Introduction
Basic rules to strictly-equal-to comparisons:
- The number of operands on the right-hand-side is always 1. No risk of hijacking parameters.
- Contents are compared strictly, i.e. data type and contents must match perfectly. No wildcards are supported here.
- Comparing values of different types, e.g. numerals with strings, will always be unequal.
- When comparing sets, the same elements in both left and right hand side must exist, and they need to be in the same order.
- Comparing two void values will always return true.
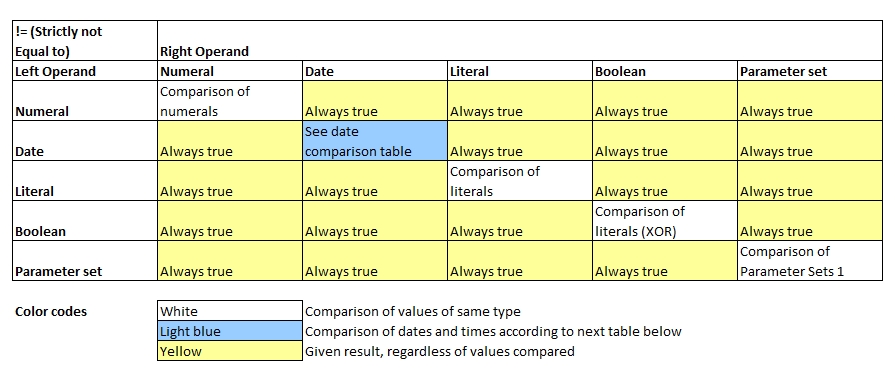
1 Contents in both sets must be the same and in the same ordering E.g. {1,2,3} = {3,2,1} returns false.
echo("Basic comparisons:");
a[0] = 3 != 3; // false
a[1] = 5.1 != 5; // true
a[2] = {1,2,3} != {3,2,1}; // true
a[3] = {1,2,3} != {1,2,3}; // false
for all variables( a[], x[] ) echo( x[] );
echo("String with other types always return false:");
b[0] = 123 != "123"; // true
b[1] = '123' != 123; // true
b[2] = false != 'false'; // true
b[3] = date("2020-08-01") != "2020-08-01"; // true
for all variables( b[], x[] ) echo( x[] );Basic comparisons:
false
true
true
false
String with other types always return false:
true
true
true
true
Comparing Dates
Note that value of type date may assume 4 states: date only, time only, date and time combined and blank date (no value). Even for the same operator,
the rules of calculating dates and numeric operands differ.
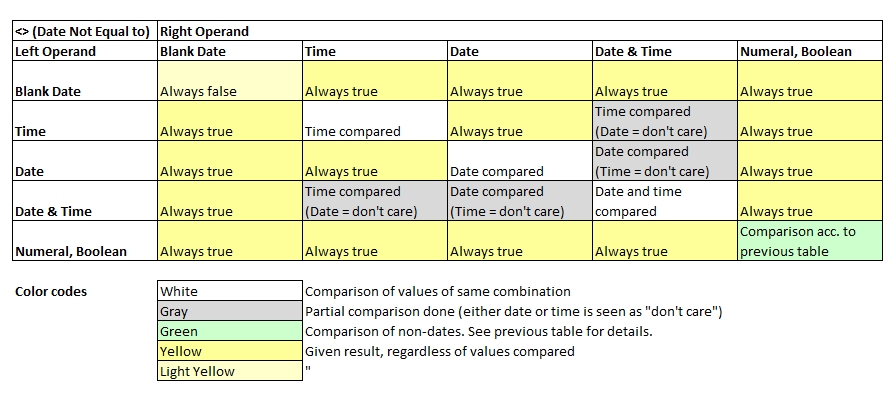
Note that in some cases, only the time or only the dates are compared.
d [] = date('2020-07-14');
dt[] = date('2020-07-14 12:30:00');
t [] = date('12:30:00');
o [] = date(''); // blank date
dz[] = date('2020-07-14 12:30:01');
a[0] = d[] != dt[]; // true (one contains time, the other not)
a[1] = t[] != dt[]; // true (one contains date, the other not)
a[2] = d[] != date("2020-07-15") - 1; // false
a[3] = dt[] != dz[]; // true (time differs)
for all variables( a[], b[] ) echo( b[] );
true
true
false
true
