You can perform the following actions on web service operations:
Adding and Editing Operations
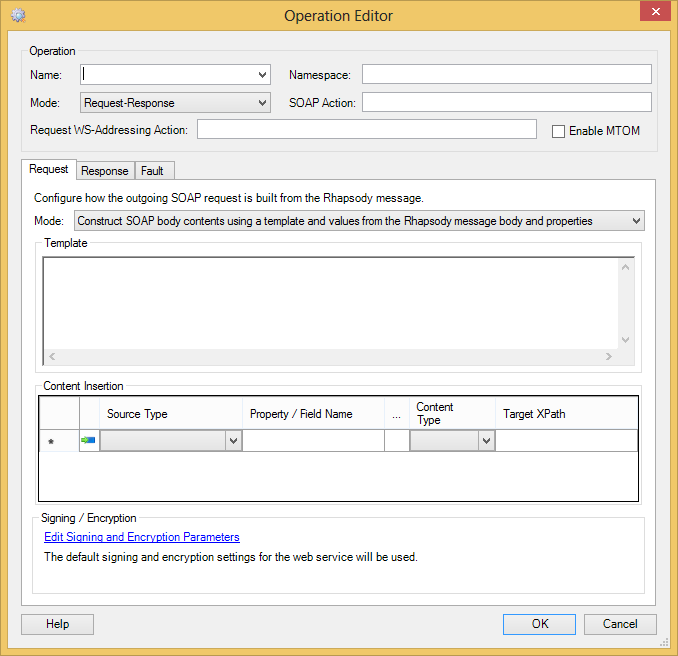
The Operation Editor dialog is displayed when you select the Add Operation or Edit Operation buttons on the Operations tab of the Web Service Client communication point. The dialog is used for:
Calling an Operation
Property |
Description |
|---|---|
Name |
Enter or select the (local) name of the operation to call. If a value is selected from the list, then the Namespace, Mode, SOAP Action and Request WS-Addressing Action fields are automatically updated to contain the appropriate values from the WSDL. |
Namespace |
The namespace URI that qualifies the operation name. This property field is automatically set if you select an operation in the Name field. |
Mode |
The operational mode:
If the operation is Output Only, then the Response tab is unavailable as there is no response. (Technically, there should be no faults either, but as some systems send faults anyway, the Fault tab is available). Note that the communication point must be running in Out->In mode to handle request-response messages. It can run in Output Only mode if it only handles Output Only messages. This property field is automatically set if you select an operation in the Name field. |
SOAP Action |
The value sent for the SOAPAction HTTP header in the SOAP request. Some Web services, particularly those using SOAP 1.1, use this HTTP header to determine which operation is being called. This is generally (but not always) not required when using WS-Addressing as the value of the This property field is automatically set if you select an operation in the Name field, and the operation defined a SOAP action. |
Request WS-Addressing Action |
The value of the This property field is automatically set if you select an operation in the Name field. |
Enable MTOM |
Select the checkbox to enable MTOM (W3C Message Transmission Optimization Mechanism), a method of efficiently sending binary data to and from web services. Refer to Configuring MTOM for details. |
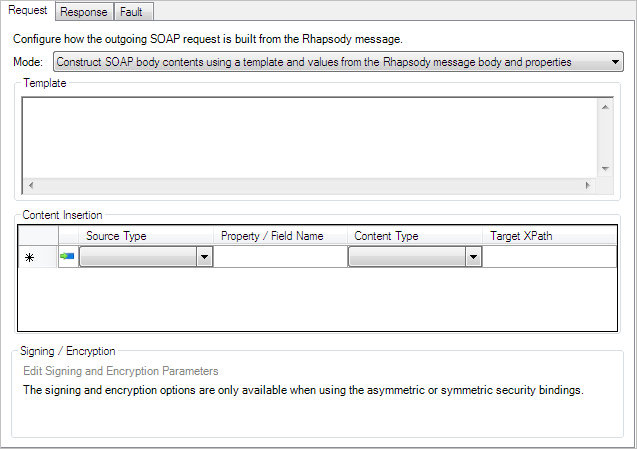
Generating the SOAP Request
The Request tab is used to configure how the SOAP requests are generated:
Property |
Description |
|---|---|
Mode |
Determines the mechanism used to generate the SOAP request. The available options are:
|
Template |
The XML template to use to build the contents of the SOAP body. The template must be valid XML and should declare namespaces appropriately. Where the WSDL includes valid type information, Rhapsody will generate default templates when an operation loaded from the WSDL is selected. This field is only available if the mode is |
Content Insertion |
Allows values to be inserted into the template that are retrieved from message properties, the entire message body or fields within the message.
This field is only available if the mode is |
JavaScript |
The JavaScript editor replaces the above controls when the
The SOAP request also exposes the following additional JavaScript objects:
|
Signing / Encryption |
Allows the signing and encryption options to be overridden for this request message. The default option is to inherit settings from the web service, but it can be changed to use customized settings. Refer to Signing and Encryption Parameters for details. Only available when using asymmetric or symmetric security binding. |
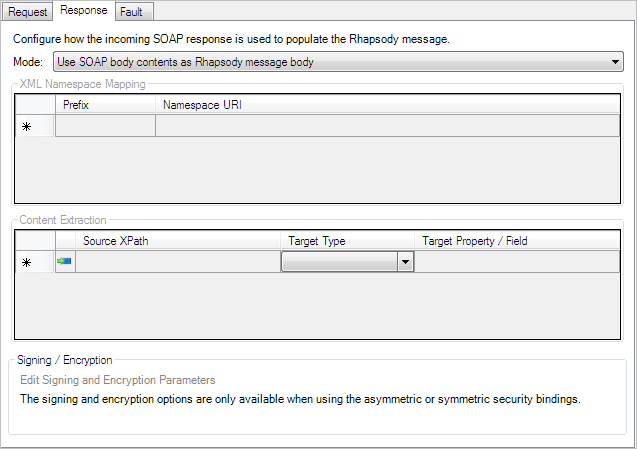
Processing the SOAP Response
The Response tab is used to configure the response message handling. This tab is unavailable if the operation is Output Only.
Property |
Description |
|---|---|
Mode |
Determines the mechanism used to process the SOAP response. The available options are:
|
XML Namespace Mapping |
Used to define namespace URI to XML prefixes that are used in the XPaths. This is required because Rhapsody cannot control what XML prefixes are used in the response messages (as they are generated by the external Web service) and they may not be consistent from message to message. By default, an entry is added to this table for the operation namespace (as this is the namespace most likely to be used). If not set, another entry is also added for the SOAP envelope namespace using a prefix of This property is only available when Mode is set to |
Content Extraction |
The values to be retrieved from the SOAP response. It is only available when Mode is set to
|
JavaScript |
A JavaScript editor is provided when the mode is
The SOAP response also exposes the following additional JavaScript objects:
|
Signing / Encryption |
Allows the signing and encryption options to be overridden for this request message. The default option is to inherit settings from the web service, but it can be changed to use customized settings. Refer to Signing and Encryption Parameters for details. Only available when using asymmetric or symmetric security binding. |
Responses are classified as valid by the communication point if they are non-fault SOAP responses, and returned using an HTTP status code of 200, 400, or 500.
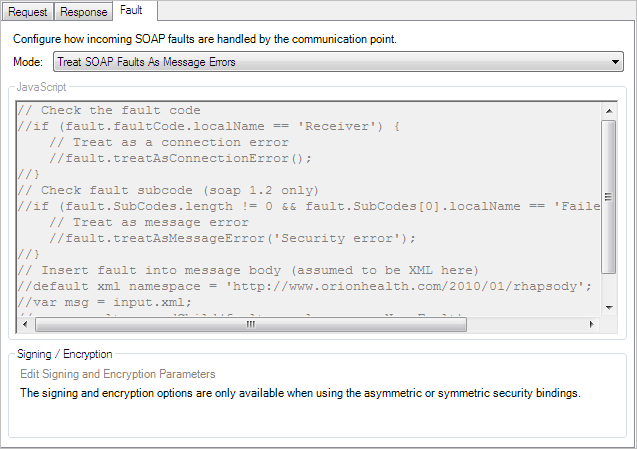
Handling SOAP Faults
The Fault tab provides several options to deal with SOAP faults received in response to a SOAP request.
Property |
Description |
|---|---|
Mode |
Determines how SOAP faults are treated by the communication point. The available options are:
|
JavaScript |
A JavaScript editor is provided if
The SOAP fault also exposes the following additional JavaScript objects:
The methods are as follows:
The following script excerpt illustrates how to process a fault response // Check the fault code
if (fault.faultCode.localName == "Receiver") {
// Fault in the web service - treat as a connection error so we retry
fault.treatAsConnectionError();
}
if (fault.faultSubCodes.length != 0 && fault.SubCodes[0].localName == "FailedAuthentication") {
// Authentication failed - treat as message error
fault.treatAsMessageError("Invalid security");
}
// Otherwise we insert the body of the fault into message (which is assumed to be XML)
default xml namespace = "http://www.orionhealth.com/2010/01/rhapsody";
var msg = new XML(output.text);
msg..result.appendChild(fault.envelope..soapNs::Fault);
output.text = msg;
|
When a SOAP response message is received representing a SOAP fault, the following message properties are populated on the Rhapsody Message:
rhapsody:SoapFaultis set to true.rhapsody:SoapFaultCodeis set to the local name of the SOAP fault code if present.rhapsody:SoapFaultSubCodeis set to the local name of the SOAP fault sub-code if present.
Not all errors that occur when calling a web service necessarily have a SOAP fault available. If a SOAP fault is available in the response and an HTTP status code of 200, 400, or 500 is received, then the configured fault processing action is used.
If an HTTP 4xx or 5xx error occurs but no SOAP fault is available in the response, then:
-
- The error is treated as a message error if the status code is a 401 (unauthorized) or 403 (forbidden) and if any of the following parameters are configured dynamically using message properties:
Endpoint URL,Username, orPassword; the error is treated as a connection error if none of those settings are configured dynamically using message properties. - The error is treated as a message error if the status code is neither 401 nor 403, or unavailable and if the Endpoint URL is configured dynamically using message properties. The error is treated as a connection error if the Endpoint URL is not configured dynamically.
- The error is treated as a message error if the status code is a 401 (unauthorized) or 403 (forbidden) and if any of the following parameters are configured dynamically using message properties:
Configuring MTOM
To configure the Web Service Client communication point to use MTOM to send elements as separate parts in a multi-part message, ensure:
- The
rhapsody:XopFieldsproperty list contains the XPath for each element that should be sent as a separate part. If the property list is not specified, only a single-part message is sent. - The
rhapsody:XopFieldsNamespacesproperty list is populated if the prefix used in the XPaths inrhapsody:XopFieldsis different than those used in the message.
For example, the following code excerpt specifies the XPaths in the XOP fields:
var next = output.append(input[0]);
next.addPropertyValue("rhapsody:XopFields", "//ns1:ProvideAndRegisterDocumentSetRequest/ns1:Document");
next.addPropertyValue("rhapsody:XopFields", "//ns1:ProvideAndRegisterDocumentSetRequest/lcm:SubmitObjectsRequest/rim:RegistryObjectList/rim:ExtrinsicObject/rim:Slot[1]/rim:ValueList/rim:Value");
next.addPropertyValue("rhapsody:XopFieldsNamespaces", "ns1=urn:ihe:iti:xds-b:2007");
If any specified element is empty or evaluates to a complex element, the Web Service Client communication throws an error.
Removing Operations
The Remove Operation button enables you to delete the selected operation after prompting you to confirm the action.