adding `R` to your query is basic but useful and often overlooked. Including the package name, if you're using one, is another. Finally, what is it you want to do? For example "R dplyr create new variable based on value of another."
+ Copy and pasting error messages is also helpful!
* **StackOverflow**
+ Many of your Google queries will take you here anyways so you might try going directly to the source! Filter by `R` and make sure to include a `reprex` so people can actually understand what your issue is.
* **Reprex**
+ Short for minimal `repr`oducible `ex`ample this is a version of your code that someone could copy and run on their own machine, making it possible for them to help you troubleshoot your problem.
+ You want to strip away everything not pertinent to the issue you're having so that it's simple and straightforward.
+ You can use the [`reprex`](https://reprex.tidyverse.org/) package for assistance with this!^[`dput()` is also a useful function for quickly creating a snippet of your data to share with others to illustrate your issue.]
* **Putting in the work up front**
+ It's cliché, but investing in your learning right now will pay off down the road.
+ Learning how to do something, why `R` works in a certain way, and developing practices that keep you organized will make you more efficient and help prevent minor and major frustrations going forward.
:::
# Homework{.section-title background-color="#1e4655"}
## {data-menu-title="Homework 3" background-iframe="https://vsass.github.io/CSSS508/Homework/HW3/homework3.html" background-interactive=TRUE}