## 介紹
線段樹是演算法競賽中常用的用來維護 **區間資訊** 的資料結構。 線段樹可在 的時間複雜度內實現單點修改、區間修改、區間查詢(區間求和,求區間最大值,求區間最小值)等操作。
## 線段樹基本
??? info "記憶體空間: 4n"
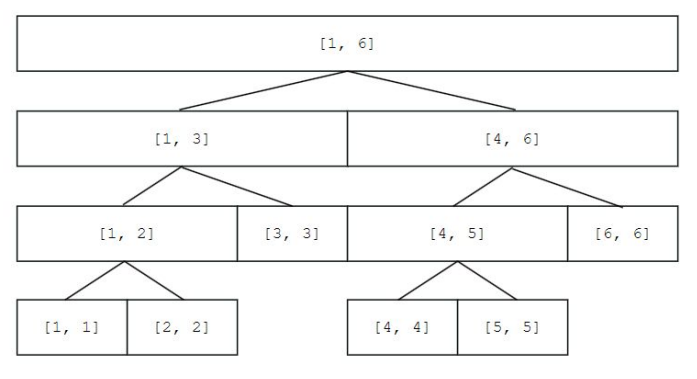
假設當前線段樹為 full binary tree,那麼節點數量就是 n + n/2 + n/4 + … + 1 = 2n - 1。可是當某些情況線段樹會往下多遞迴一層,例如下面這個 case
{ width="400" }
這時就會是為多一層的 full binary tree,節點數量為 2n + n + n/2 + n/4 + … + 1 = 4n - 1。
??? note "Node 資訊"
```cpp linenums="1"
struct Node {
Node* lc = nullptr;
Node* rc = nullptr;
int l, r;
int sum;
Node(int l, int r) : l(l), r(r) {
sum = 0;
}
void pull() { // 合併左節點與右節點的值
sum = lc->sum + rc->sum;
}
};
```
??? note "build"
```cpp linenums="1"
Node* build(int l, int r) {
Node* root = new Node(l, r);
if (l == r) {
root->sum = a[l];
return root;
}
int mid = (l + r) / 2;
root->lc = build(l, mid);
root->rc = build(mid + 1, r);
root->pull();
return root;
}
```
??? note "query"
```cpp linenums="1"
int query(Node* root, int ql, int qr) {
if (qr < root->l || root->r < ql) {
return 0;
}
if (ql <= root->l && root->r <= qr) {
return root->sum;
}
return query(root->lc, ql, qr) + query(root->rc, ql, qr);
}
```
??? note "update"
```cpp linenums="1"
void update(Node* root, int pos, int val) {
if (root->l == root->r) {
root->sum = val;
return;
}
if (pos <= root->lc->r) {
update(root->lc, pos, val);
} else {
update(root->rc, pos, val);
}
root->pull();
}
```
## 懶人標記
??? info "區間修改時,盡量不要讓 0 設為未改動的狀態"
若 chg != 0 才會改動,那麼如果要將一個區間都設為 0 就不會跑到了,所以最好還是將 chg 未改動的狀態設為 INF。
可以觀察到多個區間操作中有很多重疊的區域,重疊多次的地方可以將操作先整理起來,再一起更新,沒有必要細化到每個葉子結點,只要修改到該區間所對應的那些節點
??? note "Node 資訊 & push"
```cpp linenums="1"
struct Node {
Node* lc = nullptr;
Node* rc = nullptr;
int l, r;
int chg, sum;
Node(int l, int r) : l(l), r(r) {
chg = INF;
sum = 0;
}
void push() {
if (chg != INF) {
lc->chg = chg;
lc->sum = (lc->r - lc->l + 1) * chg;
rc->chg = chg;
rc->sum = (rc->r - rc->l + 1) * chg;
chg = INF;
}
}
void pull() {
sum = lc->sum + rc->sum;
}
};
```
??? note "區間改值"
```cpp linenums="1"
void update(Node* root, int ml, int mr, int val) {
if (mr < root->l || root->r < ml) {
return;
}
if (ml <= root->l && root->r <= mr) {
root->sum = (root->r - root->l + 1) * val;
root->chg = val;
return;
}
root->push();
update(root->lc, ml, mr, val);
update(root->rc, ml, mr, val);
root->pull();
}
```
??? note "區間查詢總和"
```cpp linenums="1"
int query(Node* root, int ql, int qr) {
if (qr < root->l || root->r < ql) {
return 0;
}
if (ql <= root->l && root->r <= qr) {
return root->sum;
}
root->push();
return query(root->lc, ql, qr) + query(root->rc, ql, qr);
}
```
## 線段樹 walk
??? note "code"
```cpp linenums="1"
#include
#define int long long
#define pb push_back
using namespace std;
const int MAXN = 2e5 + 5;
struct Node {
Node* lc = nullptr;
Node* rc = nullptr;
int l, r;
long long sum;
Node(int l, int r) : l(l), r(r) {
sum = 0;
}
void pull() {
sum = lc->sum + rc->sum;
}
};
int n, q;
int a[MAXN];
Node* build(int l, int r) {
Node* root = new Node(l, r);
if (l == r) {
root->sum = a[l];
return root;
}
int mid = (l + r) / 2;
root->lc = build(l, mid);
root->rc = build(mid + 1, r);
root->pull();
return root;
}
void update(Node* root, int pos, int val) {
if (root->l == root->r) {
root->sum = val;
return;
}
if (pos <= root->lc->r) {
update(root->lc, pos, val);
} else {
update(root->rc, pos, val);
}
root->pull();
}
int walk(Node* root, int k) {
if (root->l == root->r) {
return root->l;
}
if (k <= root->lc->sum) {
return walk(root->lc, k);
} else {
return walk(root->rc, k - root->lc->sum);
}
}
signed main() {
cin >> n >> q;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
cin >> a[i];
}
Node* root = build(0, n - 1);
while (q--) {
int op;
cin >> op;
if (op == 1) {
int pos;
cin >> pos;
a[pos] ^= 1;
update(root, pos, a[pos]);
} else if (op == 2) {
int k;
cin >> k;
k++;
cout << walk(root, k) << '\n';
}
}
}
```
???+note "CSES - List Removals"
給一個長度為 n 的陣列 a[1], a[2], … , a[n],有 q 筆操作,給 k,將從左數過去第 k 個數移除,並輸出被移除的數字是多少
$1\le n, q\le 2\times 10^5$
??? note "思路"
問在哪個 index 的 prefix sum 恰好超過 k。也就是在線段樹上「二分搜」。具體來說,看左子樹的 sum 是否足夠 k,是的話就往左走,不是的話就往右走,並將 k -= lc.sum
## 矩形覆蓋相關問題
???+note "不用離散化版 [CSES - Area of Rectangles](https://cses.fi/problemset/task/1741)"
給 $n$ 個矩形 $(x_1, x_2)$ 到 $(y_1, y_2)$,問他們的聯集面積
$n\le 10^5, -10^6\le x_1, x_2, y_1, y_2 \le 10^6$
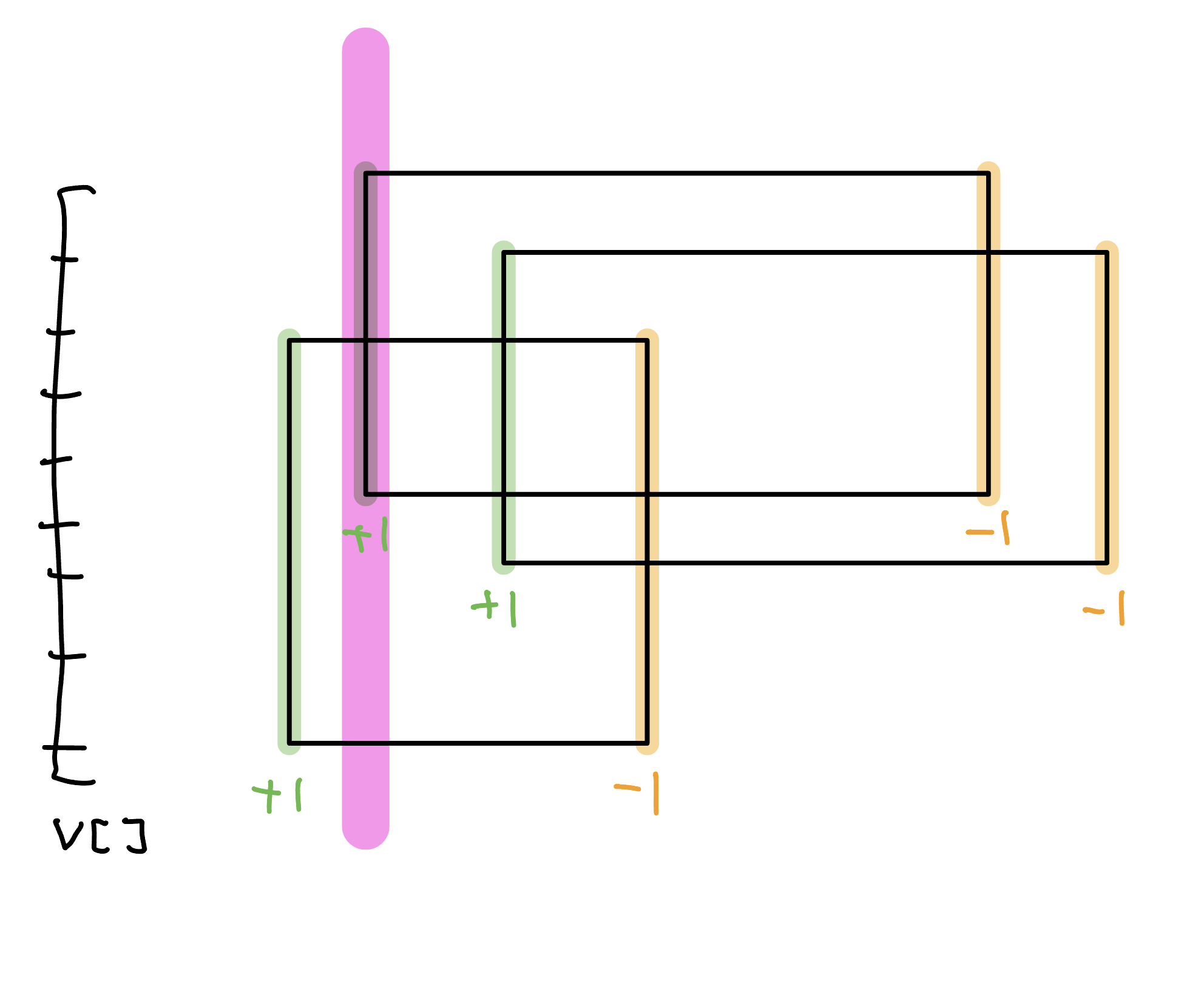
將問題轉換成在一維上的操作,也就是好幾個 events,變成好幾個區間 +1, -1。
{ width="400" }
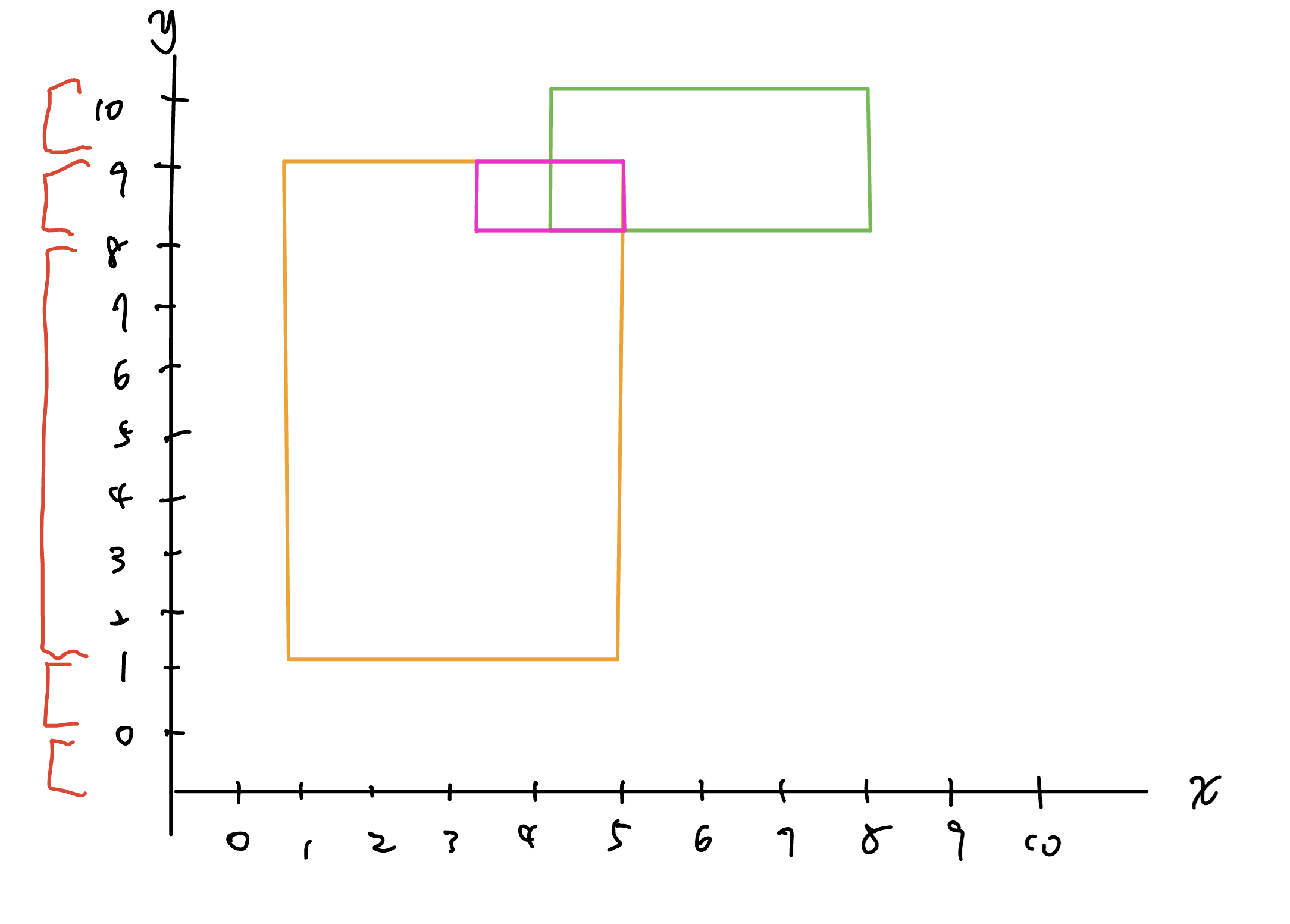
v[i]: 存當前掃描線的 y = i 被多少矩形 cover。對於每一個 x,答案就是 v[i] > 0 的數量,我們可以用線段樹維護區間最小值 minv,以及出現幾次 cntv。
- 若 minv = 0 ⇒ ans = total - cntv
- 若 minv > 0 ⇒ ans = total
需要離散化的話只要將 leaf 的 cntv 改成維護「離散化前的長度」即可
{ width="400" }
??? note "[TIOJ 1224](https://tioj.ck.tp.edu.tw/problems/1224) 離散化的 code"
```cpp linenums="1"
#include
#define int long long
#define pii pair
#define pb push_back
#define mk make_pair
#define F first
#define S second
#define ALL(x) x.begin(), x.end()
using namespace std;
const int INF = 2e18;
struct Node {
int l, r;
Node *lc = nullptr;
Node *rc = nullptr;
int cnt;
int mn;
int add = 0;
Node(int l, int r) : l(l), r(r) {}
void pull() {
mn = min(lc->mn, rc->mn);
cnt = 0;
if (mn == lc->mn) {
cnt += lc->cnt;
}
if (mn == rc->mn) {
cnt += rc->cnt;
}
}
void push() {
if (add) {
lc->mn += add;
lc->add += add;
rc->mn += add;
rc->add += add;
add = 0;
}
}
};
struct OP {
int x, y1, y2, val;
bool operator<(const OP &rhs) const {
return x < rhs.x;
}
};
int n;
vector sortedY;
vector op;
// {1, 8, 9, 10}
// i 維護 i~i+1
// lb(i), lb(i - 1)
Node* build(int l, int r) {
Node* root = new Node(l, r);
if (l == r) {
root->cnt = sortedY[l + 1] - sortedY[l];
root->mn = 0;
return root;
}
int mid = (l + r) / 2;
root->lc = build(l, mid);
root->rc = build(mid + 1, r);
root->pull();
return root;
}
void modify(Node* root, int ml, int mr, int val) {
if (ml <= root->l && root->r <= mr) {
root->mn += val;
root->add += val;
return;
}
if (root->r < ml || mr < root->l) {
return;
}
root->push();
modify(root->lc, ml, mr, val);
modify(root->rc, ml, mr, val);
root->pull();
}
void init() {
cin >> n;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int x1, x2, y1, y2;
cin >> x1 >> x2 >> y1 >> y2;
op.pb({x1, y1, y2, +1});
op.pb({x2, y1, y2, -1});
sortedY.pb(y1);
sortedY.pb(y2);
}
sort(ALL(sortedY));
sortedY.resize(unique(ALL(sortedY)) - sortedY.begin());
sort(ALL(op));
}
void solve() {
int range = sortedY.back() - sortedY.front();
Node* root = build(0, sortedY.size() - 2);
int lastX = INF, ans = 0;
for (auto [x, y1, y2, val] : op) {
int yl = lower_bound(ALL(sortedY), y1) - sortedY.begin();
int yr = lower_bound(ALL(sortedY), y2) - sortedY.begin() - 1;
if (lastX != INF && x != lastX) {
int dy = (root->mn == 0) ? (range - root->cnt) : range;
ans += (x - lastX) * dy;
}
modify(root, yl, yr, val);
lastX = x;
}
cout << ans << '\n';
}
signed main() {
init();
solve();
}
```
???+note "[2021 全國賽 pF. 歡樂外送點](https://tioj.ck.tp.edu.tw/problems/2228)"
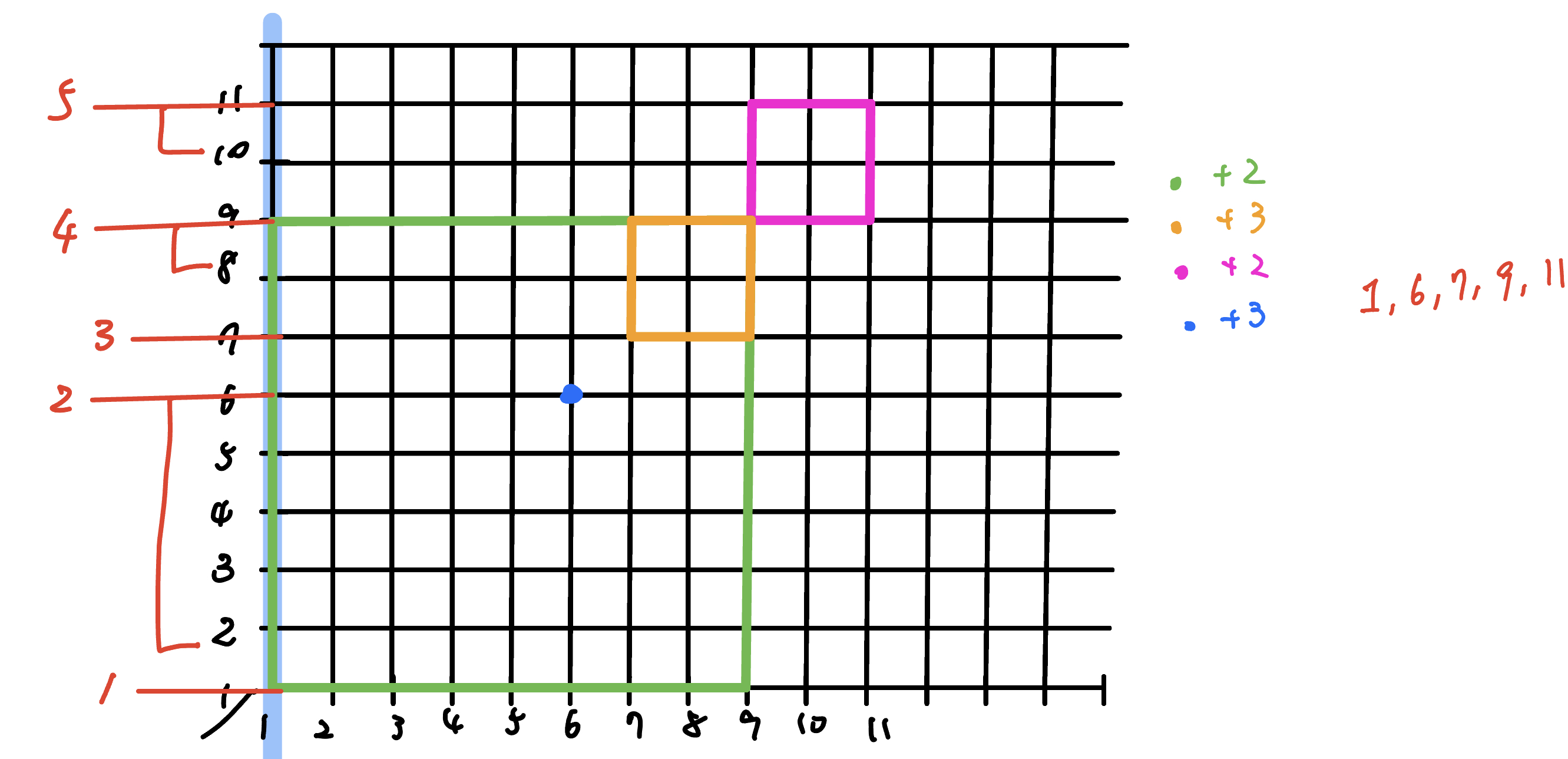
給 $n$ 個菱形,中心點為 $(x_i, y_i)$,半徑為 $r_i$,權值為 $w_i$。問所有格子點的上被覆蓋到的權值總和最大值
$n\le 3\times 10^5, 0\le x_i, y_i, r_i\le 10^8, 1\le w_i \le 100$
??? note "思路"
將菱形變成 $(x+y,x-y)$ 就可以變成一般的矩形覆蓋問題
{ width="400" }
???+note "矩形周長 [POJ 1177](https://vjudge.net/problem/POJ-1177)"
給 $n$ 個矩形 $(x_1, x_2)$ 到 $(y_1, y_2)$,問他們所形成的輪廓週長
$n\le 5000, -10^4\le x_1, x_2, y_1, y_2 \le 10^4$
??? note "思路"
用掃描線,線段樹一樣維護當前有幾個非 0 的點
目前線段貢獻的周長是,目前的總長度減去上一次的總長度的絕對值
> 參考自 :
???+note "[CSES - Intersection Points](https://cses.fi/problemset/task/1740)"
給 n 個線段,只可能是水平線或鉛直線,問這些線段的交點有幾個
$n\le 10^6, -10^6 \le x_1, x_2, y_1, y_2 \le 10^6$
??? note "思路"
把每個線段都想成一個矩形,用 sweep line 從左邊掃到右邊,過程中可能會有三種情況:
1. 遇到一個平行線段的起始點
2. 遇到一個平行線段的終點
3. 遇到一個垂直線段
其中當遇到 3. 的時候,會需要詢問當前的一段區間有幾條線段經過,而遇到 1. 2. 的時候,會需要將一個點加值或減值
???+note "[LOJ #6276.果树](https://loj.ac/p/6276)"
給出一棵 $n$ 個點的樹,每個點有一種顏色。問有多少條路徑滿足路徑上任意兩點的顏色都不同。
$n\le 10^5$,滿足每種顏色至多出現 $20$ 次。
??? note "思路"
將 path $(u,v)$ 的 $\texttt{dfn}[u],\texttt{dfn}[v]$ 打在二維平面上,同樣顏色的點會形成一些矩形,那些矩形就不能選的地方,答案就是沒被任何矩形覆蓋到的二維座標點。由於需要 $O(20^2)$ 枚舉同樣顏色的點,每次會生成 $4$ 個矩形,所以 worst case $O((C^{20}_2 \times 4 \times \frac{n}{C^{20}_2})\times \log n)\approx 7.6\times 10^7$
## 線段樹分治
考慮這樣一個問題:
- 有一些操作,每個操作只在 $l\sim r$ 的時間內有效。
- 有一些詢問,每個詢問某一個時間點所有操作的貢獻。
對於這樣的詢問,我們可以在離線後在**時間軸上建一棵線段樹**,這樣對於每個操作,相當於在線段樹上進行區間操作。遍歷整顆線段樹,到達每個節點時執行對應的操作,然後繼續向下遞歸,到達葉子節點時統計貢獻,回溯時撤銷操作即可。這樣的想法被稱為**線段樹分治**,可以在低時間複雜度內解決一類**在線演算法並不優秀**的問題。
???+note "[洛谷 P5787 二分图 /【模板】线段树分治](https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P5787)"
給一張 $n$ 個點的圖,有 $m$ 條邊與 $k$ 個時間點,每條邊只存在於 $[l_i, r_i)$ 這些時間點,求每個時間點時這張圖是否為二分圖。
$n\le 10^5, m,k\le 2\times 10^5$
??? note "思路"
首先,圖是二分圖的充要條件是不存在奇環,這個可以用帶權並查集維護。依照上述思想建一棵線段樹,對於每條邊,將它依照線段樹區間操作的方式分成 $O(\log k)$ 段,用 vector 掛在線上段樹的節點上。遍歷時,從根節點出發,每到一個節點,將掛在該節點上的所有邊合併,然後遞歸處理左兒子和右兒子。如果發現有某邊合併會出現奇環,那麼目前線段樹節點所對應的時間區間都不會形成二分圖。當到達葉子節點時,如果合併了所有掛在當前節點上的邊,依舊滿足二分圖的性質,那麼可以直接輸出 Yes。回溯時,由於並查集不支援刪邊,我們可以使用可rollback dsu。
每條邊會跑 $O(\log k)$ 次,共 $m$ 條,在乘上 rollback dsu 的複雜度是 $O(m \log n \log k)$
??? note "code"
```cpp linenums="1"
const int N = 1e5 + 7, M = 2e5 + 7;
int n, m, k, u[M], v[M], f[N<<1], d[N<<1];
struct T {
int l, r;
vi e;
} t[N<<2];
stack< pi > s;
void build(int p, int l, int r) {
t[p].l = l, t[p].r = r;
if (l == r) return;
build(ls, l, md), build(rs, md + 1, r);
}
void ins(int p, int l, int r, int x) {
if (t[p].l >= l && t[p].r <= r) return t[p].e.pb(x), void();
if (l <= md) ins(ls, l, r, x);
if (r > md) ins(rs, l, r, x);
}
inline int get(int x) {
while (x ^ f[x]) x = f[x];
return x;
}
inline void merge(int x, int y) {
if (x == y) return;
if (d[x] > d[y]) swap(x, y);
s.push(mp(x, d[x] == d[y])), f[x] = y, d[y] += d[x] == d[y];
}
void dfs(int p, int l, int r) {
bool ok = 1;
ui o = s.size();
for (ui i = 0; i < t[p].e.size(); i++) {
int x = t[p].e[i], u = get(::u[x]), v = get(::v[x]);
if (u == v) {
for (int j = l; j <= r; j++) prints("No");
ok = 0;
break;
}
merge(get(::u[x] + N), v), merge(get(::v[x] + N), u);
}
if (ok) {
if (l == r) prints("Yes");
else dfs(ls, l, md), dfs(rs, md + 1, r);
}
while (s.size() > o) d[f[s.top().fi]] -= s.top().se, f[s.top().fi] = s.top().fi, s.pop();
}
int main() {
rd(n), rd(m), rd(k), build(1, 1, k);
for (int i = 1, l, r; i <= m; i++) {
rd(u[i]), rd(v[i]), rd(l), rd(r);
if (l ^ r) ins(1, l + 1, r, i);
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) f[i] = i, f[i+N] = i + N;
dfs(1, 1, k);
return 0;
}
```
???+note "[CF 1681 F. Unique Occurrences](https://codeforces.com/contest/1681/problem/F)"
給一棵 $n$ 個點的樹,邊帶權。定義 $f(u,v)$ 為 $u$ 到 $v$ 的路徑上只出現一次的邊權數量,問對於所有 $u 參考自 :
??? note "code"
```cpp linenums="1"
#include
#define int long long
using namespace std;
const int N = 5e5 + 5;
int n, ans;
vector> G[N];
struct Graph {
int n, cnt;
vector sz;
vector par;
stack> stk;
int find(int x) {
if (par[x] == x)
return x;
else
return find(par[x]);
}
void init(int _n) {
n = _n;
sz = vector(n, 1);
par = vector(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
par[i] = i;
}
}
void merge(int u, int v) {
int x = find(u), y = find(v);
if (x == y) {
stk.push({x, x});
return;
}
if (sz[x] < sz[y]) swap(x, y);
sz[x] += sz[y];
par[y] = x;
stk.push({x, y});
}
void undo() {
auto [x, y] = stk.top();
stk.pop();
if (x == y) return;
sz[x] -= sz[y];
par[y] = y;
}
} dsu;
void divide(int l, int r) {
if (l == r) {
for (auto [a, b] : G[l]) {
a = dsu.find(a), b = dsu.find(b);
ans += dsu.sz[a] * dsu.sz[b];
}
return;
}
int mid = (l + r) / 2;
for (int i = l; i <= mid; i++) {
for (auto [u, v] : G[i]) {
dsu.merge(u, v);
}
}
divide(mid + 1, r);
for (int i = l; i <= mid; i++) {
for (auto [u, v] : G[i]) {
dsu.undo();
}
}
for (int i = mid + 1; i <= r; i++) {
for (auto [u, v] : G[i]) {
dsu.merge(u, v);
}
}
divide(l, mid);
for (int i = mid + 1; i <= r; i++) {
for (auto [u, v] : G[i]) {
dsu.undo();
}
}
}
signed main() {
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
int u, v, w;
cin >> u >> v >> w;
G[w].push_back({u, v});
}
dsu.init(n + 1);
divide(1, n);
cout << ans << '\n';
}
```
???+note "[CF 601 E. A Museum Robbery](https://codeforces.com/contest/601/problem/E)"
給 $n$ 個物品以及背包容量 $k$,有以下 $q$ 筆操作 :
- $\text{add}(w, v):$ 加入一個重量為 $w$,價值為 $v$ 的物品
- $\text{del}(x):$ 刪除編號 $x$ 的物品
- $\text{query}:$ 令 $s(m)$ 表示容量為 $m$ 所能獲取的最大價值,求 $\sum \limits_{m=1}^k s(m) \times p^{m-1} \pmod{q}$
$n\le 5000, k\le 1000, q\le 3\times 10^4$
??? note "思路"
我們處理出每個物品會出現在哪些區間中。其它都和線段樹分治一樣,唯一的不同就是dfs 的時候,我們不去回溯,而是選擇直接把 $dp$ 數組傳下去(其實也跟 CF 1442 D. sum 的做法差不多)。
> 參考自 :
## 二維 BIT
???+note "[CSES - Forest Queries II](https://cses.fi/problemset/task/1739)"
$n\times n$ 的 grid 上,$q$ 個以下操作 :
- 改變一格的狀態(0/1)
- 詢問一個矩形區域的和
$n\le 1000, q\le 2\times 10^5$
??? note "思路"
yuihuang code
??? note "code"
```cpp linenums="1"
```
## 打架線段樹
???+note "區間數字個數"
給一個長度為 $n$ 陣列,$q$ 筆詢問 :
- $\text{query}(l,r,x):a_l,\ldots ,a_r$,$x$ 出現的次數
- $\text{update}(i,x):$ 將 $a_i=x$
$n,q\le 2\times 10^5,x\le 10^9$
??? note "思路"
(靜態)沒 update : vec[x] 放 $a_i=x$ 的所有 $x$
(動態)有 update : DS[x] 支援
- insert(i)
- erase(i)
- lower_bound(i)
使用 Treap 或 `pb_ds::tree`
??? note "code"
```cpp linenums="1"
// using pbds
tree,rb_tree_tag,tree_order_statistics_node_update> T;
// update(i, x)
T.erase({a[i], i});
a[i] = x;
T.insert({a[i], i});
// query(l, r, x)
cout << T.order_of_key(mk(id, r + 1)) - T.order_of_key(mk(id, l));
```
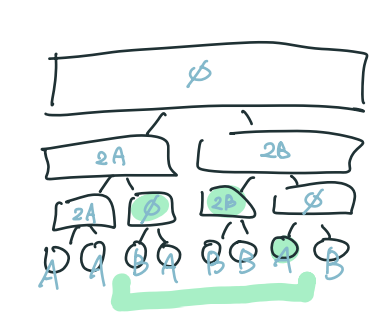
???+note "[資芽 OJ 794 — 區間絕對眾數](https://neoj.sprout.tw/problem/794/)"
輸入一個長度為 $N$ 的正整數序列 $a_1, \ldots, a_N$,接下來有 $Q$ 筆詢問。
每筆詢問輸入 $l_i, r_i$,輸出區間 $[l_i, r_i]$ 的絕對眾數,若不存在請輸出 $0$。
$N, Q \leq 5 \times 10^5, 1 \leq a_i \leq 5 \times 10^5$
??? note "思路"
{ width="300" }
??? note "code"
```cpp linenums="1"
#include
#include
#define int long long
#define pii pair
#define pb push_back
#define mk make_pair
#define F first
#define S second
#define ALL(x) x.begin(), x.end()
using namespace std;
using namespace __gnu_pbds;
tree,rb_tree_tag,tree_order_statistics_node_update> T;
const int INF = 2e18;
const int maxn = 5e5 + 5;
const int M = 1e9 + 7;
struct Node {
Node* lc = nullptr;
Node* rc = nullptr;
int l, r;
int id = -1, cnt = 0;
Node(int l, int r) : l(l), r(r) {}
void pull () {
if (lc->cnt == 0) {
id = rc->id;
cnt = rc->cnt;
return;
}
if (rc->cnt == 0) {
id = lc->id;
cnt = lc->cnt;
return;
}
if (lc->id == rc->id) {
id = lc->id;
cnt = lc->cnt + rc->cnt;
} else {
if (lc->cnt > rc->cnt) {
id = lc->id;
cnt = lc->cnt - rc->cnt;
} else {
id = rc->id;
cnt = rc->cnt - lc->cnt;
}
}
}
};
int n, q;
int a[maxn];
Node* build (int l, int r) {
Node* root = new Node(l, r);
if (l == r) {
root->id = a[l];
root->cnt = 1;
return root;
}
int mid = (l + r) / 2;
root->lc = build(l, mid);
root->rc = build(mid + 1, r);
root->pull();
return root;
}
pii query(const Node* root, int ql, int qr) {
if (qr < root->l || root->r < ql) return {-1, 0};
if (ql <= root->l && root->r <= qr) {
return {root->id, root->cnt};
}
pii tmp = {-1, 0};
if (ql <= root->lc->r) {
pii ret = query(root->lc, ql, qr);
if (tmp.S == 0) {
tmp = ret;
} else if (ret.S != 0) {
if (ret.F == tmp.F) {
tmp.S += ret.S;
} else {
if (ret.S > tmp.S) {
tmp.F = ret.F;
tmp.S = ret.S - tmp.S;
} else {
tmp.S = tmp.S - ret.S;
}
}
}
}
if (root->rc->l <= qr) {
pii ret = query(root->rc, ql, qr);
if (tmp.S == 0) {
tmp = ret;
} else if (ret.S != 0) {
if (ret.F == tmp.F) {
tmp.S += ret.S;
} else {
if (ret.S > tmp.S) {
tmp.F = ret.F;
tmp.S = ret.S - tmp.S;
} else {
tmp.S = tmp.S - ret.S;
}
}
}
}
return tmp;
}
void init() {
cin >> n >> q;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
cin >> a[i];
T.insert ({a[i], i});
}
}
void solve() {
Node* root = build(0, n - 1);
while (q--) {
int l, r;
cin >> l >> r;
l--, r--;
auto [id, c] = query(root, l, r);
if (c == 0) {
cout << 0 << '\n';
continue;
}
int cnt = T.order_of_key(mk(id, r + 1)) - T.order_of_key(mk(id, l));
if (cnt > (r - l + 1) / 2) {
cout << id << '\n';
} else {
cout << 0 << '\n';
}
}
}
signed main() {
int t = 1;
while (t--) {
init();
solve();
}
}
```
## 題目
???+note "[NPSC 2020 高中組初賽 pF. 兔田建設](https://contest.cc.ntu.edu.tw/npsc2020/teamclient/semi_senior.pdf#page=15)"
給一個長度為 $n$ 的序列 $a_1, \ldots, a_n$,給 $k$,有 $q$ 筆詢問 :
- $\text{query}(v,l,r,c):$ 問 $a_l, \ldots, a_r$ 有沒有長度為 $k$ 的區間中,恰有 $c$ 個 $\le v$ 的數
$n,q,k\le 10^6$
??? note "思路"
把詢問按 $v$ 排序,就可以先把 $ 參考自 :
???+note "[HDU 5726 GCD](https://vjudge.net/problem/HDU-5726)"
給一個長度為 $n$ 的序列 $a_1, \ldots ,a_n$,$q$ 次詢問 :
- $\text{query}(l,r):$ 問有幾個 $\gcd(a_{l'},\ldots ,a_{r'})=\gcd(a_l,\ldots ,a_r)$
$n, q\le 10^5$
??? note "思路"
區間 gcd 的值利可以用 Sparse Table 或 Segment Tree 算出來,但要怎麼求有幾個子區間的 gcd = x 呢 ? 觀察到,對於一個左界,當右界遞增時 gcd 是單調遞減的,所以我們假設已用 map 存以 a[i - 1] 結尾的 distinct 區間 gcd,那我們就只要將這些 gcd 在去跟 a[i] 取 gcd 存入 map 即可
詳見代碼,抄錄自以下博客
> 參考 :
??? note "code"
```cpp linenums="1"
#include
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int mod = 1000000007;
const int maxn = 1e5 + 10;
int g[maxn * 4], a[maxn];
map ans; // 存最终答案
map p[maxn]; // p[i]表示以i结尾的gcd的区间集合,前者为gcd,后者为对应的区间个数
int t, n, q, x, y;
int Gcd(int a, int b) {
return b == 0 ? a : Gcd(b, a % b);
}
void update(int id) {
g[id] = Gcd(g[id << 1], g[id << 1 | 1]);
}
void build(int l, int r, int id) {
if (l == r) {
g[id] = a[l];
return;
}
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
build(l, mid, id << 1);
build(mid + 1, r, id << 1 | 1);
update(id);
}
int query(int l, int r, int x, int y, int id) {
if (x <= l && r <= y)
return g[id];
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
int le = 0, ri = 0;
if (x <= mid)
le = query(l, mid, x, y, id << 1);
if (y > mid)
ri = query(mid + 1, r, x, y, id << 1 | 1);
if (!le) swap(le, ri); // le为0, 不能求ri%0
return Gcd(le, ri); // Gcd(x, 0) = x
}
int main() {
// freopen("/Users/zhangkanqi/Desktop/11.txt","r",stdin);
scanf("%d", &t);
int Case = 1;
while (t--) {
printf("Case #%d:\n", Case++);
scanf("%d", &n);
ans.clear(); // 清空!!
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
p[i].clear();
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
scanf("%d", &a[i]);
build(1, n, 1);
ans[a[1]] = 1, p[1][a[1]] = 1;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
ans[a[i]]++, p[i][a[i]] += 1;
for (map::iterator it = p[i - 1].begin(); it != p[i - 1].end(); it++) {
int tmp = Gcd(a[i], it->first); // 求a[i]和之前的数的gcd
p[i][tmp] += it->second;
ans[tmp] += it->second;
}
}
scanf("%d", &q);
while (q--) {
scanf("%d %d", &x, &y);
int k = query(1, n, x, y, 1);
printf("%d %lld\n", k, ans[k]);
}
}
return 0;
}
```
???+note "區間除法 [2023 YTP 國中組初賽 p6](/wiki/ds/images/YTP2023PreliminaryContest_J1.pdf)"
給一個長度為 $N$ 的序列 $a_1,a_2,\ldots, a_N$,$Q$ 筆以下操作 :
- $\texttt{f}\space l\space r\space x:$ 對於 $l\le i\le r$,$a_i$ 變成 $\displaystyle \lfloor \frac{a_i}{x} \rfloor$
- $\texttt{c}\space l\space r\space x:$ 對於 $l\le i\le r$,$a_i$ 變成 $\displaystyle \lceil \frac{a_i}{x} \rceil$
- $\texttt{?}\space k:$ 輸出 $a_k$
$N,Q\le 2\times 10^5,1\le a_i,x\le 10^9$
??? note "思路"
ceil 除法的話是把 floor 的除法改一下變區間最大值是 1 的時候不遞迴做下去
???+note "[2016 全國賽 直升機抓寶 (Helicopter)](https://tioj.ck.tp.edu.tw/problems/1941)"
有一個 $n\times n$ 的 grid。你一開始在左下角,要走到右上角去,你只能往上或往右走。每一個 row 都有一個特殊的區間,範圍是 $l_i$ 到 $r_i$,求你最多能經過幾個特殊區間。
$n\le 8\times 10^5$
??? note "思路"
考慮 dp(i, j) = 走到 (i, j) 最多經過幾個,轉移式 dp(i, j) = max(dp(i, j - 1), dp(i - 1, j) + 1 | if (i, j) is in interval)
可以觀察到一個 row 的 dp(i, j) 會是單調遞增的,且會被改變的只有 interval 以及 interval 以後的一個前綴
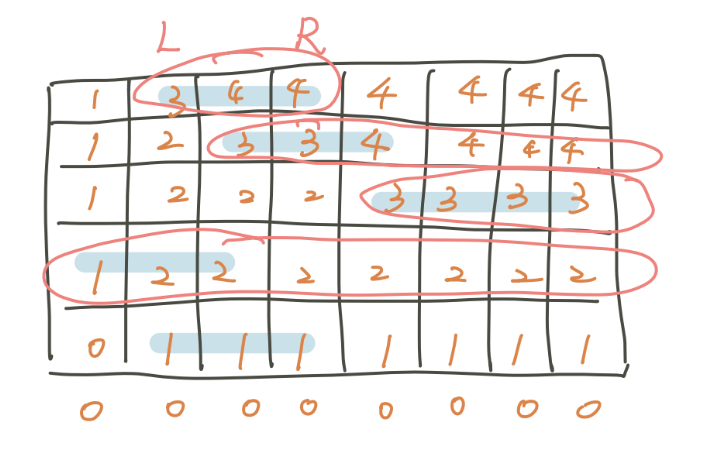{ width="400" }
這樣我們就只要維護一個 segment tree 代表當前 row 的 dp 值,看到 interval 的時候就在上面 walk 到最後一個小於等於的。
???+note "[TIOJ 2140. 殿壬愛序列](https://tioj.ck.tp.edu.tw/problems/2140)"
給一個長度為 $n$ 的序列,請支援三種操作:
1. 給定 $i,x$,將 $a_i$ 設成 $x$
2. 給定 $l,r,k$,$\forall l\le i\le r,a_i=\lfloor \frac{a_i}{k} \rfloor$
3. 給定 $l,r$,輸出 $a_l,a_{l+1},\ldots ,a_r$ 的絕對多數,若不存在輸出 $-1$
$n,q\le 10^5$
??? note "思路"
> 參考 :
區間除法的部分,因為 $k = 1$ 不會影響陣列,所以可以視為 $k \geq 2$。當區間的最大值 $>0$ 的時候才繼續遞迴下去。這樣一來每個數最多只會被除 $\log C$ 次。實作上每次將一個點除到 $0$ 需要 $O(\log C\times \log n)$,又每次修改只是單點修改,所以複雜度會是 $O((n + q)\log C \log n)\approx 1.2\times 10^8$。
```cpp linenums="1"
// 區間除法代碼
void division(Node* root, int mL, int mR, int val) {
if (root->r < mL || mR < root->l) return;
if (root->l == root->r) {
root->id /= val;
root->mx = root->id;
return;
}
if (mL <= root->lc->r && root->lc->mx) {
division(root->lc, mL, mR, val);
}
if (root->rc->l <= mR && root->rc->mx) {
division(root->rc, mL, mR, val);
}
root->pull();
}
```
單點修改,區間絕對眾數上面都有提到,略。
??? note "實作細節"
記得要特判 k = 1
??? note "code"
```cpp linenums="1"
#include
#include
#define int long long
#define pii pair
#define pb push_back
#define mk make_pair
#define F first
#define S second
#define ALL(x) x.begin(), x.end()
using namespace std;
using namespace __gnu_pbds;
tree,rb_tree_tag,tree_order_statistics_node_update> T;
const int INF = 2e18;
const int maxn = 3e5 + 5;
const int M = 1e9 + 7;
struct Node{
int l, r;
Node *lc = nullptr;
Node *rc = nullptr;
int id = -1, cnt = 0;
int mx;
Node (int l, int r) : l(l), r(r) {}
void pull () {
if (lc->cnt == 0) {
id = rc->id;
cnt = rc->cnt;
} else if (rc->cnt == 0) {
id = lc->id;
cnt = lc->cnt;
} else {
if (lc->id == rc->id) {
id = lc->id;
cnt = lc->cnt + rc->cnt;
} else {
if (lc->cnt > rc->cnt) {
id = lc->id;
cnt = lc->cnt - rc->cnt;
} else {
id = rc->id;
cnt = rc->cnt - lc->cnt;
}
}
}
mx = max(lc->mx, rc->mx);
}
};
int n, q;
int a[maxn];
Node* build (int l, int r) {
Node* root = new Node(l, r);
if (l == r) {
root->id = a[l];
root->cnt = 1;
root->mx = a[l];
return root;
}
int mid = (l + r) / 2;
root->lc = build(l, mid);
root->rc = build(mid + 1, r);
root->pull();
return root;
}
void update(Node* root, int pos, int val) {
if (root->l == root->r) {
T.erase({root->id, root->l});
root->id = val;
root->cnt = 1;
root->mx = val;
T.insert({root->id, root->l});
return;
}
if (pos <= root->lc->r) {
update(root->lc, pos, val);
} else {
update(root->rc, pos, val);
}
root->pull();
}
void division(Node* root, int mL, int mR, int val) {
if (root->r < mL || mR < root->l) return;
if (root->l == root->r) {
T.erase({root->id, root->l});
root->id /= val;
root->mx = root->id;
T.insert({root->id, root->l});
return;
}
if (mL <= root->lc->r && root->lc->mx) {
division(root->lc, mL, mR, val);
}
if (root->rc->l <= mR && root->rc->mx) {
division(root->rc, mL, mR, val);
}
root->pull();
}
pii query(const Node* root, int ql, int qr) {
if (qr < root->l || root->r < ql) return {-1, 0};
if (ql <= root->l && root->r <= qr) {
return {root->id, root->cnt};
}
pii tmp = {-1, 0};
if (ql <= root->lc->r) {
pii ret = query(root->lc, ql, qr);
if (tmp.S == 0) {
tmp = ret;
} else if (ret.S != 0) {
if (ret.F == tmp.F) {
tmp.S += ret.S;
} else {
if (ret.S > tmp.S) {
tmp.F = ret.F;
tmp.S = ret.S - tmp.S;
} else {
tmp.S = tmp.S - ret.S;
}
}
}
}
if (root->rc->l <= qr) {
pii ret = query(root->rc, ql, qr);
if (tmp.S == 0) {
tmp = ret;
} else if (ret.S != 0) {
if (ret.F == tmp.F) {
tmp.S += ret.S;
} else {
if (ret.S > tmp.S) {
tmp.F = ret.F;
tmp.S = ret.S - tmp.S;
} else {
tmp.S = tmp.S - ret.S;
}
}
}
}
return tmp;
}
void init() {
cin >> n >> q;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
cin >> a[i];
T.insert({a[i], i});
}
}
void solve() {
Node* root = build(0, n - 1);
int op;
while(q--) {
cin >> op;
if (op == 1) {
int i, x;
cin >> i >> x;
i--;
update(root, i, x);
} else if (op == 2) {
int l, r, k;
cin >> l >> r >> k;
l--, r--;
if (k > 1) division(root, l, r, k);
} else {
int l, r;
cin >> l >> r;
l--, r--;
auto [id, c] = query(root, l, r);
if (c == 0) {
cout << "-1" << '\n';
continue;
}
int cnt = T.order_of_key(mk(id, r + 1)) - T.order_of_key(mk(id, l));
if (cnt > (r - l + 1) / 2) {
cout << id << '\n';
} else {
cout << "-1" << '\n';
}
}
}
}
signed main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
int t = 1;
//cin >> t;
while (t--) {
init();
solve();
}
}
```
???+note "[CSES - Increasing Array Queries](https://cses.fi/problemset/task/2416)"
給一個長度為 $n$ 的陣列 $a_1, \ldots ,a_n$,有 $q$ 筆查詢 :
$\text{query}(l,r):$ 每次可以將某一項 +1,問需要做幾次 $a_l, \ldots ,a_r$ 才會非嚴格遞增
$n,q\le 2\times 10^5, 1\le a_i\le 10^9$
??? note "思路"
將詢問按照 $l_i$ 大到小排序,用單調 stack 維護支配的項
??? note "code"
```cpp linenums="1"
#include
#define int long long
#define ALL(x) x.begin(), x.end()
using namespace std;
const int INF = 2e18;
struct Query{
int l, r, id;
bool operator<(const Query &rhs) const {
return l > rhs.l;
}
};
struct Node{
Node* lc = nullptr;
Node* rc = nullptr;
int l, r;
int chg, sum;
Node(int l, int r) : l(l), r(r) {
chg = 0;
}
void pull() {
sum = lc->sum + rc->sum;
}
void push() {
if (chg) {
lc->sum = chg * (lc->r - lc->l + 1);
rc->sum = chg * (lc->r - lc->l + 1);
lc->chg = chg;
rc->chg = chg;
chg = 0;
}
}
};
Node* build(int l, int r) {
Node* root = new Node(l, r);
if (l == r) {
root->sum = 0;
return root;
}
int mid = (l + r) / 2;
root->lc = build(l, mid);
root->rc = build(mid + 1, r);
root->pull();
return root;
}
void update(Node* root, int ml, int mr, int val) {
if (mr < root->l || root->r < ml) {
return;
}
if (ml <= root->l && root->r <= mr) {
root->sum = val * (root->r - root->l + 1);
root->chg = val;
return;
}
root->push();
update(root->lc, ml, mr, val);
update(root->rc, ml, mr, val);
root->pull();
}
int ask(Node* root, int ql, int qr) {
if (qr < root->l || root->r < ql) {
return 0;
}
if (ql <= root->l && root->r <= qr) {
return root->sum;
}
root->push();
return ask(root->lc, ql, qr) + ask(root->rc, ql, qr);
}
const int N = 2e5 + 5;
int n, q;
int a[N], pre[N], ans[N];
signed main() {
cin >> n >> q;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
cin >> a[i];
pre[i] = pre[i - 1] + a[i];
}
vector query;
for (int i = 1; i <= q; i++) {
int l, r;
cin >> l >> r;
query.push_back({l, r, i});
}
sort(ALL(query));
Node* root = build(1, n);
stack stk;
int l = n + 1;
for (auto &i : query) {
while (i.l < l) {
l--;
while (stk.size() && a[stk.top()] <= a[l]) {
int ml = stk.top();
stk.pop();
int mr;
if (stk.size()) {
mr = stk.top() - 1;
} else {
mr = n;
}
update(root, ml, mr, a[l]);
}
update(root, l, l, a[l]);
stk.push(l);
}
ans[i.id] = ask(root, i.l, i.r) - (pre[i.r] - pre[i.l - 1]);
}
for (int i = 1; i <= q; i++) {
cout << ans[i] << '\n';
}
}
```
???+note "[CSES - Polynomial Queries](https://cses.fi/problemset/task/1736)"
給一個長度為 $n$ 的序列 $a_1, \ldots ,a_n$,有 $q$ 次以下操作 :
- $\text{update}(i):$ 將 $a_i$ += 1, $a_{i+1}$ += 2, ...
- $\text{query}(l,r):$ 輸出 $a_l + \ldots ,a_r$
$1\le n,q \le 2\times 10^5$
??? note "思路"
開兩顆 Segment Tree,Seg1 維護 $1\times i_1, 2\times i_2, 3\times i_3, \ldots$,Seg2 就是一般的線段樹
- update
- Seg1 : 區間每項都 +1
- Seg2 : 區間每項都 -(l - 1)
- query
- Seg1[l, r] + Seg2[l, r]
???+note "區間開根號 [LOJ #10128. 「一本通 4.3 练习 2」花神游历各国](https://loj.ac/p/10128)"
給一個長度為 n 的陣列 $a_1,\ldots ,a_n$,跟 $q$ 個操作,操作有兩種:
- $\text{query}(l,r):$ 查詢序列 $a$ 在區間 $[l, r]$ 的和。
- $\text{sqrt}(l,r):$ 把 $a_l,\ldots ,a_r$ 的值個別開根號後取下高斯。
$n\le 10^5,q\le 2\times 10^5,a_i\le 10^9$
??? note "思路"
跟區間除法一樣 mx > 0 再跟新,區間和就用線段樹的 pull 維護就好了
???+note "[IOI 2014 - Wall](https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P4560)"
給定長度為 $n$ 的初始值都為 0 的序列,有 $q$ 次操作,問 $q$ 次操作過後的整個序列。操作有以下兩種:
1. 對區間 $[l,r]$ 中的所有元素與 $h$ 取最大值。
2. 對區間 $[l,r]$ 中的所有元素與 $h$ 取最小值。
$n \leq 2\times 10^6, q \leq 5\times 10^5, 0\le h\le 10^5$
??? note "思路"
線段樹的每一個節點維護著兩個限制,即「已經對這個區間進行,但還沒有對這個區間的孩子應用 (apply) 的限制」。如果我們把我們的數想象成一排金屬球,那麼取最大值操作可以想象成用一塊鋼板從下往上推區間內的球,一直推到高度 $t$,使之不低於 $t$;取最小值操作可以想象成用一塊鋼板從上往下壓,一直壓到高度 $t$。於是“每個區間的限制”有兩種,一種是向下壓的板到達的最小高度,一種是向上推的板到達的最大高度。初始時長度大於 1 的區間都沒有限制——向下壓的板的最小高度(記為 $l_n$)為 $\infty$,向上推的板的最大高度(記為 $l_m$)為 0;可以認為初始時長度為 1 的區間的 $l_n$ 和 $l_m$ 都是 0。
現在考慮對一個區間進行取最大值操作。用一塊自下而上的上推鋼板推這個區間,會有什麼變化呢?如果原來的下界鋼板低於 $t$,當然會被推到 $t$ 位置,否則不變;上界同理。因此,這個操作對這個區間的變化是 $l=\max(l,t)$,$r=\max(r,t)$。
再考慮取最小值操作,類似地,$l=\min(l,t)$,$r=\min(r,t)$。加上 lazy tag 維護即可。
???+note "[Atcoder abc342 G. Retroactive Range Chmax](https://atcoder.jp/contests/abc342/tasks/abc342_g)"
給定長度為 $n$ 的序列 $a_1, \ldots ,a_n$,有 $q$ 次操作:
- $\max(l,r,x):$ 對區間 $[l,r]$ 中的所有元素與 $x$ 取最大值。
- $\text{rollback}(i):$ 撤銷第 $i$ 次 max 操作
- $\text{query}(i):$ 輸出 $a_i$ 的值
$n,q \leq 2\times 10^5, 1\le x,a_i\le 10^9$
??? note "思路"
線段樹上每個節點維護一個 multiset,每次區間 max 時,就往 multiset 裡加數,每次撤銷就是刪除數。每次查詢操作則是尋找根到該點路徑上所有 multiset 中的最大值的最大值。
---
## 參考
-
-
-
-
-