Analytics APIs
Adobe Analytics access is supplied via Randy Zwitch’s RSiteCatalyst library.
Authentication is a little harder to configure for Adobe so a live example is not shown here, but steps to download data are shown below.
Installation
## This installs a package for downloading Adobe Analytics data
if(!require(RSiteCatalyst)) install.packages("RSiteCatalyst")Authentication (New)
This is the new OAuth2 method of authentication. Use this one if you can.
Link your Adobe Analytics login to the Adobe ID account to use this method of signin.
Create Application
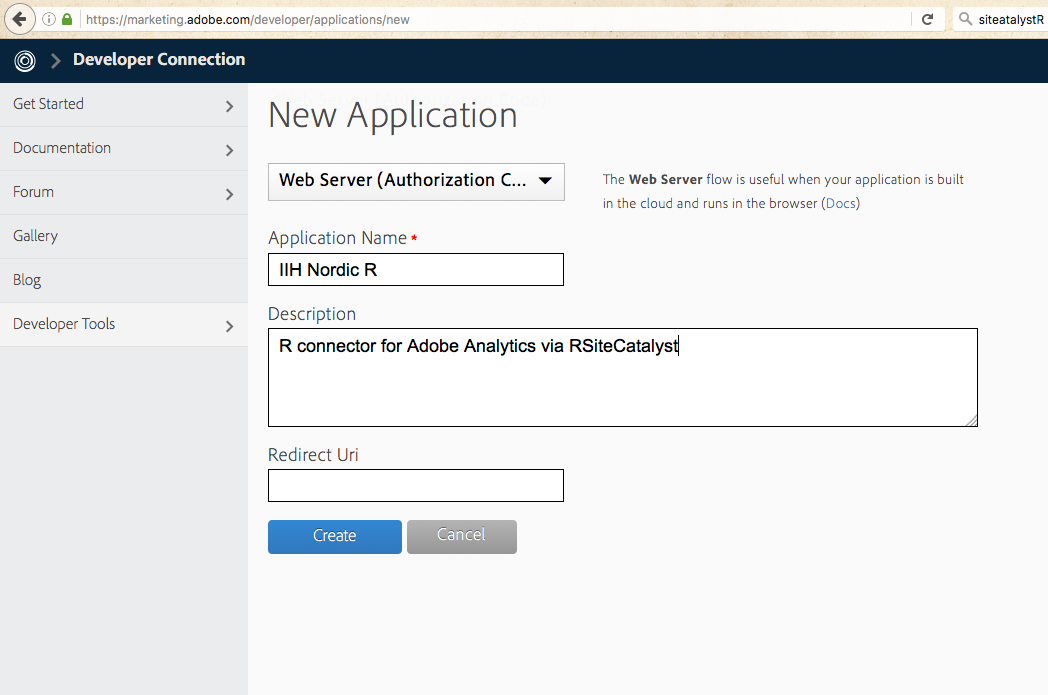
If you have no application for your Adobe Analytics account, here is how to make one:
- Create an app by visiting developer console and navigating to Developer > Applications
- Select “Web Server (Authorization Code)”
- Name the application
- Leave the Redirect Uri field blank.
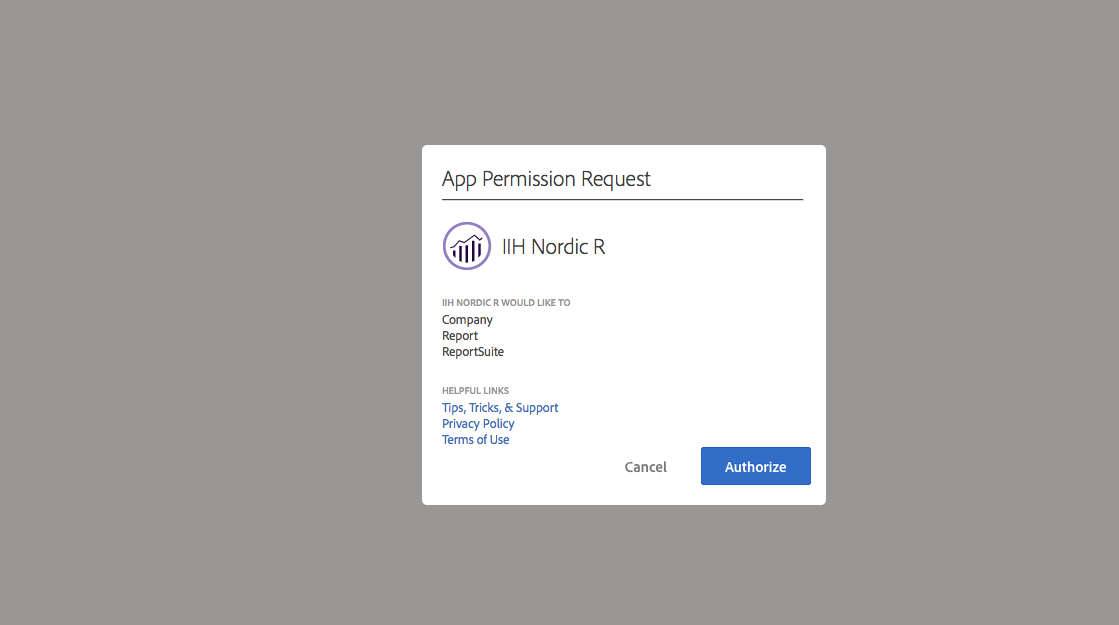
You should then see this screen to grant permission after running SCAuth
Authentication (Old)
This is the deprecated method and will dissappear ‘soon’.
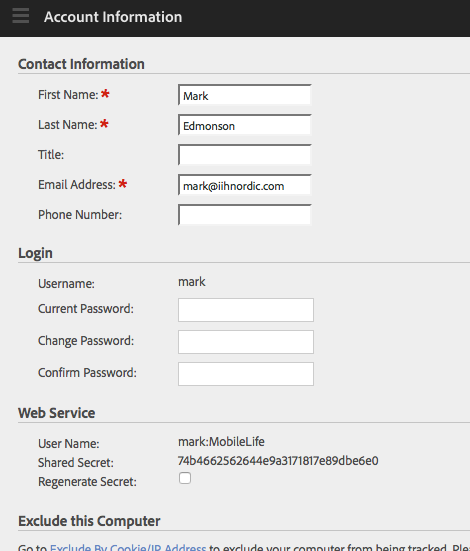
Get the Web Service key under the Adobe Analytics Account Information page.
- User Name is used as the key
- Sharted Secret is used as the secret
If you use this method, then you authenticate via:
library(RSiteCatalyst)
key <- Sys.getenv("ADOBE_KEY_OLD")
secret <- Sys.getenv("ADOBE_SECRET_OLD")
SCAuth(key, secret)Recording secret keys
I save these values to a .Renviron file in my home directory to keep them safe and call then via the commands below (this stops them being accidently put on github for example)
Example .Renviron file
This is in my root directory: ~/.Renviron
ADOBE_KEY="a7xxxxx639-iih-nordic-r"
ADOBE_SECRET="2eadxxxxx1495ea49"
ADOBE_KEY_OLD="mark:XXXXXX"
ADOBE_SECRET_OLD="74b46625xxxxx7e89dbe6e0"Calling Adobe Analytics
Once you have setup your authentication method, you can call data using the below.
The SCAuth() function will open your browser or read the existing auth-adobe file if using the newer OAuth2 method, or return [1] "Credentials Saved in RSiteCatalyst Namespace." if using legacy.
library(RSiteCatalyst)
## New OAuth method
key <- Sys.getenv("ADOBE_KEY")
secret <- Sys.getenv("ADOBE_SECRET")
SCAuth(key, secret,
company = "XXXXX",
token.file = "auth-adobe",
auth.method = "OAUTH2")
## Old legacy method
key <- Sys.getenv("ADOBE_KEY_OLD")
secret <- Sys.getenv("ADOBE_SECRET_OLD")
SCAuth(key, secret)
You should be then able to see the report suites via:
suites <- GetReportSuites()
head(suites)Pulling Data Reports
There are 5 different types of Adobe Analytics reports that can be pulled out via the API:
- Overtime -
QueueOvertime() - Ranked -
QueueRanked() - Trended -
QueueTrended() - Pathing -
QueuePathing() - Fallout -
QueueFallout()
See the characteristics of the reports here
We set some common parameters here:
date.from <- "2016-03-01"
date.to <- "2016-03-29"
reportsuite.id <- "xxxxxxx"Overtime
Returns an overtime report. This is similar to the key metrics report in that the only granularity allowed is time.
QueueOvertime requires a start and end date, a reportsuite ID, and a character vector of metrics.
metrics <- c("visits","uniquevisitors","pageviews")
report.data <- QueueOvertime(reportsuite.id, date.from, date.to, metrics)
head(report.data)You may also wish to set any of the 5 optional named parameters.
report.data <- QueueOvertime(reportsuite.id,
date.from, date.to,
metrics,
date.granularity = "hour",
segment.id = "Visit_Natural_Search",
anomaly.detection = FALSE,
data.current = TRUE,
expedite = FALSE) ## only if you have permission
head(report.data)A similar workflow is available for the other report types.