Arrays
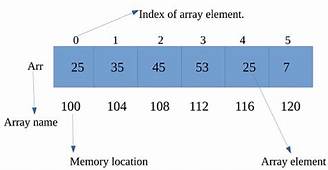
An array is a collection of similar types of items stored in contiguous manner.Position of any element can be calculated directly by simply adding an offset to a base value, i.e., the memory location of the first element of the array
(generally denoted by the name of the array). The base value is index 0 and the difference between the two indexes is the offset.
Instead of declaring individual variables, such as number0, number1, ..., and number99, you declare one array variable such as numbers and use numbers[0], numbers[1], and ..., numbers[99] to represent individual variables. A specific
element in an array is accessed by an index.
Types of Arrays
-
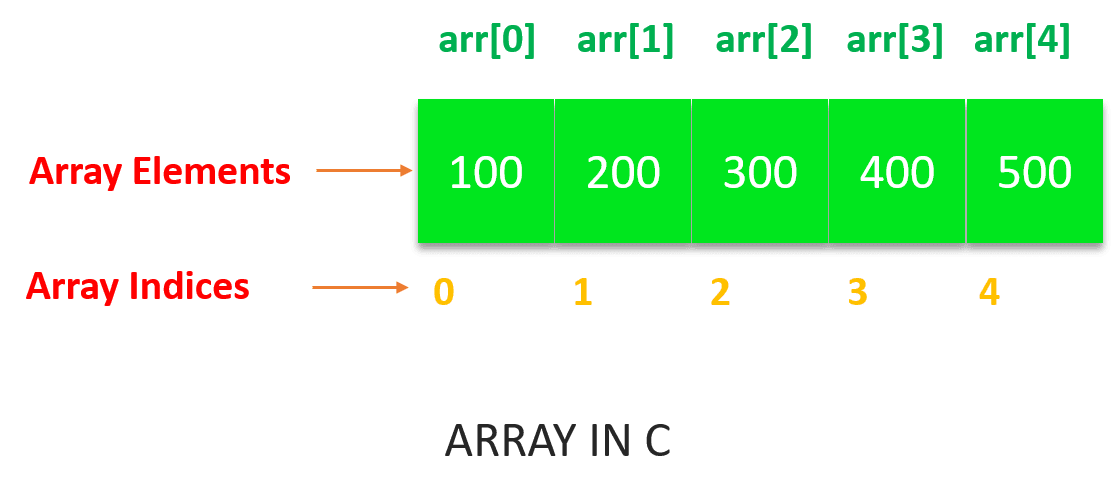
Single Dimensional Arrays: Single dimensional array or 1-D array is the simplest form of arrays that can be found in C. This type of array consists of elements of similar types and these elements can be accessed through their indices.
-
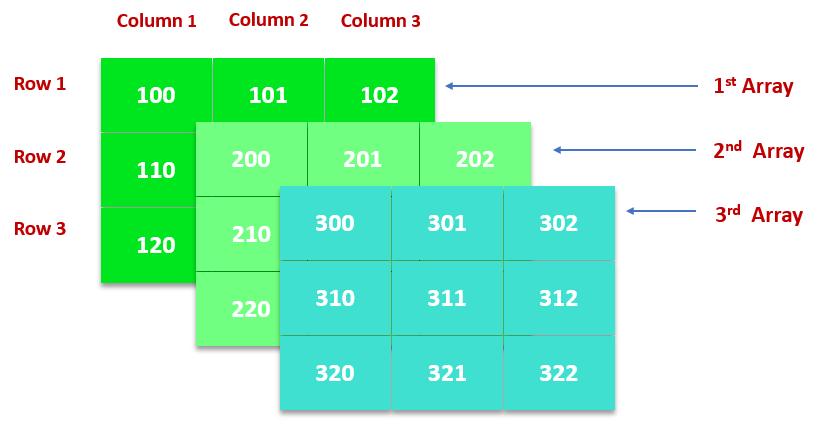
Multi-dimensional Arrays: The most common type of multi-dimensional array that is used in the C language is a 2-D array. However, the number of dimensions can be more than 2 depending upon the compiler of the user’s system. These arrays consist of elements that are array themselves.
Array Declaration and Initialization
C/C++
Fixed-Size Array:Size of the array is fixed and can't be changed accordingly.
Various ways to declare fixed size array are as follows:
Static array:Array size is decided at compile time.
-
Array declaration by specifying size :
SYNTAX: int arr1[10];
or
int n = 10;
int arr2[n]; -
Array declaration by initializing elements:
SYNTAX: int arr[] = { 10, 20, 30, 40 }; -
Array declaration by specifying size and initializing elements:
SYNTAX: int arr[6] = { 10, 20, 30, 40 };
Dynamic Memory Allocation:Array size is decided at run-time.
In C malloc/calloc is used for dynamic memory allocation while in C++ new keyword is used for dynamically allocating array.
SYNTAX:pointer_variable = new data_type;
The pointer_variable is the name of the pointer variable.
The data_type must be a valid C++ data type.
The keyword then returns a pointer to the first item. After creating the dynamic array, we can delete it using the delete keyword.
Deleting the dynamically created array
SYNTAX:int n=10;
int *arr = new int(n);
delete [] arr;
Vector: Vectors are same as dynamic arrays with the ability to resize itself automatically when an element is inserted or deleted, with their storage being handled automatically by the container. Vector elements are placed in
contiguous storage so that they can be accessed and traversed using iterators. In vectors, data is inserted at the end. Inserting at the end takes differential time, as sometimes there may be a need of extending the array. Removing the last
element takes only constant time because no resizing happens. Inserting and erasing at the beginning or in the middle is linear in time.
To read more about vectors Click Here
