???+note "[CSES - Tree Isomorphism I](https://cses.fi/problemset/task/1700)"
給兩顆 $n$ 個點的有根樹
問他們有沒有可能可以以某種畫法把他們畫出來使他們兩個長得一模一樣
$n\le 10^5$
我們令 leaf 的 hash 是 1繼續往上,如果目前的子樹是我們沒看過的就把這個子樹存入 map 中
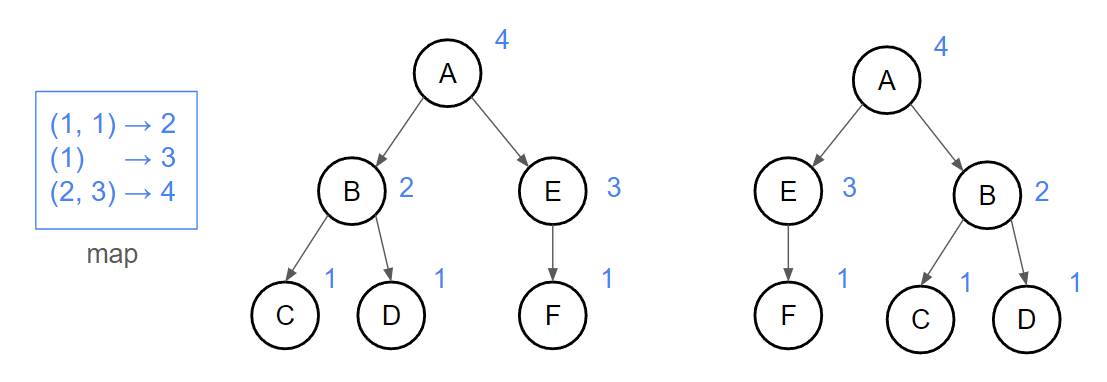{ width="500" }
我們利用 vector 存子樹的 hash 值,注意記得要照 hash 值小到大 sort,才不會當兩個子樹明明是相同,但是順序不同就被判成 NO
??? note "code"
```cpp linenums="1"
int hash(int u, int par) {
int sum = 0;
vector res;
for (auto v : G[u]) {
if (v == par) continue;
res.push_back(hash(v, u));
}
sort(res.begin(), res.end());
if (!mp[res]) mp[res] = idx++;
return mp[res];
}
```
???+note "[CSES - Tree Isomorphism II](https://cses.fi/problemset/task/1701)"
給兩顆 $n$ 個點的無根樹
問他們有沒有可能可以以某種畫法把他們畫出來使他們兩個長得一模一樣
$n\le 10^5$
??? note "思路 1"
我們發現它的 root 是不確定的,所以我們需要一個有效率的方法來取兩棵樹的點當 root 來做比較,而恰好樹跟樹之間最小的差異就是在**樹重心**(樹重心每個樹最多只有兩個,兩顆樹總共也只有 4 種情況)
??? note "code 1"
```cpp linenums="1"
#include
#define int long long
#define pii pair
#define pb push_back
#define mk make_pair
#define F first
#define S second
#define ALL(x) x.begin(), x.end()
using namespace std;
using PQ = priority_queue, greater>;
const int INF = 2e18;
map, int> mp;
int idx = 1;
struct Tree {
static const int M = 1000696969;
static const int X = 131;
vector> G;
vector C;
vector sz;
int n;
void init(int _n) {
n = _n;
sz.resize(n + 1);
G.resize(n + 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
sz[i] = 0;
}
}
void add_edge(int u, int v) {
G[u].pb(v);
G[v].pb(u);
}
void find(int u, int par) {
sz[u] = 1;
int w = 0;
for (auto v : G[u]) {
if (v == par) continue;
find(v, u);
sz[u] += sz[v];
w = max(w, sz[v]);
}
w = max(n - sz[u], w);
if (w <= n / 2) {
C.pb(u);
}
}
int hash(int u, int par) {
int sum = 0;
vector res;
for (auto v : G[u]) {
if (v == par) continue;
res.pb(hash(v, u));
}
sort(ALL(res));
if (!mp[res]) mp[res] = idx++;
return mp[res];
}
};
void solve() {
int n;
cin >> n;
Tree A;
Tree B;
int u, v;
A.init(n);
B.init(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
cin >> u >> v;
A.add_edge(u, v);
}
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
cin >> u >> v;
B.add_edge(u, v);
}
A.find(1, 0);
B.find(1, 0);
int res = 0;
for (auto a : A.C) {
for (auto b : B.C) {
if (A.hash(a, 0) == B.hash(b, 0)) {
res = 1;
}
}
}
if (res)
cout << "YES\n";
else
cout << "NO\n";
}
signed main() {
// ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
// cin.tie(0);
int t = 1;
cin >> t;
while (t--) {
solve();
}
}
```
??? note "思路 2"
這題的 hash 其實有另外一種寫法,例如有棵樹如下
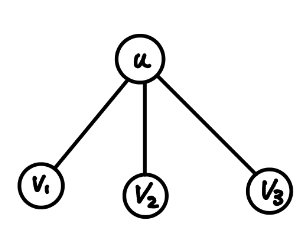{ width="200" }
$H[u]=H[v_1]\times X^1+H[v_2]\times X^2+H[v_3]\times X^3$
```cpp linenums="1"
int hash(int u, int par) {
int sum = 0;
vector res;
for (auto v : G[u]) {
if (v == par) continue;
res.pb(hash(v, u));
}
sort(ALL(res));
int cnt = 1;
// 注意 hash 從 X^1 開始而非 X^0 因為若從 X^0 chain 的 hash value 會跟 leaf 的一樣
for (auto h : res) {
sum = (sum + (H[cnt] * h) % M) % M;
cnt++;
}
if (G[u].size() == 1) sum = 1; // leaf 的 hash value 是 1
return sum;
}
```
??? note "code 2"
```cpp linenums="1"
#include
#define int long long
#define pii pair
#define pb push_back
#define mk make_pair
#define F first
#define S second
#define ALL(x) x.begin(), x.end()
using namespace std;
using PQ = priority_queue, greater>;
const int INF = 2e18;
struct Tree {
static const int M = 1000696969;
static const int X = 131;
vector> G;
vector C;
vector sz;
vector H;
int n;
void init(int _n) {
n = _n;
sz.resize(n + 1);
H.resize(n + 1);
G.resize(n + 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
sz[i] = 0;
H[i] = 0;
}
H[0] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
H[i] = (H[i - 1] * X) % M;
}
}
void add_edge(int u, int v) {
G[u].pb(v);
G[v].pb(u);
}
void find(int u, int par) {
sz[u] = 1;
int w = 0;
for (auto v : G[u]) {
if (v == par) continue;
find(v, u);
sz[u] += sz[v];
w = max(w, sz[v]);
}
w = max(n - sz[u], w);
if (w <= n / 2) {
C.pb(u);
}
}
int hash(int u, int par) {
int sum = 0;
vector res;
for (auto v : G[u]) {
if (v == par) continue;
res.pb(hash(v, u));
}
sort(ALL(res));
int cnt = 1;
for (auto h : res) {
sum = (sum + (H[cnt] * h) % M) % M;
cnt++;
}
sum = (sum + (H[cnt] * (sum)) % M) % M;
if (G[u].size() == 1) sum = 1;
return sum;
}
};
void solve() {
int n;
cin >> n;
Tree A;
Tree B;
int u, v;
A.init(n);
B.init(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
cin >> u >> v;
A.add_edge(u, v);
}
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
cin >> u >> v;
B.add_edge(u, v);
}
A.find(1, 0);
B.find(1, 0);
int res = 0;
for (auto a : A.C) {
for (auto b : B.C) {
if (A.hash(a, 0) == B.hash(b, 0)) {
res = 1;
}
}
}
if (res)
cout << "YES\n";
else
cout << "NO\n";
}
signed main() {
// ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
// cin.tie(0);
int t = 1;
cin >> t;
while (t--) {
solve();
}
}
```