Previous Page [RF Capture Guide](RF-Capture-Guide)
Next Page [Exporting To Video Files](Video-Exporting-&-Gen-Chroma-Scripts)
# Welcome to the 21st, its the future.
Software decoding simply is just doing what was done on dedicated components, then on dedicated IC's and finally on FPGAs and all in one IC's, its not magic and its not black box hardware either its entirely software emulating the ability's of hardware with an order of magnitude more flexibility.
Do you need to know about programming?
***No.***
Do you need to know how to use basic command systems on a computer.
**Yes.**
Do you need to have a basic understanding of a VCR does and what a TBC does?
**Yes.**
**It makes life easier** and decoding a thoughtless copy-paste clean, new tape, clean, hit enter and decode workflow after hardware hook-up.
## Format Notes
Decoding can be broken into 3 types.
`FM Modulated Colour-Under` / `FM Modulated CVBS` / `RAW Baseband Composite / CVBS`
Composite/CVBS Sources are always 1 CVBS `.tbc` file.
Colour-Under formats are 2 `.tbc` files an S-Video (Y+C) TBC Pair.
VHS, SVHS, Betamax, Umatic, Umatic SP, EIAJ, Video8, Hi8, Philips VCR, Video2000 - `Colour Under`
SMPTE-A, SMPTE-B, SMPTE-C, 2" Quadruplex, LaserDisc - `Composite Modulated`
Betacam, Betacam SP, W-VHS - Duel Channel Component (Support not yet implemented)
LaserDisc HDVS, Hi-Vision are MUSE system that we need more samples of baseband and direct RF really.
# What does decoding do?
[Technical Doc](Technical-Breakdowns)
`vhs-decode` (tape decoding) creates a 4fsc sampled Composite `.tbc` or S-Video `.tbc` & `_chroma.tbc` file pair Y/C or S-Video style.
This 4fsc file allows inspection or dedicated selection of what channels are used in video export if the Luma or Y channel has something usable but the colour is so bad as to destroy the image you can just export the luma data for example before its combined with colour information to make a standard colourised video frame.
`ld-decode` (LaserDisc Decoding) produces only a Composite `.tbc` and `.pcm` for stereo/mono analogue audio.
`.efm` Produced by ld-decode for digital data.
Audio data is decoded to `.dts` or `.ac3` with `ld-efm-decoder`, but there can also be outher data such as in the case of the Domesday 86 discs.
`cvbs-decode` (RAW Composite decoding) produces only a Composite `.tbc` it basically just re-samples and TBC's the input file as its not actually "decoding" the signal to anything just cleaning and reformatting it to decode standard `.tbc` for use with the toolchain.
> [!NOTE]
> All 3 decoders produce a critical `.log` & `.json` metadata file that contains format, SNR, Timecode, TV System and more it should always be saved.
> [!TIP]
> During decoding, ld-analyse can be used to view the state of progress visually and to see the current statistics data of your decode such as bSNR (black signal to noise ratio) values.
### Post Decode - Video
After inital decoding, the black & white video levels & chroma decoder settings can be adjusted inside of [ld-analyse](ld-analyse-User-Guide).
> [!CAUTION]
> chroma-decoder settings are not saved into the metadata, these values will have to be manually set on tbc-video-export or ld-chroma-decoder.
The main thing users needs to check and adjust is the horizontal output adjustment i.g where the left and right start/end of the active image area from the decoded .tbc files begins allowing you to correct left/right bias offsets which is very common on tape or some CVBS sources.
So your final chroma-decoded and encoded video file is nice and properly centred, this "centering" metadata is then passed to the export end of things.
### Post Export - Audio
Linear audio in `FLAC` or `WAV` PCM format assumed captured from a [clockgen](clockgen-mod) or [MISRC]() setup should only require passing to [auto audio align](auto-audio-align) after the video decoding has finished so it can be re-timed to the decoded picture frames and not have any synchronisation issues.
`HiFi-Decode` decodes your FM RF HiFi audio captures to a PCM sampled audio stream it can be direct PCM `.wav` files or 2:1 compressed with FLAC so a `.flac` with 48khz 24-bit default for the sampling.
`RTLSDR-Decode` is a real-time GNURadio based decoder/encode script that creates a 8msps `.u8` RF file, a 48khz `.flac` audio file and decodes the signal live with a 1-3sec delay, this is more useful as a probe testing tool to find and test HiFi signal test points then it is as a capture method. this is due to the issue of not using a shared clock source with the video capture, it will not have a common time base to use for off-set calculations.
## Export to Video
The final export is mainly automated with [tbc-video-export](TBC-to-Video-Export-Guide) it will use said adjusted values applyed to the metadata with ld-analyse associated with the input `.tbc` when generating your final video file.
## Resource Usage
Chroma-Decoder can use around 20GB+ of system memory (RAM) with FFmpeg if a high thread queue size is used.
The decoders are CPU bound and will use normally less then 500MB of ram, and up to 4~6 threads, the bias is for single core & cache speed.
# Running the decoders
There are 4 decoders & 1 tool are bundled inside vhs-decode repository and binary versions, please familierise yourself with the call command for your installation type.
## Mandatory Settings
- TV System i.g `--system pal` or `ntsc`, `palm`, `ntscj` (PAL-M - Brazil / NTSC-J - Japan), `MESECAM` (Consumer recorded SECAM)
- Input Sample Rate `-f` or `--frequency` this is the sampling rate of your RF capture file. (40msps is the assumed/internal rate `-f 40`)
- Input file & Out file Name.
- Tape Format i.g `--tape_format VHS` or `SVHS`, `UMATIC`, `UMATIC_HI`, `Hi8`, `Video8`, `BETAMAX`, `BETAMAX_HIFI`, `EIAJ`, `TYPEC`, `VCR`.
- Tape Speed i.g `--tape_speed LP` or `SP` or `ELP` this can make a large difference on some tapes so it is always good to note and use the correct speed config or `SP` will be assumed.
> [!NOTE]
> HiFi-Decode only has NTSC/PAL speed rates (VHS & 8mm), and only a single 8mm mode for Video8/Hi8.
### Basic Command line Control:
Ctrl+C Will kill the current process, use this to stop the decode manually.
Press Ctrl+C to copy then Ctrl+P to past the command use <+> to move edit position on the command line to edit the name or command and Enter to run the command.
## Basic Decoding Command Examples
There is 2 ways to write commands, long hand and short hand such as
- `--tape_format` & `--tf` or `-f` & `--frequency`
Each version is documented together in the [command list](Command-List) master doc.
`--debug` for a slight speed hit gives more logging and better error reporting.
## VHS-Decode:
Example Long: `vhs-decode --debug --tape_format vhs --frequency 40 --system pal --ire0_adjust --recheck_phase --threads 4 --recheck_phase my-tape.u8 my-tape-decoded`
Example Short: `decode.exe vhs --debug -p -t 4 --tf vhs -f 40 --ire0_adjust --recheck_phase --recheck_phase my-tape.u8 my-tape-decoded`
## LD-Decode:
> [!IMPORTANT]
> NTSC AC3 Audio discs need `--AC3` enabled to decode that data to a `.efm`.
`ld-process-efm` also needs a dedicated flag but for `DTS audio`, but AC3 is automatic as its flagged on the initial decode.
Example Long: `ld-decode --system pal --threads 4 DdD_8.5_Gain.ldf First_Decoded_LD`
Example Short: `decode.exe ld -p -t 4 DdD_8.5_Gain.ldf First_Decoded_LD`
EFM Decoder `ld-process-efm First_Decoded_LD.efm
## CVBS-Decode:
[CVBS-Decode Wiki Page](https://github.com/oyvindln/vhs-decode/wiki/hifi-decode).
CVBS-Decode, decodes raw RF captured composite signals, you capture the normal composite video signal out of a device, in raw RF values then save it to file.
> [!WARNING]
> `-A` - Automatic is mandatory for decoding ot work currently.
Example Long: `cvbs-decode --debug --threads 4 --system pal -A --frequency 40 CX_White_Level_0db_6db_off.flac CX_Blue_Level_0db_6db_off_CXADC`
Example Short: `decode.exe cvbs --debug -t 4 -p -A -f 40 CX_Blue_Level_0db_6db_off.flac CX_White_Level_0db_6db_off`
You have full control over the baseband processing, fine control over how colour is processed with virtual vector scope and scan-line oscilloscope with the chroma-decoder in ld-analyse, you have a full 625/525 lines of image information to work with.
## HiFi-Decode:
[HiFi-Decode Wiki Page](https://github.com/oyvindln/vhs-decode/wiki/hifi-decode).
HiFi-Decode provides the FM audio decoding for VHS, SVHS, BetaMax, Video8, Hi8
A single command decoder for HiFi RF to make playable FLAC files
Example Long: `HiFi-decode --system pal -t 8 --audio_rate 48000 HiFi_Capture_40msps.s16 Tape-name_HiFi_Decode.flac`
Example Short: `decode.exe hifi -p -t 8 --audio_rate 48000 HiFi_Capture_40msps.s16 Tape-name_HiFi_Decode.flac`
> [!WARNING]
> Unlike video decoding, hifi-decode has full multi-threading support
## RTL-SDR Decode:
[RTL-SDR Decode Wiki Page](RTLSDR).
Primitive version of HiFi-Decode using a GNURadio script, open GNUradio load script, set output names, plug and play an RTLSDR device, hit run.
Ideal for testing HiFi tap points or tracking/physical calibration, and capture for DdD users.
> [!WARNING]
> This will require manual sync alinement, not recommended for full captures without a reference capture.
## Audio Alinement
> [!NOTE]
> This tool is only useful for 8mm single cahnnel captures and outher formats if they have Video & HiFi captured via shared clock source i.g MISRC, CX Card Clockgen Mod etc.
[Auto Audio Align](Auto-Audio-Align) can be used to sync audio based on your json metadata, if the audio is captured in sync.
AAA takes your following files:
`tbc-media.json` / `HiFi-Decode-48khz.wav` / `Linear-Baseband.wav`
Then trims the files based off missing fields/frames in the video based off logged frame information inside your `.JSON` file produced by the video decoders.
## Console Debug Messages
These are the warning and automatic notes you will see genarated during the decoding process.
# Decode Debug Messages - Quick Reference
## Normal Operation
```
File Frame 1234: VHS
File Frame 1235: VHS
```
## Sync Detection Issues
**Vsync arbitrage failed** *(vsyncserration.py:363)*
```
WARNING - Unexpected vsync arbitrage
```
→ Clean heads, adjust tracking.
**Field drop** *(core.py:2214, field.py:1327)*
```
ERROR - Unable to determine start of field - dropping field
```
→ RF dropout or tape deadspace, field lost (~16.7ms NTSC / 20ms PAL)
## Field Order Problems
**Missing field detected**
```
ERROR - Possibly skipped field (Two fields with same isFirstField in a row),
duplicating the last field to compensate...
```
→ Gap detected, duplicate previous field
**Overlapping fields**
```
ERROR - Possibly skipped field (Two fields with same isFirstField in a row),
dropping the last field to compensate...
```
→ Remove duplicate field
**Progressive content**
```
ERROR - Detected progressive video content..., manually flipping the field
order to compensate
```
→ 240p or 288p frames detected (3+ same-order fields)
## Notes
The following commands are your key commands for speeding things up with vhs-decode.
`--no_resample` for example can speed up tape decodes drastically for non 40msps captures i.e 20msps as it skips internal re-sampling to 40msps.
`--level_detect_divisor` Currently, 1-6 value, 1 every sample, 2 every other sample and so on, changes vsync serration code only use every nth sample when determining sync/blank levels higher value lower accuracy. - set to 6 for speed.
`--use_saved_levels` Experimental Skips doing most of the level detect code on each frame and only does it at the start or if there are issues detecting syncs. Provides a speedup in decoding and seems to work okay on captures that only have one single recording of media.
## VBI Data Decoding
> [!TIP]
> Always backup your `.json` file by making a quick zip/rar archive after decoding and processing.
**V**ertical **B**lanking **I**nterval Data.
| VBI Data Type | Support Level | Workflow Support Level |
|---------------------------------------|---------------|------------------------|
| CC - Closed Captions | Supported | Export Supported |
| VITC - Vertical Interval Timecode | Supported | Export Supported |
| WSS - Wide Screen Signalling | Not Supported | Manually Supported |
| VITS - Vertical Interval Test Signals | Supported | |
| Teletext | Supported | Supported by 3rd party |
| XDS - Extended Data Services | Basic Support | |
| VIDEO ID (IEC 61880) | Supported | |
| 40-bit FM Codes (LaserDisc) | Supported | |
| Philips Codes "White Flags" | Supported | |
> [!NOTE]
> VITC timecode does not yet have full data stream embedded into video files, nor chapter marking based off resets.
There is 3 tools for processing VBI data currently:
There is [VHS-Teletext](Teletext) for decoding Teletext data.
The Standard VBI Processor
ld-process-vbi input.tbc
The Test Signals VBI Processor
ld-prcoess-vits input.tbc
This data is decoded and stored in the updated `.json` file.
TBC-Video-Export automatically runs vbi processing and embeds the `.json` into mkv files for safety.
# ld-analyse - Viewing & Adjusting
[Full Wiki Page For ld-analyse](ld-analyse-User-Guide)
Your available frames will update as the data is written to the JSON file during decoding.
You can open it as a standard GUI application or call it with `ld-analyse` in the terminal.
 # Determining Capture Quality
There is 2 ways to assess the quality of a decode.
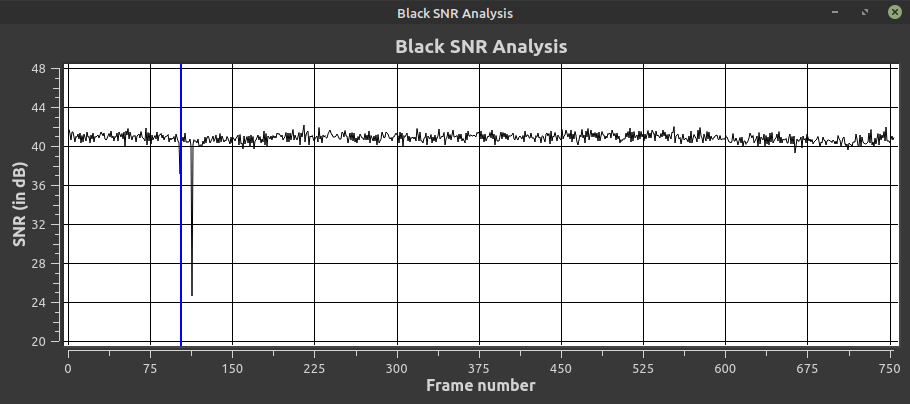
## Black Signal To Noise Ratio
# Determining Capture Quality
There is 2 ways to assess the quality of a decode.
## Black Signal To Noise Ratio
 (Open window & screenshot it currently)
Visually you can tell how noisy the signal is by how black the VBI space is if its a clear grey colour this means a high SNR.
LaserDiscs will normally have a curve to the graph ware as tape will mostly be level per each recorded segment.
Sudden dips in the graph are ware there are dropouts, interference or weak signal.
`60~70 dB` - Live Composite
`40~50 dB` - Great Signal
`30~40 dB` - Good Signal
`20~30 dB` - Weak Signal
`10~20 dB` - Poor Signal
> [!CAUTION]
> The SNR measurement is relative and can be highly affected by format, and is only sampled based off a single line in the VBI space as its code is still from ld-decode directy and does not avarage the whole black area of the VBI and or sync signal spaces.
## Export Dropout Analysis
(Open window & screenshot it currently)
(Open window & screenshot it currently)
Visually you can tell how noisy the signal is by how black the VBI space is if its a clear grey colour this means a high SNR.
LaserDiscs will normally have a curve to the graph ware as tape will mostly be level per each recorded segment.
Sudden dips in the graph are ware there are dropouts, interference or weak signal.
`60~70 dB` - Live Composite
`40~50 dB` - Great Signal
`30~40 dB` - Good Signal
`20~30 dB` - Weak Signal
`10~20 dB` - Poor Signal
> [!CAUTION]
> The SNR measurement is relative and can be highly affected by format, and is only sampled based off a single line in the VBI space as its code is still from ld-decode directy and does not avarage the whole black area of the VBI and or sync signal spaces.
## Export Dropout Analysis
(Open window & screenshot it currently)
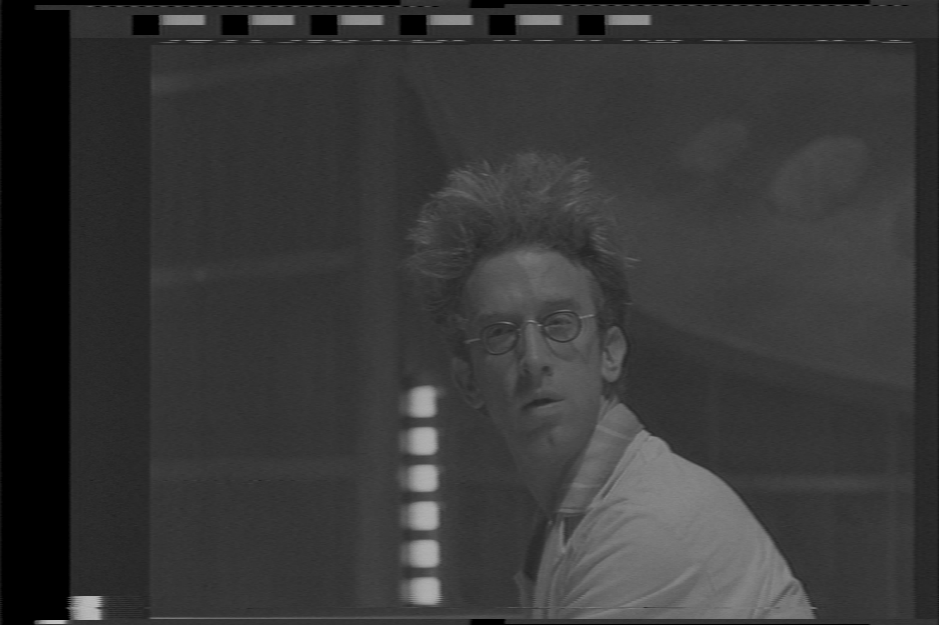
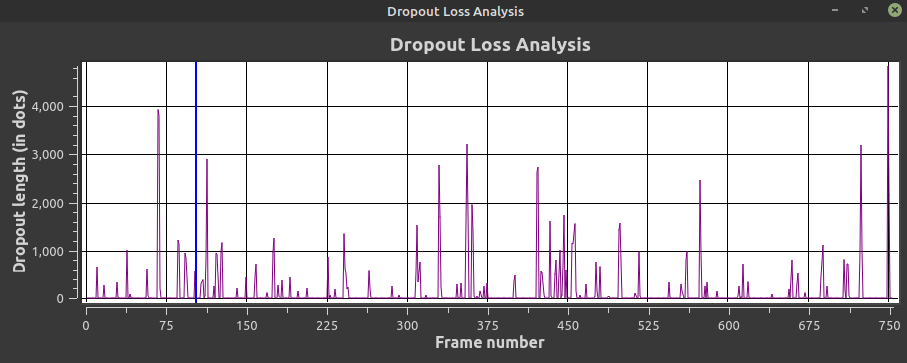 ## Visually Checking
[Visual Video Errors Doc](Visual-Video-Signal-Errors) / [VBI Data Identification Doc](Identifying-vbi-data)
Very Bad Signal Example
## Visually Checking
[Visual Video Errors Doc](Visual-Video-Signal-Errors) / [VBI Data Identification Doc](Identifying-vbi-data)
Very Bad Signal Example
 Normal Good Signal Example
Normal Good Signal Example
 > [!NOTE]
> This example contains a dropout.
Clean Macrovision Example
> [!NOTE]
> This example contains a dropout.
Clean Macrovision Example
 ## Adjusting For Export
As [ld-analyse](ld-analyse-User-Guide) reads the `.tbc` & `_chroma.tbc` (& JSON) files and combines them together in real-time with the ld-chroma-decoder this allows you to play with different chroma decoders and filtering settings on a basic level.
With ld-analyse can adjust JSON metadata alongside reading it, you can ignore this step however it is useful to learn to make better finer adjusted exports.
- PAL Transform 2D & Simple PAL 2D for Tape
- PAL Transform 3D for CVBS sources for example.
This is to the same effect as [SoX combining commands](https://github.com/oyvindln/vhs-decode/wiki/ld-analyse-User-Guide#y--c-combining-with-sox) on some media consider it good enough for checking but make a short video export with `tbc-video-export --length 300 input-tbc-name` script to see the real media result.
- Black Level Adjust
- White Level Adjust
You can adjust these sliders and `save` an updated `.json` with these values that the `tbc-video-export` tool will read.
You can manually set the 16:9 Flag for widescreen content (`iswidescreen` inside the `.json`)
## Adjusting For Export
As [ld-analyse](ld-analyse-User-Guide) reads the `.tbc` & `_chroma.tbc` (& JSON) files and combines them together in real-time with the ld-chroma-decoder this allows you to play with different chroma decoders and filtering settings on a basic level.
With ld-analyse can adjust JSON metadata alongside reading it, you can ignore this step however it is useful to learn to make better finer adjusted exports.
- PAL Transform 2D & Simple PAL 2D for Tape
- PAL Transform 3D for CVBS sources for example.
This is to the same effect as [SoX combining commands](https://github.com/oyvindln/vhs-decode/wiki/ld-analyse-User-Guide#y--c-combining-with-sox) on some media consider it good enough for checking but make a short video export with `tbc-video-export --length 300 input-tbc-name` script to see the real media result.
- Black Level Adjust
- White Level Adjust
You can adjust these sliders and `save` an updated `.json` with these values that the `tbc-video-export` tool will read.
You can manually set the 16:9 Flag for widescreen content (`iswidescreen` inside the `.json`)
 https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/0d858753-68c7-42e5-bc39-31bdd1efd1b4
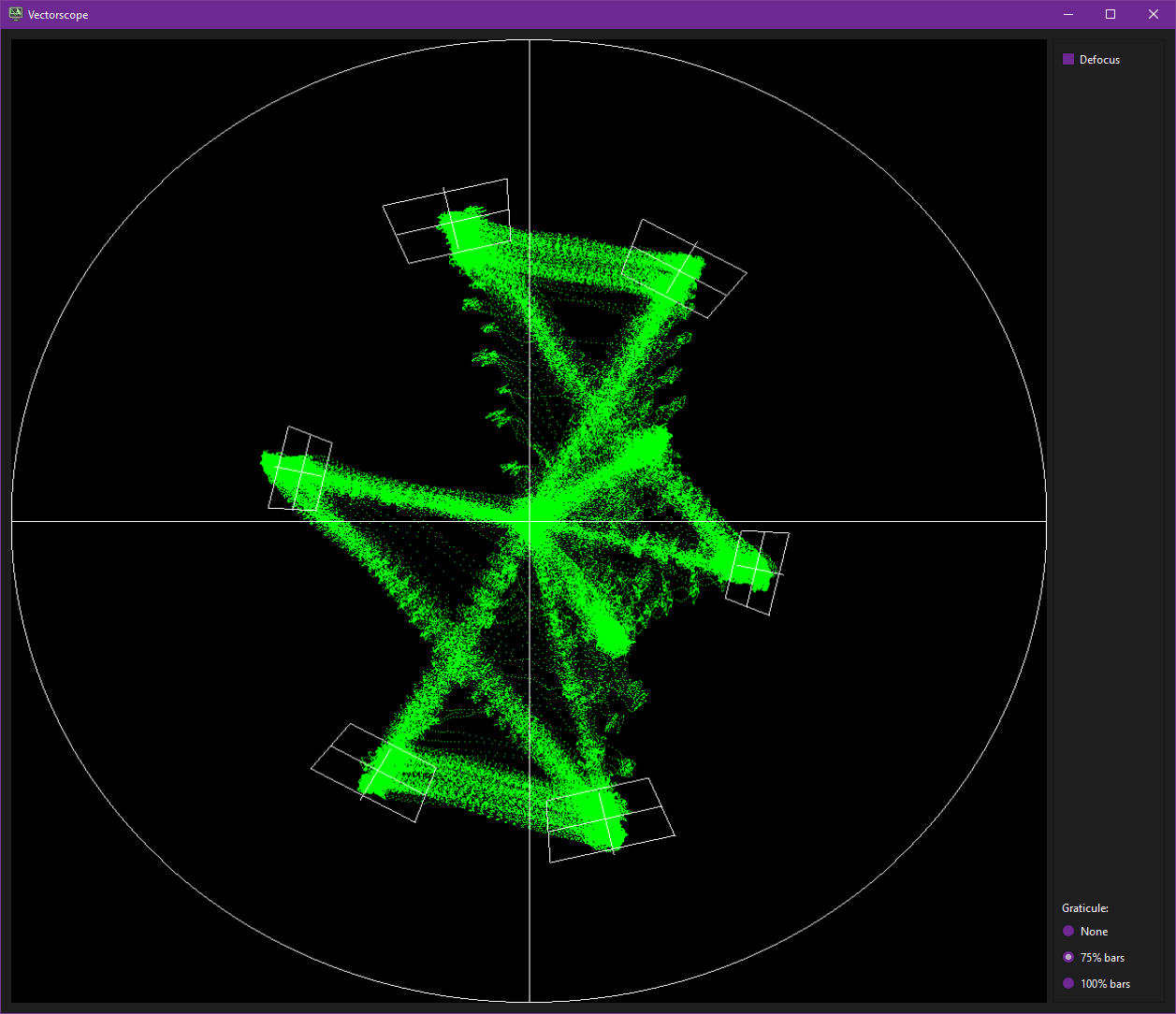
## Vector Scope & Chroma Decoder
> [!NOTE]
> Final output will be determined by fully running the chroma-decoder so run a 10sec test export.
For media with test bar signals you can select 75% or 100% bars you can adjust your image with the chroma-decoder.
https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/0d858753-68c7-42e5-bc39-31bdd1efd1b4
## Vector Scope & Chroma Decoder
> [!NOTE]
> Final output will be determined by fully running the chroma-decoder so run a 10sec test export.
For media with test bar signals you can select 75% or 100% bars you can adjust your image with the chroma-decoder.
 | EBU 75% Colour Bars | EBU 100% Colour Bars | SMPTE 75% Color Bars | SMPTE 100% HDTV Color Bars |
|---------------------|----------------------|----------------------|----------------------------|
|
| EBU 75% Colour Bars | EBU 100% Colour Bars | SMPTE 75% Color Bars | SMPTE 100% HDTV Color Bars |
|---------------------|----------------------|----------------------|----------------------------|
|  |
|  |
|  |
|  |
|
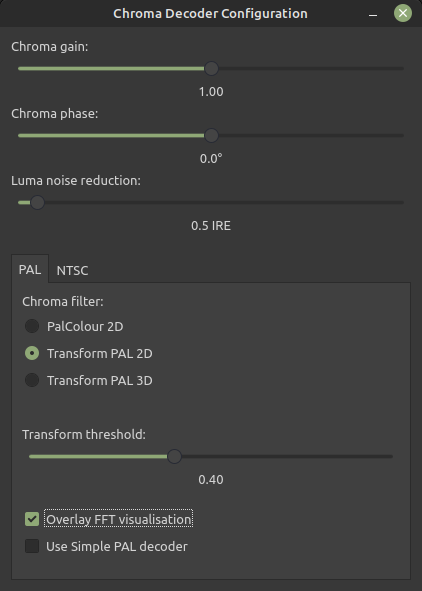
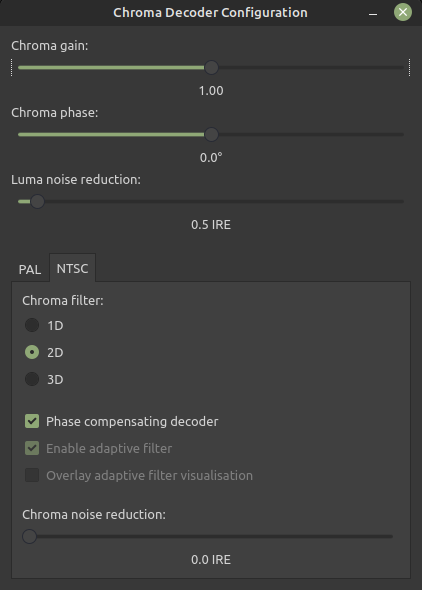 * Chroma Gain (Intensity)
* Chroma Phase (Hue Control)
* Luma Noise Reduction (PAL/NTSC)
* Chroma Noise Reduction (NTSC Only)
## HiFi-Decode Notes
FM Audio decoding has been normal for decades if you ever have used a car you know it has a radio and it picks up and decodes FM audio signals from local stations.
HiFi decode allows you to have full control over the de-modulation and noise filtering process this can remove and improve on sound quality drastically in some cases and or save you money if you don't have the best amplifiers or a decent audio interface capture solution, if you have good hearing you will notice the difference quickly with even 15USD Behringer ''studio'' headphones.
You can use an cheep RTLSDR or the DdD & CX Cards for HiFi capture, it does not require very high bandwidth.
Linear Audio will have to be captured via standard ADC solutions, such as [the clockgen mod](Clockgen-Mod).
As decent quality conventional capture workflow hardware is mandatory on the linear audio front, this can range from an GV2-USB to an Blackmagic Analog to SDI setup or Zoom F3 field recorders for example, but modern 24-bit ADCs in basic recorders are very affordable and higher SNR then linear tape audio in most cases.
# Page End
Previous Page [RF Capture Guide](https://github.com/oyvindln/vhs-decode/wiki/RF-Capture-Guide)
Next Page [Video Export Guide](https://github.com/oyvindln/vhs-decode/wiki/TBC-to-Video-Export-Guide)
* Chroma Gain (Intensity)
* Chroma Phase (Hue Control)
* Luma Noise Reduction (PAL/NTSC)
* Chroma Noise Reduction (NTSC Only)
## HiFi-Decode Notes
FM Audio decoding has been normal for decades if you ever have used a car you know it has a radio and it picks up and decodes FM audio signals from local stations.
HiFi decode allows you to have full control over the de-modulation and noise filtering process this can remove and improve on sound quality drastically in some cases and or save you money if you don't have the best amplifiers or a decent audio interface capture solution, if you have good hearing you will notice the difference quickly with even 15USD Behringer ''studio'' headphones.
You can use an cheep RTLSDR or the DdD & CX Cards for HiFi capture, it does not require very high bandwidth.
Linear Audio will have to be captured via standard ADC solutions, such as [the clockgen mod](Clockgen-Mod).
As decent quality conventional capture workflow hardware is mandatory on the linear audio front, this can range from an GV2-USB to an Blackmagic Analog to SDI setup or Zoom F3 field recorders for example, but modern 24-bit ADCs in basic recorders are very affordable and higher SNR then linear tape audio in most cases.
# Page End
Previous Page [RF Capture Guide](https://github.com/oyvindln/vhs-decode/wiki/RF-Capture-Guide)
Next Page [Video Export Guide](https://github.com/oyvindln/vhs-decode/wiki/TBC-to-Video-Export-Guide) # Determining Capture Quality
There is 2 ways to assess the quality of a decode.
## Black Signal To Noise Ratio
# Determining Capture Quality
There is 2 ways to assess the quality of a decode.
## Black Signal To Noise Ratio
 (Open window & screenshot it currently)
Visually you can tell how noisy the signal is by how black the VBI space is if its a clear grey colour this means a high SNR.
LaserDiscs will normally have a curve to the graph ware as tape will mostly be level per each recorded segment.
Sudden dips in the graph are ware there are dropouts, interference or weak signal.
`60~70 dB` - Live Composite
`40~50 dB` - Great Signal
`30~40 dB` - Good Signal
`20~30 dB` - Weak Signal
`10~20 dB` - Poor Signal
> [!CAUTION]
> The SNR measurement is relative and can be highly affected by format, and is only sampled based off a single line in the VBI space as its code is still from ld-decode directy and does not avarage the whole black area of the VBI and or sync signal spaces.
## Export Dropout Analysis
(Open window & screenshot it currently)
(Open window & screenshot it currently)
Visually you can tell how noisy the signal is by how black the VBI space is if its a clear grey colour this means a high SNR.
LaserDiscs will normally have a curve to the graph ware as tape will mostly be level per each recorded segment.
Sudden dips in the graph are ware there are dropouts, interference or weak signal.
`60~70 dB` - Live Composite
`40~50 dB` - Great Signal
`30~40 dB` - Good Signal
`20~30 dB` - Weak Signal
`10~20 dB` - Poor Signal
> [!CAUTION]
> The SNR measurement is relative and can be highly affected by format, and is only sampled based off a single line in the VBI space as its code is still from ld-decode directy and does not avarage the whole black area of the VBI and or sync signal spaces.
## Export Dropout Analysis
(Open window & screenshot it currently)
 ## Visually Checking
[Visual Video Errors Doc](Visual-Video-Signal-Errors) / [VBI Data Identification Doc](Identifying-vbi-data)
Very Bad Signal Example
## Visually Checking
[Visual Video Errors Doc](Visual-Video-Signal-Errors) / [VBI Data Identification Doc](Identifying-vbi-data)
Very Bad Signal Example
 Normal Good Signal Example
Normal Good Signal Example
 > [!NOTE]
> This example contains a dropout.
Clean Macrovision Example
> [!NOTE]
> This example contains a dropout.
Clean Macrovision Example
 ## Adjusting For Export
As [ld-analyse](ld-analyse-User-Guide) reads the `.tbc` & `_chroma.tbc` (& JSON) files and combines them together in real-time with the ld-chroma-decoder this allows you to play with different chroma decoders and filtering settings on a basic level.
With ld-analyse can adjust JSON metadata alongside reading it, you can ignore this step however it is useful to learn to make better finer adjusted exports.
- PAL Transform 2D & Simple PAL 2D for Tape
- PAL Transform 3D for CVBS sources for example.
This is to the same effect as [SoX combining commands](https://github.com/oyvindln/vhs-decode/wiki/ld-analyse-User-Guide#y--c-combining-with-sox) on some media consider it good enough for checking but make a short video export with `tbc-video-export --length 300 input-tbc-name` script to see the real media result.
- Black Level Adjust
- White Level Adjust
You can adjust these sliders and `save` an updated `.json` with these values that the `tbc-video-export` tool will read.
You can manually set the 16:9 Flag for widescreen content (`iswidescreen` inside the `.json`)
## Adjusting For Export
As [ld-analyse](ld-analyse-User-Guide) reads the `.tbc` & `_chroma.tbc` (& JSON) files and combines them together in real-time with the ld-chroma-decoder this allows you to play with different chroma decoders and filtering settings on a basic level.
With ld-analyse can adjust JSON metadata alongside reading it, you can ignore this step however it is useful to learn to make better finer adjusted exports.
- PAL Transform 2D & Simple PAL 2D for Tape
- PAL Transform 3D for CVBS sources for example.
This is to the same effect as [SoX combining commands](https://github.com/oyvindln/vhs-decode/wiki/ld-analyse-User-Guide#y--c-combining-with-sox) on some media consider it good enough for checking but make a short video export with `tbc-video-export --length 300 input-tbc-name` script to see the real media result.
- Black Level Adjust
- White Level Adjust
You can adjust these sliders and `save` an updated `.json` with these values that the `tbc-video-export` tool will read.
You can manually set the 16:9 Flag for widescreen content (`iswidescreen` inside the `.json`)
 https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/0d858753-68c7-42e5-bc39-31bdd1efd1b4
## Vector Scope & Chroma Decoder
> [!NOTE]
> Final output will be determined by fully running the chroma-decoder so run a 10sec test export.
For media with test bar signals you can select 75% or 100% bars you can adjust your image with the chroma-decoder.
https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/0d858753-68c7-42e5-bc39-31bdd1efd1b4
## Vector Scope & Chroma Decoder
> [!NOTE]
> Final output will be determined by fully running the chroma-decoder so run a 10sec test export.
For media with test bar signals you can select 75% or 100% bars you can adjust your image with the chroma-decoder.
 | EBU 75% Colour Bars | EBU 100% Colour Bars | SMPTE 75% Color Bars | SMPTE 100% HDTV Color Bars |
|---------------------|----------------------|----------------------|----------------------------|
|
| EBU 75% Colour Bars | EBU 100% Colour Bars | SMPTE 75% Color Bars | SMPTE 100% HDTV Color Bars |
|---------------------|----------------------|----------------------|----------------------------|
|  |
|  |
|  |
|  |
|

 * Chroma Gain (Intensity)
* Chroma Phase (Hue Control)
* Luma Noise Reduction (PAL/NTSC)
* Chroma Noise Reduction (NTSC Only)
## HiFi-Decode Notes
FM Audio decoding has been normal for decades if you ever have used a car you know it has a radio and it picks up and decodes FM audio signals from local stations.
HiFi decode allows you to have full control over the de-modulation and noise filtering process this can remove and improve on sound quality drastically in some cases and or save you money if you don't have the best amplifiers or a decent audio interface capture solution, if you have good hearing you will notice the difference quickly with even 15USD Behringer ''studio'' headphones.
You can use an cheep RTLSDR or the DdD & CX Cards for HiFi capture, it does not require very high bandwidth.
Linear Audio will have to be captured via standard ADC solutions, such as [the clockgen mod](Clockgen-Mod).
As decent quality conventional capture workflow hardware is mandatory on the linear audio front, this can range from an GV2-USB to an Blackmagic Analog to SDI setup or Zoom F3 field recorders for example, but modern 24-bit ADCs in basic recorders are very affordable and higher SNR then linear tape audio in most cases.
# Page End
Previous Page [RF Capture Guide](https://github.com/oyvindln/vhs-decode/wiki/RF-Capture-Guide)
Next Page [Video Export Guide](https://github.com/oyvindln/vhs-decode/wiki/TBC-to-Video-Export-Guide)
* Chroma Gain (Intensity)
* Chroma Phase (Hue Control)
* Luma Noise Reduction (PAL/NTSC)
* Chroma Noise Reduction (NTSC Only)
## HiFi-Decode Notes
FM Audio decoding has been normal for decades if you ever have used a car you know it has a radio and it picks up and decodes FM audio signals from local stations.
HiFi decode allows you to have full control over the de-modulation and noise filtering process this can remove and improve on sound quality drastically in some cases and or save you money if you don't have the best amplifiers or a decent audio interface capture solution, if you have good hearing you will notice the difference quickly with even 15USD Behringer ''studio'' headphones.
You can use an cheep RTLSDR or the DdD & CX Cards for HiFi capture, it does not require very high bandwidth.
Linear Audio will have to be captured via standard ADC solutions, such as [the clockgen mod](Clockgen-Mod).
As decent quality conventional capture workflow hardware is mandatory on the linear audio front, this can range from an GV2-USB to an Blackmagic Analog to SDI setup or Zoom F3 field recorders for example, but modern 24-bit ADCs in basic recorders are very affordable and higher SNR then linear tape audio in most cases.
# Page End
Previous Page [RF Capture Guide](https://github.com/oyvindln/vhs-decode/wiki/RF-Capture-Guide)
Next Page [Video Export Guide](https://github.com/oyvindln/vhs-decode/wiki/TBC-to-Video-Export-Guide)