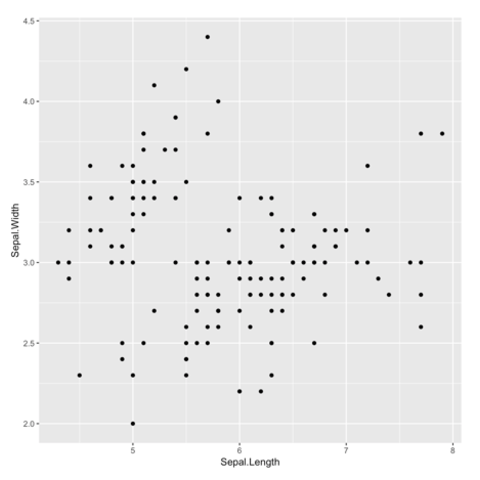
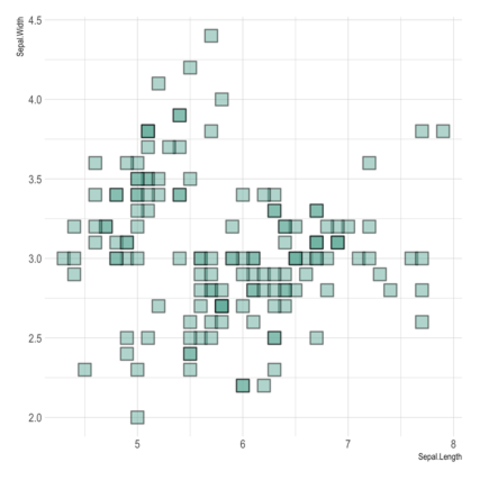
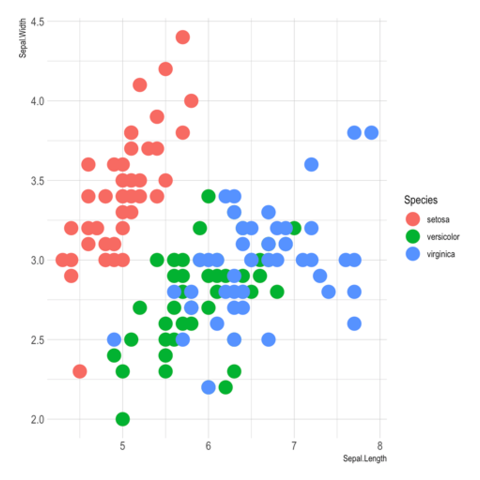
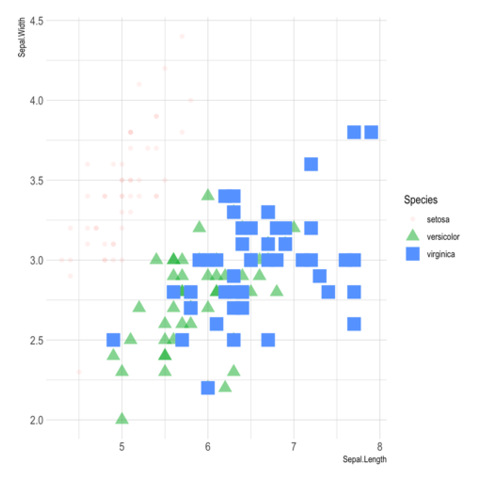
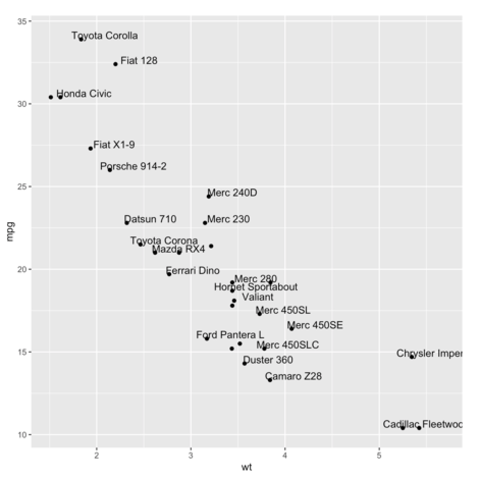
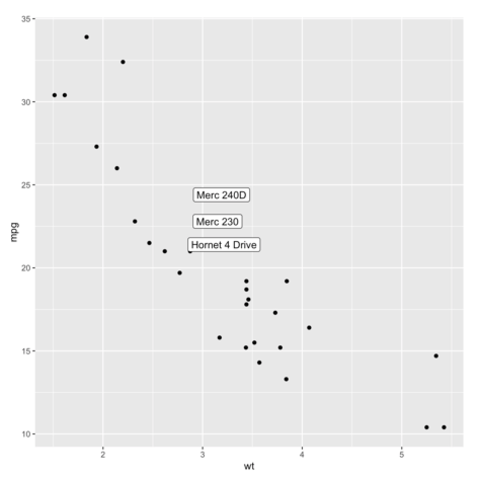
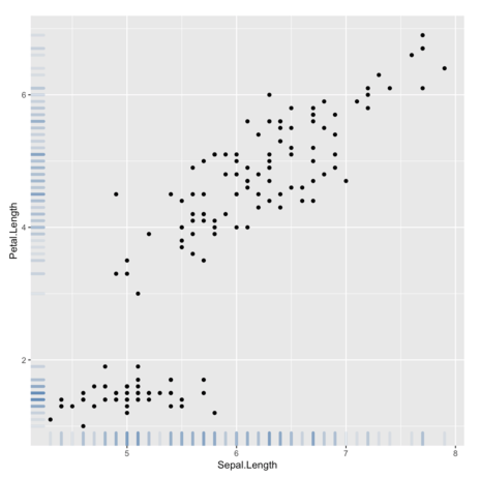
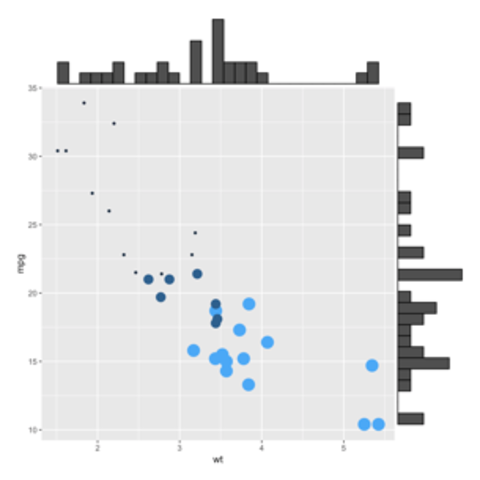
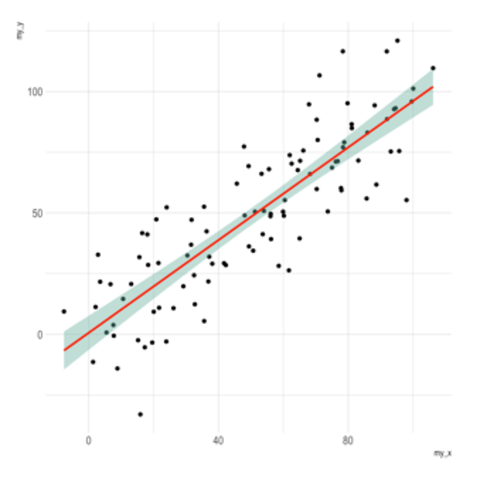
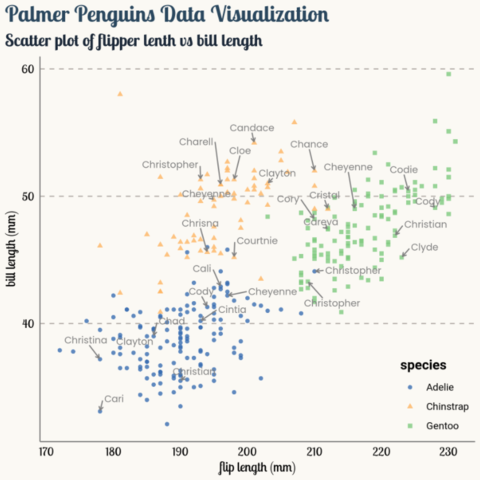
ggplot2 packageScatterplots are built with ggplot2 thanks to the geom_point() function. Discover a basic use case in graph #272, and learn how to custom it with next examples below.
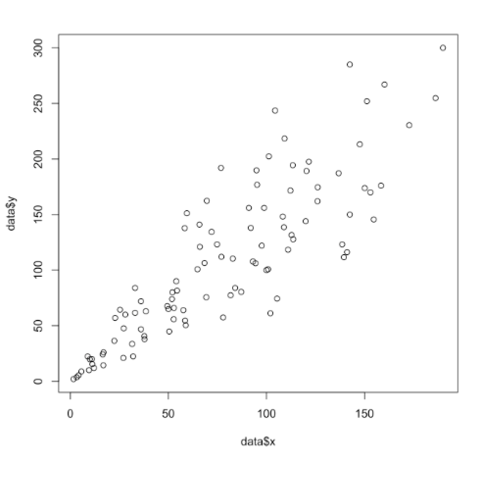
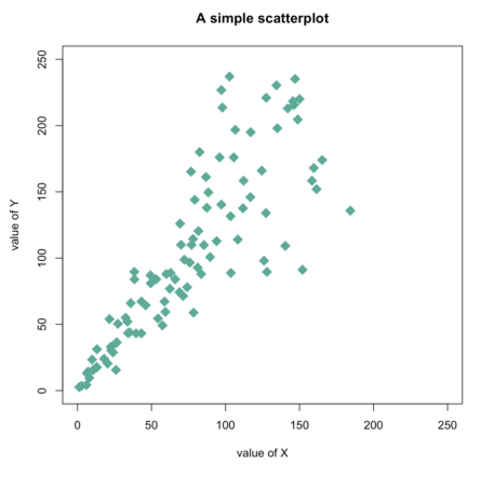
Base R is also a good option to build a scatterplot, using the plot() function. The chart #13 below will guide you through its basic usage. Following examples allow a greater level of customization.
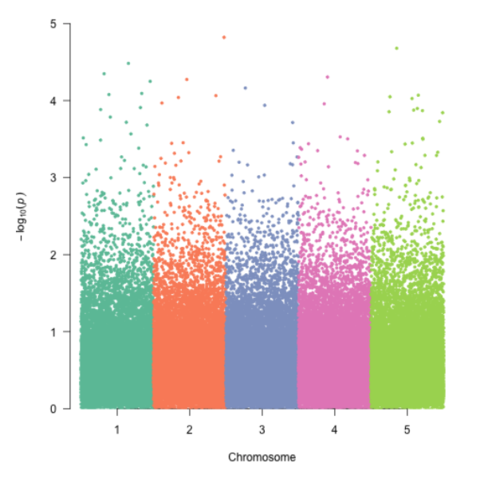
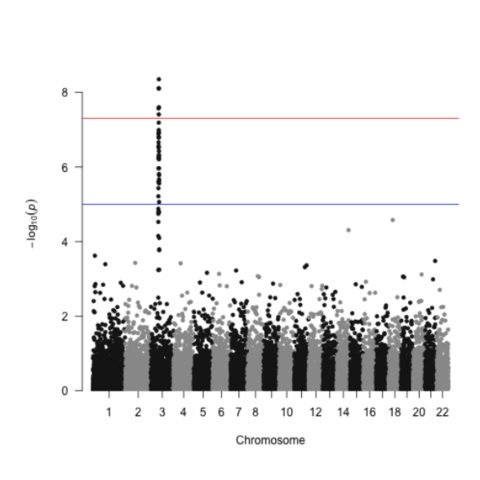
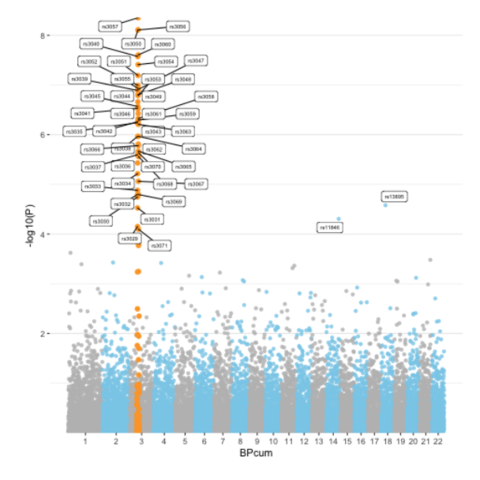
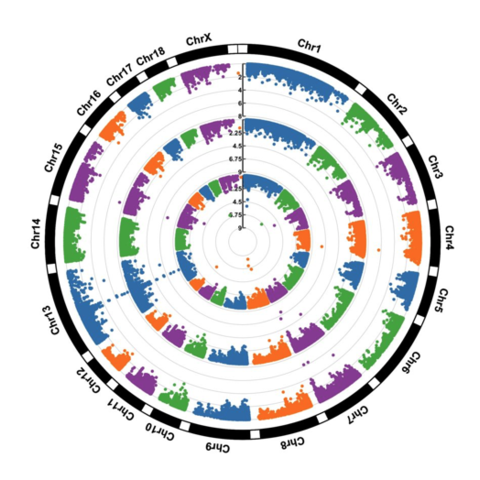
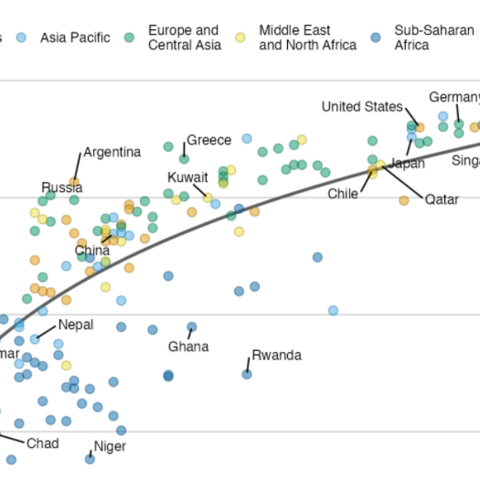
A Manhattan plot is a particular type of scatterplot used in genomics. The X axis displays the position of a genetic variant on the genome. Each chromosome is usually represented using a different color. The Y axis shows p-value of the association test with a phenotypic trait.