Linked List
A linked list is a linear data structure, in which the elements are not stored at contiguous memory locations. The elements in a linked list are linked using pointers.
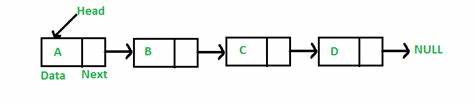
Need of Linked List
- Size: Since data can only be stored in contiguous blocks of memory in an array, its size cannot be altered at runtime due to the risk of overwriting other data. However, in a linked list, each node points to the next one such that data can exist at scattered (non-contiguous) addresses; this allows for a dynamic size that can change at runtime.
- Memory Allocation: For arrays at compile time and at runtime for linked lists. but, a dynamically allocated array also allocates memory at runtime.
- Memory efficiency: For the same number of elements, linked lists use more memory as a reference to the next node is also stored along with the data. However, size flexibility in linked lists may make them use less memory overall; this is useful when there is uncertainty about size or there are large variations in the size of data elements; memory equivalent to the upper limit on the size has to be allocated (even if not all of it is being used) while using arrays, whereas linked lists can increase their sizes step-by-step proportionately to the amount of data.
- Execution time: Any element in an array can be directly accessed with its index; however in the case of a linked list, all the previous elements must be traversed to reach any element. Also, better cache locality in arrays (due to contiguous memory allocation) can significantly improve performance. As a result, some operations (such as modifying a certain element) are faster in arrays, while some others (such as inserting/deleting an element in the data) are faster in linked lists.
Types of Linked List
-
Singly Linked List: The singly linked list is a data structure that contains two parts, i.e., one is the data part, and the other one is the address part, which contains the address of the next or the successor node. The address part in a node is also known as a pointer.
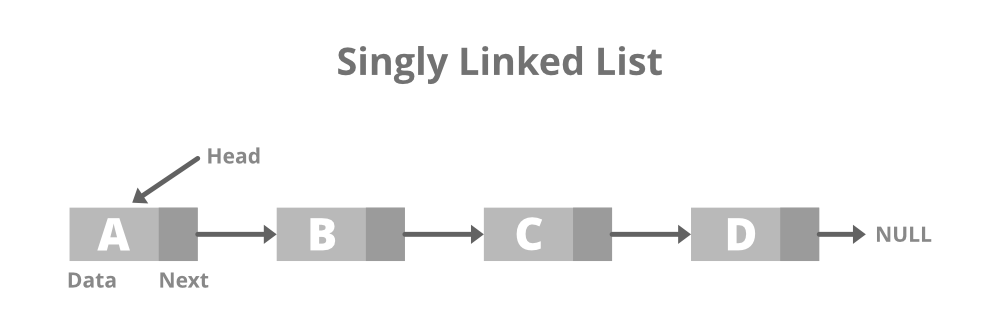
Representation of the node in a singly linked list
struct node
{
int data;
struct node *next;
} -
Doubly linked list: The doubly linked list contains two pointers. We can define the doubly linked list as a linear data structure with three parts: the data part and the other two address part. In other words, a doubly linked list is a list that has three parts in a single node, includes one data part, a pointer to its previous node, and a pointer to the next node.
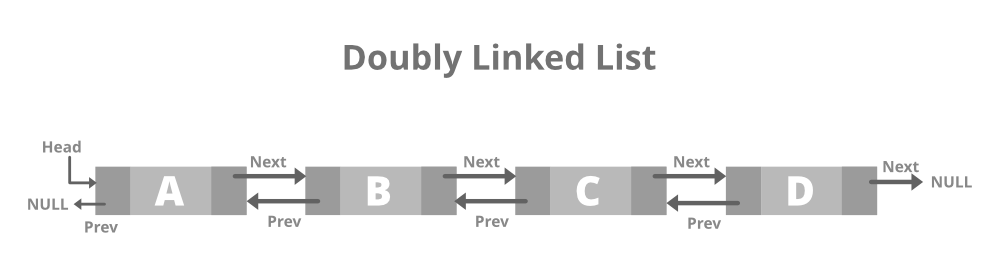
Representation of the node in a doubly linked list
struct node
{
int data;
struct node *next;
struct node *prev;
} -
Circular linked list: A circular linked list is a variation of a singly linked list. The only difference between the singly linked list and a circular linked list is that the last node does not point to any node in a singly linked list, so its link part contains a NULL value. On the other hand, the circular linked list is a list in which the last node connects to the first node, so the link part of the last node holds the first node's address. The circular linked list has no starting and ending node. We can traverse in any direction.
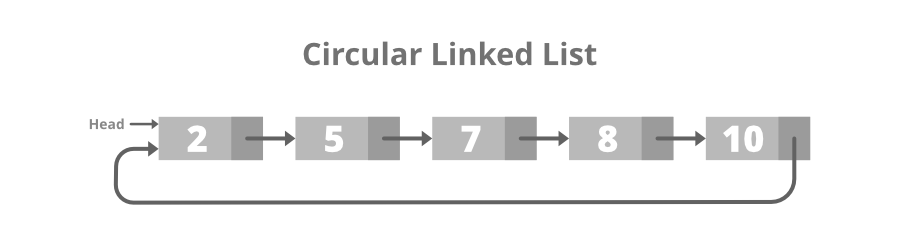
Representation of the node in a circular linked list
struct node
{
int data;
struct node *next;
} -
Doubly Circular linked list: A Doubly Circular linked list or a circular two-way linked list is a more complex type of linked-list that contains a pointer to the next as well as the previous node in the sequence. The difference between the doubly linked and circular doubly list is the same as that between a singly linked list and a circular linked list. The circular doubly linked list does not contain null in the previous field of the first node.
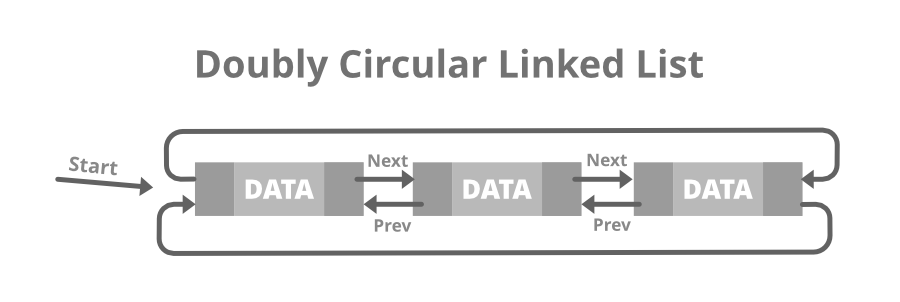
Representation of the node in a circular linked list
struct node
{
int data;
struct node *next;
struct node *prev;
}
