Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
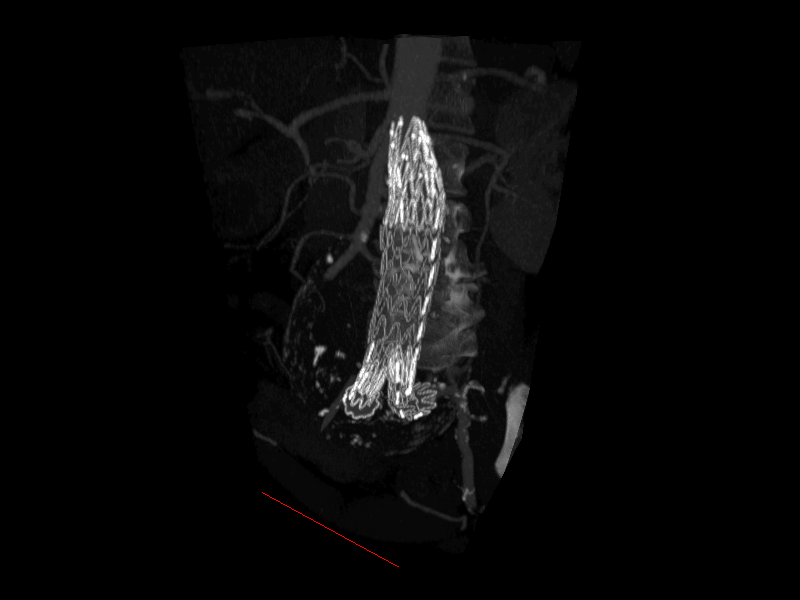
Aspect Ratios#
Example demonstrating the use of aspect ratio, and also the flipping of axis using negative aspect ratios.
Keys: * 1: flip x dimension * 2: flip y dimension * 3: flip z dimension * 4: cycle through up-vectors * 5: cycle through cameras
from itertools import cycle
import numpy as np
from vispy import app, scene, io
# Read volume
vol1 = np.load(io.load_data_file('volume/stent.npz'))['arr_0']
# Prepare canvas
canvas = scene.SceneCanvas(keys='interactive', size=(800, 600), show=True)
canvas.measure_fps()
# Set up a viewbox to display the image with interactive pan/zoom
view = canvas.central_widget.add_view()
# Create the volume visuals, only one is visible
volume1 = scene.visuals.Volume(vol1, parent=view.scene, threshold=0.5)
# volume1.method = 'iso'
volume1.threshold = 0.1
# Plot a line that shows where positive x is, with at the end a small
# line pointing at positive y
arr = np.array([(100, -1, -1), (-1, -1, -1), (-1, 10, -1)])
line1 = scene.visuals.Line(arr, color='red', parent=view.scene)
# Create cameras
cam1 = scene.cameras.PanZoomCamera(parent=view.scene, aspect=1, name='PanZoom')
cam2 = scene.cameras.FlyCamera(parent=view.scene, name='Fly')
cam3 = scene.cameras.TurntableCamera(fov=60, parent=view.scene,
name='Turntable')
cam4 = scene.cameras.ArcballCamera(fov=60, parent=view.scene, name='Arcball')
cams = (cam1, cam2, cam3, cam4)
view.camera = cam3 # Select turntable at first
ups = cycle(('+z', '-z', '+y', '-y', '+x', '-x'))
# Implement key presses
@canvas.events.key_press.connect
def on_key_press(event):
if event.text == '1':
for cam in cams:
flip = cam.flip
cam.flip = not flip[0], flip[1], flip[2]
elif event.text == '2':
for cam in cams:
flip = cam.flip
cam.flip = flip[0], not flip[1], flip[2]
elif event.text == '3':
for cam in cams:
flip = cam.flip
cam.flip = flip[0], flip[1], not flip[2]
elif event.text == '4':
up = next(ups)
print('up: ' + up)
for cam in cams:
cam.up = up
if event.text == '5':
cam_toggle = {cam1: cam2, cam2: cam3, cam3: cam4, cam4: cam1}
view.camera = cam_toggle.get(view.camera, cam2)
print(view.camera.name + ' camera')
elif event.text == '0':
for cam in cams:
cam.set_range()
if __name__ == '__main__':
print(__doc__)
app.run()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 0.903 seconds)
