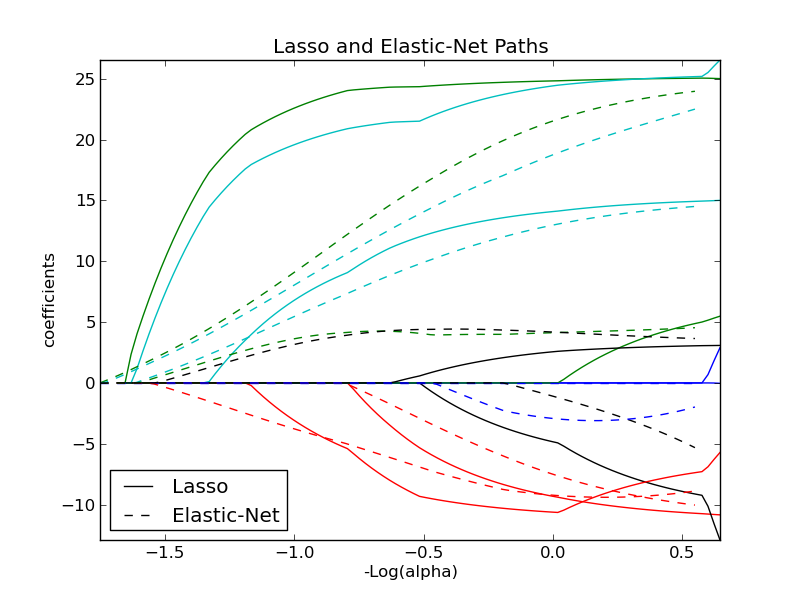
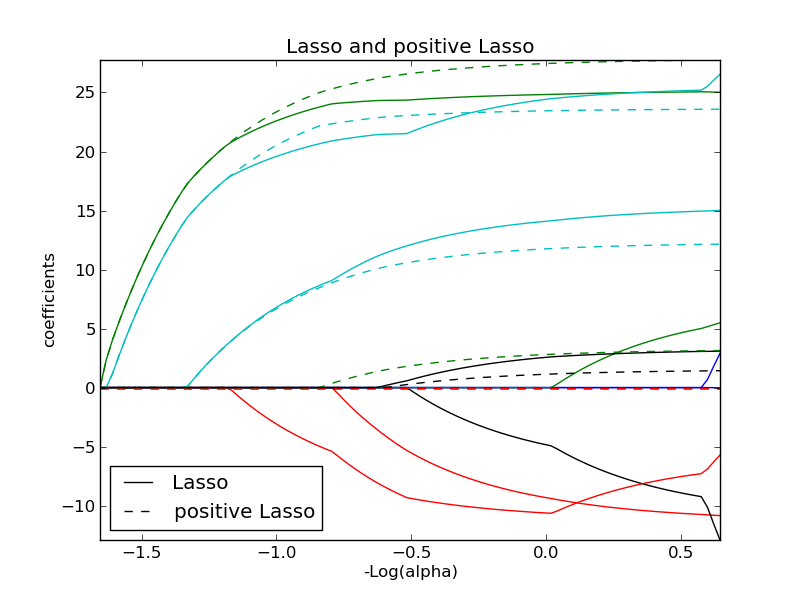
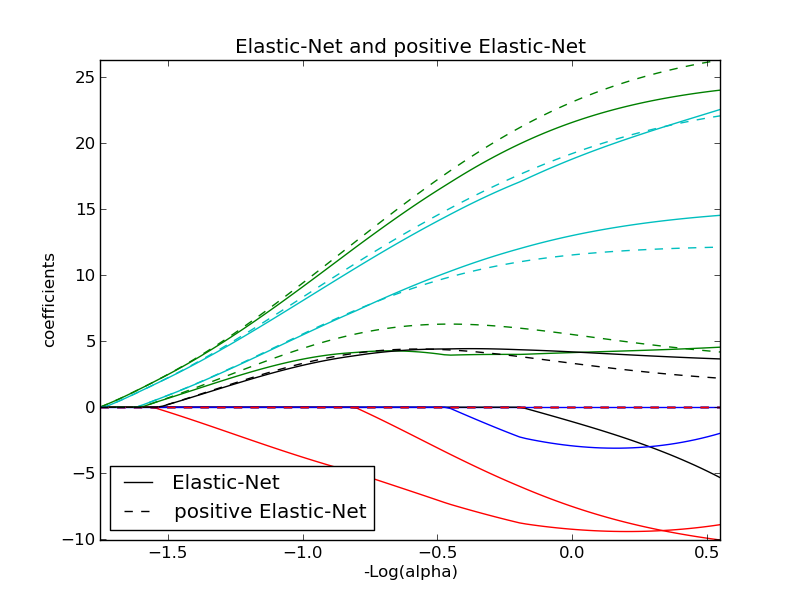
Lasso and Elastic Net¶
Lasso and elastic net (L1 and L2 penalisation) implemented using a coordinate descent.
The coefficients can be forced to be positive.
Script output:
Computing regularization path using the lasso...
Computing regularization path using the positive lasso...
Computing regularization path using the elastic net...
Computing regularization path using the positve elastic net...
Python source code: plot_lasso_coordinate_descent_path.py
print(__doc__)
# Author: Alexandre Gramfort <alexandre.gramfort@inria.fr>
# License: BSD 3 clause
import numpy as np
import pylab as pl
from sklearn.linear_model import lasso_path, enet_path
from sklearn import datasets
diabetes = datasets.load_diabetes()
X = diabetes.data
y = diabetes.target
X /= X.std(axis=0) # Standardize data (easier to set the l1_ratio parameter)
# Compute paths
eps = 5e-3 # the smaller it is the longer is the path
print("Computing regularization path using the lasso...")
# The return_models parameter sets that lasso_path will return
# the alphas and the coefficients as output, instead of a list
# of models as it does by default. Returning the list of models
# is deprecated and will eventually be removed in 0.15
alphas_lasso, coefs_lasso, _ = lasso_path(X, y, eps, return_models=False,
fit_intercept=False)
print("Computing regularization path using the positive lasso...")
alphas_positive_lasso, coefs_positive_lasso, _ = lasso_path(
X, y, eps, positive=True, return_models=False, fit_intercept=False)
print("Computing regularization path using the elastic net...")
alphas_enet, coefs_enet, _ = enet_path(
X, y, eps=eps, l1_ratio=0.8, return_models=False, fit_intercept=False)
print("Computing regularization path using the positve elastic net...")
alphas_positive_enet, coefs_positive_enet, _ = enet_path(
X, y, eps=eps, l1_ratio=0.8, positive=True, return_models=False,
fit_intercept=False)
# Display results
pl.figure(1)
ax = pl.gca()
ax.set_color_cycle(2 * ['b', 'r', 'g', 'c', 'k'])
l1 = pl.plot(-np.log10(alphas_lasso), coefs_lasso.T)
l2 = pl.plot(-np.log10(alphas_enet), coefs_enet.T, linestyle='--')
pl.xlabel('-Log(alpha)')
pl.ylabel('coefficients')
pl.title('Lasso and Elastic-Net Paths')
pl.legend((l1[-1], l2[-1]), ('Lasso', 'Elastic-Net'), loc='lower left')
pl.axis('tight')
pl.figure(2)
ax = pl.gca()
ax.set_color_cycle(2 * ['b', 'r', 'g', 'c', 'k'])
l1 = pl.plot(-np.log10(alphas_lasso), coefs_lasso.T)
l2 = pl.plot(-np.log10(alphas_positive_lasso), coefs_positive_lasso.T,
linestyle='--')
pl.xlabel('-Log(alpha)')
pl.ylabel('coefficients')
pl.title('Lasso and positive Lasso')
pl.legend((l1[-1], l2[-1]), ('Lasso', 'positive Lasso'), loc='lower left')
pl.axis('tight')
pl.figure(3)
ax = pl.gca()
ax.set_color_cycle(2 * ['b', 'r', 'g', 'c', 'k'])
l1 = pl.plot(-np.log10(alphas_enet), coefs_enet.T)
l2 = pl.plot(-np.log10(alphas_positive_enet), coefs_positive_enet.T,
linestyle='--')
pl.xlabel('-Log(alpha)')
pl.ylabel('coefficients')
pl.title('Elastic-Net and positive Elastic-Net')
pl.legend((l1[-1], l2[-1]), ('Elastic-Net', 'positive Elastic-Net'),
loc='lower left')
pl.axis('tight')
pl.show()
Total running time of the example: 0.21 seconds