Examples > Digital
Button State Change Detection (Edge Detection)
This program checks when the button changes state from off to on, and counts how many times this change of state happens. This is called state change detection or edge detection.
Hardware Required
- MSP-EXP430G2 LaunchPad
- pushbutton [available already on-board as part of the LaunchPad]
- LED [available already on-board as a part of the Launchpad]
- momentary button or switch
- 10K ohm resistor
- breadboard
- hook-up wire
Relevant Groundwork
In order detect the state change, the current button state is compared with the last button state and if the current button state is high, then the button changed from off to on. A counter is incremented whenever this state change happens. The button push counter's value is checked, and if it's an even multiple of four, it turns the LED on pin 14 ON. Otherwise, it turns it off.
Circuit
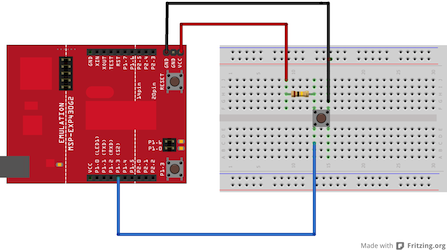
image developed using Fritzing. For more circuit examples, see the Fritzing project page
No external circuitry is required.
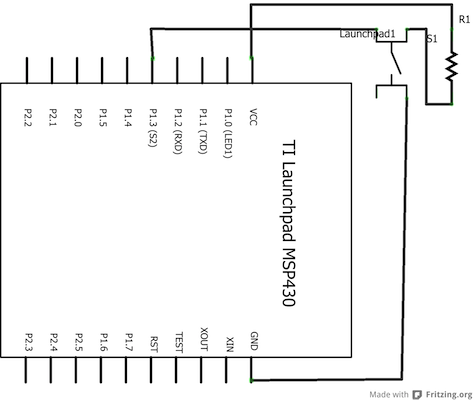
For external push buttonConnect three wires to the Launch pad board. The first two, red and black, connect to the two long vertical rows on the side of the breadboard to provide access to the 3 volt supply and ground. The third wire goes from digital pin p1.3 to one leg of the pushbutton. That same leg of the button connects through a pull-up resistor (here 10 K Ohms) to Vcc. The other leg of the button connects to the ground.
Schematic
Code Explanation
In the program, pin 14, which has green LED connected to it, is set up as output in the setup function.
pinMode(ledPin, OUTPUT);
Here the ledpin refers to the GREEN_LED which is set as output. The push button which is connected to pin 5 is set up as input. The pull-up resistor connected to this pin is enabled.
pinMode(buttonPin, INPUT_PULLUP);
Begin serial communications, at 9600 bits of data per second, between your Launchpad and your computer with the line
Serial.begin(9600);
In the main loop, the state of the pushbutton is saved in the variable “ButtonState”.
int ButtonState = digitalRead(buttonPin);
If the state of the pushbutton has changed from its previous stored state
if (ButtonState != lastButtonState)
If the ButtonState is High, then the ButtonPush counter is incremented and the value is output to serial terminal. Every time the value of the counter is checked, if it has reached 4. If the ButtonPush counter reaches a value of 4, then the LED is turned ON.
if (buttonPushCounter % 4 == 0) {
digitalWrite(ledPin, HIGH);
} else {
digitalWrite(ledPin, LOW);
}
Code
/*
State change detection (edge detection)
Often, you don't need to know the state of a digital input all the time,
but you just need to know when the input changes from one state to another.
For example, you want to know when a button goes from OFF to ON. This is called
state change detection, or edge detection.
created 27 Sep 2005
modified 30 Aug 2011
by Tom Igoe
modified 27 Apr 2012
Robert Wessels
This example code is in the public domain.
*/
const int buttonPin = PUSH2; // the pin that the pushbutton is attached to
const int ledPin = RED_LED; // the pin that the LED is attached to
// Variables will change:
int buttonPushCounter = 0; // counter for the number of button presses
int buttonState = 0; // current state of the button
int lastButtonState = 0; // previous state of the button
void setup() {
// initialize the button pin as a input:
pinMode(buttonPin, INPUT_PULLUP);
// initialize the LED as an output:
pinMode(ledPin, OUTPUT);
// initialize serial communication:
Serial.begin(9600);
}
void loop() {
// read the pushbutton input pin:
buttonState = digitalRead(buttonPin);
// compare the buttonState to its previous state
if (buttonState != lastButtonState) {
// if the state has changed, increment the counter
if (buttonState == HIGH) {
// if the current state is HIGH then the button
// wend from off to on:
buttonPushCounter++;
Serial.println("on");
Serial.print("number of button pushes: ");
Serial.println(buttonPushCounter);
}
else {
// if the current state is LOW then the button
// wend from on to off:
Serial.println("off");
}
}
// save the current state as the last state,
//for next time through the loop
lastButtonState = buttonState;
// turns on the LED every four button pushes by
// checking the modulo of the button push counter.
// the modulo function gives you the remainder of
// the division of two numbers:
if (buttonPushCounter % 4 == 0) {
digitalWrite(ledPin, HIGH);
} else {
digitalWrite(ledPin, LOW);
}
}
Working Video
(Insert Video Here)Try it out:
- use the button to print something in binary to the serial monitor
See Also:
- pinMode()
- digitalWrite()
- digialRead()
- if()
- millis()
- BareMinimum: The bare minimum of code needed to start an Energia sketch.
- Blink: Turn an LED on and off.
- DigitalReadSerial: Read a switch, print the state out to the Energia Serial Monitor. <
- BlinkWithoutDelay: Blinking an LED without using the delay() function
Corrections, suggestions, and new documentation should be posted to the Forum.
The text of the Energia reference is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 License. Energia reference is based on the Arduino reference. Code samples in the reference are released into the public domain.