Examples > Control Structures
For Loop (aka The Knight Rider)
A for loop is a section of code that repeat until a conditional is met. Usually this is based on a counter that you define in a code. For example, run this code as long as the counter is under 100 and each time through the loop increment the counter by one. If we intialize the counter to zero in the beginning, then the loop will run through 100 iterations of the code before exiting the loop and continuing on with the rest of program.
Hardware Required
- MSP430 LaunchPad
- (9) 220 ohm resistors
- (9) LEDs
- hook-up wire
- breadboard
Relevant Groundwork
Often you want to iterate over a series of pins and do something to each one. For instance, this example blinks 9 LEDs attached the LaunchPad by using a for() loop to cycle back and forth through digital pins 2-10. The LEDS are turned on and off, in sequence, by using both the digitalWrite() and delay() functions .
We also call this example "Knight Rider" in memory of a TV-series from the 80's where David Hasselhoff had an AI machine named KITT driving his Pontiac. The car had been augmented with plenty of LEDs in all possible sizes performing flashy effects. In particular, it had a display that scanned back and forth across a line. This example duplicates the KITT display.
Circuit
Connect nice LEDS, with 220 ohm resistors in series, to digital pins 2-10 on your LaunchPad.
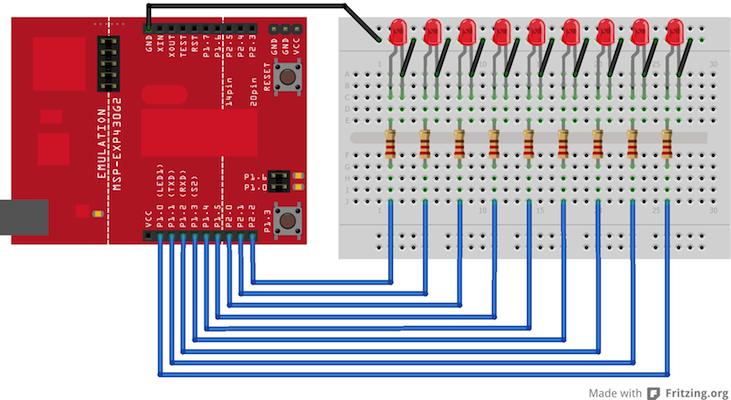
image developed using Fritzing. For more circuit examples, see the Fritzing project page
Schematic:
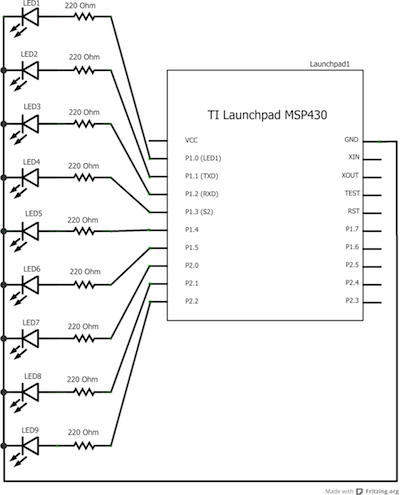
Code Explanation
The code below begins by utilizing a for() loop to assign digital pins 2-10 as outputs for the 9 LEDs used.
In the main loop of the code, two for() loops are used to loop incrementally, stepping through the LEDs, one by one, from pin 2 to pin 10. Once pin 10 is lit, the process reverses, stepping back down through each LED.
Code
/*
For Loop Iteration
Demonstrates the use of a for() loop.
Lights multiple LEDs in sequence, then in reverse.
The circuit:
* LEDs from pins 2 through 10 to ground
created 2006
by David A. Mellis
modified 16 Apr 2011
by Adrian Fernandez
This example code is in the public domain.
*/
int timer = 100; // The higher the number, the slower the timing.
void setup() {
// use a for loop to initialize each pin as an output:
for (int thisPin = 2; thisPin < 11; thisPin++) {
pinMode(thisPin, OUTPUT);
}
}
void loop() {
// loop from the lowest pin to the highest:
for (int thisPin = 2; thisPin < 11; thisPin++) {
// turn the pin on:
digitalWrite(thisPin, HIGH);
delay(timer);
// turn the pin off:
digitalWrite(thisPin, LOW);
}
// loop from the highest pin to the lowest:
for (int thisPin = 10; thisPin >= 2; thisPin--) {
// turn the pin on:
digitalWrite(thisPin, HIGH);
delay(timer);
// turn the pin off:
digitalWrite(thisPin, LOW);
}
}
See Also:
- for()
- digitalWrite()
- delay()
- WhileLoop - Use a While Loop to calibrate a sensor while a button is being pressed.
- SwitchCase - Choose between a number of discrete values in a manner that is the equivalent of using multiples If statements. This example shows how to divide a sensor's range into a set of four bands and to take four different actions depending on which band the result is in.
- Array: a variation on the For Loop example that demonstrates how to use an array.
Corrections, suggestions, and new documentation should be posted to the Forum.
The text of the Energia reference is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 License. Energia reference is based on the Arduino reference. Code samples in the reference are released into the public domain.