` to render as a byte array.
`Render.AsStreamBytes` is useful for Fable-based and other web app scenarios. Render to a byte array on the server, and transfer the bytes to the client using Fable Remoting. On the client use the `SaveFileAs` extension function to start a browser download. Make sure you have opened the `Fable.Remoting.Client` to get the `SaveFileAs` method of a byte array.
For a working example, see http://www.pushbuttonreceivetables.com/, in particular https://github.com/misterspeedy/HtmlExcel/blob/main/src/Server/Html.fs#L105.
#!fsharp
open FsExcel
[
Cell [ String "Hello world!" ]
]
|> Render.AsStreamBytes
|> fun bytes ->
$"Bytes length: {bytes.Length}"
#!markdown
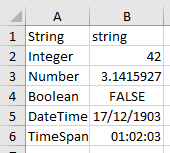
## Data Types
FsExcel supports the following data types for cell content:
- String
- Integer
- Float
- Boolean
- DateTime
- TimeSpan
#!fsharp
open System
open System.IO
open FsExcel
[
Cell [ String "String"]; Cell [ String "string" ]
Go NewRow
Cell [ String "Integer" ]; Cell [ Integer 42 ]
Go NewRow
Cell [ String "Number" ]; Cell [ Float Math.PI ]
Go NewRow
Cell [ String "Boolean" ]; Cell [ Boolean false ]
Go NewRow
Cell [ String "DateTime" ]; Cell [ DateTime (System.DateTime(1903, 12, 17)) ]
Go NewRow
Cell [ String "TimeSpan" ]
Cell [
TimeSpan (System.TimeSpan(hours=1, minutes=2, seconds=3))
FormatCode "hh:mm:ss"
]
]
|> Render.AsFile (Path.Combine(savePath, "DataTypes.xlsx"))
#!markdown
 #!markdown
## Rendering as HTML
You can render a workbook as a set of HTML tables. You will get one table per worksheet.
This feature is primarily for use in Dotnet Interactive Notebooks, where you can use the `HTML()` helper method to display the resulting HTML. This can be useful when experimenting with cell layouts, to avoid having to view an Excel file on every iteration.
The styling representation is approximate:
- Bold and italic font emphasis should show correctly. (Note that VS Code does not default to representing `
#!markdown
## Rendering as HTML
You can render a workbook as a set of HTML tables. You will get one table per worksheet.
This feature is primarily for use in Dotnet Interactive Notebooks, where you can use the `HTML()` helper method to display the resulting HTML. This can be useful when experimenting with cell layouts, to avoid having to view an Excel file on every iteration.
The styling representation is approximate:
- Bold and italic font emphasis should show correctly. (Note that VS Code does not default to representing `` items in bold)
- Underlining, where present, will always be be shown as a single underline.
- Cell borders, where present, will always be a single line. (Note that VS Code does not yet show borders on tables.)
- Font names, sizes, cell alignment and any kind of color are not currently supported.
The `AsHtml` function takes a function parameter which is called for every cell rendered, with a row and column index (both zero based, originating from the top-left-most occupied cell). When this function returns true, the cell is rendered as ` | `, otherwise it is rendered as ` | `.
#!fsharp
open System
open System.IO
open FsExcel
open ClosedXML.Excel
let isHeader r c =
r = 0 || c = 0
[
Worksheet "Worksheet 1"
Style [ FontEmphasis Bold ]
Cell [ String "Item" ]
Cell [ String "Example" ]
Style []
Go NewRow
Cell [ String "String"]
Cell [ String "string" ]
Go NewRow
Cell [ String "Integer" ]
Cell [ Integer 42 ]
Go NewRow
Cell [ String "Number" ]
Cell [ Float Math.PI ]
Go NewRow
Cell [ String "Boolean" ]
Cell [ Boolean false ]
Go NewRow
Cell [ String "DateTime" ]
Cell [ DateTime (System.DateTime(1903, 12, 17)) ]
Go NewRow
Cell [ String "TimeSpan" ]
Cell [
TimeSpan (System.TimeSpan(hours=1, minutes=2, seconds=3))
FormatCode "hh:mm:ss"
]
Go NewRow
Cell [ String "Bold" ]
Cell [
String "I am bold"
FontEmphasis Bold
]
Go NewRow
Cell [ String "Italic" ]
Cell [
String "I am Italic"
FontEmphasis Italic
]
Go NewRow
Cell [ String "Underlined" ]
Cell [
String "I am underlined"
FontEmphasis (Underline XLFontUnderlineValues.Single)
]
Go NewRow
Worksheet "Worksheet 2"
Cell [String "I am another table"]
]
|> Render.AsHtml isHeader
|> HTML
#!markdown
## AutoFilter
You can add filters to a WorkSheet.
* Enable Only: Enables but does not apply an AutoFilter.
* Apply filter: Enables and applies an AutoFilter.
* Clear filter: Clears an AutoFilter.
### AutoFilterRange
There can be multiple `AutoFilters` on a given worksheet. This means that the area to be filtered has to be specified when defining the filter. This is done with `AutoFilterRange`.
* `RangeUsed`: The entire range used in the worksheet.
* `CurrentRegion` of string: The current region around a spcified cell.
* `Range` of string: A specified range.
Examples:
```F#
AutoFilter [ EnableOnly RangeUsed ]
AutoFilter [ EnableOnly CurrentRegion ]
AutoFilter [ GreaterThanInt ("A1:E6", 2, 3) ]
```
### List of available filters
```F#
EnableOnly of AutoFilterRange
Clear of AutoFilterRange
EqualToString of range : AutoFilterRange * column : int * value : string
EqualToInt of range : AutoFilterRange * column : int * value : int
EqualToFloat of range : AutoFilterRange * column : int * value : float
EqualToDateTime of range : AutoFilterRange * column : int * value : DateTime
EqualToBool of range : AutoFilterRange * column : int * value : bool
NotEqualToString of range : AutoFilterRange * column : int * value : string
NotEqualToInt of range : AutoFilterRange * column : int * value : int
NotEqualToFloat of range : AutoFilterRange * column : int * value : float
NotEqualToDateTime of range : AutoFilterRange * column : int * value : DateTime
NotEqualToBool of range : AutoFilterRange * column : int * value : bool
BetweenInt of range : AutoFilterRange * column : int * min : int * max : int
BetweenFloat of range : AutoFilterRange * column : int * min : float * max : float
BetweenDateTime of range : AutoFilterRange * column : int * min : DateTime * max : DateTime
NotBetweenInt of range : AutoFilterRange * column : int * min : int * max : int
NotBetweenFloat of range : AutoFilterRange * column : int * min : float * max : float
NotBetweenDateTime of range : AutoFilterRange * column : int * min : DateTime * max : DateTime
ContainsString of range : AutoFilterRange * column : int * value : string
NotContainsString of range : AutoFilterRange * column : int * value : string
BeginsWithString of range : AutoFilterRange * column : int * value : string
NotBeginsWithString of range : AutoFilterRange * column : int * value : string
EndsWithString of range : AutoFilterRange * column : int * value : string
NotEndsWithString of range : AutoFilterRange * column : int * value : string
Top of range : AutoFilterRange * column : int * value : int * topType : XLTopBottomType
Bottom of range : AutoFilterRange * column : int * value : int * bottomType : XLTopBottomType
GreaterThanInt of range : AutoFilterRange * column : int * value : int
GreaterThanFloat of range : AutoFilterRange * column : int * value : float
GreaterThanDateTime of range : AutoFilterRange * column : int * value : DateTime
LessThanInt of range : AutoFilterRange * column : int * value : int
LessThanFloat of range : AutoFilterRange * column : int * value : float
LessThanDateTime of range : AutoFilterRange * column : int * value : DateTime
EqualOrGreaterThanInt of range : AutoFilterRange * column : int * value : int
EqualOrGreaterThanFloat of range : AutoFilterRange * column : int * value : float
EqualOrGreaterThanDateTime of range : AutoFilterRange * column : int * value : DateTime
EqualOrLessThanInt of range : AutoFilterRange * column : int * value : int
EqualOrLessThanFloat of range : AutoFilterRange * column : int * value : float
EqualOrLessThanDateTime of range : AutoFilterRange * column : int * value : DateTime
AboveAverage of range : AutoFilterRange * column : int
BelowAverage of range : AutoFilterRange * column : int
```
### Known Issues
EqualToDateTime:
> Works but, both Equals and Custom Filter are blank.
NotEqualToDateTime:
> Does not work. Does contains. Should be not contains.
BetweenDateTime
> Does not work. Excel filter shows 07/01/1900. Reapply hides all rows.
NotBetweenDateTime
> Works but, shows as a Custom filter with 07/01/1900 in Excel.
NotContains
> Works but, shows as a Contains filter in Excel. Reapply does Contains.
GreaterThanDateTime
> Works but, filter name is After and shows 07/01/1900.
LessThanDateTime
> Works but, filter name is Before and shows 07/01/1900.
EqualOrGreaterThanDateTime
> Works but, filter name is Custom Filter and shows 07/01/1900.
EqualOrLessThanDateTime
> Works but, filter name is Custom Filter and shows 07/01/1900.
Some of the above issues may be related to one of these:
* [Setting AutoFilter EqualTo on Date Column Doesn't Display Values When Spreadsheet Is Opened Until Filters Are Reapplied #701](https://github.com/ClosedXML/ClosedXML/issues/701)
* [Text to number coercion doesn't work correctly #1891](https://github.com/ClosedXML/ClosedXML/issues/1891)
#!markdown
### Enable Only
In the example below and `AutoFilter` is enabled for the `RangeUsed`, but no filter is applied.
#!fsharp
open System
open System.IO
open FsExcel
let headings =
[ Cell [ String "StringCol"; HorizontalAlignment Center ]
Cell [ String "IntCol"; HorizontalAlignment Center ]
Cell [ String "FloatCol"; HorizontalAlignment Center ]
Cell [ String "DateTimeCol"; HorizontalAlignment Center ]
Cell [ String "BooleanCol"; HorizontalAlignment Center ]
Go NewRow ]
let rows =
[ 1 .. 5 ]
|> Seq.map(fun i ->
[ Cell [ String $"String{i}" ]
Cell [ Integer i ]
Cell [ Float ((i |> float) + 0.1) ]
Cell [ DateTime (DateTime.Parse("15-July-2017 05:33:00").AddMinutes(i)) ]
Cell [ Boolean (i % 2 |> Convert.ToBoolean) ]
Go NewRow ])
|> Seq.collect id
|> List.ofSeq
headings @ rows @ [ AutoFit All; AutoFilter [ EnableOnly RangeUsed ] ]
|> Render.AsFile (Path.Combine(savePath, "AutoFilterEnableOnly.xlsx"))
#!markdown
 #!markdown
### Apply AutoFilter
In the example below `AutoFilter` is enabled (this is automatic if you create a filter).
The following compound filter is created:
* `RangeUsed`, column 2 is filtered for greater than 3
* and `RangeUsed`, column 5 is filtered to equal `true`
#!fsharp
open System
open System.IO
open FsExcel
let headings =
[ Cell [ String "StringCol"; HorizontalAlignment Center ]
Cell [ String "IntCol"; HorizontalAlignment Center ]
Cell [ String "FloatCol"; HorizontalAlignment Center ]
Cell [ String "DateTimeCol"; HorizontalAlignment Center ]
Cell [ String "BooleanCol"; HorizontalAlignment Center ]
Go NewRow ]
let rows =
[ 1 .. 5 ]
|> Seq.map(fun i ->
[ Cell [ String $"String{i}" ]
Cell [ Integer i ]
Cell [ Float ((i |> float) + 0.1) ]
Cell [ DateTime (DateTime.Parse("15-July-2017 05:33:00").AddMinutes(i)) ]
Cell [ Boolean (i % 2 |> Convert.ToBoolean) ]
Go NewRow ])
|> Seq.collect id
|> List.ofSeq
headings @ rows @ [ AutoFit All; AutoFilter [ GreaterThanInt (RangeUsed, 2, 3); EqualToBool (RangeUsed, 5, true) ] ]
|> Render.AsFile (Path.Combine(savePath, "AutoFilterCompound.xlsx"))
#!markdown
No AutoFilter:
#!markdown
### Apply AutoFilter
In the example below `AutoFilter` is enabled (this is automatic if you create a filter).
The following compound filter is created:
* `RangeUsed`, column 2 is filtered for greater than 3
* and `RangeUsed`, column 5 is filtered to equal `true`
#!fsharp
open System
open System.IO
open FsExcel
let headings =
[ Cell [ String "StringCol"; HorizontalAlignment Center ]
Cell [ String "IntCol"; HorizontalAlignment Center ]
Cell [ String "FloatCol"; HorizontalAlignment Center ]
Cell [ String "DateTimeCol"; HorizontalAlignment Center ]
Cell [ String "BooleanCol"; HorizontalAlignment Center ]
Go NewRow ]
let rows =
[ 1 .. 5 ]
|> Seq.map(fun i ->
[ Cell [ String $"String{i}" ]
Cell [ Integer i ]
Cell [ Float ((i |> float) + 0.1) ]
Cell [ DateTime (DateTime.Parse("15-July-2017 05:33:00").AddMinutes(i)) ]
Cell [ Boolean (i % 2 |> Convert.ToBoolean) ]
Go NewRow ])
|> Seq.collect id
|> List.ofSeq
headings @ rows @ [ AutoFit All; AutoFilter [ GreaterThanInt (RangeUsed, 2, 3); EqualToBool (RangeUsed, 5, true) ] ]
|> Render.AsFile (Path.Combine(savePath, "AutoFilterCompound.xlsx"))
#!markdown
No AutoFilter:
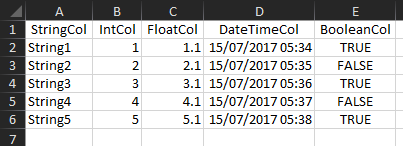 AutoFilter applied:
AutoFilter applied:
 #!markdown
## Freeze Panes
You can `Freeze Panes` for a WorkSheet.
* [Freeze Panes](#freeze-panes)
* [Freeze Top Row](#freeze-top-row)
* [Freeze First Column](#freeze-first-column)
* [Unfreeze Columns](#unfreeze-panes)
> Note: There is an issue with `Freeze Panes`. If it is disabled in Excel `Split` is left enabled. If you disable `Freeze Panes` in Excel, you will also have to disable `Split`.
> `ClosedXml` issue: [Distorted Header when Scrolling](https://github.com/ClosedXML/ClosedXML/issues/1681#issuecomment-1129045199)
### Freeze Panes
In the example below cell `B2` is selected. `Freeze Panes` is set to `Freeze Panes`.
#!fsharp
open System
open System.IO
open FsExcel
let headings =
[ Cell [ String "StringCol"; HorizontalAlignment Center ]
Cell [ String "IntCol"; HorizontalAlignment Center ]
Cell [ String "FloatCol"; HorizontalAlignment Center ]
Cell [ String "DateTimeCol"; HorizontalAlignment Center ]
Cell [ String "BooleanCol"; HorizontalAlignment Center ]
Go NewRow ]
let rows =
[ 1 .. 5 ]
|> Seq.map(fun i ->
[ Cell [ String $"String{i}" ]
Cell [ Integer i ]
Cell [ Float ((i |> float) + 0.1) ]
Cell [ DateTime (DateTime.Parse("15-July-2017 05:33:00").AddMinutes(i)) ]
Cell [ Boolean (i % 2 |> Convert.ToBoolean) ]
Go NewRow ])
|> Seq.collect id
|> List.ofSeq
headings @ rows @ [ AutoFit All; FreezePanes (Panes (1, 1)) ]
|> Render.AsFile (Path.Combine(savePath, "FreezePanes.xlsx"))
#!markdown
Cursor at `B2` > `Freeze Panes`:
#!markdown
## Freeze Panes
You can `Freeze Panes` for a WorkSheet.
* [Freeze Panes](#freeze-panes)
* [Freeze Top Row](#freeze-top-row)
* [Freeze First Column](#freeze-first-column)
* [Unfreeze Columns](#unfreeze-panes)
> Note: There is an issue with `Freeze Panes`. If it is disabled in Excel `Split` is left enabled. If you disable `Freeze Panes` in Excel, you will also have to disable `Split`.
> `ClosedXml` issue: [Distorted Header when Scrolling](https://github.com/ClosedXML/ClosedXML/issues/1681#issuecomment-1129045199)
### Freeze Panes
In the example below cell `B2` is selected. `Freeze Panes` is set to `Freeze Panes`.
#!fsharp
open System
open System.IO
open FsExcel
let headings =
[ Cell [ String "StringCol"; HorizontalAlignment Center ]
Cell [ String "IntCol"; HorizontalAlignment Center ]
Cell [ String "FloatCol"; HorizontalAlignment Center ]
Cell [ String "DateTimeCol"; HorizontalAlignment Center ]
Cell [ String "BooleanCol"; HorizontalAlignment Center ]
Go NewRow ]
let rows =
[ 1 .. 5 ]
|> Seq.map(fun i ->
[ Cell [ String $"String{i}" ]
Cell [ Integer i ]
Cell [ Float ((i |> float) + 0.1) ]
Cell [ DateTime (DateTime.Parse("15-July-2017 05:33:00").AddMinutes(i)) ]
Cell [ Boolean (i % 2 |> Convert.ToBoolean) ]
Go NewRow ])
|> Seq.collect id
|> List.ofSeq
headings @ rows @ [ AutoFit All; FreezePanes (Panes (1, 1)) ]
|> Render.AsFile (Path.Combine(savePath, "FreezePanes.xlsx"))
#!markdown
Cursor at `B2` > `Freeze Panes`:
 ### Freeze Top Row
In the example below `Freeze Panes` is set to `Freeze Top Row`.
#!fsharp
open System
open System.IO
open FsExcel
let headings =
[ Cell [ String "StringCol"; HorizontalAlignment Center ]
Cell [ String "IntCol"; HorizontalAlignment Center ]
Cell [ String "FloatCol"; HorizontalAlignment Center ]
Cell [ String "DateTimeCol"; HorizontalAlignment Center ]
Cell [ String "BooleanCol"; HorizontalAlignment Center ]
Go NewRow ]
let rows =
[ 1 .. 5 ]
|> Seq.map(fun i ->
[ Cell [ String $"String{i}" ]
Cell [ Integer i ]
Cell [ Float ((i |> float) + 0.1) ]
Cell [ DateTime (DateTime.Parse("15-July-2017 05:33:00").AddMinutes(i)) ]
Cell [ Boolean (i % 2 |> Convert.ToBoolean) ]
Go NewRow ])
|> Seq.collect id
|> List.ofSeq
headings @ rows @ [ AutoFit All; FreezePanes TopRow ]
|> Render.AsFile (Path.Combine(savePath, "FreezePanesTopRow.xlsx"))
#!markdown
`Freeze Panes` > `Freeze Top Row`:
### Freeze Top Row
In the example below `Freeze Panes` is set to `Freeze Top Row`.
#!fsharp
open System
open System.IO
open FsExcel
let headings =
[ Cell [ String "StringCol"; HorizontalAlignment Center ]
Cell [ String "IntCol"; HorizontalAlignment Center ]
Cell [ String "FloatCol"; HorizontalAlignment Center ]
Cell [ String "DateTimeCol"; HorizontalAlignment Center ]
Cell [ String "BooleanCol"; HorizontalAlignment Center ]
Go NewRow ]
let rows =
[ 1 .. 5 ]
|> Seq.map(fun i ->
[ Cell [ String $"String{i}" ]
Cell [ Integer i ]
Cell [ Float ((i |> float) + 0.1) ]
Cell [ DateTime (DateTime.Parse("15-July-2017 05:33:00").AddMinutes(i)) ]
Cell [ Boolean (i % 2 |> Convert.ToBoolean) ]
Go NewRow ])
|> Seq.collect id
|> List.ofSeq
headings @ rows @ [ AutoFit All; FreezePanes TopRow ]
|> Render.AsFile (Path.Combine(savePath, "FreezePanesTopRow.xlsx"))
#!markdown
`Freeze Panes` > `Freeze Top Row`:
 ### Freeze First Column
In the example below `Freeze Panes` is set to `Freeze First Column`.
#!fsharp
open System
open System.IO
open FsExcel
let headings =
[ Cell [ String "StringCol"; HorizontalAlignment Center ]
Cell [ String "IntCol"; HorizontalAlignment Center ]
Cell [ String "FloatCol"; HorizontalAlignment Center ]
Cell [ String "DateTimeCol"; HorizontalAlignment Center ]
Cell [ String "BooleanCol"; HorizontalAlignment Center ]
Go NewRow ]
let rows =
[ 1 .. 5 ]
|> Seq.map(fun i ->
[ Cell [ String $"String{i}" ]
Cell [ Integer i ]
Cell [ Float ((i |> float) + 0.1) ]
Cell [ DateTime (DateTime.Parse("15-July-2017 05:33:00").AddMinutes(i)) ]
Cell [ Boolean (i % 2 |> Convert.ToBoolean) ]
Go NewRow ])
|> Seq.collect id
|> List.ofSeq
headings @ rows @ [ AutoFit All; FreezePanes FirstColumn ]
|> Render.AsFile (Path.Combine(savePath, "FreezePanesFirstColumn.xlsx"))
#!markdown
`Freeze Panes` > `Freeze First Column`:
### Freeze First Column
In the example below `Freeze Panes` is set to `Freeze First Column`.
#!fsharp
open System
open System.IO
open FsExcel
let headings =
[ Cell [ String "StringCol"; HorizontalAlignment Center ]
Cell [ String "IntCol"; HorizontalAlignment Center ]
Cell [ String "FloatCol"; HorizontalAlignment Center ]
Cell [ String "DateTimeCol"; HorizontalAlignment Center ]
Cell [ String "BooleanCol"; HorizontalAlignment Center ]
Go NewRow ]
let rows =
[ 1 .. 5 ]
|> Seq.map(fun i ->
[ Cell [ String $"String{i}" ]
Cell [ Integer i ]
Cell [ Float ((i |> float) + 0.1) ]
Cell [ DateTime (DateTime.Parse("15-July-2017 05:33:00").AddMinutes(i)) ]
Cell [ Boolean (i % 2 |> Convert.ToBoolean) ]
Go NewRow ])
|> Seq.collect id
|> List.ofSeq
headings @ rows @ [ AutoFit All; FreezePanes FirstColumn ]
|> Render.AsFile (Path.Combine(savePath, "FreezePanesFirstColumn.xlsx"))
#!markdown
`Freeze Panes` > `Freeze First Column`:
 ### Unfreeze Panes
In the example below `Freeze Panes` is set to `Unfreeze Panes`.
> Not that in the code below I first `Freeze Panes` prior to unfreezing them. This is for demonstration purposes only.
#!fsharp
open System
open System.IO
open FsExcel
let headings =
[ Cell [ String "StringCol"; HorizontalAlignment Center ]
Cell [ String "IntCol"; HorizontalAlignment Center ]
Cell [ String "FloatCol"; HorizontalAlignment Center ]
Cell [ String "DateTimeCol"; HorizontalAlignment Center ]
Cell [ String "BooleanCol"; HorizontalAlignment Center ]
Go NewRow ]
let rows =
[ 1 .. 5 ]
|> Seq.map(fun i ->
[ Cell [ String $"String{i}" ]
Cell [ Integer i ]
Cell [ Float ((i |> float) + 0.1) ]
Cell [ DateTime (DateTime.Parse("15-July-2017 05:33:00").AddMinutes(i)) ]
Cell [ Boolean (i % 2 |> Convert.ToBoolean) ]
Go NewRow ])
|> Seq.collect id
|> List.ofSeq
headings @ rows @ [ AutoFit All; FreezePanes TopRow; FreezePanes UnfreezePanes ]
|> Render.AsFile (Path.Combine(savePath, "FreezePanesUnfreezePanes.xlsx"))
#!markdown
`Freeze Panes` > `Unfreeze Panes`:
### Unfreeze Panes
In the example below `Freeze Panes` is set to `Unfreeze Panes`.
> Not that in the code below I first `Freeze Panes` prior to unfreezing them. This is for demonstration purposes only.
#!fsharp
open System
open System.IO
open FsExcel
let headings =
[ Cell [ String "StringCol"; HorizontalAlignment Center ]
Cell [ String "IntCol"; HorizontalAlignment Center ]
Cell [ String "FloatCol"; HorizontalAlignment Center ]
Cell [ String "DateTimeCol"; HorizontalAlignment Center ]
Cell [ String "BooleanCol"; HorizontalAlignment Center ]
Go NewRow ]
let rows =
[ 1 .. 5 ]
|> Seq.map(fun i ->
[ Cell [ String $"String{i}" ]
Cell [ Integer i ]
Cell [ Float ((i |> float) + 0.1) ]
Cell [ DateTime (DateTime.Parse("15-July-2017 05:33:00").AddMinutes(i)) ]
Cell [ Boolean (i % 2 |> Convert.ToBoolean) ]
Go NewRow ])
|> Seq.collect id
|> List.ofSeq
headings @ rows @ [ AutoFit All; FreezePanes TopRow; FreezePanes UnfreezePanes ]
|> Render.AsFile (Path.Combine(savePath, "FreezePanesUnfreezePanes.xlsx"))
#!markdown
`Freeze Panes` > `Unfreeze Panes`:
 #!markdown
## Excel Tables
To create [Excel Tables](https://support.microsoft.com/en-us/office/overview-of-excel-tables-7ab0bb7d-3a9e-4b56-a3c9-6c94334e492c), see the separate [Excel Table Tutorial](https://github.com/misterspeedy/FsExcel/blob/main/ExcelTableTutorial.md).
#!markdown
## Excel Tables
To create [Excel Tables](https://support.microsoft.com/en-us/office/overview-of-excel-tables-7ab0bb7d-3a9e-4b56-a3c9-6c94334e492c), see the separate [Excel Table Tutorial](https://github.com/misterspeedy/FsExcel/blob/main/ExcelTableTutorial.md).
|  [](https://twitter.com/fsexcel)
[](https://www.nuget.org/packages/FsExcel/)
## Welcome!
Welcome to FsExcel, a library for generating Excel spreadsheets using very simple code.
FsExcel is based on [ClosedXML](https://github.com/ClosedXML/ClosedXML) but abstracts away many of the complications of building spreadsheets cell by cell.
This tutorial is also available as an interactive notebook. Download it, open in Visual Studio Code, and start generating spreadsheets for real!
* *Contributors* - please see [Contributing.md](/Contributing.md) for getting-started information.
* *Usage example* - for an example of FsExcel in action, see http://www.pushbuttonreceivetables.com. Source code on [GitHub](https://github.com/misterspeedy/HtmlExcel).
#!markdown
## Hello World
Here's the complete code to generate a spreadsheet with a single cell containing a string.
Run this and you should find a spreadsheet called `HelloWorld.xlsx` in your `/temp` folder. (Change the path to suit.)
#!fsharp
// For scripts only; for programs, use NuGet to install FsExcel:
#r "nuget: FsExcel"
let savePath = "/temp"
open System.IO
open FsExcel
[
Cell [ String "Hello world!" ]
]
|> Render.AsFile (Path.Combine(savePath, "HelloWorld.xlsx"))
#!markdown
[](https://twitter.com/fsexcel)
[](https://www.nuget.org/packages/FsExcel/)
## Welcome!
Welcome to FsExcel, a library for generating Excel spreadsheets using very simple code.
FsExcel is based on [ClosedXML](https://github.com/ClosedXML/ClosedXML) but abstracts away many of the complications of building spreadsheets cell by cell.
This tutorial is also available as an interactive notebook. Download it, open in Visual Studio Code, and start generating spreadsheets for real!
* *Contributors* - please see [Contributing.md](/Contributing.md) for getting-started information.
* *Usage example* - for an example of FsExcel in action, see http://www.pushbuttonreceivetables.com. Source code on [GitHub](https://github.com/misterspeedy/HtmlExcel).
#!markdown
## Hello World
Here's the complete code to generate a spreadsheet with a single cell containing a string.
Run this and you should find a spreadsheet called `HelloWorld.xlsx` in your `/temp` folder. (Change the path to suit.)
#!fsharp
// For scripts only; for programs, use NuGet to install FsExcel:
#r "nuget: FsExcel"
let savePath = "/temp"
open System.IO
open FsExcel
[
Cell [ String "Hello world!" ]
]
|> Render.AsFile (Path.Combine(savePath, "HelloWorld.xlsx"))
#!markdown