A web service definition contains the configuration information to host the web service, including its name and namespace, addressing information, the operations and types, and any security.
Rhapsody supports two methodologies for creating web services: top-down and bottom-up.
- The top-down approach uses an existing Web Services Description Language (WSDL). The WSDL is imported and is used to generate the web service configuration. You can then modify the configuration, and your changes will be reflected in the WSDL that is hosted by Rhapsody.
- The bottom-up approach does not require a WSDL. Instead, you create a new web service, and configure all the settings manually. We recommend this approach when exposing an existing Rhapsody route as a web service.
The Web Services Manager provides a central location for managing web services:
Viewing Web Services
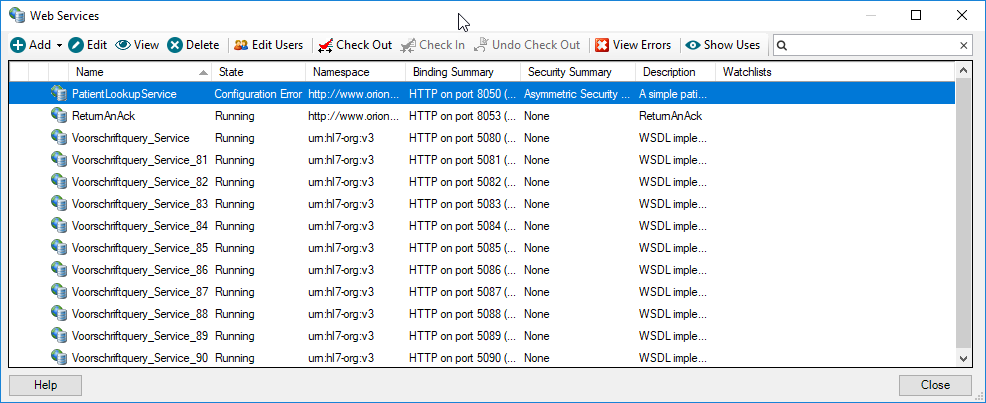
The Web Services Manager lists the web services hosted by Rhapsody:
The Web Services Manager displays the following information:
Column |
Description |
|---|---|
Name |
The name of the web service. |
State |
The current state of the web service:
|
Namespace |
The namespace URI of the web service. |
Binding Summary |
Whether HTTP or HTTPS is in use, the port, the local address bindings (if in use), and the SOAP bindings supported. |
Security Summary |
The security binding and authentication mechanism in use. |
Description |
A description of the web service. |
Watchlist |
The watchlist associated with the web service. |
Managing Web Services
The Web Services manager enables you to perform the following actions:
|
Action
|
Description
|
|---|---|
| Add | Add a web service using the Web Services Properties dialog. |
| Edit | Edit a selected web service using the Web Services Properties dialog. |
| View | View a web service using the Web Services Properties dialog in read-only mode. |
| Delete | Delete a selected web service. |
| Edit Users | Launch the Web Services User Store manager to manage users. Refer to Managing Web Service User Stores for details. |
| Check Out | Check out a selected web service. |
| Check In | Check in a selected web service using the Check-in dialog. Any mandatory or improperly configured fields trigger a warning before you can check in your changes. Refer to Checking In for details. |
| Undo Check Out | Undo the changes in a checked out web service. |
| Show Uses | Display the components a web service is being used in. |
| View Errors | Determine why any web service are unconfigured. |
| Filter | Perform text-based filtering to filter the list of displayed web services. |
Editing a Web Service
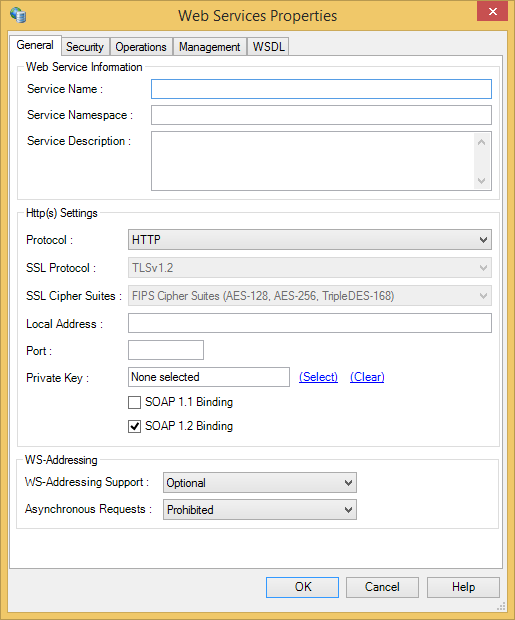
General Settings
Field |
Description |
|---|---|
Service Name |
Web service names must not conflict with the Rhapsody API Web service names (namely, |
Service Namespace |
Every web service needs a unique namespace in order for client applications to distinguish it from other services on the Web. The namespace is typically in the form of an internet URL for an owned domain. For example, you can use your company's Internet domain name as part of the namespace, The namespace need not point to the actual web service URL. |
Service Description |
Comments describing the web service. |
Protocol |
Options: It is strongly recommended that all web services be secured either using HTTPS or the symmetric or asymmetric security bindings. |
SSL Protocol |
The SSL Protocol that should be used. Disabled if connecting to an older Rhapsody engine that does not support this functionality. Newly created web service clients default to Refer to SSL Protocol Versions for details. |
SSL Cipher Suites |
Limits the SSL cipher suites that can be used, allowing a minimum encryption level to be set:
Disabled if connecting to an older Rhapsody engine that does not support this functionality. Refer to SSL Cipher Suites for details. |
Local Address |
The local binding for the HTTP(S) connector. If a value is not specified, it binds to all local addresses. The local address can be set using Rhapsody variables or literals. |
Port |
The local port for the HTTP(S) connector. The local port can be set using Rhapsody variables or literals. Multiple Web services can run on the same port if the settings on the HTTP(S) connector are compatible. |
Private Key |
Click the Select Private Key link to select an existing private key from the Certificate Manager. A private key is required if using HTTPS, or the asymmetric or symmetric security bindings. Only RSA SSL private keys are available for selection if using HTTP. |
SOAP 1.1 Binding |
Select this checkbox if the Web service applications use SOAP 1.1 binding. |
SOAP 1.2 Binding |
Select this checkbox if the Web service applications use SOAP 1.2 binding. |
WS-Addressing Support |
Whether WS-Addressing headers are permitted or mandatory:
WS-Addressing headers are converted into Rhapsody message properties to allow the user to provide conditional processing and routing.
|
Asynchronous Requests |
Whether Asynchronous Requests are permitted or mandatory:
This field is only available if you select |
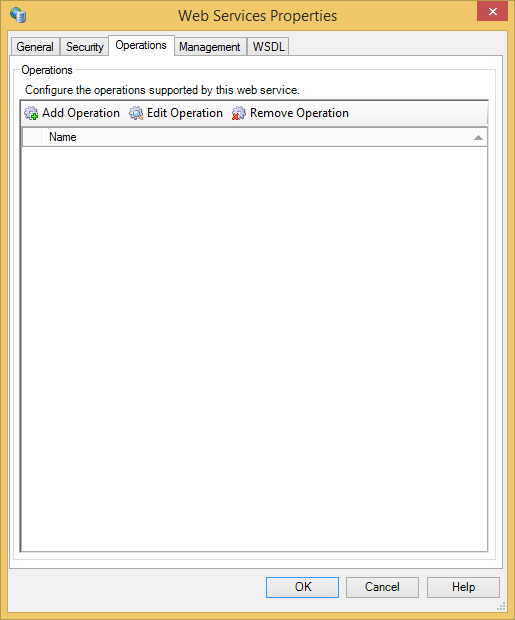
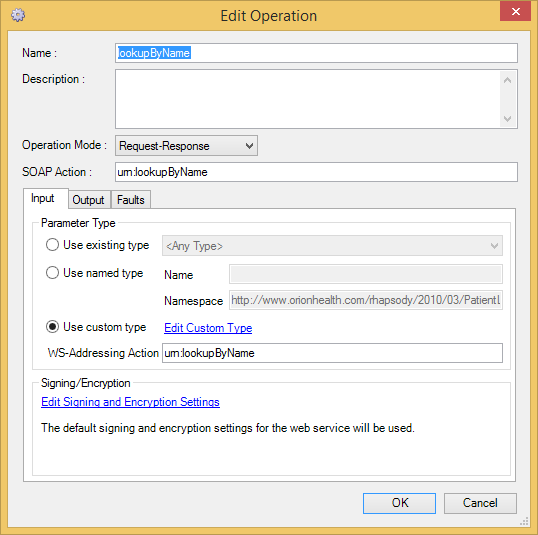
Operations
You can perform Add, Edit and Remove operations.
Each of the parameter types (Input, Output and Faults) have the same configuration options.
Field |
Description |
|---|---|
Name |
The (local) name of the operation to call. |
Description |
A description of the Web service operation. |
Operation Mode |
Options: If this is an Input Only operation, then the Output and Faults tabs are not available. If this is a Request-Response operation, then the Output parameters are required, but the Faults parameters are optional. The Input parameters are always required. |
SOAP Action |
The expected value in the SOAP Action HTTP header when this operation is called. If this is not set, an appropriate default value is used ( |
Use existing type |
Select from a list of standard XML types or any elements defined in the schema from an imported WSDL (if available), and two special values:
|
Use named type |
Select this option if the data type of the operation is defined in a schema related to this web service. The Name and Namespace reference the data type in the schema. |
Use custom type |
Simple data types can be created within the web service framework using a custom type. Click the Edit Custom Type link to create a new custom data type. Refer to Custom Types for details. |
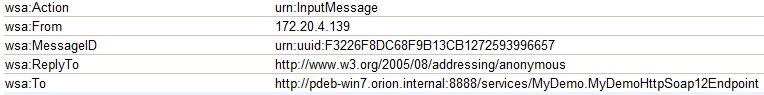
WS-Addressing Action |
The URI of the expected value in the |
Signing/Encryption |
Options to sign and encrypt message content. The messages are effectively always signed and encrypted when using transport security binding as it uses HTTPS. The signing and encryption options are very similar to those at the Web service level. However, each has a new value (which is the default) to use the settings defined at the Web service level. Note that as with the options at the Web service level, these options must be extended to allow the user to map between namespaces and prefixes.
Only available when using asymmetric or symmetric security binding. |
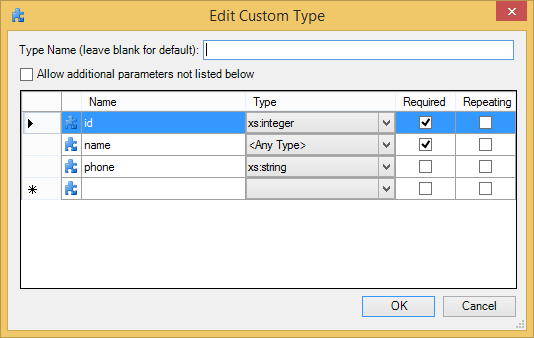
Custom Types
You can add any number of parameters and order them as required. It is perfectly valid to create a custom type with no parameters at all.
Field |
Description |
|---|---|
Allow additional parameters not listed below |
Allows the parameter to accept any other children that may be found by adding an |
Name |
A valid XML NCName. |
Type |
Select a type from the list. The available types are the standard XML types, types defined in the original WSDL used to generate the Web service (not available for bottom-up Web services), and two special values:
|
Required |
Whether required or optional. |
Repeating |
Whether repeating or not. |
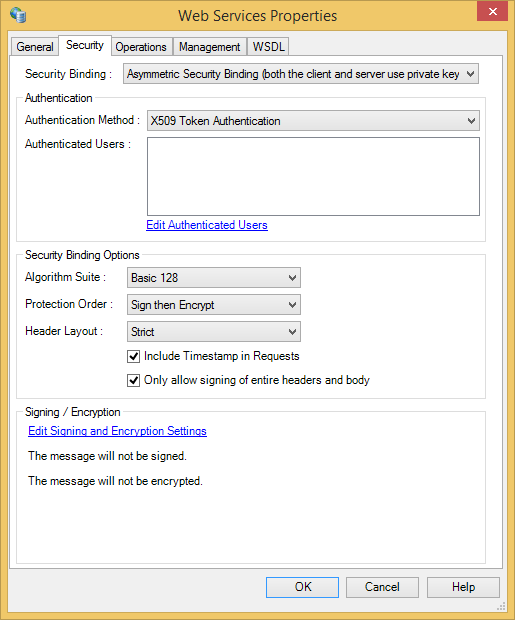
Security Settings
Field |
Description |
|---|---|
Security Binding |
Asymmetric and symmetric security bindings require a private key to be configured:
|
Authentication Method |
The authentication method:
It is strongly recommended that client authentication is enabled using one of the available methods. As Basic HTTP Authentication and Username Token Authentication can result in an effective plaintext password being sent, it is recommended that these methods only be used with HTTPS. |
Authenticated Users |
Displays the users in the Web Service User Store. Click the Edit Authenticated Users link to add or edit users, or edit the certificates associated with the users. This property is disabled if Authentication Method is set to |
Algorithm Suite |
Lists the available algorithm suites as defined in the WS-SecurityPolicy 1.1 specification (the default is It is only available when using asymmetric or symmetric binding. |
Protection Order |
Determines whether messages are signed first or encrypted first:
Only available when using asymmetric or symmetric security binding. |
Header Layout |
The header layout strictness:
|
Include Timestamp in Requests |
Determines whether a timestamp is included in the security header of the SOAP request. Only available when using transport, asymmetric or symmetric security binding (although it does not add anything when used with transport binding). By default, this checkbox is selected. |
Only allow signing of entire headers and body |
This checkbox is selected by default. It does not apply when using the transport security binding. |
Use Derived Keys |
Enables use of the |
| Encrypt Signatures | Encrypts the signature. Refer to Section 6.4 of the WS-SecurityPolicy 1.3 document for details. |
Signing / Encryption |
Options to sign and encrypt message content. The messages are effectively always signed and encrypted when using transport security binding as it uses HTTPS. Refer to Signing and Encryption Parameters for details. Only available when using asymmetric or symmetric security binding. |
| Use Endorsing Supporting Tokens | Enables Endorsing Supporting Tokens. Refer to Section 8.3 of the WS-SecurityPolicy 1.3 document for details. |
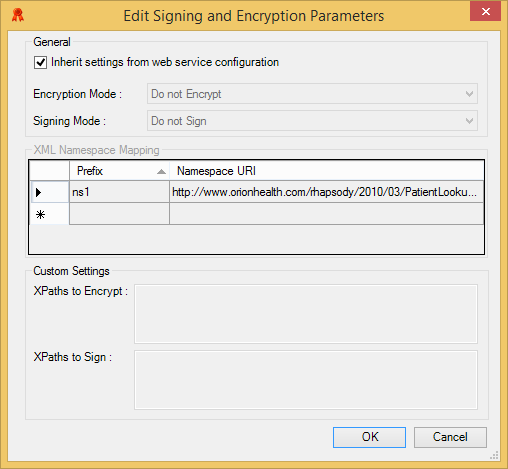
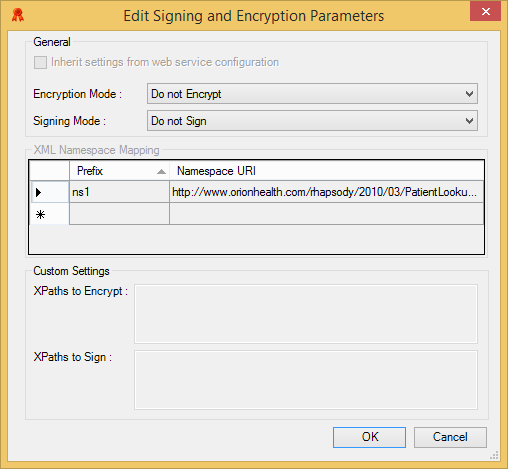
Signing and Encryption Parameters
Property |
Description |
|---|---|
Inherit settings from web service configuration |
Select this checkbox if you want to inherit the signing and encryption settings from the web service. |
Encryption Mode |
Determines whether the messages are encrypted:
|
Signing Mode |
Determines whether the messages are signed:
The |
XML Namespace Mapping |
Provides a mapping of XML prefixes to namespace URIs. It is used to declare namespace prefixes used in the XPaths that select the components to sign and encrypt. If this map is empty and one of the encryption or signing modes is changed to sign/encrypt parts of the message, then an entry is automatically added here for the service namespace (as that is the namespace that is likely to be used). Only available if either the encryption or signing mode indicates that parts of the message body will be encrypted or signed. |
XPaths to Encrypt |
A set of XPaths (one per line) identifying components in the message that should be encrypted. A value here does not mean that the message must include a value at that location. Rather, it means that if the value is present, it must be encrypted. |
XPaths to Sign |
A set of XPaths (one per line) identifying components in the message that should be signed. |
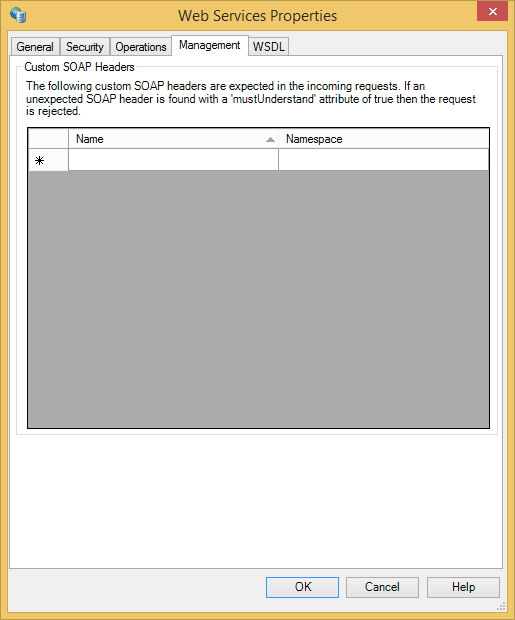
Management Settings
Field |
Description |
|---|---|
Custom SOAP Headers |
The custom SOAP headers that are expected in the incoming requests. Custom headers can be enforced by clients by setting the If you define any custom headers, then you are responsible for implementing support for them in the Rhapsody configuration. If you want to use a Rhapsody variable that contains XML to set the custom header, ensure you pre-escape the XML to avoid configuration errors. For example, use the following value in a Rhapsody variable:
Escaped XML
<urn:SessionHeader xmlns:urn="urn:enterprise.soap.sforce.com"><urn:sessionId>00D630000008yXI!A</urn:sessionId></urn:SessionHeader> instead of:
Unescaped XML
<urn:SessionHeader xmlns:urn="urn:enterprise.soap.sforce.com"<urn:sessionId>00D630000008yXI!A</urn:sessionId></urn:SessionHeader> |
Generating the WSDL
The WSDL tab enables you to view the WSDL that will be used for this Web service.
When a web service is generated from an existing WSDL, but existing WSDL has external references to other WSDLs or schemas using absolute paths (for example, http://<server>:<port>/path/to/schema.xsd), those external schemas need to be loaded whenever the web service is reconfigured (for example, startup, RLC load, etc.). Timeouts are applied to connect them. If they are no longer available due to invalid hostnames, for example, during Rhapsody startup or RLC loading, the connection or read timeouts are reported but Rhapsody continues to startup and RLC loading. The default timeout of 10 seconds is used and the value can be changed by setting WebServicesProducerService.wsdl.timeoutInSeconds property in rhapsody.properties file.
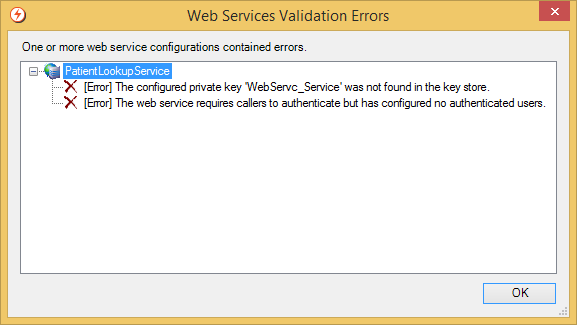
Selecting the Generate WSDL button sends the current configuration to the engine (without checking in any changes) and generates the WSDL for that configuration. The WSDL is then cached until any changes are made to the configuration. Any errors or warnings that are found when generating the WSDL are displayed as follows: