https://www.cnblogs.com/grandyang/p/6007336.html
題目:
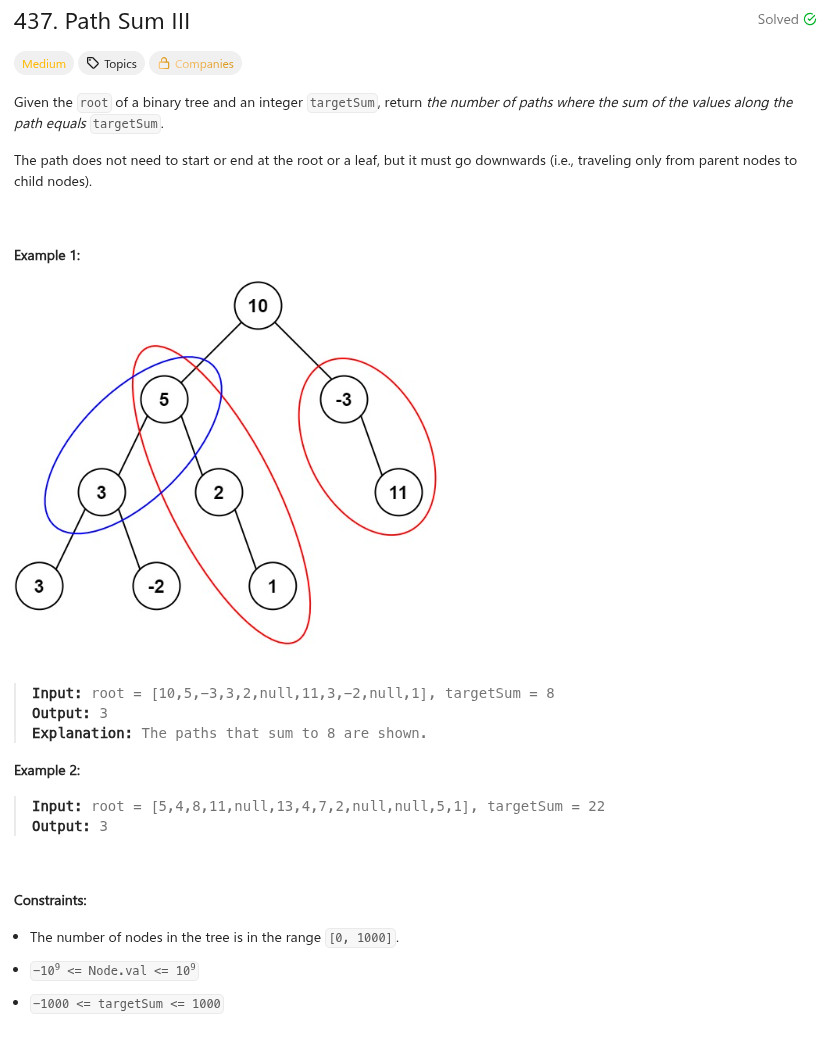
解答:
參考資訊:
https://www.cnblogs.com/grandyang/p/6007336.html
題目:

解答:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* struct TreeNode *left;
* struct TreeNode *right;
* };
*/
int dfs(struct TreeNode *n, int targetSum, long curSum, int *buf, int *pos, int *r)
{
int i = 0;
long tmp = 0;
if (!n) {
return -1;
}
curSum += n->val;
if (curSum == targetSum) {
(*r) += 1;
}
tmp = curSum;
buf[*pos] = n->val;
for (i = 0; i < *pos; i++) {
tmp -= buf[i];
if (tmp == targetSum) {
(*r) += 1;
}
}
(*pos) += 1;
dfs(n->left, targetSum, curSum, buf, pos, r);
dfs(n->right, targetSum, curSum, buf, pos, r);
(*pos) -= 1;
return 0;
}
int pathSum(struct TreeNode* root, int targetSum)
{
int r = 0;
int pos = 0;
int buf[1001] = { 0 };
dfs(root, targetSum, 0, buf, &pos, &r);
return r;
}