## 向量運算
### 向量內積 dot
以下圖來說,dot(AB, AC) = dot(AC, AB) = |AD| * |AB|
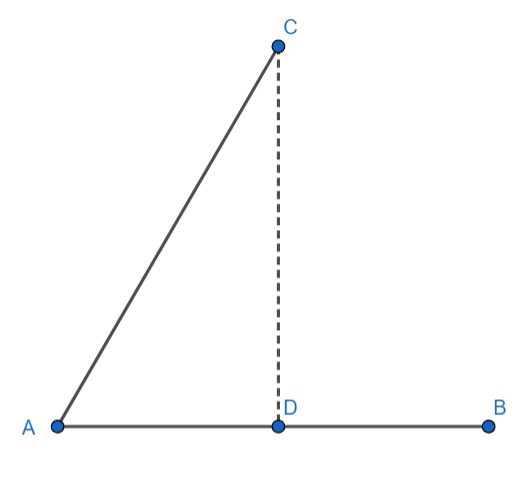{ width="200" }
### 向量外積 cross
右手定則,順時鐘為負,逆時鐘為正。以下圖來說,cross(AB, AC) = |AB| * |AD|
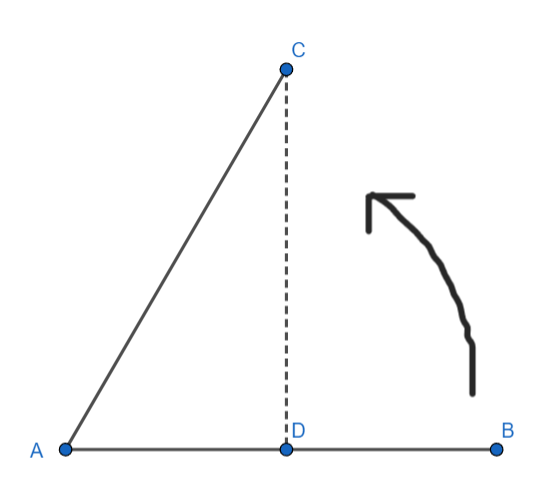{ width="200" }
??? note "模板整理"
```cpp linenums="1"
using Point = pair;
#define x first
#define y second
Point operator+(Point a, Point b) {
return {a.x + b.x, a.y + b.y};
}
Point operator-(Point a, Point b) {
return {a.x - b.x, a.y - b.y};
}
Point operator*(Point a, double d) {
return {d * a.x, d * a.y};
}
double dot(Point a, Point b) {
return a.x * b.x + a.y * b.y;
}
double cross(Point a, Point b) {
return a.x * b.y - a.y * b.x;
}
```
## 凸多邊形面積
將多邊形的各頂點逆時鐘排列,對於每個點利用外積之和可以求出一多邊形面積,
相關資訊可查詢:測量師公式(Surveyor’s Formula)
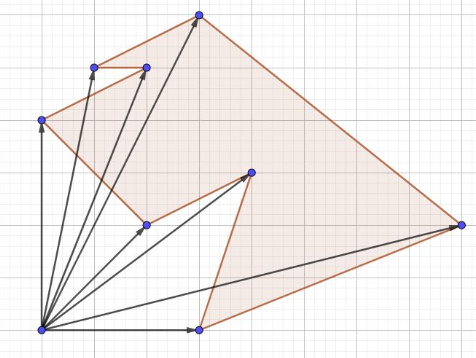{ width="300" }
???+note "code"
```cpp linenums="1"
double area(vector &points) {
int n = points.size();
double ret = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
ret += cross(points[i], points[i - 1]);
}
ret += cross(points[0], points[n - 1]);
return fabs((double)ret / 2);
}
```
???+note "[CSES - Polygon Area](https://cses.fi/problemset/task/2191)"
給一個 n 個點構成的多邊形,求其面積,點的順序可能是順時針或是逆時針
$1\le n\le 1000$
## 線段相交判定
???+note "問題"
給兩個線段的端點座標,判斷是否有交點
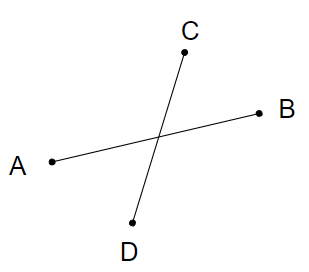{ width="250" }
我們先判斷 A, B 是否在 CD 兩側,也就是看 cross(AB, AC) 與 cross(AB, AD) 是否正負號不同,然後判斷,判斷 C, D 是否在 AB 兩側,也就是看 corss(AB, AC) 與 cross(AB, AD) 是否正負號不同,兩者都符合時,必定相交
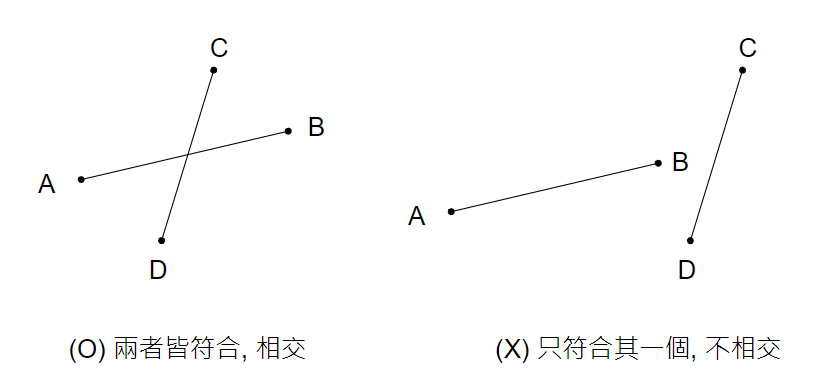{ width="400" }
???+note "目前的 code"
```cpp linenums="1"
int sign(long long x) {
if (x < 0) {
return -1;
} else if (x == 0) {
return 0;
} else {
return 1;
}
}
bool intersection(Point a, Point b, Point c, Point d) {
int c1 = sign(cross(b - a, c - a)) * sign(cross(b - a, d - a));
int c2 = sign(cross(d - c, a - c)) * sign(cross(d - c, b - c));
if (c1 == -1 && c2 == -1) return true;
return false;
}
```
但若發生 cross = 0 的 case 呢 ? 可能會發生三點共線
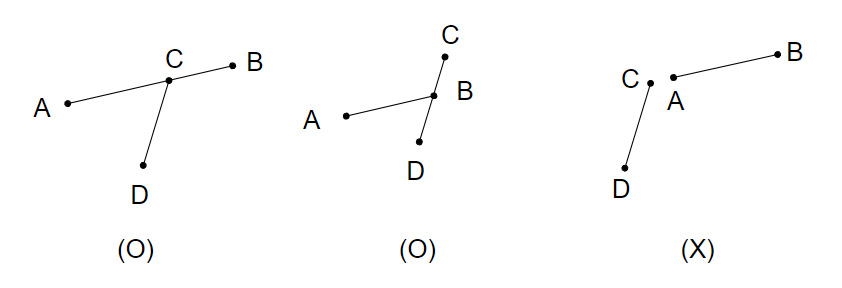{ width="450" }
cross 有 0 的合法 case 至少會有三點共線,所以我們直接將可能的 case 列出來:
- A 在 CD 線段上,回傳 true
- B 在 CD 線段上,回傳 true
- C 在 AB 線段上,回傳 true
- D 在 AB 線段上,回傳 true
??? question "如何判斷一個點 C 在一個線段 AB 上 ?"
首先要判斷 C 是否在「直線」 AB 上,也就是 cross(AB, AC) 是否為 0
若在「直線」 AB 上的話,再來就要判斷是否在 A, B 之間
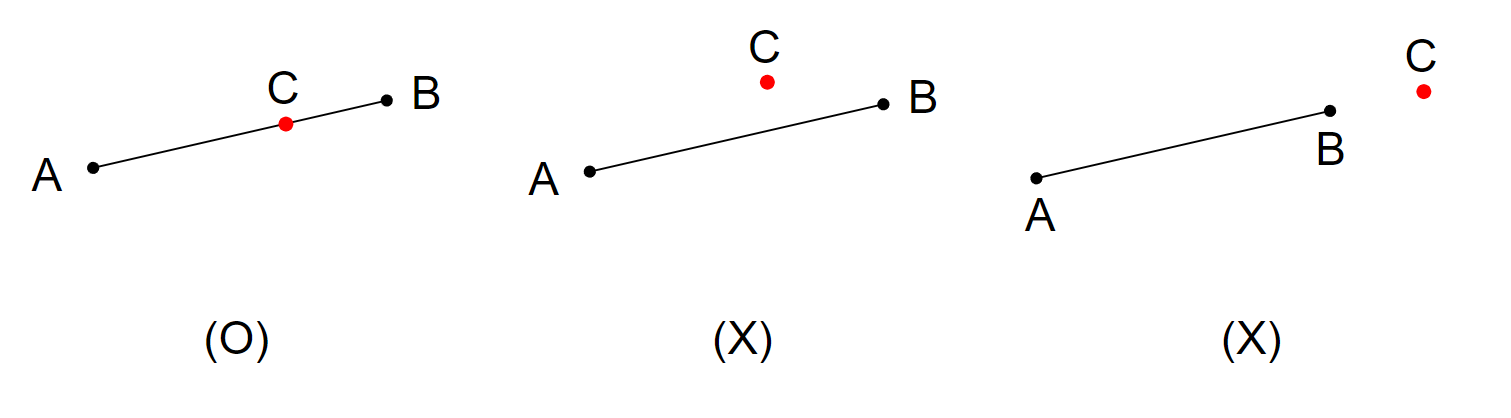{ width="450" }
```cpp linenums="1"
bool onseg(Point a, Point b, Point c) {
if (cross(b - a, c - a) != 0) return false;
if (sign(dot(b - a, c - a)) < 0) return false;
if (sign(dot(a - b, c - b)) < 0) return false;
return true;
}
```
???+note "code"
```cpp linenums="1"
bool onseg(Point a, Point b, Point c) {
if (cross(b - a, c - a) != 0) return false;
if (sign(dot(b - a, c - a)) < 0) return false;
if (sign(dot(a - b, c - b)) < 0) return false;
return true;
}
bool intersection(Point a, Point b, Point c, Point d) {
int c1 = sign(cross(b - a, c - a)) * sign(cross(b - a, d - a));
int c2 = sign(cross(d - c, a - c)) * sign(cross(d - c, b - c));
if (c1 == 1 || c2 == 1) return false;
if (c1 < 0 && c2 < 0) return true;
if (onseg(a, b, c)) return true;
if (onseg(a, b, d)) return true;
if (onseg(c, d, a)) return true;
if (onseg(c, d, b)) return true;
return false;
}
```
???+note "[CSES - Line Segment Intersection](https://cses.fi/problemset/task/2191)"
有 $t$ 筆詢問,每筆給定兩個線段,詢問是否相交(可能有三點共線)
$t\le 10^5, -10^9 \le x, y\le 10^9$
## 找到兩個直線的交點
???+note "問題"
給定兩條直線,找出交點座標
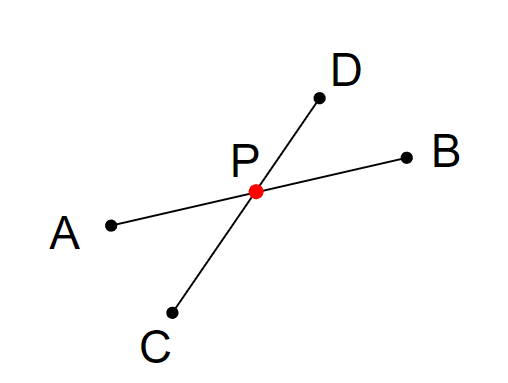{ width="200" }
利用向量伸縮,$\begin{align}\overrightarrow{CP}=\frac{\ell_2}{\ell_1}\times\overrightarrow{CD}\end{align}$
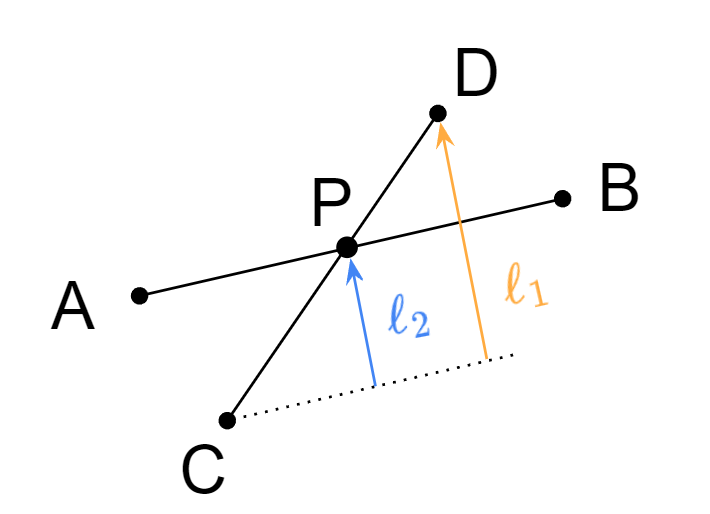{ width="300" }
至於 $\ell_1, \ell_2$ 我們都可以用外積求出來:
- $\begin{align}\ell_1=\frac{\overrightarrow{AB}\times{\overrightarrow{CD}}}{|\overrightarrow{AB}|}\end{align}$
- $\begin{align}\ell_2=\texttt{-}\frac{\overrightarrow{AB}\times{\overrightarrow{AC}}}{|\overrightarrow{AB}|}\end{align}$
注意這邊 $\ell_2$ 的計算我們有加負號,要使 $\ell_1, \ell_2$ 正負號相同。最後,可得到
$$
\begin{align}P=C+(\texttt{-}\frac{\overrightarrow{AB}\times\overrightarrow{AC}}{\overrightarrow{AB}\times \overrightarrow{CD}})\times\overrightarrow{CD}\end{align}
$$
???+note "code"
```cpp linenums="1"
Point intersection_point(Point a, Point b, Point c, Point d) {
double ratio = (double)cross(b - a, c - a) / cross(b - a, d - c);
return c - ratio * (d - c);
}
```
## 距離
### 一、點到線段
若點在線短端點之內,就看點與線段的垂直距離,若點在線段端點之外,就看點到端點的距離。
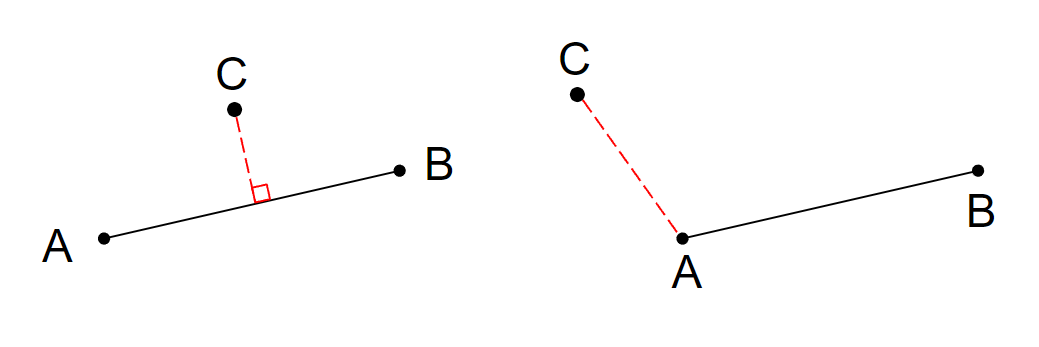{ width="400" }
???+note "code"
```cpp linenums="1"
double disPS(Point a, Point b, Point c) {
// Seg(a, b) Point(c)
if (onseg(a, b, c)) return 0;
if (dot(c - a, b - a) < 0) return dis(c, a);
if (dot(c - b, a - b) < 0) return dis(b, a);
return (double)abs(cross(c - a, b - a)) / len(b - a);
}
```
### 二、線段到線段
兩線段相交,距離為零;兩線段不相交,窮舉所有的端點到線段距離,取最短者(不可能是選在中間,因為把中間選的點往兩端其中一端移動一定會更好)
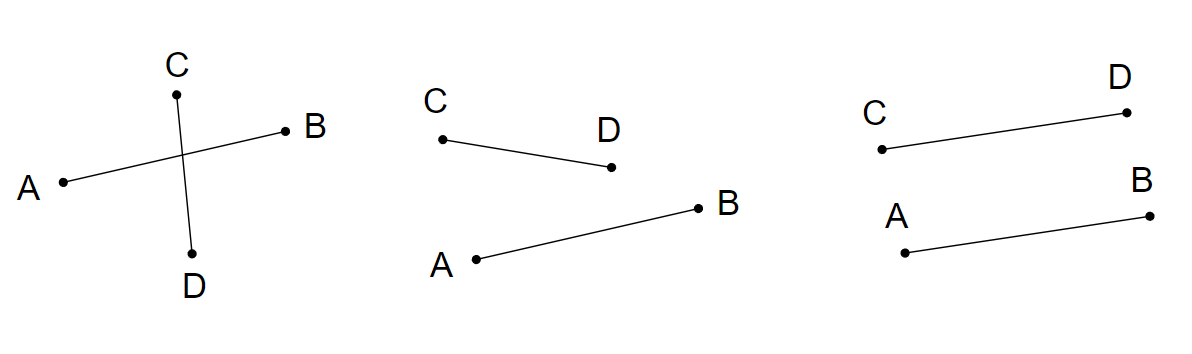{ width="400" }
???+note "code"
```cpp linenums="1"
double disSS(Point a, Point b, Point c, Point d) {
// Seg(a, b) Seg(c, d)
if (intersect(a, b, c, d)) return 0;
return min({disPS(a, b, c), disPS(a, b, d),
disPS(c, d, a), disPS(c, d, b)});
}
```
## 判斷點是否在圖形內
### 凸包包含測試
把凸包想成由一些三角形組成,可用二分搜在哪個三角形內
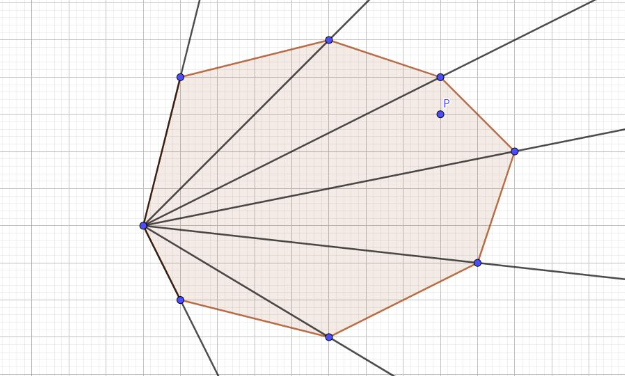{ width="300" }
??? note "code"
```cpp linenums="1"
#include
#define int long long
#define pii pair
#define pb push_back
#define mk make_pair
#define x first
#define y second
#define ALL(x) x.begin(), x.end()
using namespace std;
using PQ = priority_queue, greater>;
using Point = pair;
const int INF = 2e18;
const int maxn = 3e5 + 5;
const int M = 1e9 + 7;
const int EPS = 1e-7;
Point operator+(Point a, Point b) {
return {a.x + b.x, a.y + b.y};
}
Point operator-(Point a, Point b) {
return {a.x - b.x, a.y - b.y};
}
Point operator*(Point a, double d) {
return {a.x * d, a.y * d};
}
int dot(Point a, Point b) {
return a.x * b.x + a.y * b.y;
}
int cross(Point a, Point b) {
return a.x * b.y - a.y * b.x;
}
int abs2(Point a) {
// 計算 a 的長度平方
return dot(a, a);
}
int sign(double x) {
if (abs(x) < EPS) return 0;
return x > 0 ? 1 : -1;
}
int onseg(Point a, Point b, Point c) {
if (cross(c - a, b - a) != 0) return false;
if (dot(c - a, b - a) < 0) return false;
if (dot(a - b, c - b) < 0) return false;
return true;
}
bool traingle(Point a, Point b, Point c, Point d) {
// 判斷點是否在三角形內 traingle(a, b, c), Point(d)
if (onseg(a, b, d)) return 1;
if (onseg(b, c, d)) return 1;
if (onseg(c, a, d)) return 1;
int c1 = sign(cross(b - a, d - a));
int c2 = sign(cross(c - b, d - b));
int c3 = sign(cross(a - c, d - c));
if (c1 == 1 && c2 == 1 && c3 == 1) return 1;
return 0;
}
vector prep(vector p) {
int n = p.size();
auto comp = [&](Point a, Point b) {
return a.x < b.x || (a.x == b.x && a.y < b.y);
// x 做為排序的第一順位,再來是 y
};
int pos = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
if (comp(p[i], p[pos])) pos = i;
}
rotate(p.begin(), p.begin() + pos, p.end());
// new p = [pos ~ end] + [begin ~ pos - 1]
// ex: p = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7}
// rotate (p.begin(), p.begin() + 3, p.end())
// new p = {3,4,5,6,7,1,2}
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
p[i] = p[i] - p[0];
}
return p;
}
int inconvex(vector p, Point a) {
p = prep(p); // input 的 p 必須是逆時鐘
a = a - p[0];
int n = p.size();
// 在凸包下方
if (cross(p[1], a) != 0 &&
sign(cross(p[1], a)) != sign(cross(p[1], p[n - 1])))
return false;
// 在凸包上方
if (cross(p[n - 1], a) != 0 &&
sign(cross(p[n - 1], a)) != sign(cross(p[n - 1], p[1])))
return false;
// 在 p[1]~p[0]
if (cross(p[1], a) == 0)
return abs2(p[1]) >= abs2(a);
int l = 1, r = n - 1;
while (l < r - 1) {
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
if (cross(p[mid], a) >= 0)
l = mid;
else
r = mid;
}
return traingle({0, 0}, p[l], p[l + 1], a);
}
signed main() {
vector p = {{5, 1}, {8, 3}, {7, 6}, {3, 8}, {1, 2}};
Point tar = {-3, 3};
cout << (inconvex(p, tar) ? "YES" : "NO") << "\n";
}
```
### 多邊形包含測試
找射線,算線段交的次數,奇數次為內部,偶數次為外部。但射線可能恰好相交於端點上,這樣會壞掉,解決辦法就是讓射線的斜率射為無限大,使得沒有題目範圍內的整數點會在上面,例如說射線向量 = (1, 2e9 + 1)
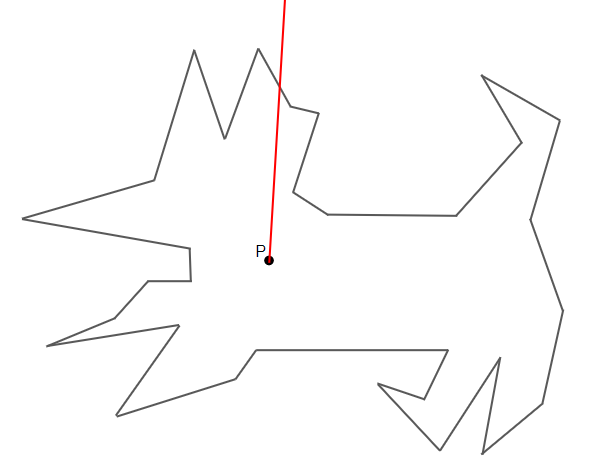{ width="300" }
??? note "code"
```cpp linenums="1"
#include
#define int long long
#define x first
#define y second
using namespace std;
using Point = pair;
int n, m;
vector p;
Point operator+(Point a, Point b) {
return {a.x + b.x, a.y + b.y};
}
Point operator-(Point a, Point b) {
return {a.x - b.x, a.y - b.y};
}
Point operator*(Point a, double d) {
return {a.x * d, a.y * d};
}
int dot(Point a, Point b) {
return a.x * b.x + a.y * b.y;
}
int cross(Point a, Point b) {
return a.x * b.y - a.y * b.x;
}
int sign(int x) {
if (x < 0) return -1;
if (x == 0) return 0;
return 1;
}
bool onseg(Point a, Point b, Point c) {
if (cross(c - a, b - a) != 0) return false;
if (dot(c - a, b - a) < 0) return false;
if (dot(a - b, c - b) < 0) return false;
return true;
}
int intersect(Point a, Point b, Point c, Point d) {
int c1 = sign(cross(b - a, c - a)) * sign(cross(b - a, d - a));
int c2 = sign(cross(d - c, b - c)) * sign(cross(d - c, a - c));
if (c1 == 1 || c2 == 1) return false;
if (c1 == -1 && c2 == -1) return true;
if (onseg(a, b, c)) return true;
if (onseg(a, b, d)) return true;
if (onseg(c, d, a)) return true;
if (onseg(c, d, b)) return true;
return false;
}
void solve() {
Point tar;
cin >> tar.x >> tar.y;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
if (onseg(p[i - 1], p[i], tar)) {
cout << "BOUNDARY";
return;
}
}
if (onseg(p[0], p[n - 1], tar)) {
cout << "BOUNDARY";
return;
}
Point cmp = tar + (Point){1, 2e9 + 1};
int cnt = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
if (intersect(p[i - 1], p[i], cmp, tar)) {
cnt++;
}
}
if (intersect(p[0], p[n - 1], cmp, tar)) {
cnt++;
}
if (cnt & 1) cout << "INSIDE";
else cout << "OUTSIDE";
}
signed main(){
cin >> n >> m;
p.resize(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++) {
cin >> p[i].x >> p[i].y;
}
while (m--) {
solve();
cout << "\n";
}
}
```
## 凸包
???+note "問題"
給一些在二為平面上的點,選一些點使得這些點連線能夠包住所有點
二維平面上的凸包是一個凸多邊形,在所有點的外圍繞一圈即得凸包。另外,**最頂端、最底端、最左端、最右端的點**,一定是凸包上的點(因為如果不是的話,就沒任何點能包住他們)
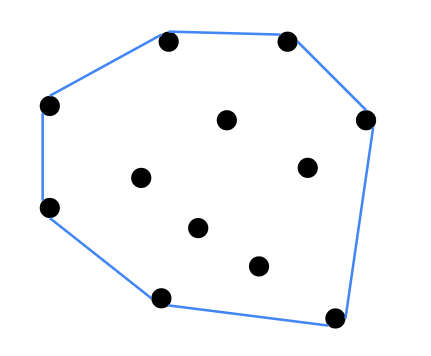{ width="200" }
### Andrew Monotone Chain(單調鏈)
首先將所有點以 x 座標小到大排序,當 x 座標相同則以 y 座標小到大排序。
用最左邊的點,與最右邊的點,可以把平面分成上下兩半,上面的就是上凸包,下面的就是下凸包。先從起點開始,按照順序掃描,找到下半凸包。再從終點開始,按照相反順序掃描,找到上半凸包。合起來就是完整的凸包
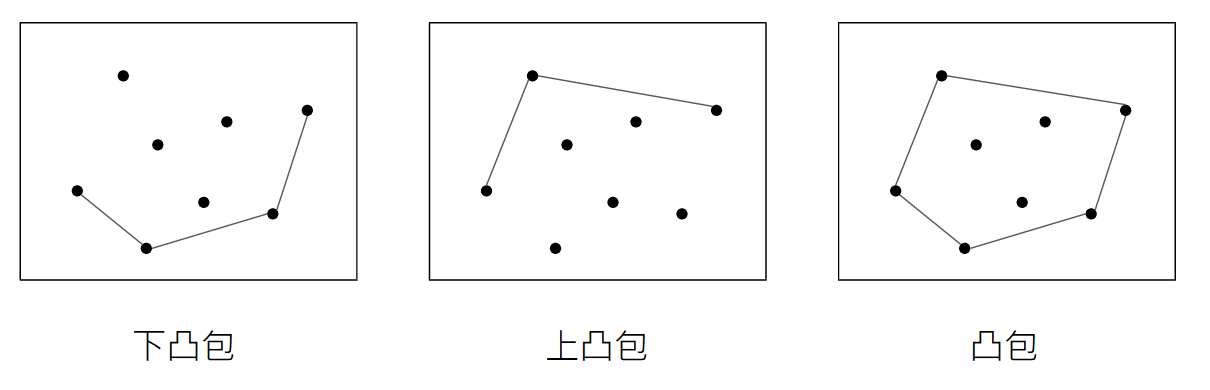{ width="550" }
這邊就以找下凸包為例,排序好後第一個點,也就是最左邊的點,一定會在凸包裡面,所以我們將他加入,之後,當新的點新增進來時,若加來發現會與前面的向量呈現「凹陷狀態」,也就是 cross < 0[^1],則一直 pop 當前凸包尾端的點直到不會凹陷,因為這些被 pop 的點都會被新的點與之前的點所連接的向量包含住
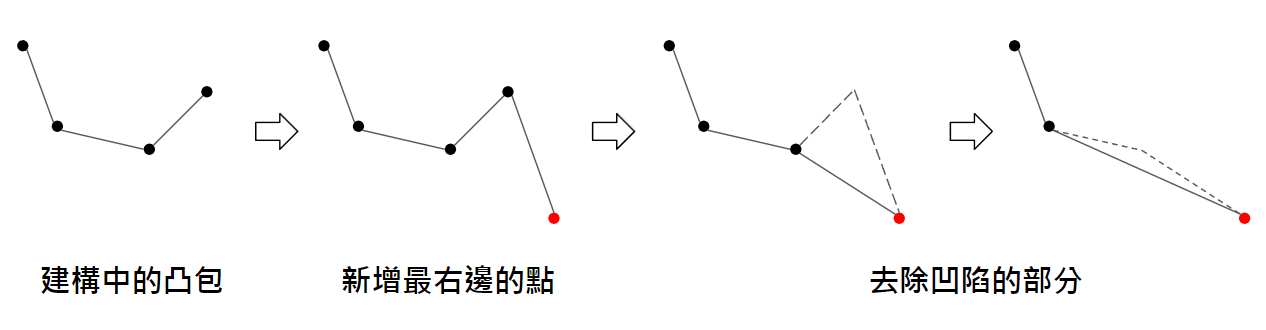{ width="650" }
複雜度的瓶頸在排序,所以複雜度是 O(n log n)
??? note "code"
```cpp linenums="1"
vector convex_hull(vector p) {
int n = p.size(), m = 0;
sort(p.begin(), p.end());
vector h;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
while (m >= 2 && cross(p[i] - h[m - 1], h[m - 1] - h[m - 2]) < 0) {
h.pop_back(), m--;
}
h.push_back(p[i]), m++;
}
// 因為 h.back() 一定是 p[n - 1], 所以可以直接接在上面繼續做
for (int i = n - 2; i >= 0; i--) {
while (m >= 2 && cross(p[i] - h[m - 1], h[m - 1] - h[m - 2]) < 0) {
h.pop_back(), m--;
}
h.push_back(p[i]), m++;
}
return h;
}
```
???+note "[CSES - Convex Hull](https://cses.fi/problemset/task/2195/)"
給 n 個二維座標點,求出凸包
$3\le n\le 2\times 10^5, |x|, |y| \le 10^9$
??? note "code"
```cpp linenums="1"
#include
#define int long long
#define pii pair
#define mk make_pair
#define pb push_back
#define x first
#define y second
#define ALL(x) x.begin(), x.end()
using namespace std;
using Point = pair;
int n;
vector p;
Point operator+(Point a, Point b) {
return {a.x + b.x, a.y + b.y};
}
Point operator-(Point a, Point b) {
return {a.x - b.x, a.y - b.y};
}
Point operator*(Point a, double d) {
return {a.x * d, a.y * d};
}
int dot(Point a, Point b) {
return a.x * b.x + a.y * b.y;
}
int cross(Point a, Point b) {
return a.x * b.y - a.y * b.x;
}
int sign(int x) {
if (x < 0) return -1;
if (x == 0) return 0;
return 1;
}
bool onseg(Point a, Point b, Point c) {
if (cross(c - a, b - a) != 0) return false;
if (dot(c - a, b - a) < 0) return false;
if (dot(a - b, c - b) < 0) return false;
return true;
}
int intersect(Point a, Point b, Point c, Point d) {
int c1 = sign(cross(b - a, c - a)) * sign(cross(b - a, d - a));
int c2 = sign(cross(d - c, b - c)) * sign(cross(d - c, a - c));
if (c1 == 1 || c2 == 1) return false;
if (c1 == -1 && c2 == -1) return true;
if (onseg(a, b, c)) return true;
if (onseg(a, b, d)) return true;
if (onseg(c, d, a)) return true;
if (onseg(c, d, b)) return true;
return false;
}
vector convex_hull(vector p) {
int n = p.size(), m = 0;
sort(p.begin(), p.end());
vector h;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
while (m >= 2 && cross(p[i] - h[m - 1], h[m - 1] - h[m - 2]) < 0) {
h.pop_back(), m--;
}
h.push_back(p[i]), m++;
}
// 因為 h.back() 一定是 p[n - 1], 所以可以直接接在上面繼續做
for (int i = n - 2; i >= 0; i--) {
while (m >= 2 && cross(p[i] - h[m - 1], h[m - 1] - h[m - 2]) < 0) {
h.pop_back(), m--;
}
h.push_back(p[i]), m++;
}
return h;
}
signed main() {
cin >> n;
p.resize(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
cin >> p[i].x >> p[i].y;
}
vector h = convex_hull(p);
cout << h.size() - 1 << "\n";
for (int i = 0; i < h.size() - 1; i++) {
cout << h[i].x << " " << h[i].y << "\n";
}
}
```
???+note "[Kattis - Robot Protection](https://open.kattis.com/contests/igo32n/problems/robotprotection)"
給 $n$ 個點,要先求出凸包,再求凸包的面積
$1\le n\le 10^4, |x_i|,|y_i|\le 10^4$
??? note "細節"
注意直接套我們上面的凸包模板,加上面積公式即可,就算凸包模板起點會現兩次也是 ok 的,不能在最後把起點 pop 掉
把最後重複出現的起點 pop 掉也可以,但要記得將 area() 函式內的細節改一下,防止 n = 1 時,凸包把所有點都 pop 掉的 edge case
```cpp
double area(vector &points) {
int n = points.size();
int ret = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
ret += cross(points[i], points[i - 1]);
}
// 前面加上 if (n),防止 n = 0
if (n) ret += cross(points[0], points[n - 1]);
return fabs((double)ret / 2);
}
```
> submission:
??? note "code"
```cpp linenums="1"
#include
#define int long long
#define pii pair
#define mk make_pair
#define pb push_back
#define x first
#define y second
#define ALL(x) x.begin(), x.end()
using namespace std;
using Point = pair;
Point operator+(Point a, Point b) {
return {a.x + b.x, a.y + b.y};
}
Point operator-(Point a, Point b) {
return {a.x - b.x, a.y - b.y};
}
Point operator*(Point a, double d) {
return {a.x * d, a.y * d};
}
int dot(Point a, Point b) {
return a.x * b.x + a.y * b.y;
}
int cross(Point a, Point b) {
return a.x * b.y - a.y * b.x;
}
double area(vector &points) {
int n = points.size();
int ret = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
ret += cross(points[i], points[i - 1]);
}
ret += cross(points[0], points[n - 1]);
return fabs((double)ret / 2);
}
vector convex_hull(vector p) {
int n = p.size(), m = 0;
sort(p.begin(), p.end());
vector h;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
while (m >= 2 && cross(p[i] - h[m - 1], h[m - 1] - h[m - 2]) < 0) {
h.pop_back(), m--;
}
h.push_back(p[i]), m++;
}
for (int i = n - 2; i >= 0; i--) {
while (m >= 2 && cross(p[i] - h[m - 1], h[m - 1] - h[m - 2]) < 0) {
h.pop_back(), m--;
}
h.push_back(p[i]), m++;
}
return h;
}
int n;
void solve() {
vector p;
p.resize(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
cin >> p[i].x >> p[i].y;
}
vector h = convex_hull(p);
cout << fixed << setprecision(2) << area(h) << '\n';
}
signed main() {
while (cin >> n) {
if (n == 0) break;
solve();
}
}
```
## 極角排序
一般用這個即可,不用自定義 cmp,其中 atan2 的值域是 [-180, 180]
??? note "code"
```cpp linenums="1"
bool cmp(Point a, Point b) {
return atan2(a.y, a.x) < atan2(b.y, b.x) ;
}
```
???+note "[TOI 2020 pD. 質感測試](https://tioj.ck.tp.edu.tw/problems/2191)"
給 $n$ 個二維座標平面的點,第 $i$ 個點有權重 $w_i$,問任意通過原點的直線,能掃過的點的權重總和最大是多少
$n\le 3\times 10^5, -1000\le w_i\le 1000, |x_i|, |y_i| \le 10^5$
??? note "思路"
【觀察】: 任意通過原點的直線 ↔ 一條斜率為 m 的直線
按照斜率排序,問題就變成了 Maximum Cirricular Subarray
???+note "[TOI 2019 pA. 四點共線 (collinearity)](https://sorahisa-rank.github.io/oi-toi/2019/problems.pdf)"
給 n 個點,問輸出四點共線中最小字典序的
$n\le 3000$
??? note "思路"
開一個 map 存斜率
枚舉第一個點 i,再枚舉其他點 j,將 (key, value) = (i 跟 j 的斜率, j) 加入 map 中,看可能的斜率中字典序最小的那個即可
延伸主體:
-
-
## 最近點對問題
### 分治
先把整個陣列 p 按照 x 小到大 sort。以中位數當 pivot,依照 x 軸分成左、右兩堆,遞迴求解子問題,再來 Combine 的部分,我們把以中位數那條線左右距離 <= d 的點都拿出來,按照 y 小到大 sort,對於每個點都只要看周圍至多 6 個點的距離即可,因為我們可以利用類似 Merge sort 的方式得到已 y 小到大 sort 的 p',所以複雜度是 O(n log n)
```
combine(d, P, mid) {
P 只留 x \in [mid - d, mid + d]
每個 P 內的 point,只和上下 8 個點算 distance
用類似雙指針維護
}
DC(P) {
(d1, P_L') = DC(P.前半)
(d2, P_R') = DC(P.後半)
P' = merge(P_L', P_R') by y 小到大
d = min(d1, d2)
combine(d, P', mid)
}
```
### sweep line
sweep line 從 y 小到大掃過每個點,維護一個 set表示目前還與 sweep line 的點距離 <= d 的點,每次只要跟距離 sweep line 前後 6 個點算距離即可
```
sort(p) y 小到大
set 由 x 小到大
l = 1
for r = 1...n:
while p[l].y <= p[r].y - D:
刪 p[l]
找 set 內, p[r].x 前後 6 個點 lower_bound 更新 D
set.insert(p[r])
```
??? note "code"
```cpp linenums="1"
#include
#define int long long
#define x first
#define y second
#define pii pair
using namespace std;
const int INF = 9e18;
int dis(pii a, pii b) {
int x = a.x - b.x, y = a.y - b.y;
return x * x + y * y;
}
signed main() {
int n;
cin >> n;
vector> p(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
cin >> p[i].x >> p[i].y;
}
sort(p.begin(), p.end());
set> s;
s.clear();
s.insert({p[0].y, p[0].x});
int l = 0, ans = INF;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
int d = ceil(sqrt(ans));
while (l < i && p[l].x < p[i].x - d) {
s.erase({p[l].y, p[l].x});
l++;
}
auto it_l = s.lower_bound({p[i].y - d, 0});
auto it_r = s.upper_bound({p[i].y + d, 0});
for (auto it = it_l; it != it_r; it++) {
ans = min(ans, dis({it->y, it->x}, p[i]));
}
s.insert({p[i].y, p[i].x});
}
cout << ans << '\n';
}
```
[^1]: 見此圖